Novel laser radar receiving lens
A laser radar and receiving lens technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high price of multi-line laser radar, cumbersome arrangement of multiple detectors, and expensive detectors, etc., and achieve excellent optical imaging. performance, the effect of compressing the size of the converging spot, and improving the uniformity of the spot
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
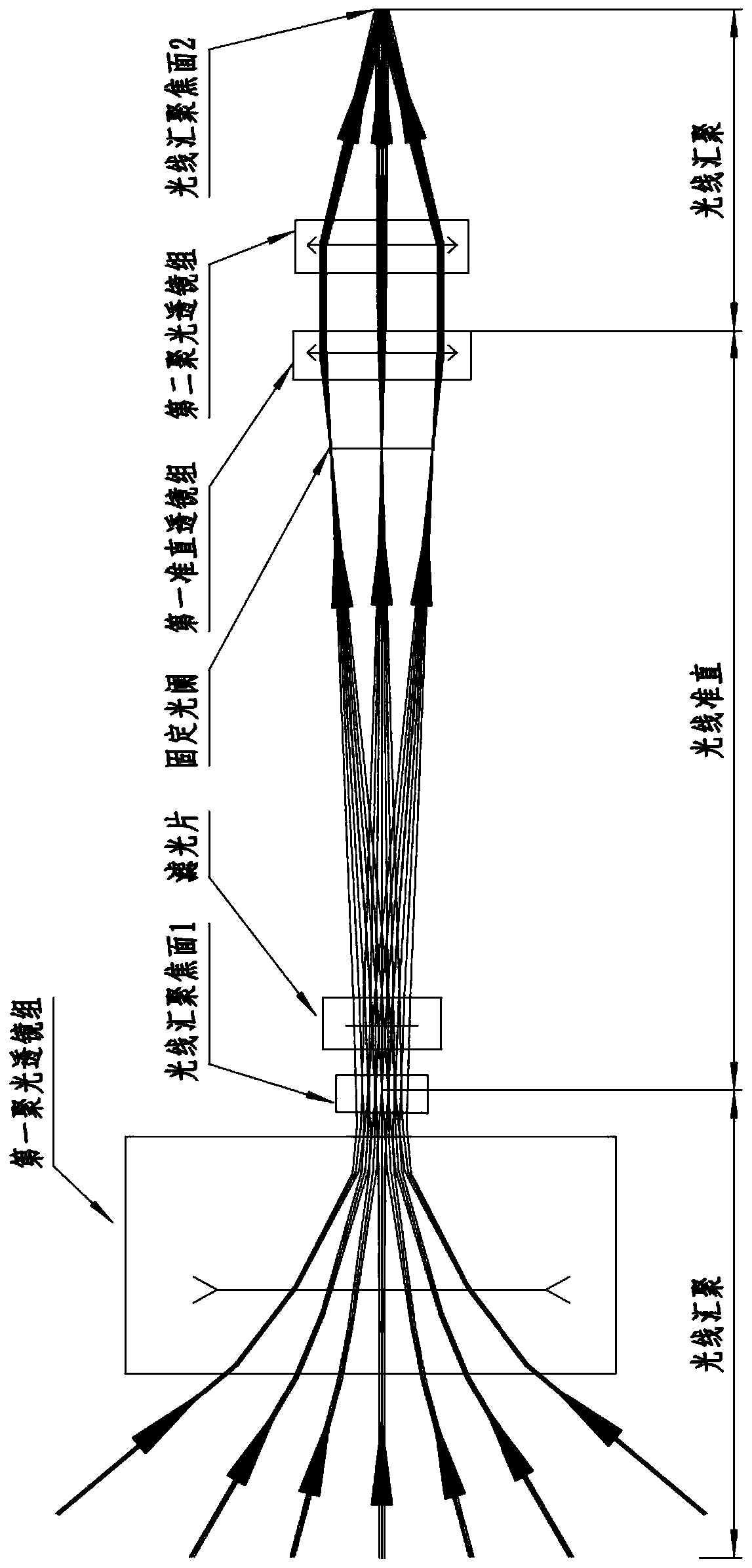
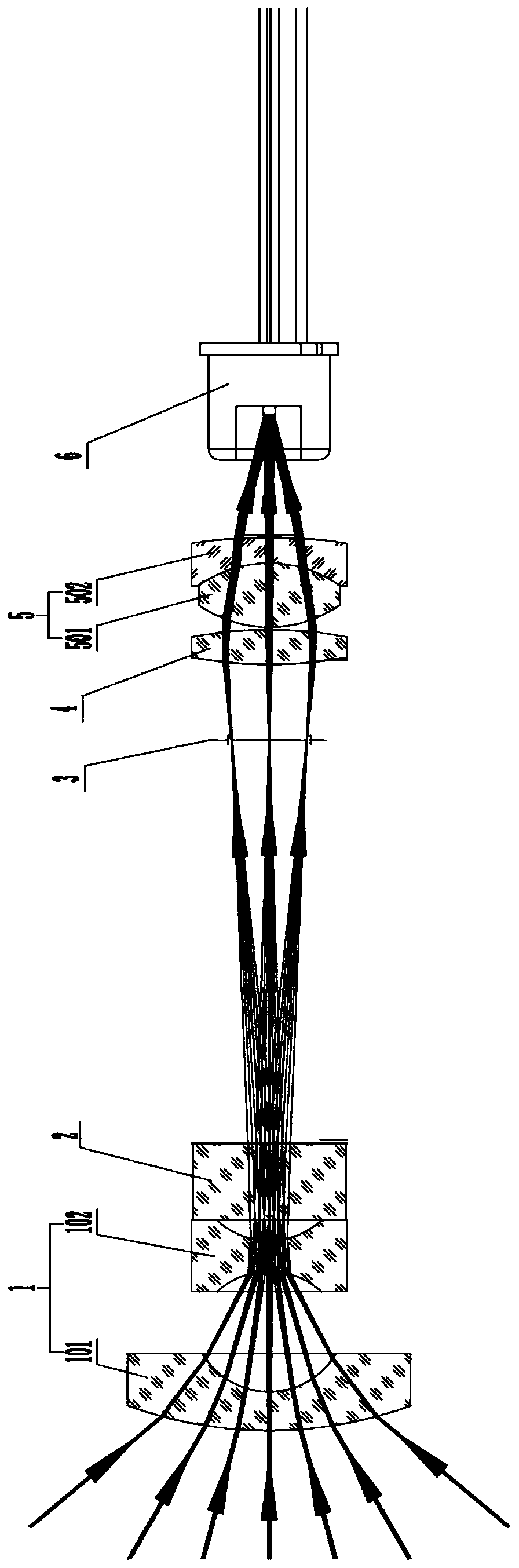
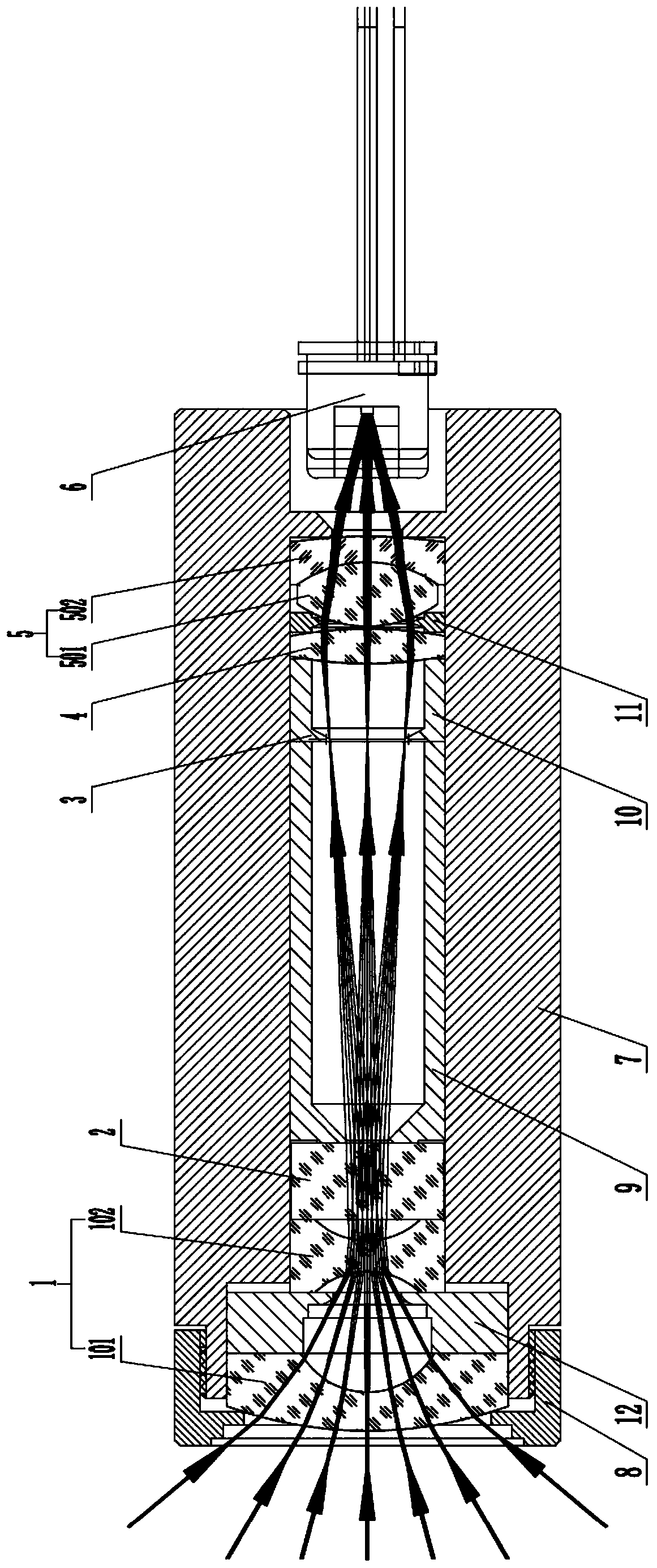
[0026] Such as Figures 1 to 3 As shown in one of them, the novel lidar receiving lens of the present invention comprises a first condenser lens group 1, an optical filter 2, a fixed diaphragm 3, a first collimator lens group 4 and a second condenser lens group arranged in sequence along the optical path. Optical lens group 5, wherein, the first condenser lens group 1 is a negative power condenser lens group, and the second condenser lens group 2 is a positive power condenser lens group, by the first condenser The optical signal received by the optical lens group 1 passes through the optical filter 2 , the fixed diaphragm 3 , the first collimating lens group 4 and the second condensing lens group 5 in sequence, and then is focused and output by the second condensing lens group 5 .
[0027] As a possible implementation form, further, the first condensing lens group 1 includes several sequentially arranged lenses, which are used to condense light signals with a large angle range...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com