Method for improving nucleation efficiency when preparing beta crystalline long-chain branching polypropylene through beta nucleating agent
A β-nucleating agent and long-chain branching technology, which is applied in the field of polymer material preparation, can solve problems such as insufficient β-crystal content, unstable welding process, and low efficiency of nucleating agents, so as to improve induction efficiency and quality , the effect of reducing dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] This example is divided into three systems, A, B, and C. Among them, system A is pure long-chain branched polypropylene; system B is 100 parts of long-chain branched polypropylene, and 0.9 parts of β-nucleating agent; 100 parts of chain branched polypropylene, 0.9 parts of complex nucleating agent. The grade of long-chain branched polypropylene used is WB140, the β nucleating agent is TMB-5, and the complex nucleating agent is 4A molecular sieve: TMB-5=1:9.
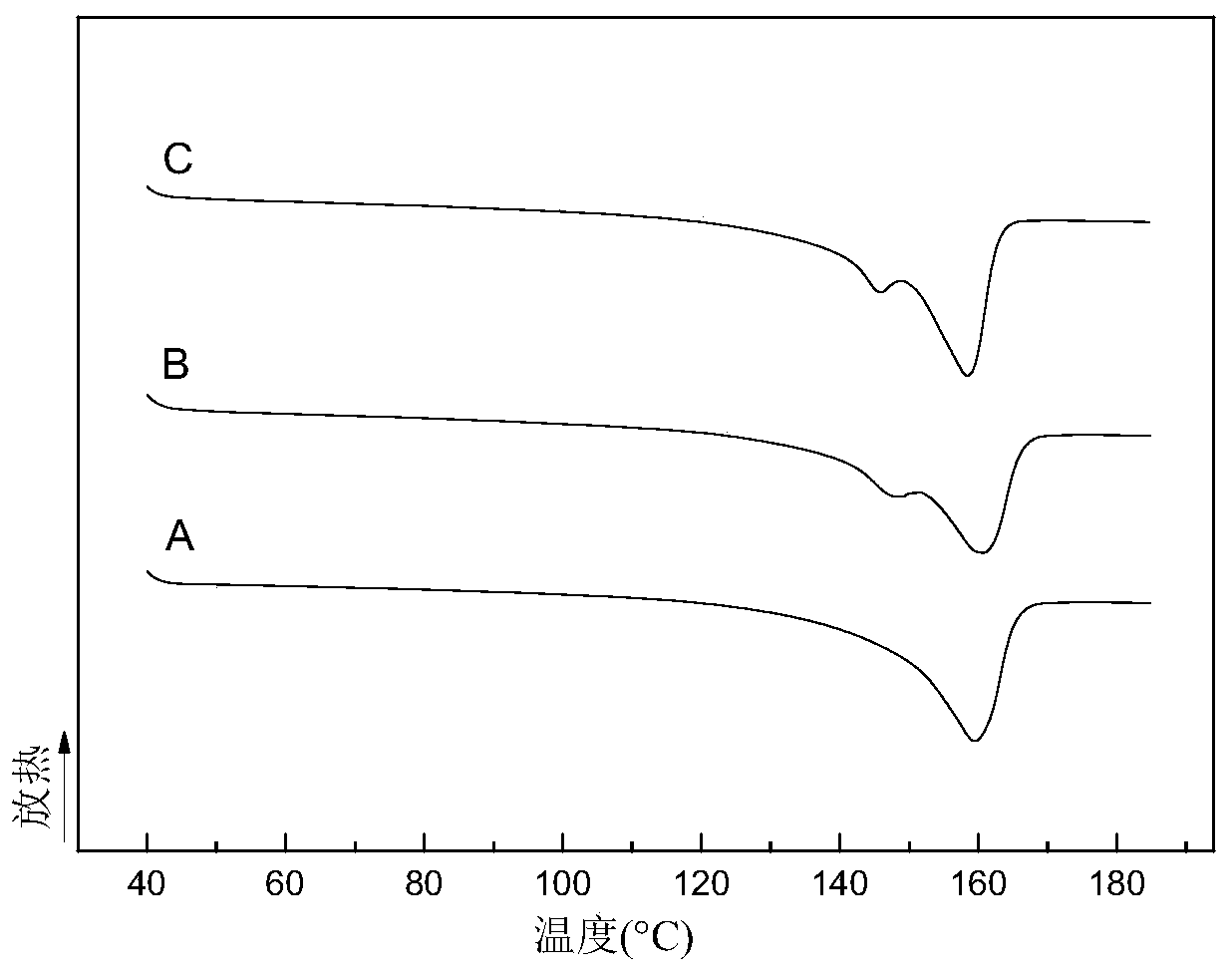
[0034] The above three systems were respectively added into a torque rheometer for melt blending at 190° C., wherein the rotation speed was 60 rads / min, and the blending time was 8 minutes. Then use a differential scanning calorimeter to perform a DSC test. The test condition is: after eliminating the heat history, the temperature is raised from 40°C to 190°C at a rate of 10°C / min. figure 1 is the melting curve of the DSC test, and Table 1 is the relevant statistical data of the DSC test.
[0035] Table 1
[003...
Embodiment 2
[0039] This example is carried out using the same three systems A, B, and C in Example 1.
