A method for increasing the production of D. spp. mycelium and polysaccharides and application of D. spp. polysaccharides
A technology of mycelium and dry fungus, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of low yield of dry fungus mycelium and polysaccharide, achieve the effects of no toxicity and side effects, promote growth and polysaccharide formation, and improve the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
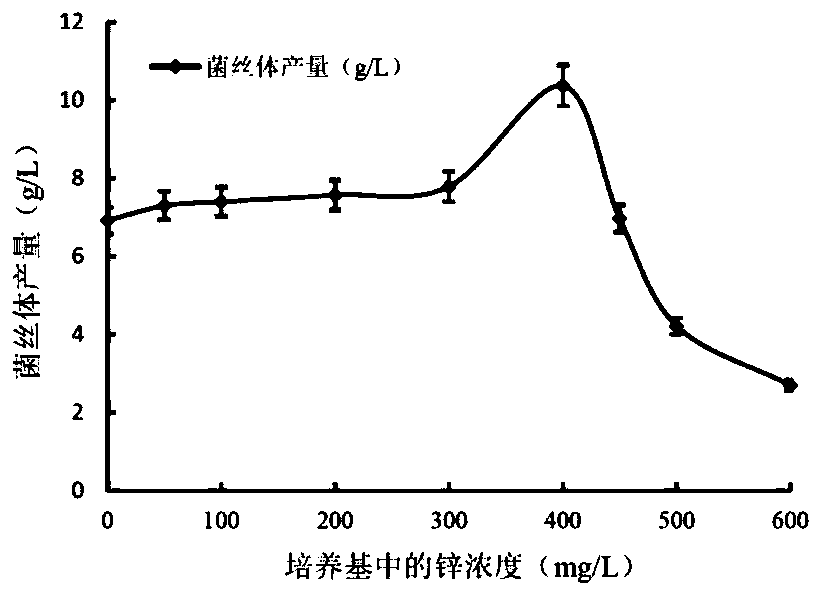
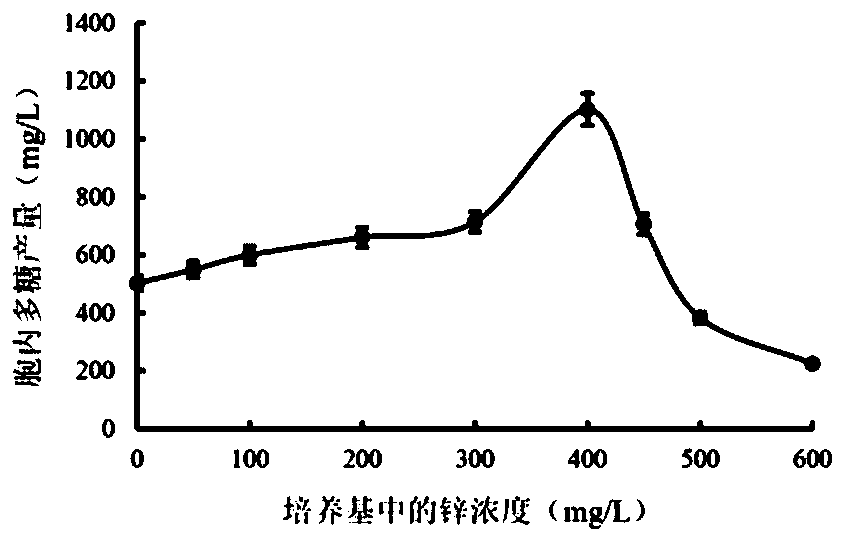
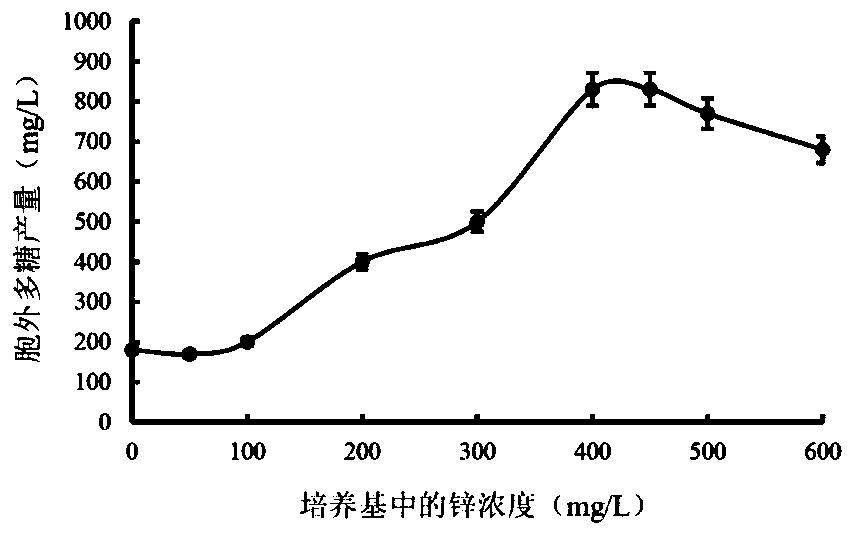
[0038] (1) Ferment and cultivate the activated D. spp. strain numbered BNCC 230987 in potato dextrose (PDA) liquid medium supplemented with different concentrations of zinc sulfate. Shake culture at 25°C for 7 days. After the fermentation, centrifuge to obtain D. For the filament, wash the mycelium of the dry mushroom 3 times, and dry it at 55°C. Drying bacteria mycelium yield (g / L) = Drying bacteria mycelium mass (g) / culture volume (L). Changes in the mycelium production of Bacillus spp. (BNCC 230987) when the concentration of zinc in the medium increased as follows figure 1 shown;
[0039] (2) Grinding the mycelium of D. spp. obtained in step (1) to obtain powder of D. spp. mycelium, mixing the powder of D. spp. with deionized water at a ratio of 1:20, and adjusting the pH value to 8 , ultrasonic crushing, the ultrasonic power is 300 W, the ultrasonic time is 15 min, and then placed in a 90°C water bath for extraction for 2 hours, and the supernatant is obtained by centri...
Embodiment 2
