Polyethyleneimine-modified ascorbic acid carbon nanodots, preparation method and application
A polyethyleneimine, carbon nanodot technology, applied in the field of chemical detection, can solve the problems of complex operation, low sensitivity, and can not meet the needs of actual water sample detection, achieve simple production, avoid the use of large-scale instruments, and quickly on-site Visualize the effect of detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A preparation method of polyethylenimine-modified ascorbic acid carbon nano-dots, comprising the following steps:
[0032] Weigh 3.0g polyethyleneimine (PEI, molecular weight is 600) and add it to 20mL containing 0.8807g ascorbic acid reaction kettle solution, the molar ratio of polyethyleneimine and ascorbic acid used is 1:1, fully stir, seal, heat to 200 ℃, reacted for 6 hours, cooled to room temperature to obtain a light yellow liquid, then filtered through a 0.45 μM needle filter to remove larger particles in the solution, and then dialyzed with ultrapure water (the dialysis bag has a Dalton molecular weight of 1000) for 8 hours , change the ultrapure water every 2 hours, freeze-dry to obtain carbon nano-dot powder, and set aside.
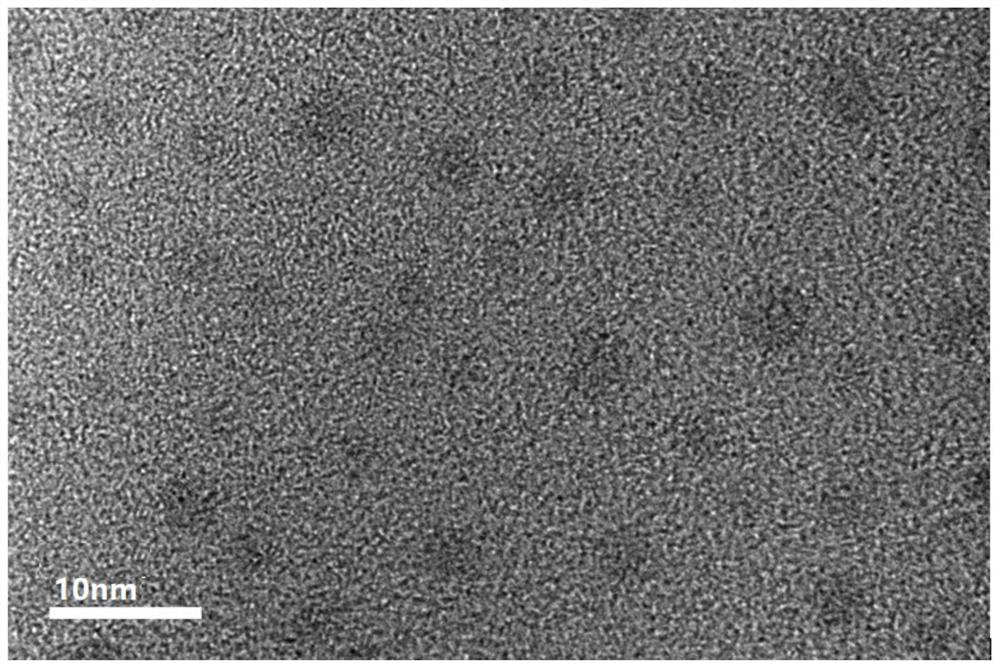
[0033] Get the carbon nano-dot powder that embodiment 1 makes, analyze its morphology and size distribution, its TEM result is as follows figure 1 As shown, the particle size of carbon nanodots is about 3nm. After continuous scanning b...
Embodiment 2
[0035] A preparation method of polyethylenimine-modified ascorbic acid carbon nano-dots, comprising the following steps:
[0036] Take 2.0g polyethyleneimine (PEI, molecular weight is 10000) and join in 20mL containing 0.7045g ascorbic acid solution, the molar ratio of polyethyleneimine and ascorbic acid used is 0.1:2, transfer to the reaction kettle, seal, heat to 200 ℃, react for 6 hours, cool to room temperature, and filter the obtained brown-yellow liquid through a 0.45 μM needle filter to remove suspended particles in the solution, and then dialyze with a dialysis bag with a Dalton molecular weight of 10,000 for 8 hours, and change it every 2 hours Ultrapure water, freeze-dried to obtain carbon nano-dot powder, and set aside.
