Surface treatment method of super-hydrophobic multifunctional cellulose-based material
A cellulose-based, multi-functional technology, applied in the direction of fiber raw material treatment, fiber treatment, wood treatment, etc., can solve the problems of wood expansion, appearance, strength, structure and function damage, deformation of cellulose products, etc., to increase hardness, Good for recycling and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] In this embodiment, the superhydrophobic multifunctional cellulose-based material surface treatment method is as follows:
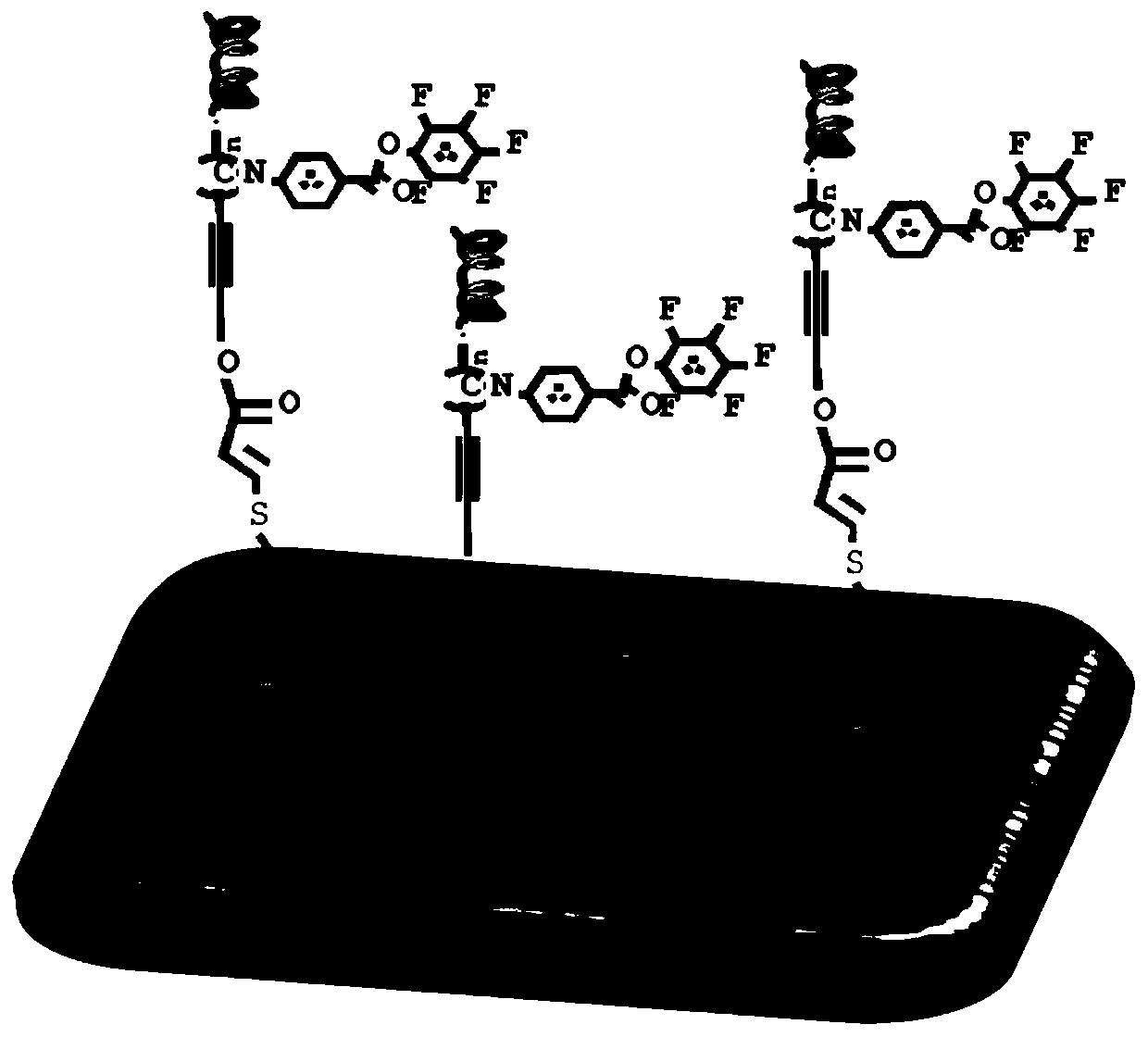
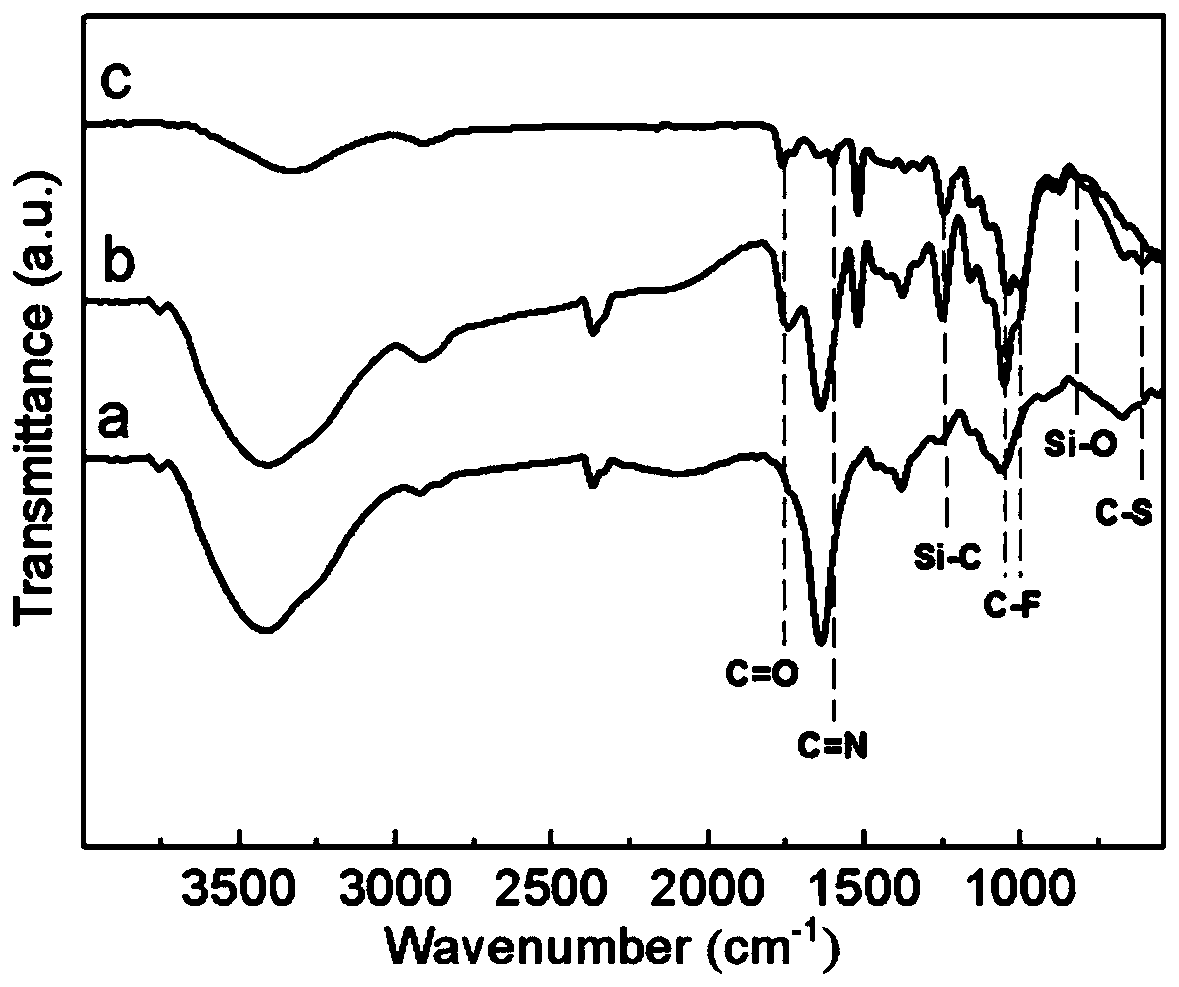
[0032] 1. Take 2ml of thioglycolic acid, 12ml of acetic anhydride, 8ml of 36% acetic acid, and 0.03ml of concentrated sulfuric acid in a small beaker. Cut 1.5g of wood into small pieces (1cm×1cm×0.3cm) and submerge them completely, seal them away from light and place them in an oven at 45°C for 12 hours, wash them with water, and dry them to obtain wood chips modified with mercapto groups on the surface;
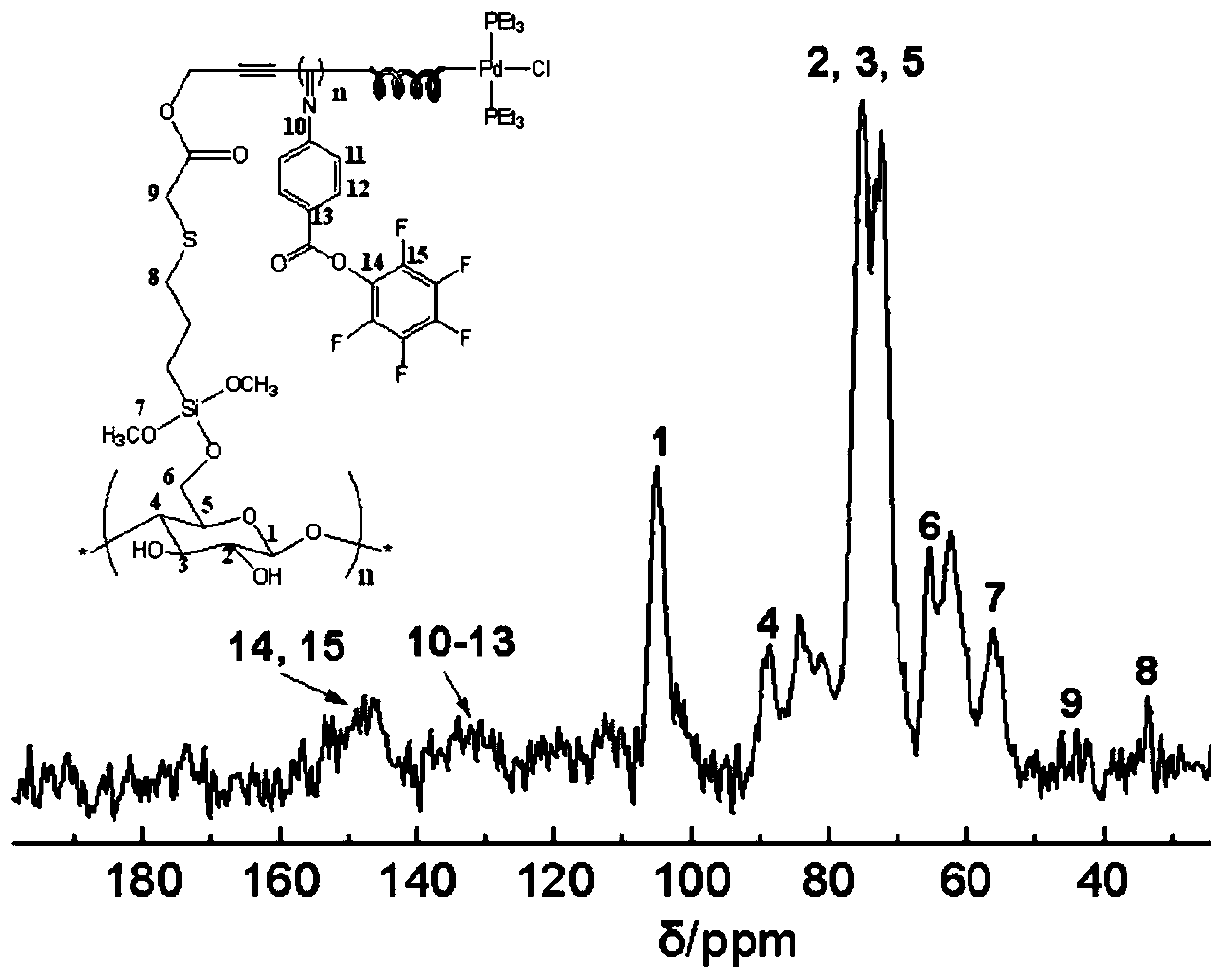
