Mesenchymal stem cell treating method for Schistosoma japonicum infection treatment
A technology of schistosomiasis and cells, applied in animal cells, anti-infective drugs, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problems that there is no MSC to treat Schistosoma japonicum infection, restrict the treatment of Schistosoma japonicum infection, etc., achieve good application prospects and promotion value, alleviate Hepatic fibrosis, good curative effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
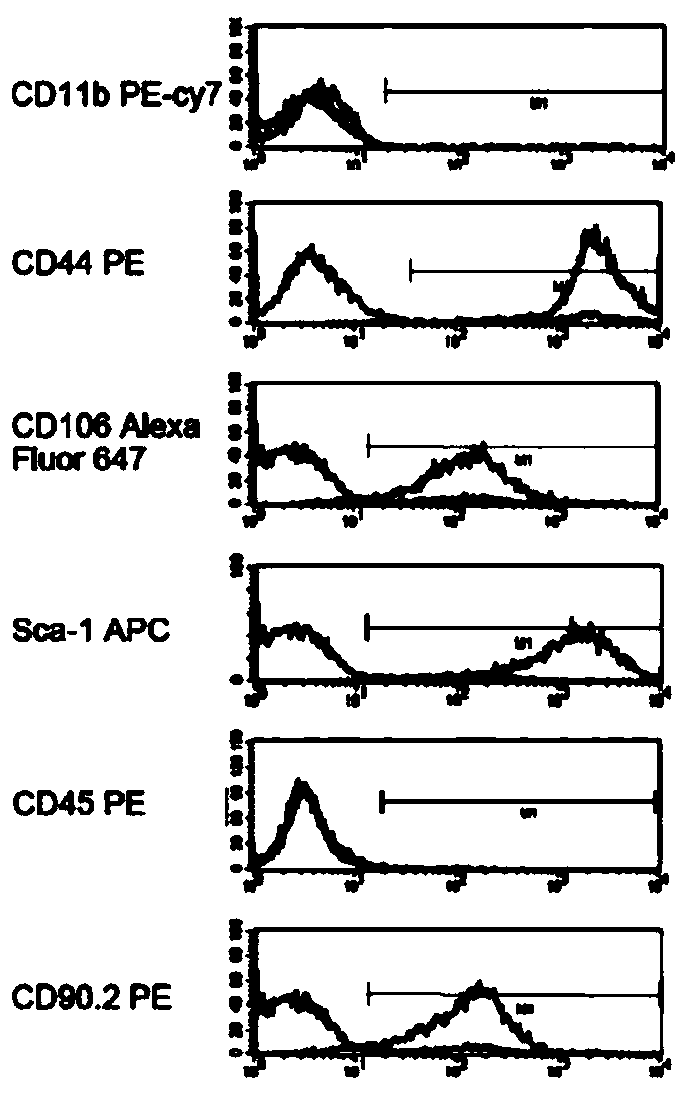
[0033] The isolation culture of embodiment 1 MSC
[0034] 1. Experimental method
[0035] Take about 5-6W mice, kill them by cervical dislocation, soak them in 75% ethanol for 5 minutes, take out both femurs under aseptic condition, carefully remove the attached tissues on the femurs, and use a syringe to draw 100mL / L-DMEM medium of L FCS, wash out the cells in the bone marrow cavity, collect the cells through a 200-mesh stainless steel mesh, dissolve the red blood cells in the erythrocyte lysate for 2 minutes, centrifuge to remove the supernatant, and use L-DMEM medium containing 100m L / L FCS Resuspend and adjust cell concentration, 3ⅹ10 4 Inoculated in 24-well plates, placed at 37°C, with a volume fraction of 5% CO 