Escherichia coli genetically-engineered bacterium for producing protocatechuic acid and construction method and application of escherichia coli genetically-engineered bacterium
A technology of protocatechuic acid and Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of protocatechuic acid recombinant Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria and its construction, can solve the problems of genetic instability and affecting the industrial application of products, and achieve genetic stability and reduce Production cost, cost reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1, the construction of Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria WJ004
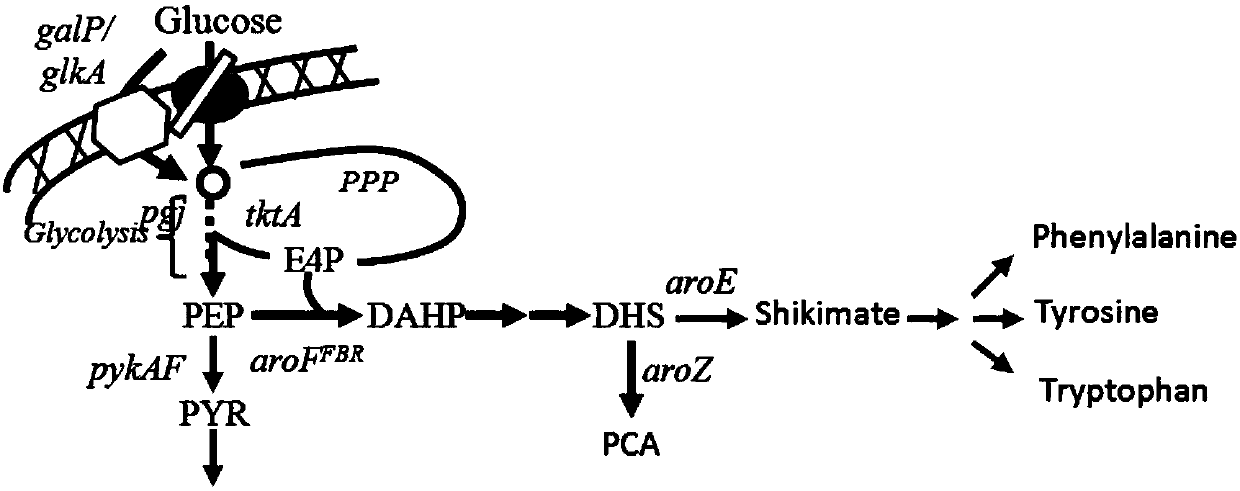
[0046] The Escherichia coli genetically engineered strain WJ004 was constructed by weakening the expression regulation of the 3-dehydrogenase shikimate dehydrogenase gene (aroE). A two-step homologous recombination method was used to insert a synthetic regulatory element upstream of the start codon of aroE. P1 (as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1), and replace the original start codon ATG with the rare start codon TTG. The specific construction steps are as follows:
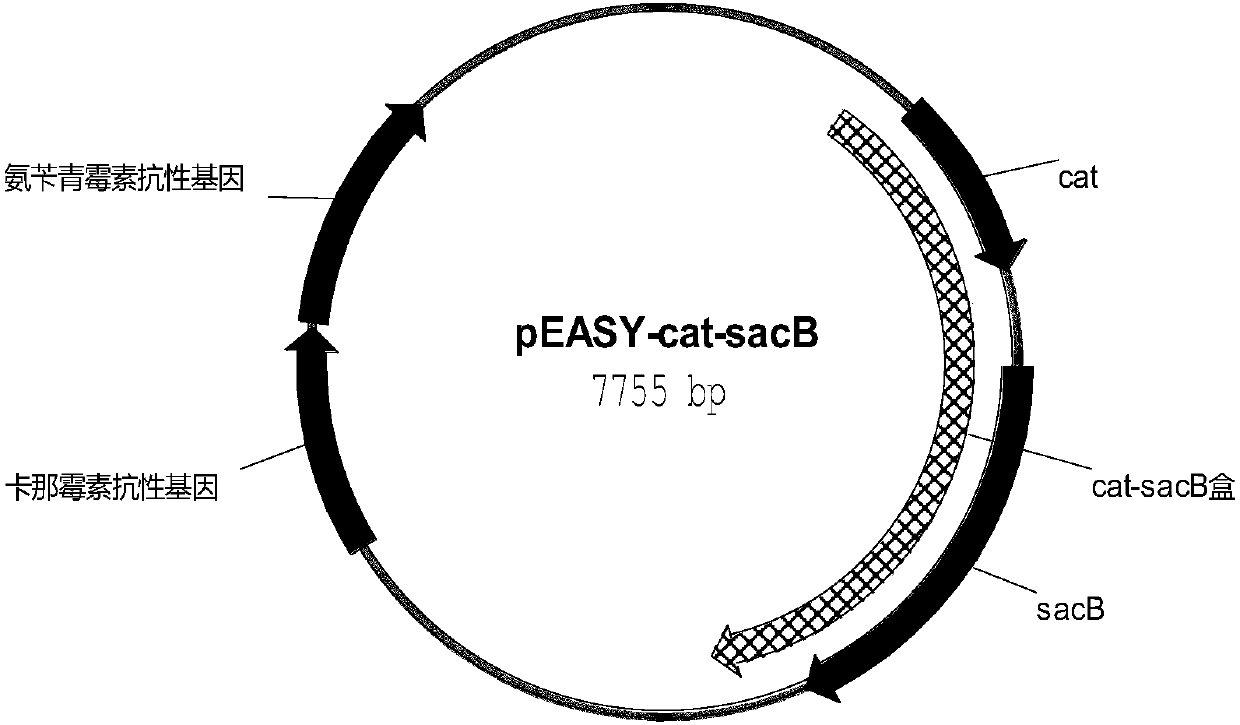
[0047] With the plasmid pEASY-cat-sacB ( figure 2 ) as a template, using primers aroE1-up / aroE1-down to amplify the fragment aroE1 of the first step of homologous recombination. The primer sequences are:
[0048] aroE1-up: GATGCCCTGACGGGTGAACTGTTTCGACAGGGGTAACATA G TGACGGAAGATCACTTC
[0049] aroE1-down: CTGTGGGCTATCGGATTACCAAAAACAGCATAGGTTTCCA ATCAAAGGGAAAACTGTCC
[0050] Amplification system: 5×TransStart TM FastPf...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2, the construction of Escherichia coli genetic engineering bacterium WJ006
