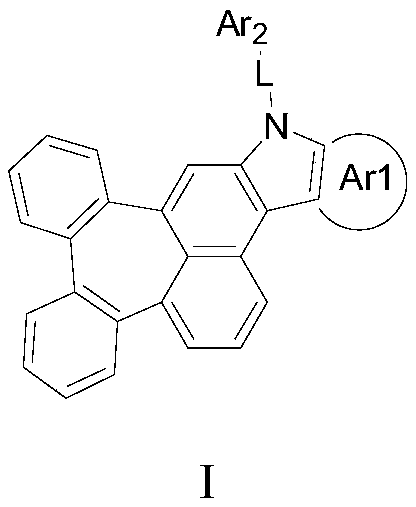
Organic electroluminescent compound containing cycloheptylnaphthalene, application thereof, and light-emitting device
A cycloheptyl naphthalene and electroluminescence technology, applied in organic chemistry, electro-solid devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reduced device efficiency, unbalanced charge in the light-emitting layer, difficult electron flow, etc., and achieve good thermal stability. , The effect of high luminous purity and high luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
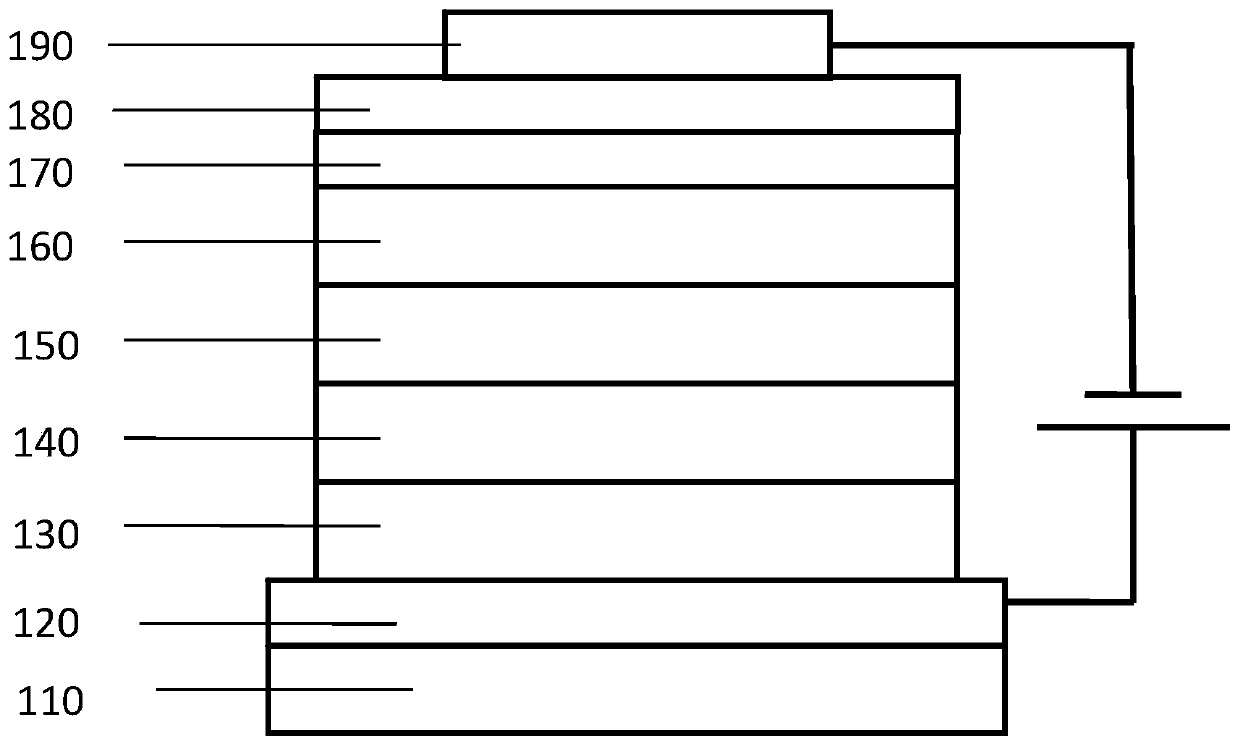
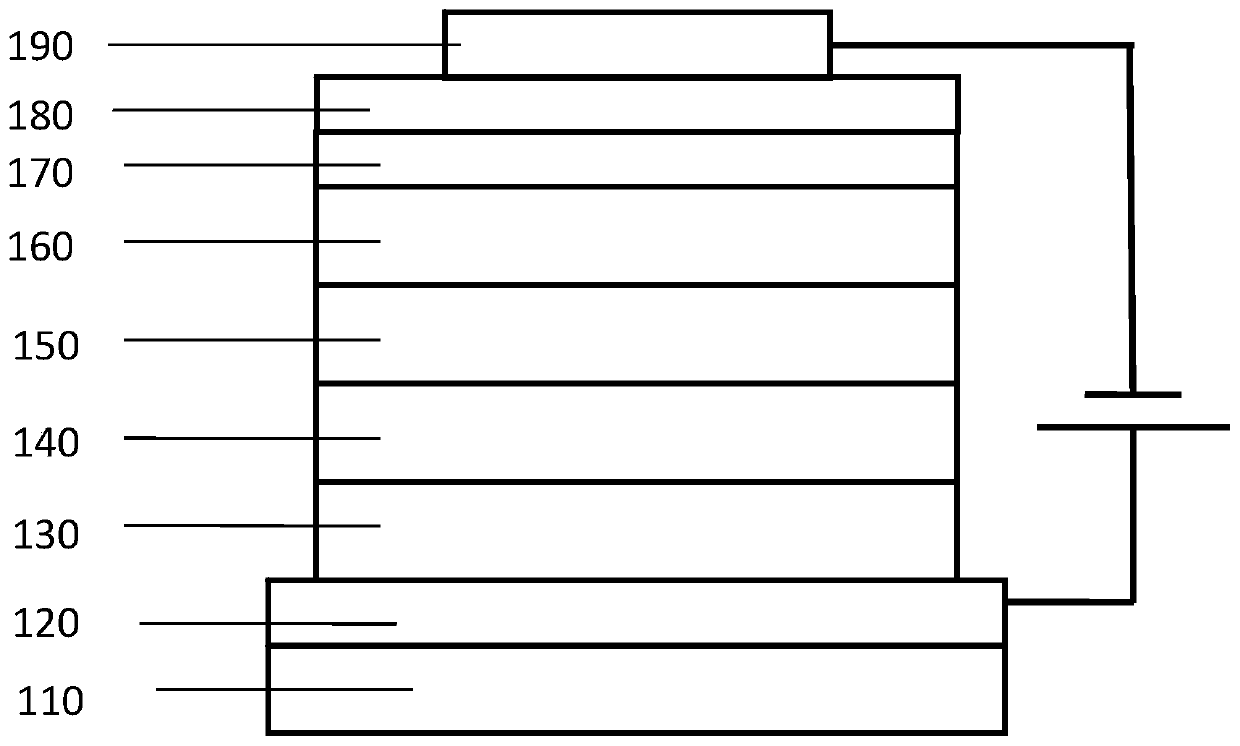
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Synthetic route of intermediates
[0052]
[0053] Synthetic method of intermediate A
[0054] In a flask, add bromodibenzocycloheptane benzene naphthalene (18 g, 47 mmol), o-nitrophenylboronic acid (8.6 g, 51 mmol), potassium carbonate (13.6 g, 100 mmol), tetrahydrofuran (300 mL), water (150 mL) ), tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium (1 g), heated back under nitrogen protection for 12 hours, cooled, extracted with dichloromethane, dried, concentrated, and the crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain 14 g in 75% yield.
[0055] Synthetic method of intermediate B
[0056] In the flask, add intermediate C (20 g, 50 mmol), 100 mL of triethyl phosphite, heat under reflux for 5 hours, cool, remove excess triethyl phosphite under reduced pressure, and the crude product is purified by column chromatography to obtain product 10.8 g, 59% yield. Synthetic method of intermediate C
