Application of heat shock protein gene from thermophilic bacteria
A heat shock protein and thermophilic bacteria technology, applied in the field of microbial engineering, can solve the problems of poor strain tolerance, affecting riboflavin production, high energy consumption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] The construction of the engineering bacteria of embodiment 1 high temperature riboflavin
[0064] 1. Construction of the carrier
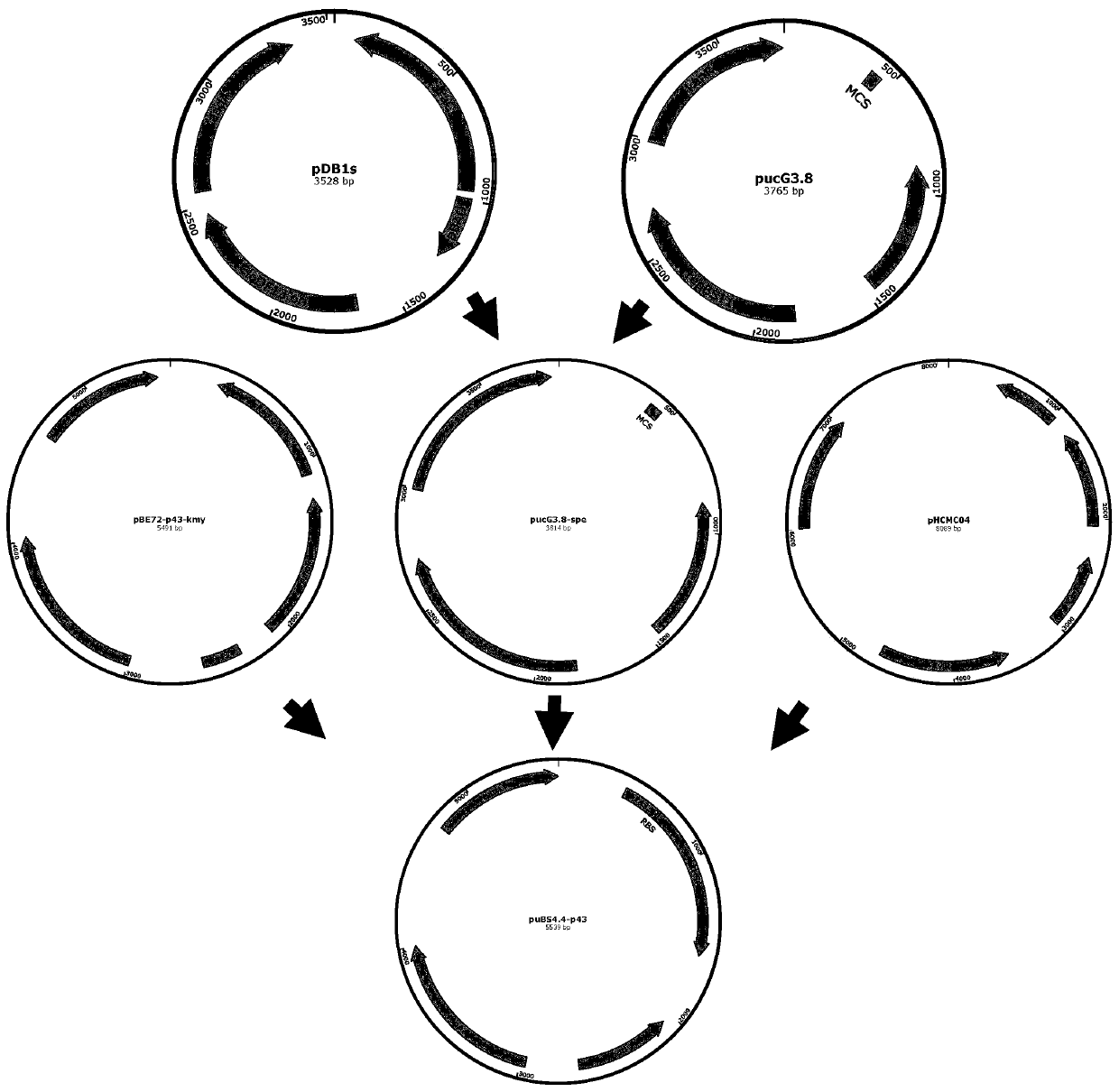
[0065]Use pUCG3.8 (Reeve et al. 2016) as the vector backbone. Using PDB1s (Lin et al.2015) as the template for PCR amplification, the primer 6.0 software was used to design and amplify the addA primer aadA-F:TCTAAAATTTATCTGAAAAGGGAATGAGGGAAGCGGTGATCGC aadA-R:AACGCGCGAGCGATCGCTCATTTGCCGACTACCTTGGTG, and a fragment containing aadA spectinomycin resistance was amplified by PCR. The pUCG3.8 vector backbone and aadA spectinomycin-resistant fragment were assembled into plasmid pUCG3.8-spe using Gibson assembly (Gibson et al. 2009). Using the pHCMC04 (Reeve et al. 2016) plasmid as a template, use primer 6.0 software to design and amplify repA primers, repA-F: