Semiconductor device manufacturing method
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, transistors, etc., can solve the problems of lowering and electron beam irradiation on the first main surface side, and achieve low recovery loss Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0046] 1. Configuration of the semiconductor device 100 in the first embodiment
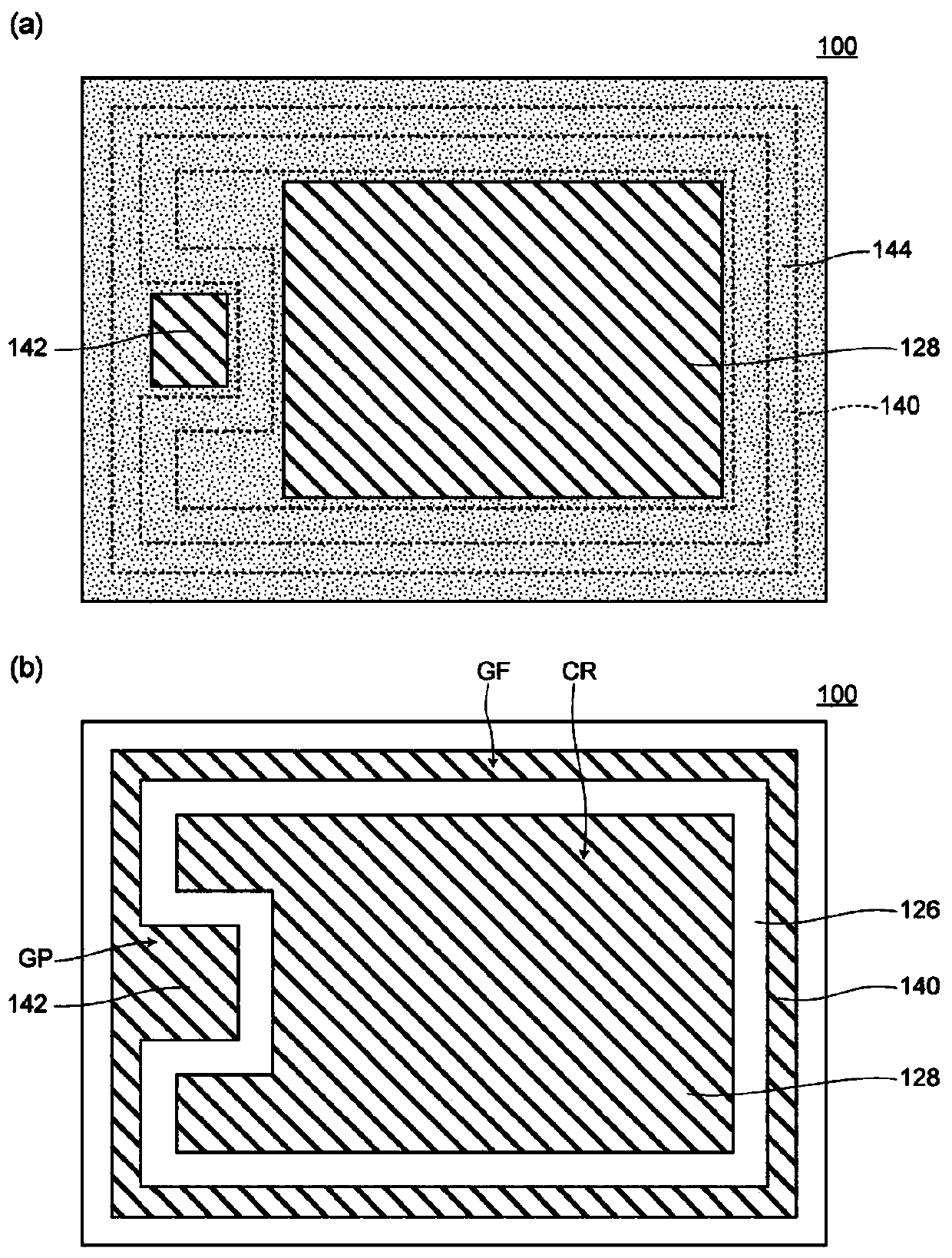
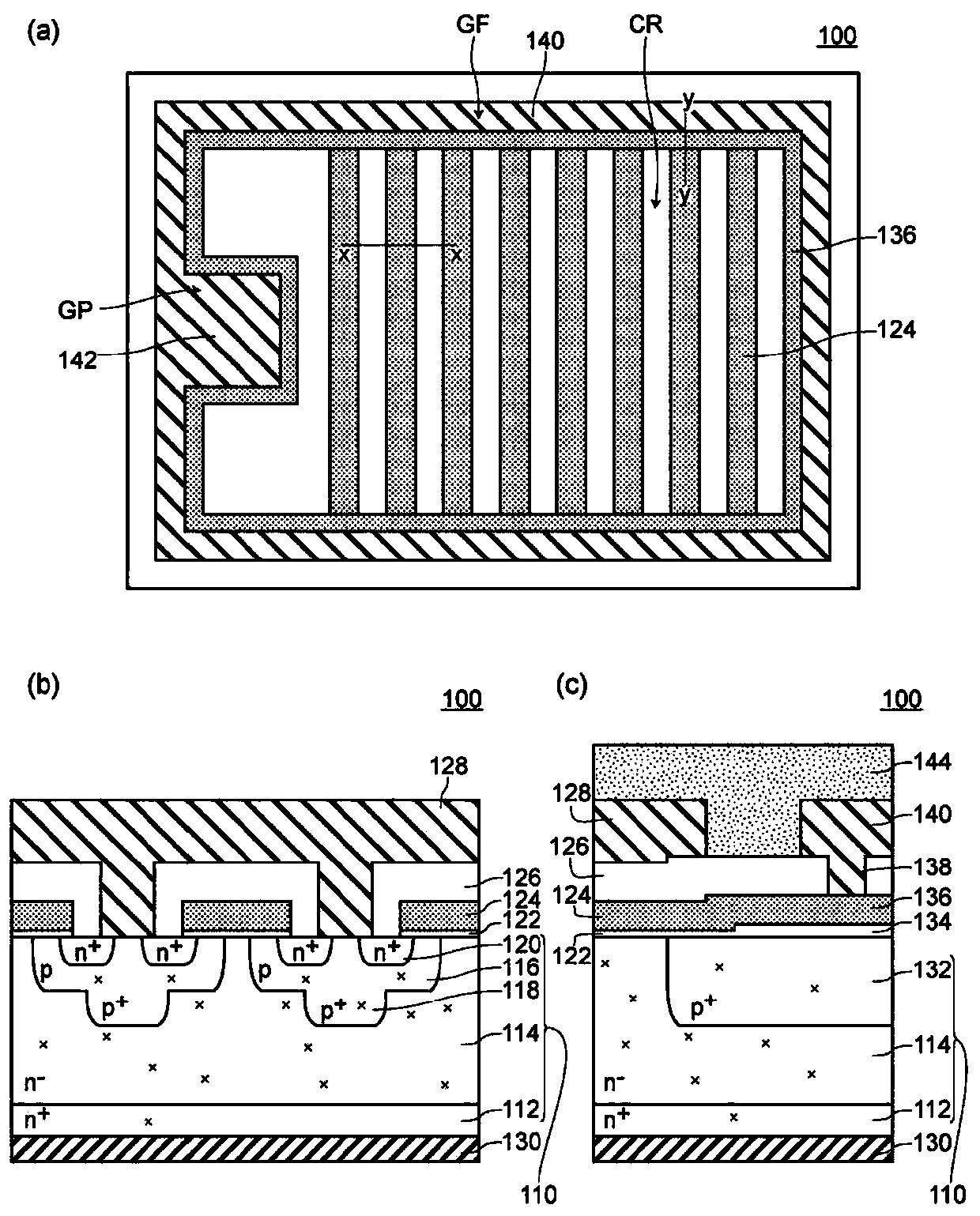
[0047] The semiconductor device 100 in Embodiment 1 is a planar semiconductor device (MOSFET) (refer to figure 2 ), which includes: are delineated in the stack with n + type low resistance semiconductor layer 112 with n - The cell region CR on the semiconductor substrate 110 of the type drift layer 114; and the peripheral region defined around the cell region CR. The peripheral region is composed of a gate wiring formation region GF surrounding the cell region CR, and a gate pad formation region GP protruding toward the cell region CR (inwardly) (refer to figure 1 (b) and figure 2 ).