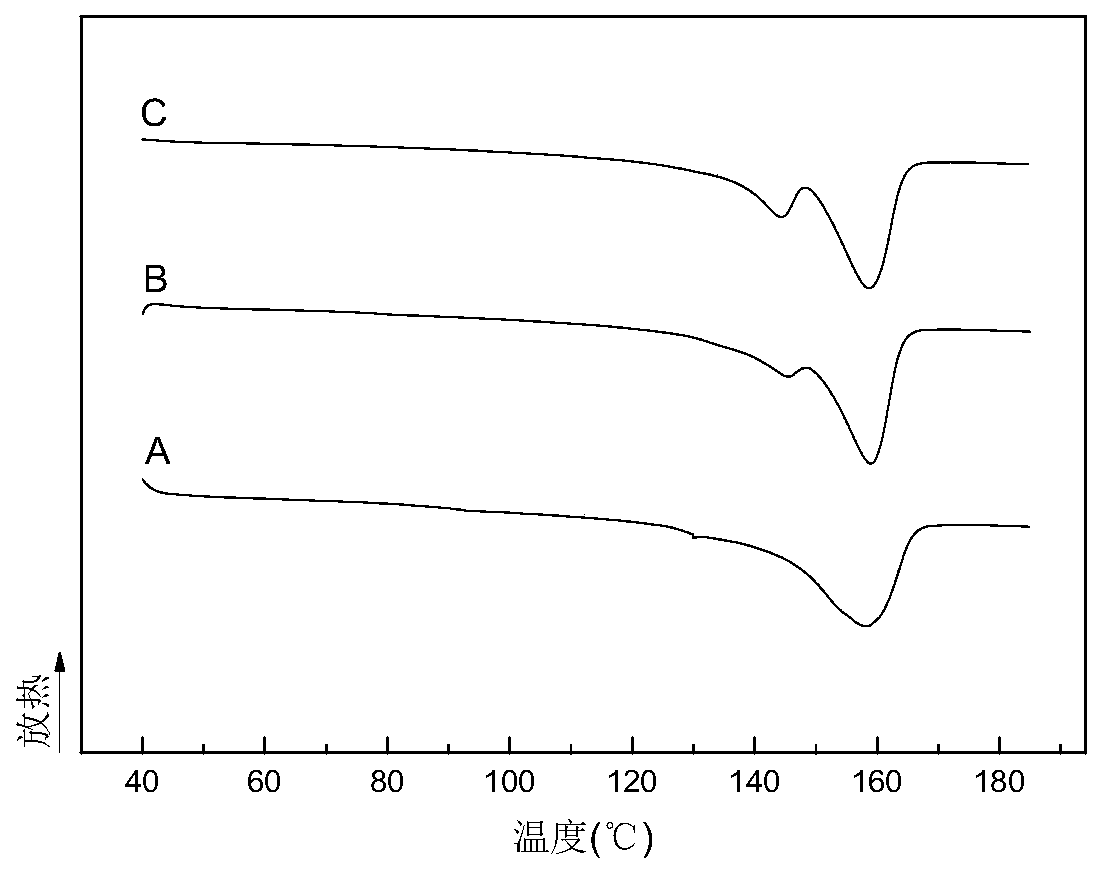
[0040] After these three systems were melted and kneaded under the conditions in Example 1, they were made into 2mm-thick sheets at 190°C, and the removed part was put into a foaming kettle, and CO 2 , Soaked at 190°C and 10MPa for 2 hours, then cooled the foaming kettle at room temperature, and after cooling down to 160°C-165°C, released the pressure and foamed to obtain a foamed material. Afterwards, a DSC test was carried out using a differential scanning calorimeter, and the test condition was: the temperature was raised from 40° C. to 190° C. at a rate of 10° C. / min. figure 2 is the melting curve of the DSC test, and Table 2 is the relevant statistical data of the DSC test.
[0041] Table 2
[0042]
[0043] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen from the contents of Table 2 that, compared with the unfoamed material in Example 1, the β-crystal melting enthalpy of the foam...
Embodiment 3
[0045] This example contains 4 systems, wherein the first three systems are the same as A, B, and C in Example 1, and the formulation of the fourth system is: 100 parts of long-chain branched polypropylene (WB140), β nucleating agent (TMB-5) 1.2 parts. The mixing method and conditions of the fourth system are the same as those of the first three systems.
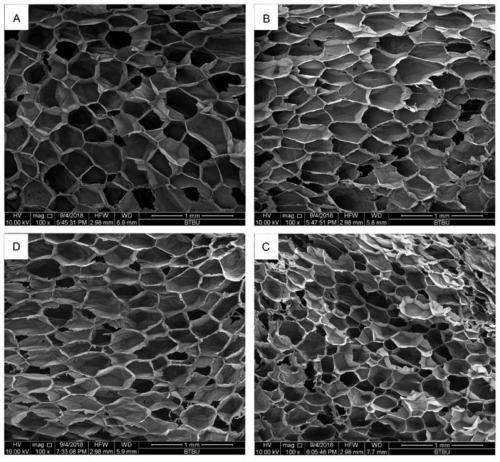
[0046] The four systems were placed in foaming kettles respectively, and foamed under the conditions of Example 2. After the foamed material was obtained, it was soaked in liquid nitrogen for 3-4 hours, and a section was obtained after taking it out. structure to observe. image 3 is the cell morphology diagram of the four systems, Table 3 is image 3 Statistical data related to the cell morphology map.
[0047] table 3
[0048]
[0049] Depend on image 3 It can be seen from the content of Table 3 that the addition of nucleating agent does not have much effect on the cell morphology, while the addition of molecular si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com