Biological magnesium alloy containing rich LPSO structures and preparing method of biological magnesium alloy
A magnesium alloy and biological technology, applied in the field of biological magnesium alloy and its preparation, can solve the problems of low structure content of LPSO and rapid degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Weigh 0.05g manganese powder (average particle size 5μm), 8.95g magnesium-zinc alloy powder (ZK30 powder, average particle size 50μm) and 1.0g gadolinium powder (average particle size 8μm), place the two in a ball mill, Uniformly dispersed mixed powder was obtained by ball milling under the atmosphere, the rotational speed of the ball mill was 400 rpm, and the ball milling time was 6 hours. Using the above mixed powder as raw material, the bio-magnesium alloy containing LPSO structure was prepared by laser selective melting process. During the preparation process, the laser power was controlled to 80W, the scanning speed was 300mm / min, and the spot diameter was 80μm.
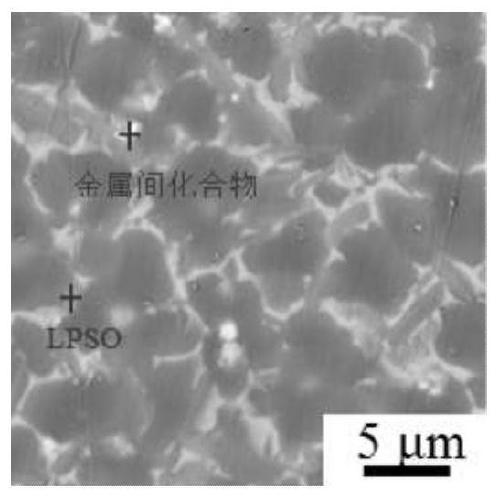
[0043] The test found that fine grains and fine LPSO phases were formed in the prepared alloy, and evenly filled the entire grain interior, and no intermetallic compounds were precipitated in the alloy ( figure 1). After alloying manganese, the degradation rate of magnesium alloy decreased from 0.61mm / ye...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Weigh 0.02g manganese powder (average particle size 5μm), 8.98g magnesium-zinc alloy powder (ZK30 powder, average particle size 50μm) and 1.0g gadolinium powder (average particle size 8μm), place the two in a ball mill, Uniformly mixed mixed powder was obtained by ball milling under atmosphere, the rotational speed of the ball mill was 400 rpm, and the ball milling time was 6 hours. Using the above mixed powder as raw material, the bio-magnesium alloy containing LPSO structure was prepared by laser selective melting process. During the preparation process, the laser power was controlled to 80W, the scanning speed was 300mm / min, and the spot diameter was 80μm.
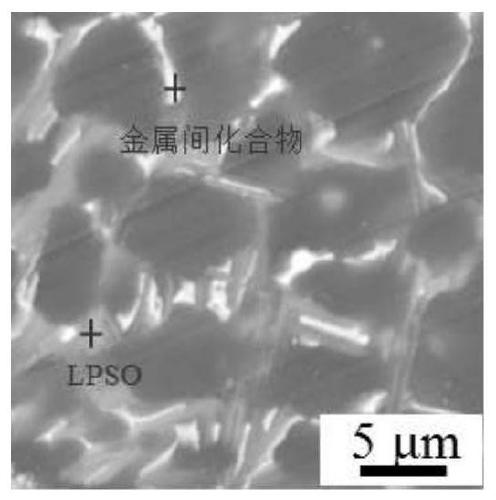
[0047] The test found that compared with the magnesium alloy without adding manganese, more LPSO structures were formed in the prepared alloy but did not fill the entire grain interior, and a small amount of intermetallic compounds were precipitated ( figure 2 ), the degradation rate of the alloy is 0.25mm / year....
Embodiment 3
[0049] Weigh 0.05g manganese powder (average particle size 5μm), 8.95g magnesium-zinc alloy powder (ZK30 powder, average particle size 50μm) and 1.0g gadolinium powder (average particle size 8μm), place the two in a ball mill, Uniformly dispersed mixed powder was obtained by ball milling under the atmosphere, the rotational speed of the ball mill was 300 rpm, and the ball milling time was 5 hours. Using the above mixed powder as raw material, a medical magnesium alloy containing LPSO structure was prepared by selective laser melting; during the preparation process, the laser power was controlled to 80W, the scanning speed was 300mm / min, and the spot diameter was 80μm.
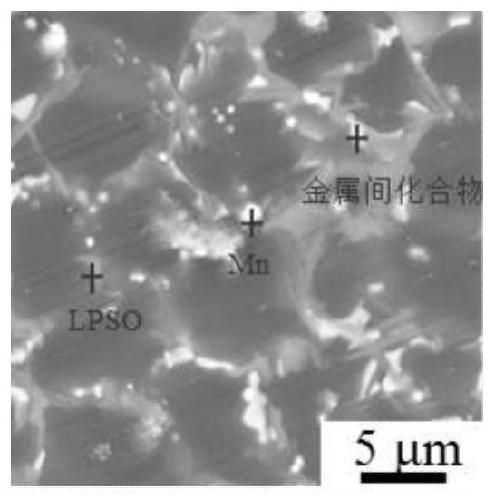
[0050] The test found that abundant LPSO structure was formed in the prepared alloy, and its degradation rate was reduced from 0.61mm / year to 0.34mm / year compared with the magnesium alloy without adding manganese.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com