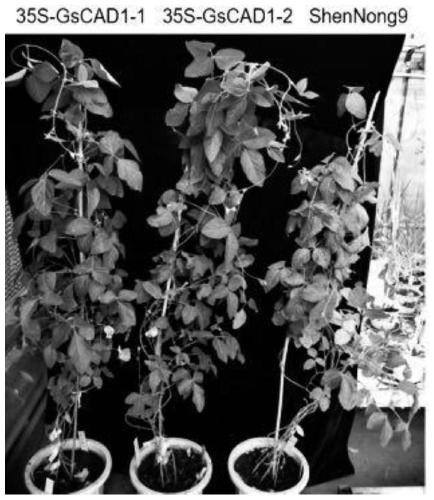
Mosaic-virus resistance GsCAD1 gene separated from wild soybeans, encoded protein and application of GsCAD1 gene
A wild soybean and mosaic virus technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of resistance loss of disease-resistant plants, etc., to achieve an improved level, ensure yield, and achieve long-term effective control effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0026] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0027] 1. Extract the RNA of wild soybean BYO-5, and use the reverse transcription kit (AT311-03) to obtain the cDNA of wild soybean BYO-5.
[0028] 2. Using primer F1: CTCTAGA ATGGCAGCACAAGCTGAA (underlined is the restriction site XbaI), primer R1: CGGATCC AATTTCAGTGTGTTTCCA (underlined is the restriction site BamHI), using the cDNA of wild soybean BYO-5 as a template for PCR, the reaction system is shown in Table 1, and the PCR amplification procedure is shown in Table 2
[0029] Table 1 Amplification system
[0030]
[0031] Table 2 PCR amplification program
[0032]
[0033]
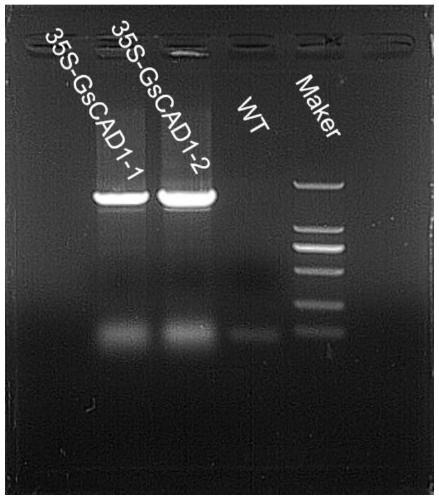
[0034] The 50uL PCR product was detected on 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis and a PCR fragment with a size of about 1080 was recovered.
[0035] 3. Clone the wild soybean GSCAD1 gene and connect it to the pMD-18T vector (the reaction system is shown in Table 3 below)
[0036] Table 3 Reaction system for linking pMD18-T vector
[0037]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com