Resin matrix composite and preparing method thereof
A composite material and resin-based technology, which is applied in the field of resin-based composite materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of large dielectric loss and large leakage current of composite materials, and can improve the dielectric constant, reduce the dielectric loss, and reduce the amount of addition. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
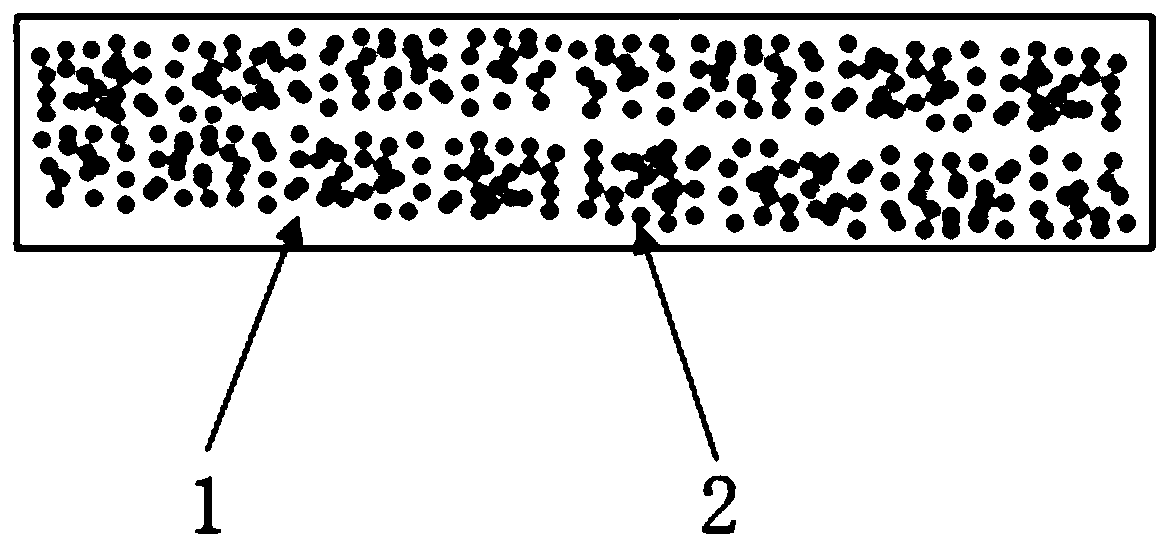
[0062] This embodiment provides a polyphenylene ether-based composite material, the core structure of the inorganic filler is spherical, the particle size of the core is 5 μm, the material of the core of the inorganic filler is barium zincate doped with barium tantalate, and the material of the first shell layer nickel with a thickness of 25 μm, and the material of the second shell layer is nickel oxide with a thickness of 5 μm. The proportion of the inorganic filler to the total volume of the composite material is 30%, the dielectric constant of the composite material is 6.72, and the dielectric loss is 0.00154. The composite material of this embodiment has a low proportion of inorganic filler, and also has a relatively high dielectric constant; the inorganic filler of this embodiment is added with a conductive first shell layer, but the dielectric loss of the composite material is still very low, There is no increase in dielectric loss due to the addition of conductive fille...
Embodiment 2
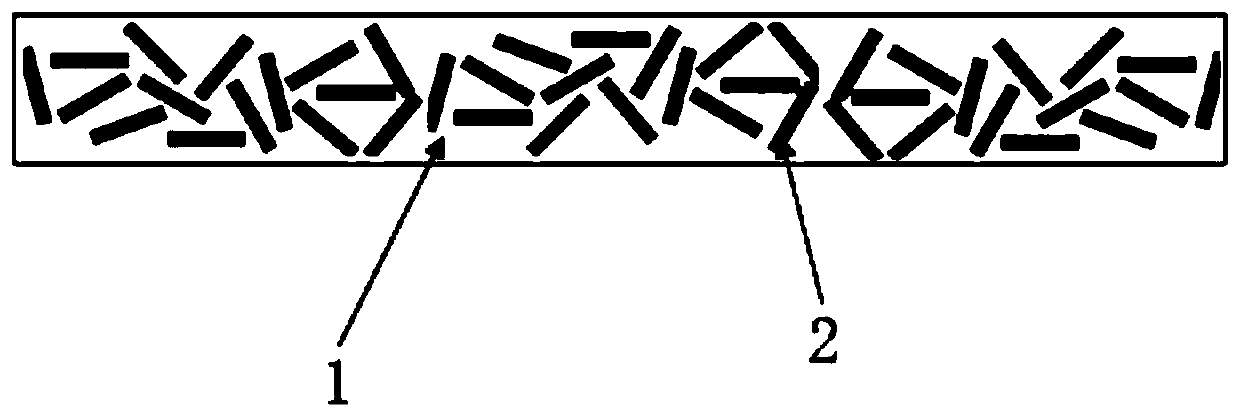
[0064] This embodiment provides a composite material based on phenylpropanolamine, in which phenylpropanolamine is the matrix, calcium titanate is used as the core of the inorganic filler, the structure of the core is fibrous, the material of the first shell layer is carbon, and the thickness is 10 μm , the material of the second shell layer is polydopamine, the thickness is 2 μm, and the proportion of the inorganic filler to the total volume of the composite material is 20%. The composite material has a dielectric constant of 9.09 and a dielectric loss of 0.00239.