TGATCTTTTTCTACCTCGAGGAGAATTAAGAAAGACATGG, repA-R: TCTTCATCGGCGGCGCGCCAAACAAGCCTCAGATGTG, and amplify repA from Bacillus subtilis as an insert. Using pUCG3.8-spe as a template, use primer 6.0...
Embodiment 2
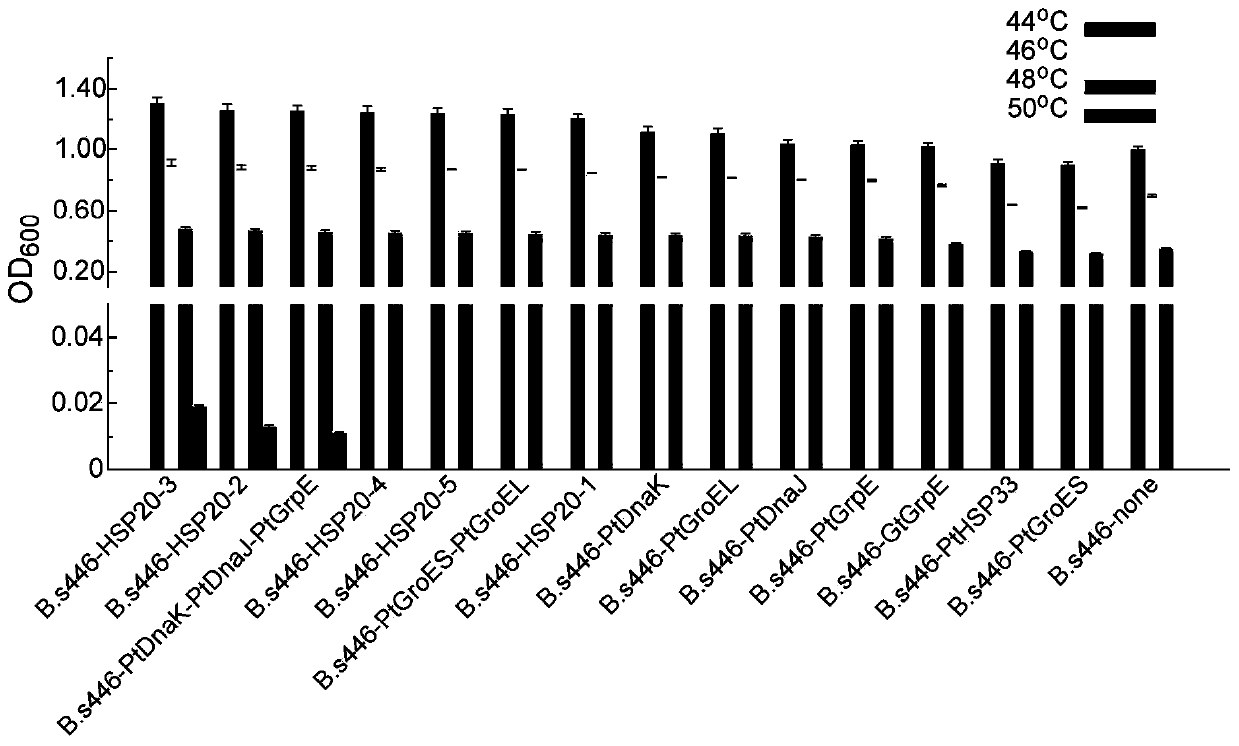
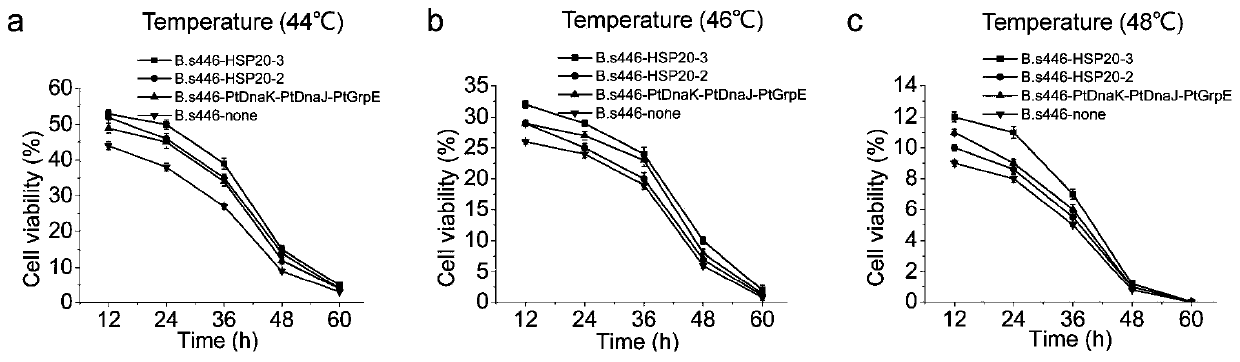
[0073] The impact of embodiment 2 high temperature on recombinant bacteria
[0074] 1. Determination of cell concentration
[0075] In order to more accurately determine the impact of high temperature on the strain, two schemes were adopted to determine the cell concentration. Scheme A: Inoculate a single clone into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL LB medium, culture at 39°C, 220rpm for 12h, then take the fermentation broth and transfer it to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL LB medium to inoculate the The inoculum with the initial OD value of the medium was 0.1 for transfer. After the transfer, first culture at 41°C and 220rpm for 12h, and then increase the culture temperature by 2°C every 12h until the culture temperature reaches 49°C after 60h of culture. During this process, samples were taken every 12 hours, and the OD was measured using a spectrophotometer 600 The blank control is the culture medium without cells. The difference between plan B and plan...
Embodiment 3
[0080] The impact of embodiment 3 hyperosmotic pressure on recombinant bacteria
[0081] The growth of B. subtilis 446 in the fermentation process is easily affected by the high osmotic pressure brought by the fermentation product riboflavin. Strains B.s446-HSP20-3, B.s446-HSP20-2 and B.s446-PtDnaK-PtDnaJ-PtGrpE containing heat shock proteins were cultured in hypertonic medium containing 10% sodium chloride at 37°C, simulating Hyperosmotic environment during strain fermentation.
[0082] To determine the cell viability of strains B.s446-HSP20-3, B.s446-HSP20-2, and B.s446-PtDnaK-PtDnaJ-PtGrpE under hypertonic conditions, inoculate single clones into 250 mL cones containing 50 mL LB medium. In a conical flask, culture at 37°C and 220rpm for 12h, then take the fermentation broth and transfer it to a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL LB medium. Then continue to culture at 37°C and 220rpm for 12 hours, then add NaCl to the culture medium during the exponential growth phase ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com