Method for cultivating miniature sweet potato seedlings
A miniature potato and seedling technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, cultivation, culture medium, etc., can solve the problems that microtubers are vulnerable to underground pests, unfavorable to high-quality pollution-free sweet potatoes, and limit the growth of seedlings, etc. Achieve the effect of avoiding pesticide residues, facilitating cultivation and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] The present embodiment discloses a method for cultivating sweet potato miniature potato seedlings, comprising the following steps:
[0040] Step 1. The machine opens a planting ditch in the greenhouse of the planting field;
[0041] The width of the planting ditch is 30cm; the depth of the planting ditch is 10cm; the bottom of the planting ditch is flat. The width and depth of the planting ditch are suitable for the discharge of micro-tubers. The flat bottom of the planting ditch is conducive to the laying of non-woven fabrics, the protection of non-woven fabrics, the uniform contact between the substrate and the micro-tubers, and the cultivation, growth and harvesting of micro-tuber seedlings. Pick.
[0042] A seedling-cutting operation path is reserved between two adjacent planting ditches, and the width of the seedling-cutting operation path is 25 cm. It is convenient for manual cutting of seedlings, and it is also convenient for the management of seedlings in the ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The main difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0067] Step 1, artificially set up planting ditch in the greenhouse of planting field;
[0068] The width of the planting ditch is 20cm; the depth of the planting ditch is 5cm; the width of the operation path for cutting seedlings is 25cm.
[0069] The substrate used in step 4 includes the following substances in parts by weight:
[0070] 3 parts peat soil;
[0071] Vermiculite 0.5 part;
[0072] Perlite 0.5 parts.
[0073] Step six, seedling hardening;
[0074] Preferably, the condition for hardening seedlings in the step 6 is: reduce the substrate temperature to 20° C. 6 days before picking the seedlings. The low temperature resistance performance of the seedlings is effectively improved by hardening the seedlings, which is beneficial to the cultivation of the seedlings.
[0075] Step seven, cut the seedlings.
[0076] The condition of preferably described step seven cutting seedlings is:
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0080] The main difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0081] Step 1, artificially set up planting ditch in the greenhouse of planting field;
[0082] The width of the planting ditch is 25cm; the depth of the planting ditch is 8cm; the width of the operation path for cutting seedlings is 22cm.
[0083] Step six, seedling hardening;
[0084] Preferably, the condition for hardening seedlings in the step 6 is: reduce the substrate temperature to 20° C. 6 days before picking the seedlings. The low temperature resistance performance of the seedlings is effectively improved by hardening the seedlings, which is beneficial to the cultivation of the seedlings.
[0085] Step seven, cut the seedlings.
[0086] The condition of preferably described step seven cutting seedlings is:
[0087] The seedlings grow more than 50cm, and the seedlings are collected in sections of 2 to 3 sections; the seedlings are collected 3 times in the whole seedling stage.
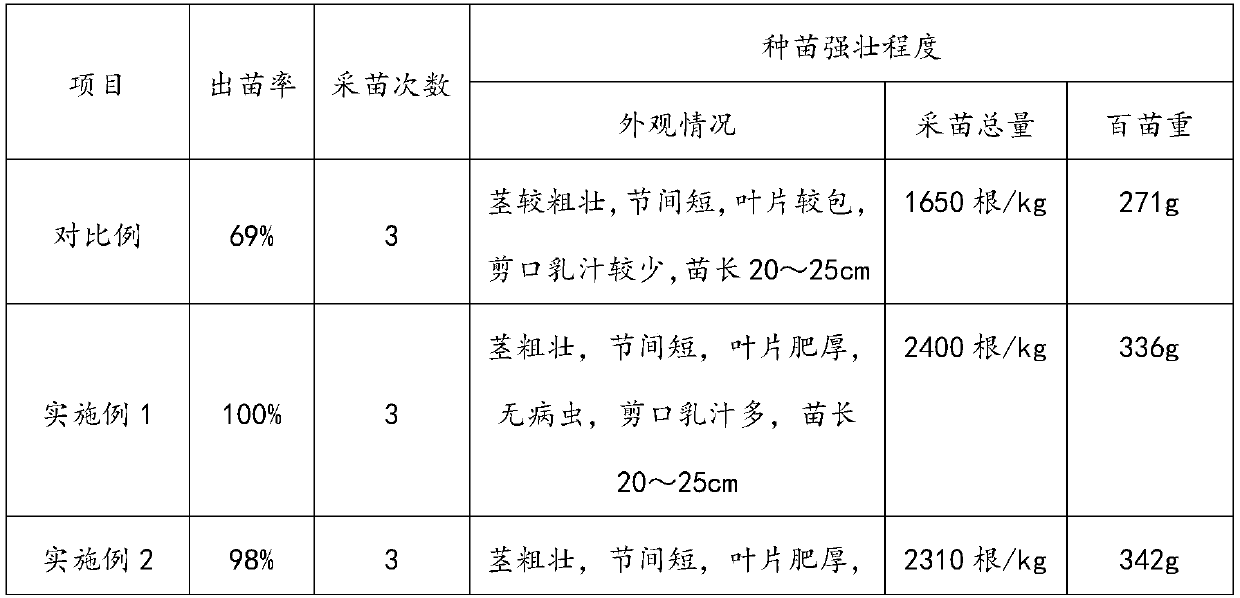
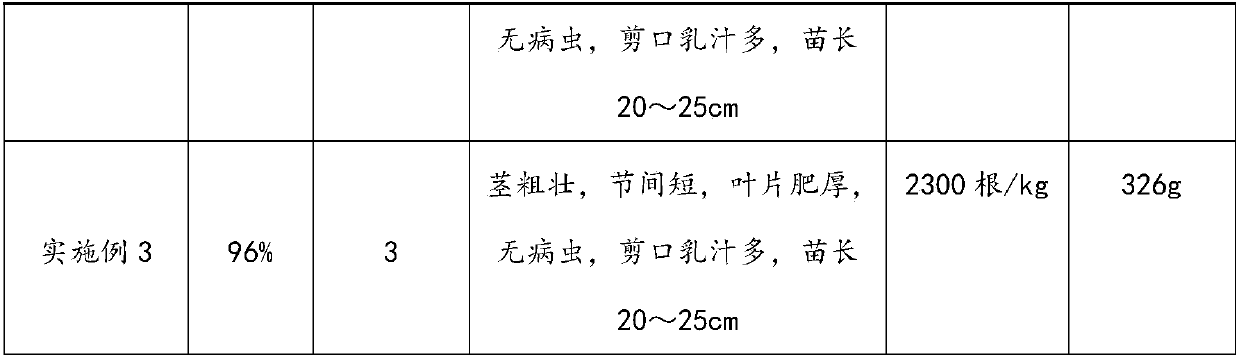
[0088] See t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com