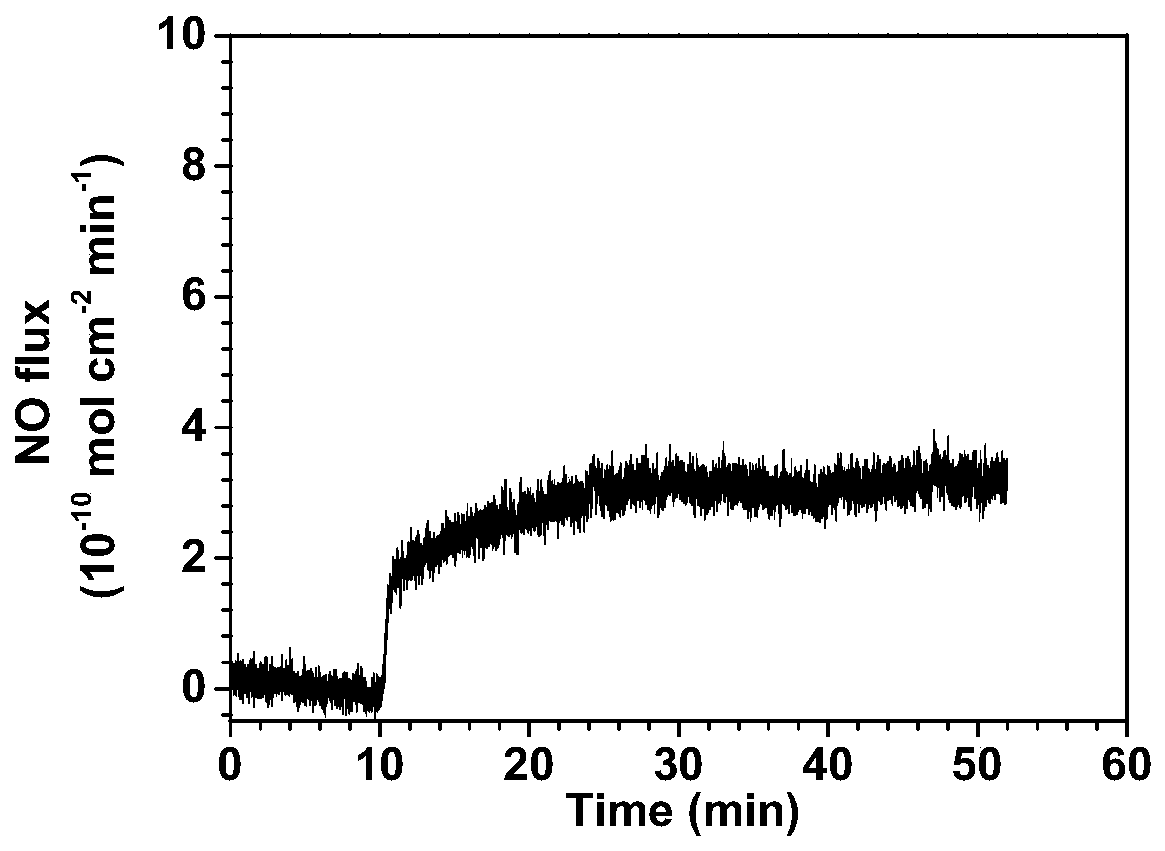
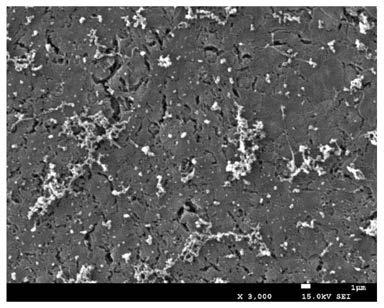
Biological material with functions of catalytic releasing NO and capturing EPCs and preparation method thereof
A biomaterial and functional technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of inflammation, difficulty in clinical treatment of stents, coagulation, etc., and achieve the effect of mild reaction conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing a biological material with NO catalytic release and EPCs capture function, which includes the following steps:
[0024] S1. Deposition of metal oxides
[0025] A metal oxide film is deposited on the surface of the material to be modified, and the deposition of the metal oxide film is conducive to increasing the strength and biocompatibility of the material, and is also conducive to the fixation of the azidated ortho-phenolic compound on the surface of the material.
[0026] The materials to be modified can be cardiovascular stents, artificial blood vessels, osteoinductive materials, etc. The introduction of functional biomolecules on the surface of such materials improves their anticoagulant properties, making them capable of inhibiting smooth muscle hyperplasia and promoting in situ re-endothelialization. Very broad application space.
[0027] Metal oxides are metal oxides with excellent biocompat...
Embodiment 1
[0050] The present embodiment provides a method for preparing a biological material with NO catalytic release and EPCs capture functions, which includes the following steps:
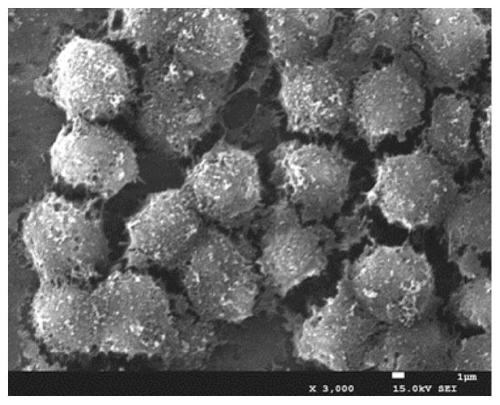
[0051] A layer of TiO thin film was deposited on the surface of the cobalt-nickel bare stent by magnetron sputtering. The deposition power was 600 W, the deposition time was 8 mins, and the film thickness was about 50 nm.
[0052] with N 2 After deoxygenation for 30 mins, PBS buffer with a pH of about 5 was used as a solvent, and the concentration was 0.01 mg / mL Ac-(DOPA)-Gly-(DOPA)-Lys(PEG5-Azido)-(DOPA)-Gly-(DOPA ) (abbreviated as ((DOPA) 4 -N 3 ), the same below), the scaffold was immersed in the solution and reacted for 12 h under anaerobic conditions at 25°C.
[0053] The alkynyl selenocystine (DBCO-SeCA) and PSLEQRTVYAKGGGGC-DBCO (abbreviated as DBCO-Peptide, the same below) were dissolved in PBS (PH=5) in a volume ratio of 0.01 mg / mL respectively: DMSO= In a 3:1 solution, the scaffold obtained...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The present embodiment provides a method for preparing a biological material with NO catalytic release and EPCs capture functions, which includes the following steps:
[0056] The titanium foil after heat treatment at 450°C was cleaned by oxygen plasma sputtering, the sputtering power was 300W, and the sputtering time was 10mins. A layer of TiO thin film was deposited on the surface of the material by magnetron sputtering. The deposition power was 600 W, the deposition time was 8 mins, and the film thickness was about 50 nm.
[0057] with N 2 After deoxygenation for 30 mins, PBS buffer with a pH of about 5 was used as a solvent, and the concentration was 0.01 mg / mL Ac-(DOPA)-Gly-(DOPA)-Lys(PEG5-Azido)-(DOPA)-Gly-(DOPA ) (abbreviated as ((DOPA) 4 -N 3 ), the same below), the scaffold was immersed in the solution and reacted for 12 h under anaerobic conditions at 25°C.
[0058] Alkynated selenocystine (DBCO-SeCA) and PSLEQRTVYAKGGGGC-DBCO (abbreviated as DBCO-Peptide,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com