[0044] (1) Ferment and culture the activated D. spp. strain TG-1 numbered CGMCC No.12977 in potato dextrose (PDA) liquid medium supplemented with different concentrations of zinc sulfate. Shake culture at 25°C for 7 days. After the fermentation , and centrifuge to obtain the mycelia of the dry mushroom, wash the dry mushroom mycelium three times, and dry it at 55° C. to obtain the dried dry mushroom mycelium. Mycelium yield (g / L) = mycelium mass (g) / culture volume (L). Changes in the mycelium yield of S. spp. (CGMCCNo.12977) when the concentration of zinc in the medium increased as follows: Figure 4 shown;
[0045] (2) Grinding the mycelium of D. spp. prepared in step (1) to obtain powder of D. spp. mycelium, mixing the powder of D. spp. with deionized water at a ratio of 1:20, and adjusting the pH value to 8 , ultrasonic crushing, the ultrasonic power is 300 W, the ultrasonic time is 15 min, and then placed in a 90°C water bath for extraction for 2 h, centrifuged to obtain...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Anti-inflammatory activity test
[0051] 72 hpf healthy transgenic Tg(Lyz:GFP) zebrafish with fluorescence were selected, randomly transferred into 24-well plates, and divided into 9 groups, 10 in each group. Among them, the NC group was the normal control group of cultured aquaculture; the MC group was the inflammation model group: the zebrafish were treated with copper sulfate for 2 h. The PC group was the positive control group: indomethacin (5 μg / mL) was co-incubated with zebrafish for 2 h, then treated with copper sulfate (20 μmol / L) for 2 h, and then treated with 4% PFA for 1 h, and cleared Zebrafish were washed with PFA and PBST; Groups I, II, and III were low (25 μg / mL), medium (50 μg / mL) and high dose (100 μg / mL) intracellular polysaccharides of D. Group: zebrafish were co-incubated with 25, 50, and 100 μg / mL mycelial intracellular polysaccharides for 2 h, then treated with copper sulfate (20 μmol / L) for 2 h, and treated with 4% PFA for 1 h, PFA was removed a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com