[0048] The active electrode 128 is formed on the surface of the first main surface of the semiconductor substrate 110 in the cell region CR (refer to figure 1 (b)). In addition, a gate wiring 140 (gate finger) is formed on the surface of the first main surface of the semiconductor base 110 in the gate wir...
Embodiment approach 2
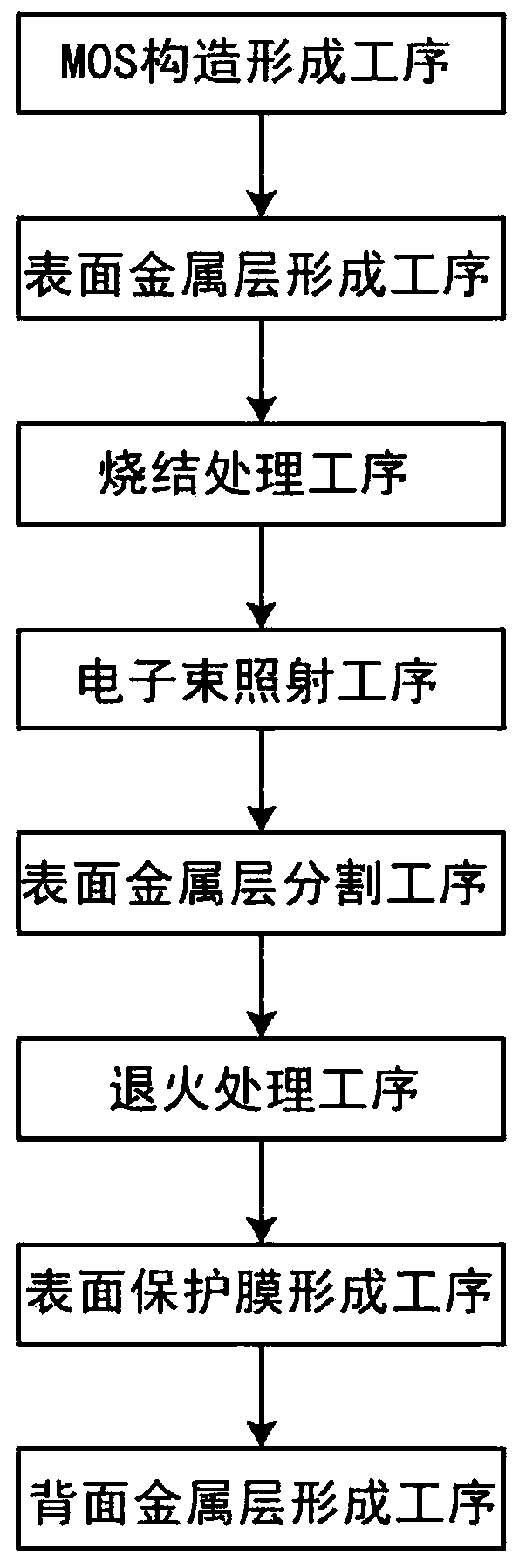
[0107] Although the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device in Embodiment Mode 2 includes basically the same steps as the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device in Embodiment Mode 1, it manufactures trench gate MOSFETs instead of planar gate MOSFETs. This point is different from the method of manufacturing the semiconductor device in Embodiment 1. like Figure 11 As shown, in the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device in the second embodiment, the semiconductor base 110 has in the cell region CR: a low-resistance semiconductor layer 112, a drift layer 114, and a p-type base region formed on the surface of the drift layer 114 116, and the source region 120 arranged in the base region 116 and formed so that at least a part is exposed on the inner peripheral surface of the trench 150 described later, the semiconductor device 102 has a first On the main surface side, the base region 116 is opened and reaches the plurality of trenches 150 of the drift ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com