[0033] 2. First, dissolve the pentafluorophenol-modified benzene isonitrile monomer a (10.39 mg) and the olefin-terminated palladium (II) catalyst b (2.2 mg) in anhydrous THF (2.5 mL). The reaction was carried out at 55°C in an oil bath for 6h. After cooling, centrifuging and washing, the yellow solid obtained is polypentafluorophenol isonitrile helical polymer with a degree of polymerization of 10.
[0034] 3. Add 0.5 g of mercapto-modified wo...
Embodiment 2
[0036] In this embodiment, the superhydrophobic multifunctional cellulose-based material surface treatment method is as follows:
[0037] 1. Take 5.02mmol of 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane in 26.901g of EtOH / H 2 In the O (95 / 5, w / w) system, add AcOH to adjust the pH value of the solution to 3.5. Weigh 2.6g (1cm×1cm×1cm) of wood block and dry it at 120°C for 2h to obtain mercapto-modified wood;
[0038] 2. Dissolve pentafluorophenol-modified benzene isonitrile monomer a (103.9mg) and alkenyl-terminated palladium(II) catalyst b (2.2mg) in anhydrous THF (2.5mL) in an oil bath at 55°C Under reaction 12h. After cooling, centrifuging and washing, the obtained yellow solid is polypentafluorophenol isonitrile helical polymer with a degree of polymerization of 100.
