Hydrogenation catalyst start-up sulfidation method
A hydrogenation catalyst and sulfurized oil technology, which is applied in catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc. Simple process and the effect of reducing consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
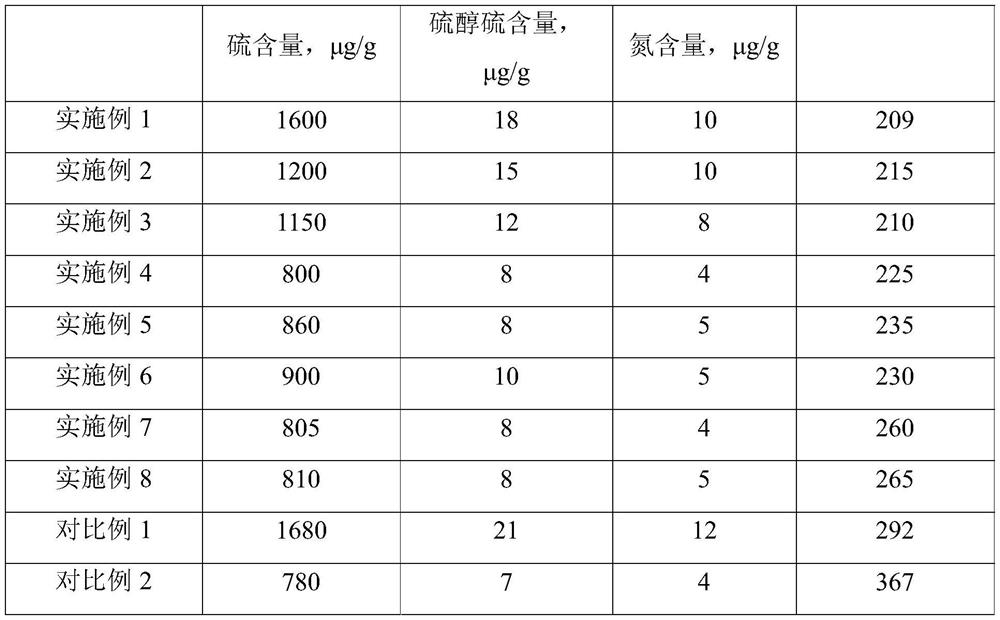
[0070] The fixed-bed reactor is filled with a hydrogenation catalyst, followed by nitrogen gas tightness, catalyst drying, introduction of hydrogen replacement, and hydrogen gas tightness. After the hydrogen gas tightness is qualified, the circulating hydrogen compressor is turned on to establish a full hydrogen circulation, and the hydrogen partial pressure is 1.6MPa. When the temperature of the catalyst bed in the reactor was raised to 150 °C, the starting sulfide oil was introduced to wet the catalyst bed, and the volumetric space velocity was 3.0 h. -1 , The high-pressure separator throws out the dirty oil until the oil is freed from solid mechanical impurities to establish a closed-circuit vulcanization cycle. The temperature of the catalyst bed was raised to 175°C at 15°C / h, and the vulcanizing agent was injected (based on the total circulating vulcanized oil in operation, the amount of the vulcanizing agent was 1% by weight) and detected H 2 S concentration. The hydro...
Embodiment 2
[0073] The hydrogenation catalyst is sulfidized according to the method of Example 1, and the difference is that the sulfidation temperature rise program is: to be heated to 230° C. at 15° C. / h (the first temperature rise stage, H 2 The S concentration is 0.1-0.3 vol%), and then constant temperature at 230°C for 6 hours (the first constant temperature stage, H 2The S concentration is 0.3-0.5% by volume), after the first constant temperature stage, 10% by volume of liquefied gas is introduced into the hydrogen mixing point, and the temperature is raised to 300 °C at 15 °C / h (the second heating stage, H 2 The S concentration is 0.5-1.0 vol%), and then constant temperature at 300°C for 8 hours (the second constant temperature stage, H 2 The S concentration is 1.0 to 1.5% by volume), and the vulcanization is completed. Then, according to the conditions of Example 1, the kerosene extracted from the constant line was introduced to carry out the hydrogenation reaction. After 48 hour...
Embodiment 3
[0075] The hydrogenation catalyst is sulfidized according to the method of Example 1, and the difference is that the sulfidation temperature rise program is: to be heated to 230° C. at 15° C. / h (the first temperature rise stage, H 2 The S concentration is 0.1-0.3 vol%), and then constant temperature at 230°C for 6 hours (the first constant temperature stage, H 2 The S concentration is 0.3-0.5% by volume), after the first constant temperature stage, 15% by volume of liquefied gas is introduced into the hydrogen mixing point, and the temperature is raised to 300 °C at 15 °C / h (the second heating stage, H 2 The S concentration is 0.5-1.0 vol%), and then constant temperature at 300°C for 8 hours (the second constant temperature stage, H 2 The S concentration is 1.0 to 1.5% by volume), and the vulcanization is completed. Then, according to the conditions of Example 1, the kerosene extracted from the constant line was introduced to carry out the hydrogenation reaction. After 48 hou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com