Embodiment 3
[0066] This embodiment provides a composite material based on polyphenylene sulfide, which uses polyphenylene sulfide as the matrix, and copper calcium titanate as the core of the inorganic filler. The structure of the core is spherical, and the particle size of the core is 5 μm. The first The shell layer is aluminum with a thickness of 15 μm and the second shell layer is aluminum oxide with a thickness of 1 μm. The inorganic filler accounts for 40% of the total volume of the composite material. The composite material has a dielectric constant of 10.45 and a dielectric loss of 0.00132.
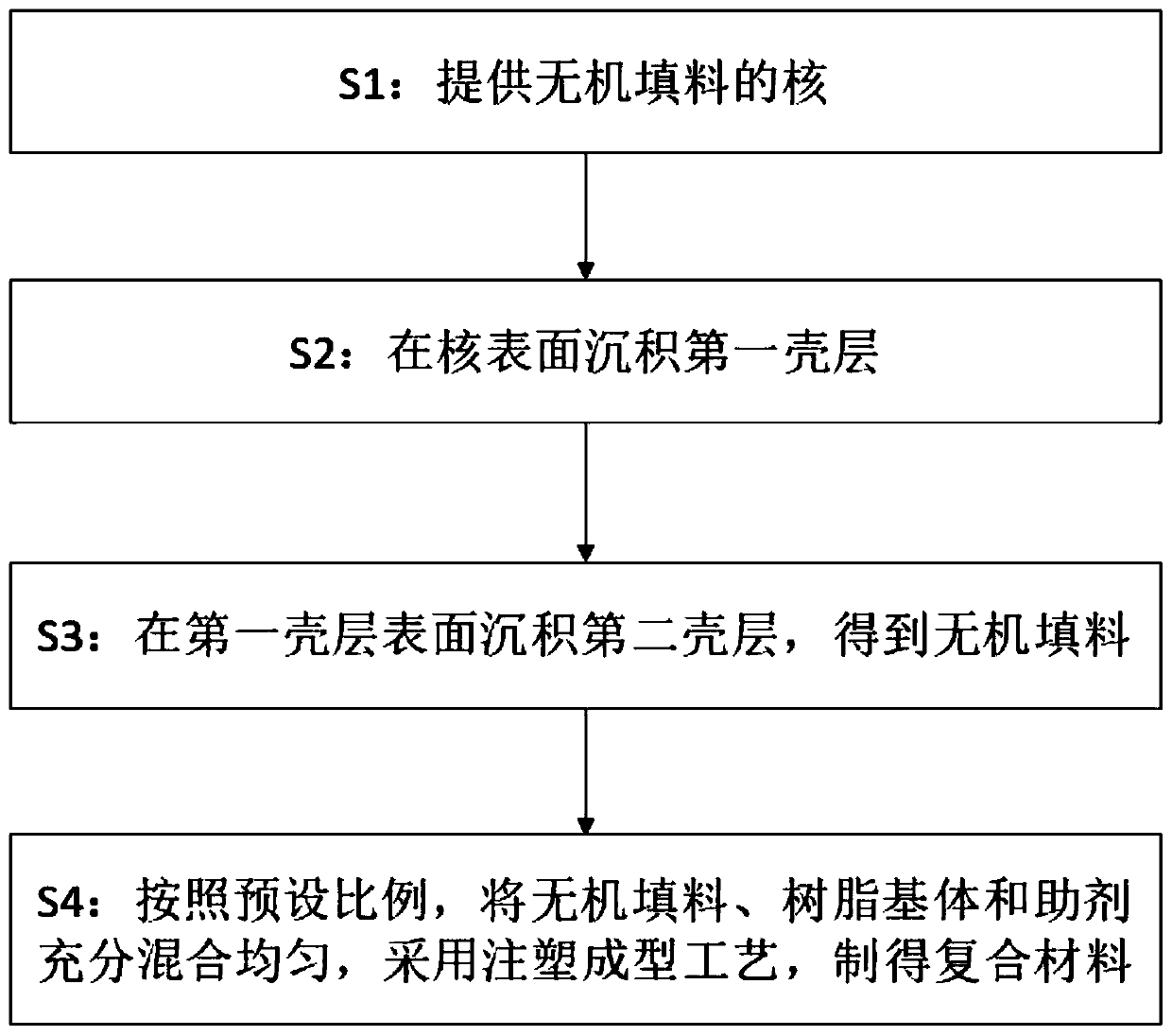
[0067] see image 3 , the present invention also provides a method for preparing a resin-based composite material, comprising the following steps:
[0068] S1: provide the core of inorganic filler;
[0069] S2: Depositing the first shell on the surface of the core;
[0070] S3: Depositing a second shell layer on the surface of the first shell layer to obtain an inorganic filler;
[0071] ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com