[0057] The synthesis method was the same as that of intermediate A, an...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Synthetic route of compound 5
[0062]
[0063] Synthetic method of compound 5
[0064] In a flask, add intermediate B (2 g, 5.4 mmol), bromophenanthrene (1.7 g, 5.4 mmol), sodium tert-butoxide (1 g, 10 mmol), palladium acetate (0.1 g), X-phos (0.3 g) , toluene (30 mL), heated to reflux for 15 hours under nitrogen protection, cooled, and the solvent was removed. The crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain 2.2 g with a yield of 69%.
[0065] The synthesis of other example compounds is the same as the synthesis of compound 5 in Example 1, and the raw material used is the reaction of intermediate B or intermediate D with other halides, as shown in Table 1 below:
[0066] Table 1 Raw materials and yields
[0067]
[0068]
[0069]
[0070]
Embodiment 14
[0072] Synthetic route of compound 29
[0073]
[0074] Synthetic method of compound 29
[0075] In a flask, add Intermediate C (2 g, 5.4 mmol), N,N-dimethylformamide (20 mL), sodium hydride (12 mmol), 2-chloro-4,6-diphenyltriazine (1.45 mmol) in sequence g, 5.4 mmol), stirred for 5 hours, added water, filtered, and recrystallized from toluene to obtain 2.6 g of the product with a yield of 79%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com