[0069] Escherichia coli genetically engineered strain WJ006 is obtained on the basis of Escherichia coli WJ004 through the mutation and expression regulation of the 3-deoxy-D-arabinoheptulose-7-phosphate synthase gene (aroF) construction, using two-step homologous recombination Method, replace the original aroF gene (such as SEQ ID NO:6) with the mutant gene aroF* (such as SEQ ID NO:5) that changes the 443rd base C to T, to remove the 3-deoxy - Tyrosine feedback inhibition of D-arabinoheptulose-7-phosphate synthase with insertion of synthesis regulatory element P2 (eg SEQ ID NO: 2) upstream of the start codon. The specific construction steps are as follows:
[0070] Using Escherichia coli DSM 1576 genomic DNA as a template, the aroF gene was amplified using primers aroF-F / aroF-R. The primer sequence is:
[0071] aroF-F: ATGCAAAAAGACGCGCTGAA
[0072] aroF-R: TTAAGCCACGCGAGCCGTCAG...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Embodiment 3, the construction of Escherichia coli genetic engineering bacterium WJ012
[0111] The Escherichia coli genetically engineered strain WJ012 was constructed on the basis of Escherichia coli WJ006 by regulating the expression of the transketolase gene (tktA). It inserted the synthesis regulation upstream of the tktA start codon through two homologous recombination methods. Element P4 (eg SEQ ID NO: 4). The specific construction steps are as follows:
[0112] With the plasmid pEASY-cat-sacB ( figure 2 ) as a template, using primers tktA1-up / tktA1-down to amplify the fragment tktA1 of the first step of homologous recombination. The primer sequences are:
[0113] tktA1-up: GCCCAAAACGCGCTGTCGTCAAGTCGTTAAGGGCGTGCCCTTCATCAT GTGACGGAAGATCACTTC
[0114] tktA1-down: CATGCTCAGCGCACGAATAGCATTGGCAAGCTCTTTACGTGAGGACAT ATCAAAGGGAAAACTGTCC
[0115] The amplification system is the same as in Example 1, and the amplified tktA1 product comprises the cat-sacB box ( ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com