Biopesticides for potato late blight disease
A potato late blight, biological technology, applied in the direction of biocides, chemicals for biological control, fungicides, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0035] Example 1: Microbial Culture
[0036] Bacterial Suspension:
[0037] Bacterial cultures maintained at -80°C were thawed and plated on Pseudomonas agar F medium (containing Difco TM Casein pancreatic digest (10.0g), No. 3 proteose peptone (10.0g), K 2 HPO 4 (1.5g), MgSO 4 (1.5g), agar (15.0g) and glycerol (10g) in water (1L)). The colony was inoculated into 125mL yeast extract glucose medium (YGM; containing yeast extract (2.0g), dextrose (2.5g), buffer solution (10mL, KH 2 PO 4 (25.0g / L) and K 2 HPO 4 (25.0g / L)) and brine solution (10mL, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O(10.0g / L), MnSO 4 ·H 2 O(1.5g / L), NaCl(5.0g / L) and FeSO 4 ·7H 2 (0.5 g / L)) in water (1 L total volume)) and incubated for 48 hours at 22° C. in a 500 mL baffled flask on a rotary shaker (150 rpm) to obtain a bacterial suspension.
[0038] Cell-free bacterial filtrate:
[0039] The bacterial suspension was centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was vacuum filtered through a 0.22 μm non-...
example 2
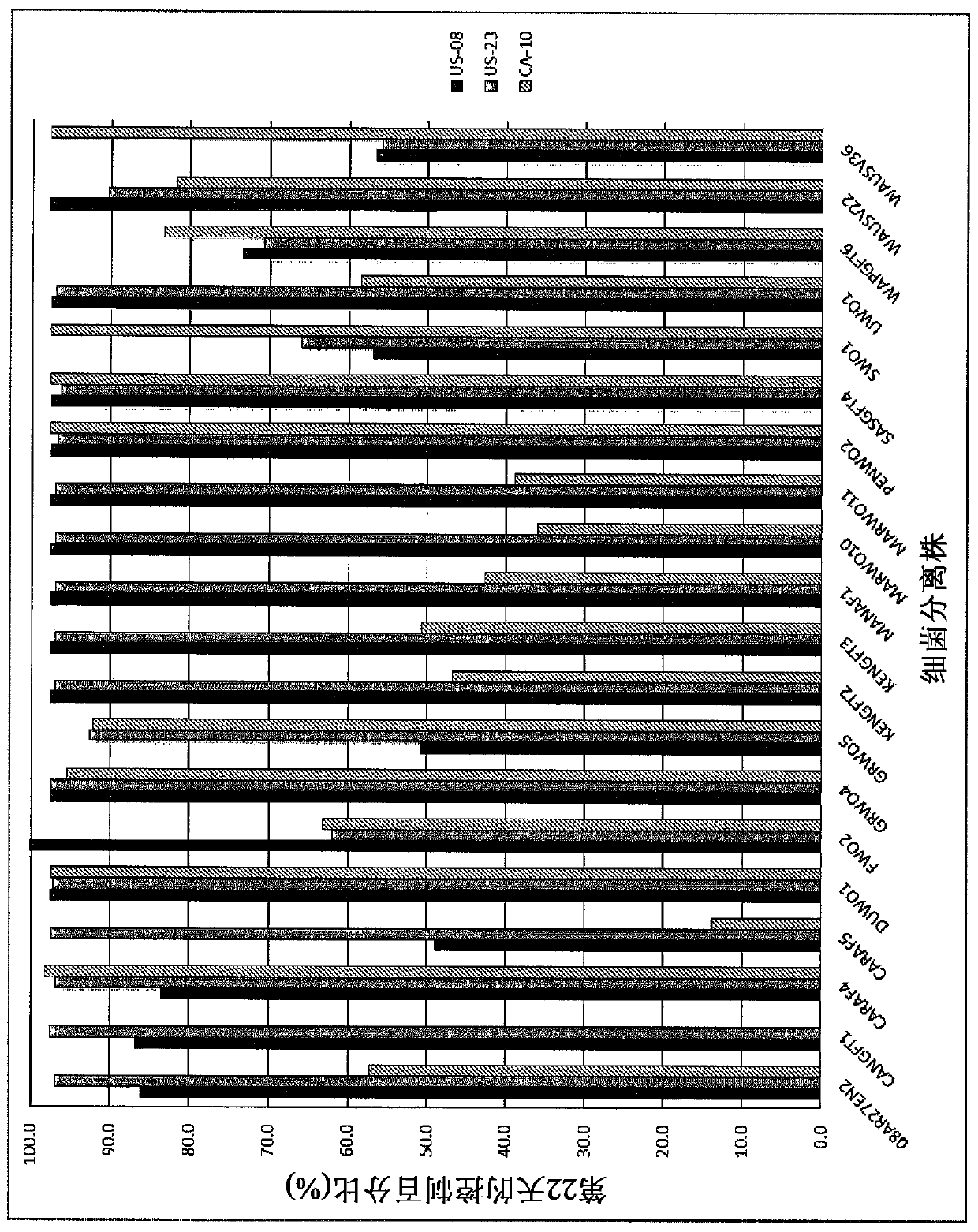
[0042] Example 2: In Vitro Bioanalysis
[0043] bacterial suspension
[0044] An agar plunger (0.5 cm diameter) of Phytophthora infestans (A1 or A2 mating type) was placed in the center of a Petri dish (9 cm diameter) containing Rye Seed A Agar (RSA). Aliquots (2 μL) of the bacterial suspension were placed close to the edge of the plate; 2-4 bacterial strains were tested on each plate. After 7 days of incubation at 15°C, the zone of inhibition was measured. Two experiments were performed, each using four replicates.
[0045] cell-free bacterial filtrate
[0046] Cell-free bacterial filtrates or sterile water as a negative control were dispensed on agar (50%, v / v). A mycelial plunger of the pathogen was placed in the center of a Petri dish (9 cm diameter) and after incubation at 22°C for 7 and 12 days, mycelial growth was measured. Two experiments were performed, each using four replicates. use SAS TM software to analyze the results. The control percentage (%) is calcul...
example 3
[0051] Example 3: Bioanalysis of in vivo feeding detached leaves
[0052] Potato leaves each containing 5 leaflets were selected and grown in 50 mL tubes containing 10% Hoagland's solution (Hoagland, D.R. and Arnon, D.I. "with The water-culture method for growing plants without soil" Univ.Calif.Coll.Agric.Exp.Sta.Circ, University of California, Berkeley, CA. . Berkeley, CA) (1938), 347-353). The leaves were dipped in the selected test or control treatment as described below and after 2 hours were sprayed with the Phytophthora infestans suspension until run off. The treated leaves were incubated at 22°C under high humidity conditions (86%-92% relative humidity) and a photoperiod of 16 hours per day / 8 hours per night.
[0053]After 7 and 10 days of incubation, disease progression and severity on leaves were measured by estimating the proportion of the photosynthetic area affected by the pathogen (James, 1971: James, W.C. Keys to plant disease assessment, their preparation and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com