2 In the incubator, change the medium for the first time after 7 days, and then change the medium once every 3 days. When the cells have cell clones, digest and collect the cell clones, transfer them to the culture flask, change the medium every 3 days, and wai...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The processing of embodiment 2 MSC
[0039] 1. Experimental method
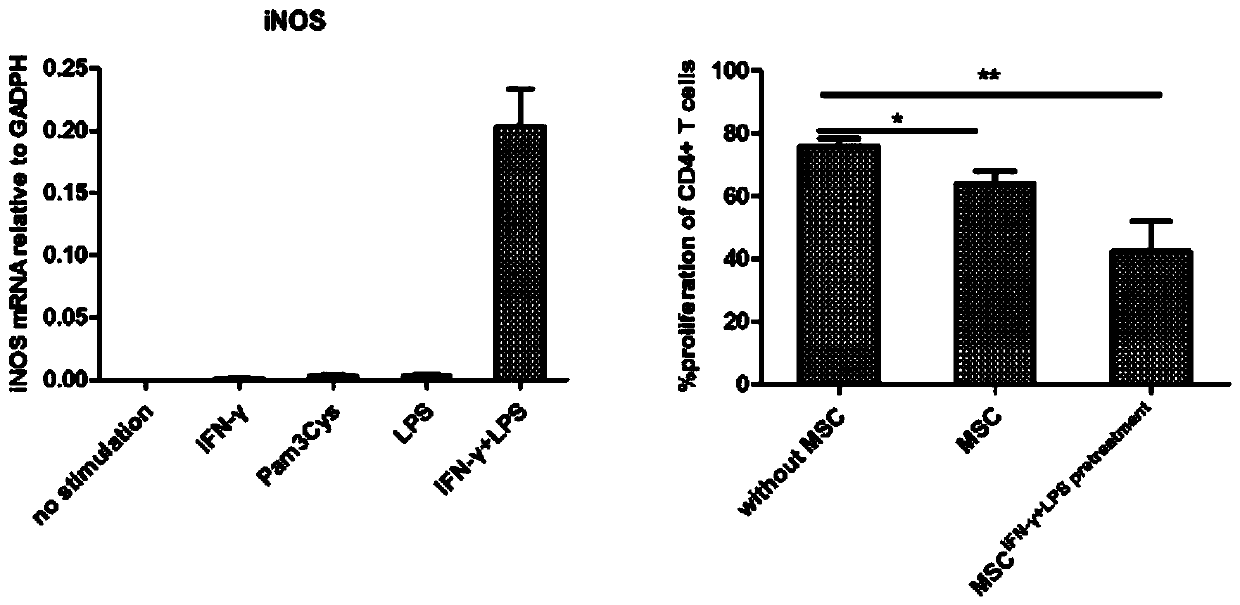
[0040]Add IFN-γ (5 ng / ml) and LPS (100 ng / ml) to the MSCs cultured in Example 1, act at 37° C. for 24 hours, 1500 rpm, centrifuge for 10 minutes, discard the culture medium, resuspend with PBS, and centrifuge to remove the supernatant. Repeat the wash once and collect the cells for later use.
[0041] The induced MSC cells were collected, mRNA was extracted, real-time PCR was used to quantitatively detect the expression of the key immune regulatory factor iNOS, and the lymphocyte proliferation inhibition experiment was further performed.
[0042] 2. Experimental results
[0043] After synergistic induction with lower concentration of IFN-γ and lower concentration of LPS, it can promote the expression of MSC iNOS and enhance the inhibitory effect on lymphocyte proliferation, showing that its immune regulation effect is enhanced, such as figure 2 shown.