Embodiment 3
[0038] The quantitative detection of hypochlorous acid by ascorbic acid carbon nano-dot fluorescent probe is as follows:
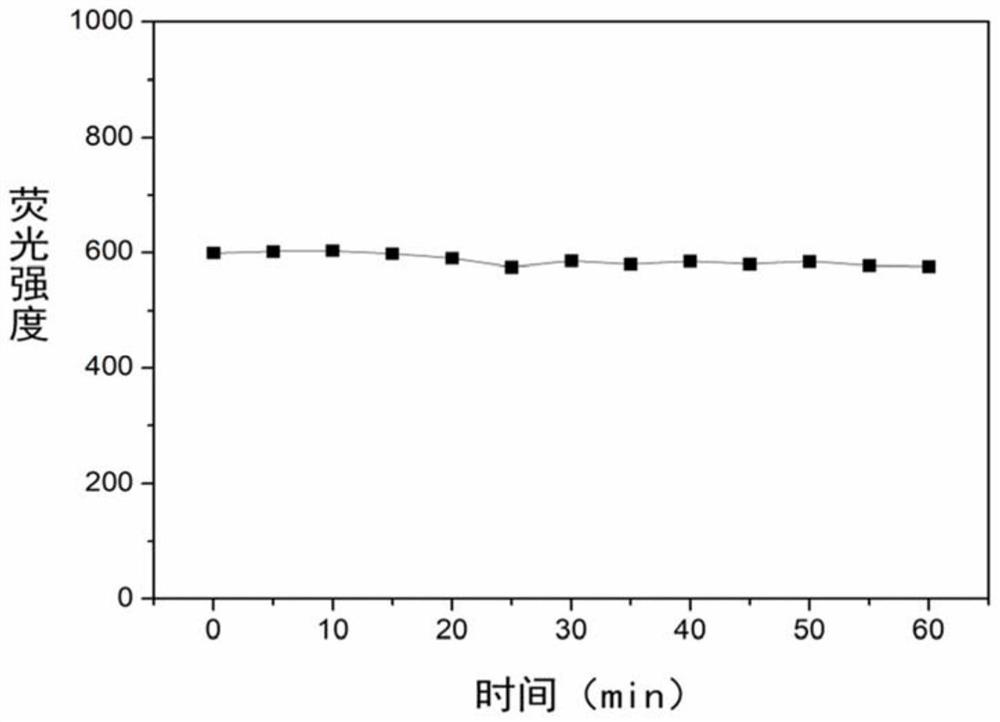
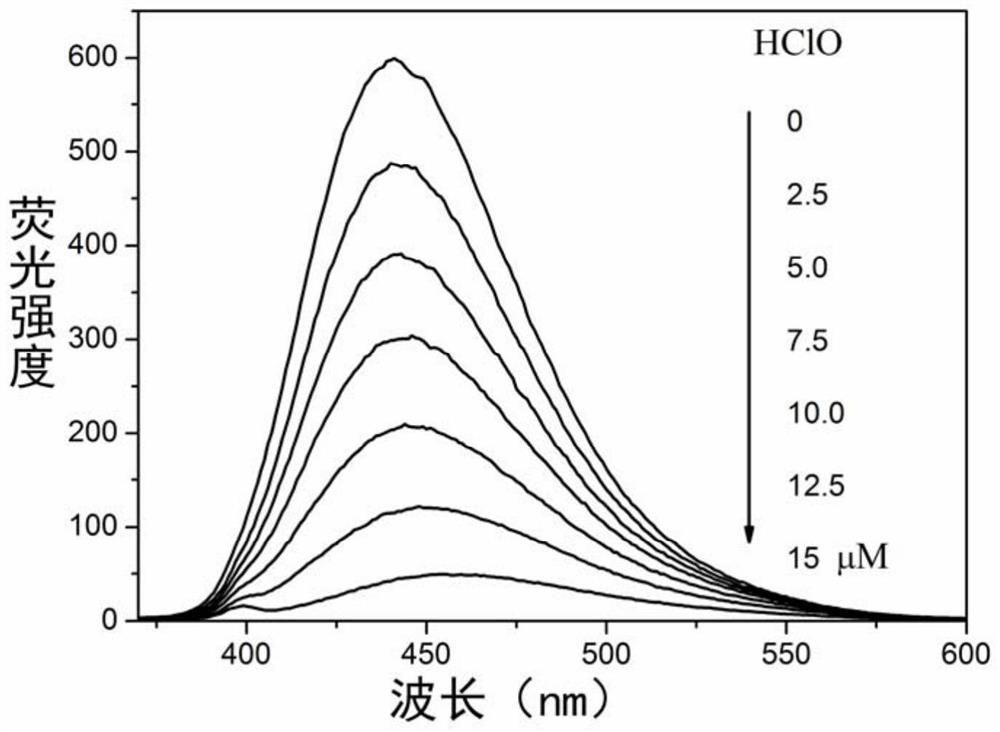
[0039] The carbon nano-dot powder synthesized in Example 1 was dispersed in ultrapure water to make a fluorescent probe dispersion with a concentration of 2 μg / mL, and a standard solution of hypochlorous acid (0.0, 2.5, 5.0, 7.5, 10.0 , 12.5 and 15μM), with the increase of hypochlorous acid concentration, the fluorescence intensity gradually decreases, and the fluorescence spectral response process is as follows image 3 shown.
[0040] The linear relationship between fluorescence quenching intensity and hypochlorous acid concentration is, Y=0.0084+0.06468[HClO], linear correlation coefficient R 2 =9927, the detection limit is 14nM, such as Figure 4 , based on this linear relationship, the quantitative detection of hypochlorous acid can be realized.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com