[0039] 3. Add 1.5 g of mercapto-modified wood, 0.15 g of polypentafluorophenol isonitrile, and 10 mg of photoinitiator α, α-dimethoxy-α-phenylacetophenone in sequence to the polymerization bottle, and place in 8 ℃ co...
Embodiment 3
[0041] In this embodiment, the superhydrophobic multifunctional cellulose-based material surface treatment method is as follows:
[0042] 1. Immerse 3g of cleaned wood blocks (1cm×1cm×1cm) into 58g of 5% 3-mercaptopropyltriethoxysilane ethyl acetate (EA) solution, and react in the solution for 8h at room temperature to obtain mercapto-modified Sexual blocks;
[0043] 2. Pentafluorophenol-modified benzene isonitrile monomer a (103.9 mg), olefin-terminated palladium (II) catalyst b (2.2 mg) was dissolved in anhydrous THF (2.5 mL), and reacted at 55 ° C in an oil bath for 12 h . After cooling, centrifuging and washing, the obtained yellow solid is polypentafluorophenol isonitrile helical polymer with a degree of polymerization of 100.
[0044]3. Add 1.5g of the above-mentioned mercapto-modified wood, 0.15g of polypentafluorophenol isonitrile, 2mg of photoinitiator α, α-dimethoxy-α-phenylacetophenone, and seal it to the polymerization bottle In a constant temperature bath at 25...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com