Embodiment 3
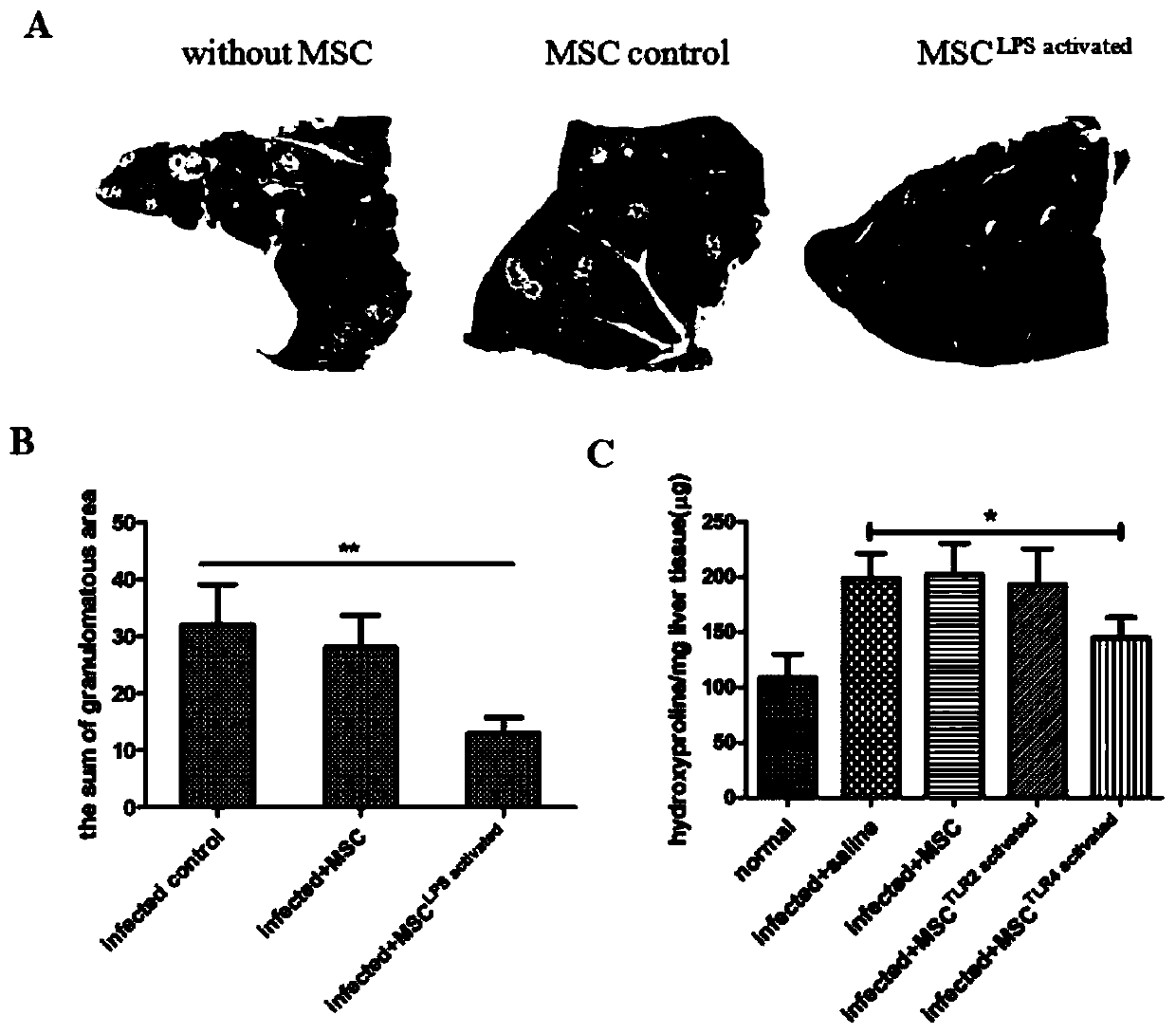
[0044] The induced MSCs of Example 3 are used for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis infected by schistosomiasis
[0045] 1. Treatment
[0046] 1. Take the cercariae of schistosomiasis and infect the mice percutaneously to establish the schistosomiasis infection model;
[0047] 2. MSC treatment
[0048] The schistosome infection model was randomly divided into three groups (each group) with 16 ± 2 cercariae of schistosomiasis, without any treatment as the blank control group, and the other two groups were given tail vein injection of MSC prepared in Example 2 respectively at 2 and 4 weeks after infection. ; Uninduced MSCs were used as the control group, 1×10 5 / per mouse;
[0049] 3. Samples were collected and analyzed 8 weeks after infection.
[0050] 1) The livers of the three groups of schistosome cercariae were collected for HE and masson staining and the quantification of hydroxyproline to analyze the effect of MSC on liver granuloma and fibrosis.
[0051] 2) The seru...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com