Bag type rapid fermentation method
A fermentation method and bag-type technology, applied in the field of bag-type rapid fermentation, can solve the problems of large area occupied by fermentation, strong odor of fermentation heap, poor fermentation environment, etc., so as to save fermentation site, promote the growth and development of crops, and improve the environment. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: Fermentation experiment of corn stalk
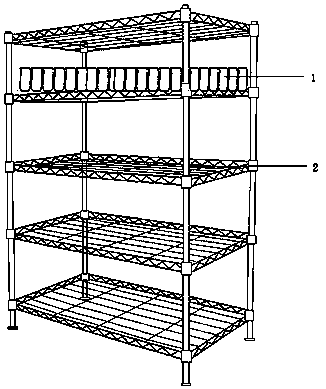
[0031] Treatment of corn stalks: crush corn stalks into particles with a particle size of 1-3 cm, add urea, adjust the C / N ratio to 30:1, add 2.5 g of gypsum powder per 1 kg of corn stalks, and add fermentation bacteria, the fermentation bacteria The agent was purchased from Hengda Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Hebi City, Henan Province. The product name was bio-organic fertilizer fermentation bacteria, and the model was Hd. The dosage was 1g of fermentation agent for every 1kg of corn stalks. The pH value of material is 7-8, fully mixes, sprays water, makes the water content of material be 65%, divides into fermentation bag 1, as figure 1 shown.
[0032] Place the single layer of fermented bags containing fermented materials evenly and vertically on the fermented frame 2, such as figure 1shown. Control the temperature in the fermentation room to be 20-25°C, and the relative air humidity to be about 70%, ventilate once...
Embodiment 2
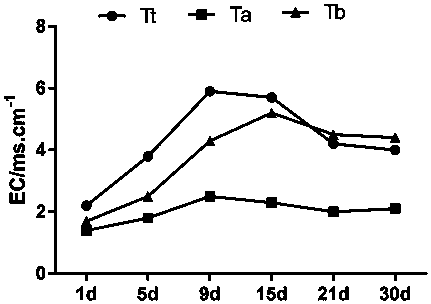
[0035] Embodiment 2: Conductivity (EC) measurement experiment of corn stalk fermentation
[0036] The treatment method of the experimental group (Tt) is as shown in Example 1.
[0037] The fermentation treatment of the control group (Ta, Tb) corn stalks was as follows:
[0038] Control group Ta: No fermenting agent was added, and other conditions were consistent with the experimental group (Tt).
[0039] Control group Tb: no fermentation agent is added, the temperature in the fermentation room is controlled at 0-5° C., the relative air humidity is 20%, and other conditions are consistent with the experimental group (Tt).
[0040] Sampling analysis: sampling the fermentation materials at different fermentation periods at the same time, and testing the conductivity of the samples. The result is as figure 2 It can be seen that with the progress of fermentation, the EC value of each treatment also increased significantly, Tt and Tb treatment reached the peak on the 9th and 15t...
Embodiment 3
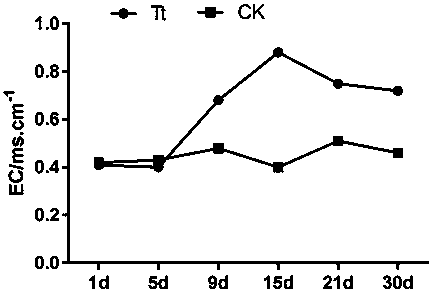
[0041] Example 3: Effect experiment of corn stalk fermentation matrix extract on tomato seed germination index
[0042] Experimental formula 1: corn stalk fermentation substrate extract solution fermented for 1 day;
[0043] Experimental formula 2: corn stalk fermentation substrate extract solution fermented for 5 days;
[0044] Experimental formula 3: corn stalk fermentation substrate extract liquid fermented for 9 days;
[0045] Experimental formula 4: corn stalk fermentation substrate extract solution fermented for 15 days;
[0046] Experimental formula 5: corn stalk fermentation substrate extract solution fermented for 21 days;
[0047] Experimental formula 6: corn stalk fermentation substrate extract liquid fermented for 30 days;
[0048] Control formula: equal amount of water.
[0049] Corn stalk fermentation substrates fermented for different times were soaked to obtain matrix extracts, which were used to detect its effect on the germination index of tomato seeds. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com