Making method of reed planting edible mushroom
A production method and technology of edible fungi, applied in the field of production of reed planting edible fungi, can solve the problems of shortage of raw materials, high pollution, low success rate, etc., and achieve the effects of no pesticide residue, fast germination, and good elasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
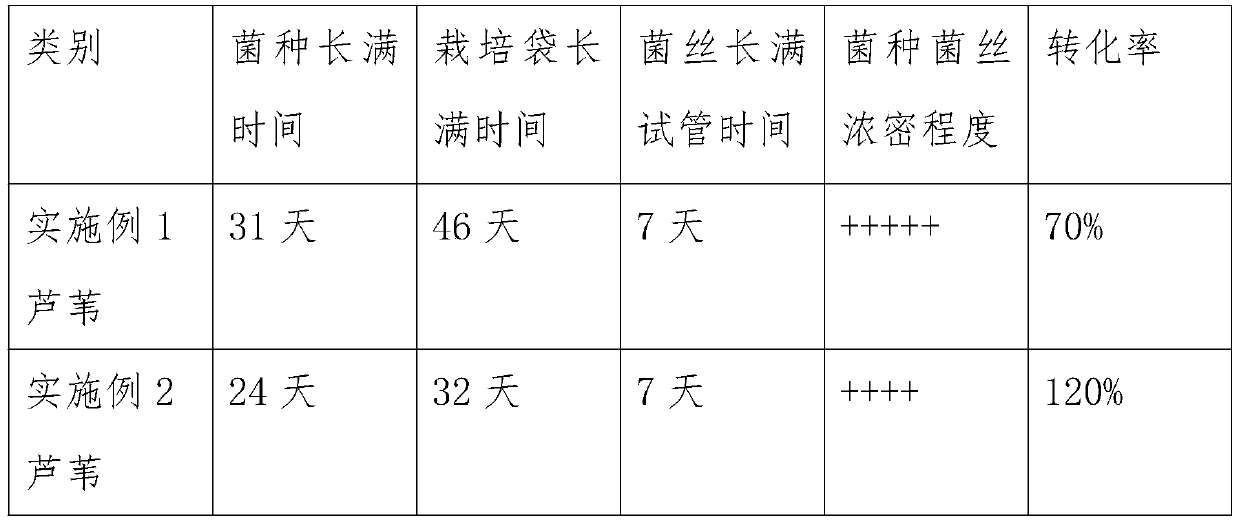
Embodiment 1
[0037] A method for making edible mushrooms grown from reeds, comprising the following steps:
[0038] Step A: clinker preparation (by mass percentage): reed 78%, bran 20%, gypsum 1%, lime 1%;
[0039] Step B: reed pretreatment: crush long reeds with a pulverizer, build piles of crushed reeds and pre-wet them for 12 hours, put the pre-wetted reeds into a pool at 100-123°C for cooking, the crushed reeds have a length of 2-3cm, the pre-wet water of the crushed reed reaches about 30%, not more than 60%, and the cooking time of the pre-wet reed is 4 hours;
[0040] Step C: Mixing materials: fully stir the pre-cooked reeds, bran, gypsum, and lime evenly, replenish water, put the evenly stirred materials into a small bacteria bag made of polypropylene with a diameter of 10 cm and a height of 20 cm, wheat Stir the bran, lime, and gypsum into nutrient materials and stir them into dry powder. Without adding water, fully stir the pre-cooked reeds, bran, gypsum, and lime evenly, and the...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A method for making edible mushrooms grown from reeds, further comprising the following steps:
[0046] Step A: fermentation material ingredients (by mass percentage): reed 100%, bran 1%, superphosphate 0.16%, urea 0.5%, salt 0.1%, gypsum 2%, lime 2%;
[0047] Step B: Reed pretreatment: crush the long reeds with a grinder, and then build the crushed reeds into a pile. The length of the crushed reeds is 2-3cm, and the water content of the crushed reeds is about 30%, not more than 60%. ;
[0048] Step C: Configure nutritional materials and induce fermentation small materials: stir wheat bran, superphosphate, urea, salt, gypsum, and lime for later use;
[0049] Step D: Mixing ingredients: fully stir the crushed dry ingredients, nutritional ingredients, and small fermented ingredients evenly, add water, and carry out fermentation;
[0050] Step E: Finished product: the first fermentation is carried out by the physical fermentation method, and the temperature is increased ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com