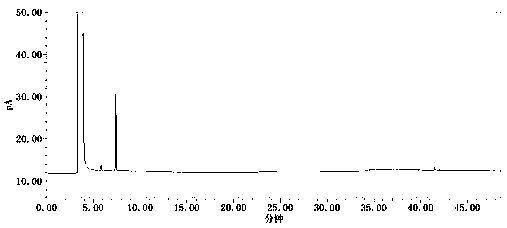
Method for simultaneously determining contents of coexisting impurities in 2, 4-difluoroaniline
A technology for difluoroaniline and impurity content, which is applied in the field of analysis and detection in chemical medicine, can solve problems such as affecting the quality of medicines, patients' health, etc., and achieves the effects of easy control, accurate detection results, and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] The raw materials used in the specific examples of the present invention are all known products, obtained by purchasing commercially available products, and the specific information is as follows in Table 1;
[0027] Table 1 Raw material information table
[0028]
[0029] A method for simultaneously detecting the content of coexisting impurities in 2,4-difluoroaniline provided by the present invention, the specific steps are as follows;
[0030] Chromatographic conditions
[0031] Instrument: Agilent 7890B Gas Chromatograph
[0032] Chromatographic column: 100% dimethylpolysiloxane (DB-1 30m×0.32mm×1.0μm or similar in polarity) as the stationary liquid
[0033] Detector: FID detector 250°C
[0034] Carrier gas: nitrogen
[0035] Carrier gas flow rate: 0.8ml / min
[0037] Injection port temperature: 200°C
[0038] Injection volume: 1.0μl
[0039] Heating program: the initial temperature is 50°C, maintained for 2 minutes, raised to 11...
Embodiment 2
[0053] System suitability test:
[0054] Add impurity need testing solution: preparation method is as embodiment 1.
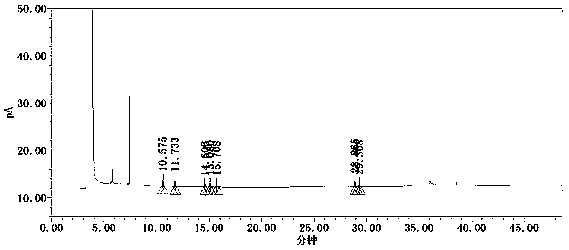
[0055] Get and add impurity need testing solution, according to the chromatographic condition in the embodiment 1 continuous sample injection 6 needles, record chromatogram, detection result is shown in Table 4.
[0056] As can be seen from Table 4, in the 6 parts of continuous sampling adding impurity need testing solution, 2,6-difluoroaniline, 2,4-difluoroaniline, 1,3-dichlorobenzene, 2,6- The retention time RSDs of difluoronitrobenzene, 2,4-difluoronitrobenzene, 2,6-dichloronitrobenzene, and 2,4-dichloronitrobenzene peaks were all less than 0.1%, and the peak area RSDs were all less than 2.0%, indicating that the system suitability of each impurity under this method meets the requirements.
[0057] Table 4: System Suitability Test Results
[0058]
Embodiment 3
[0060] Detection limit:
[0061] Preparation of LOQ solution: Take 2,6-difluoroaniline, 2,4-difluoroaniline, 1,3-dichlorobenzene, 2,6-difluoronitrobenzene, 2,4-difluoronitrobenzene, 2,6-dichloronitrobenzene and 2,4-dichloronitrobenzene reference substances were diluted with methanol to make each 1ml contain about 0.4543μg of 2,6-difluoroaniline and 2,4-difluoroaniline About 0.5350 μg of aniline, about 0.9064 μg of 1,3-dichlorobenzene, about 0.7353 μg of 2,6-difluoronitrobenzene, about 0.7848 μg of 2,4-difluoronitrobenzene, about 0.7848 μg of 2,6-dichloronitrobenzene A mixed solution of about 0.5306 μg of benzene and about 0.8222 μg of 2,4-dichloronitrobenzene is obtained.
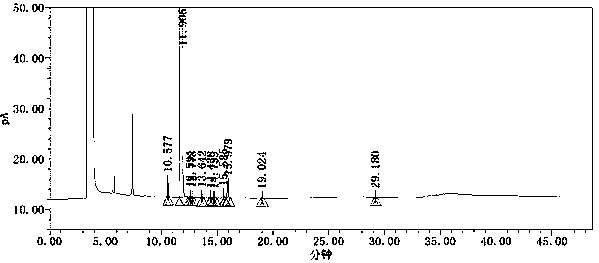
[0062] Get above-mentioned LOQ solution, measure by the chromatographic condition in the embodiment 1, detection result is as shown in table 5;
[0063] Table 5 Analysis of detection limit detection results
[0064]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com