Patents
Literature
37 results about "Schistosoma Japonicum Infection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An infection that is caused by Schistosoma japonicum.
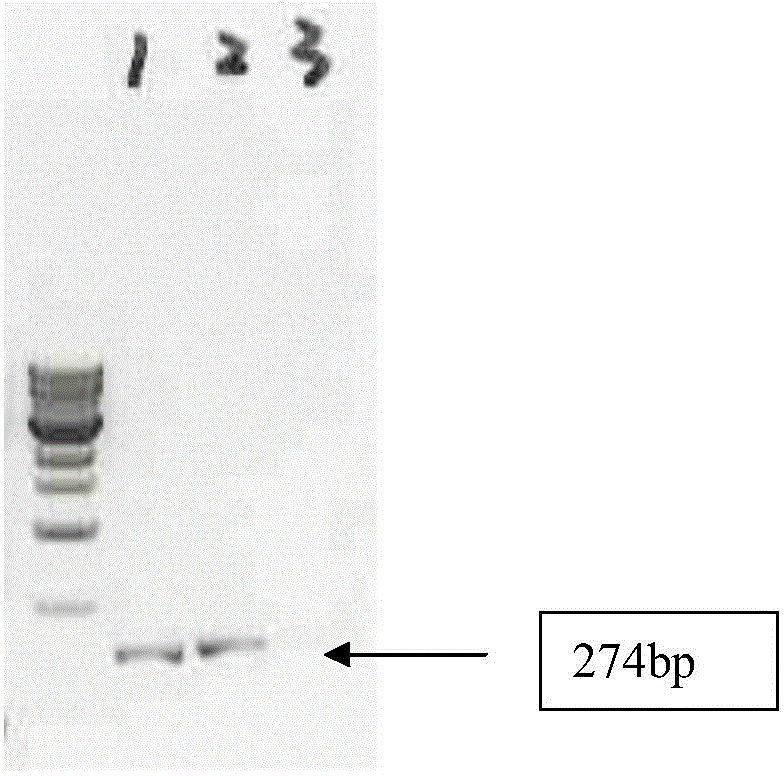
Anti-parasitical medicine in situ setting slow release injection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107811967AEasy to prepareImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryAntiparasitic agentAnti parasitic
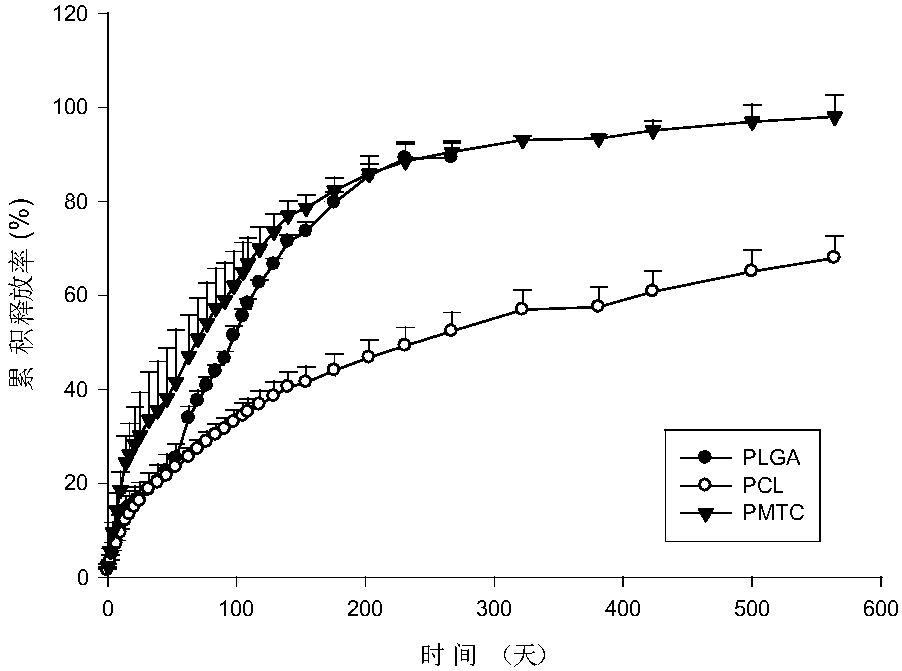
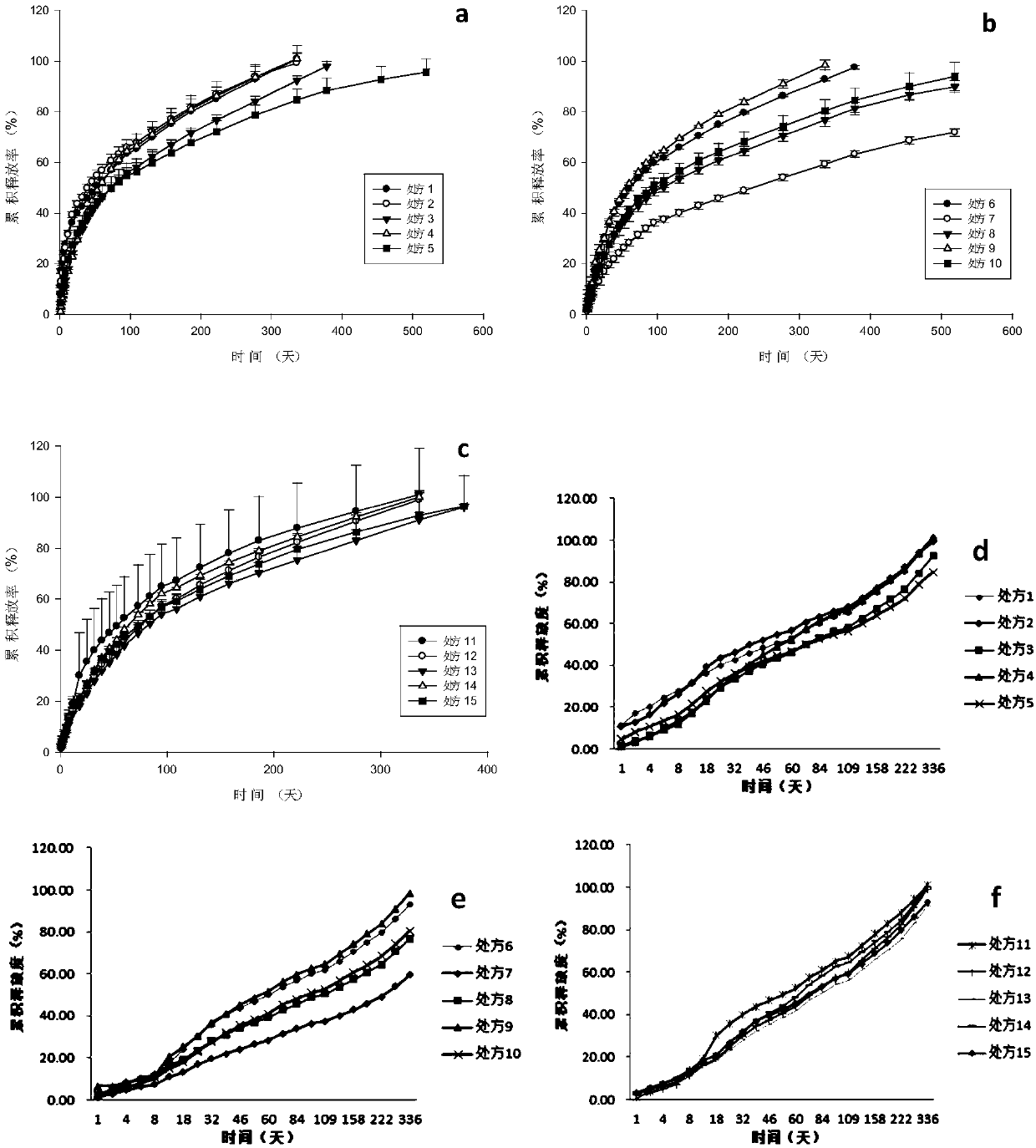
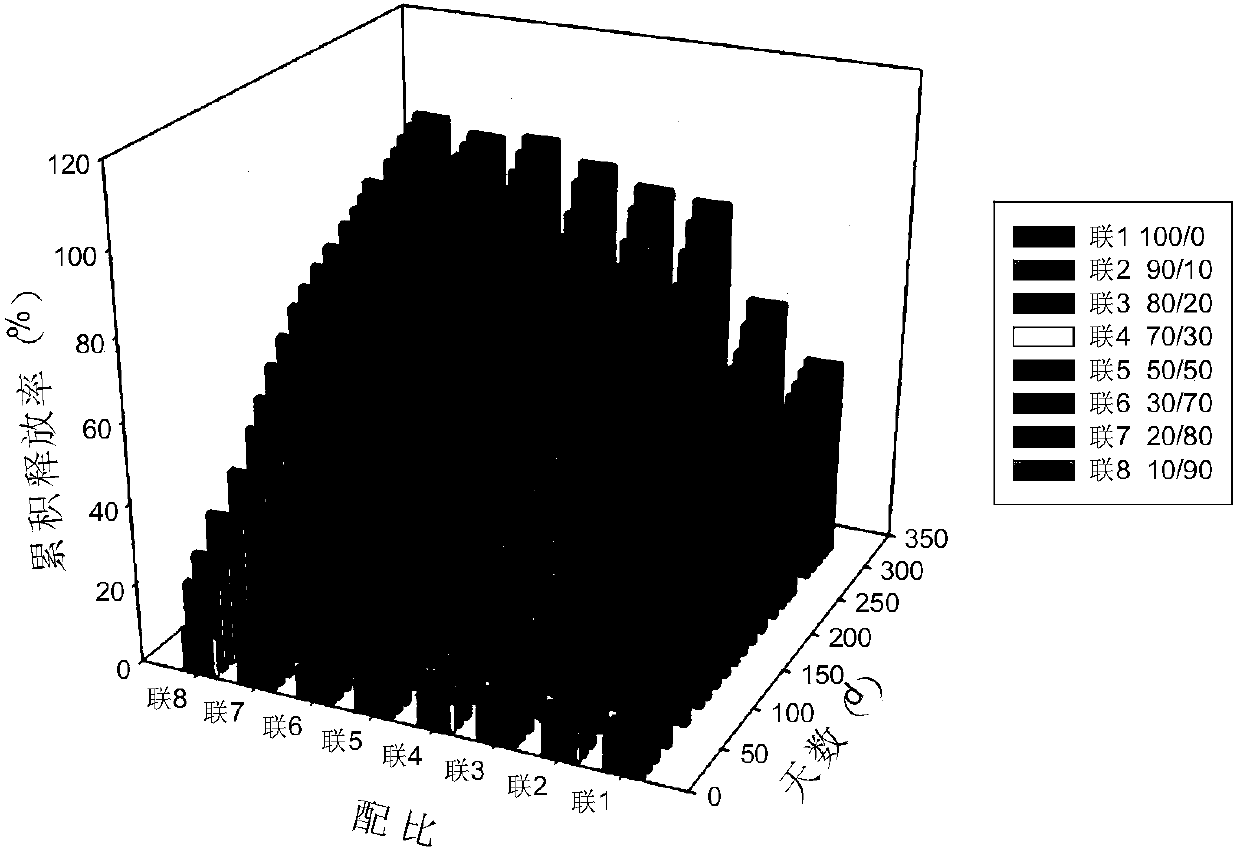
The invention discloses an anti-parasitical medicine in situ setting slow release injection and a preparation method thereof. The injection comprises the following components in ratio: 1-80g of an anti-parasitic disease medicine, 1-100g of a biodegradable high polymer material, 2-300mL of a dispersion medium and 0-50g of a solubilizer, wherein the content of the anti-parasitic disease medicine is1-800mg / mL. The injection can maintain long-term control effect when being medicated to a medicated object only once, the medicated object is protected from being infected by pathogens, propagation ofparasitic diseases can be economically and effectively controlled, material safety is high, prescription of a commercially available anti-parasitic disease medicine is simplified, compliance of the medicated object is improved, and control cost is reduced. Meanwhile, subcutaneous injection slow release injection is prepared by innovatively using a molluscicide, namely niclosamide, of the WHO, andthe effect of preventing schistosoma japonicum infection is achieved. The anti-parasitical medicine in situ setting slow release injection is simple in the preparation method, has good stability andis easy to use and popularize.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心寄生虫病预防控制所国家热带病研究中心
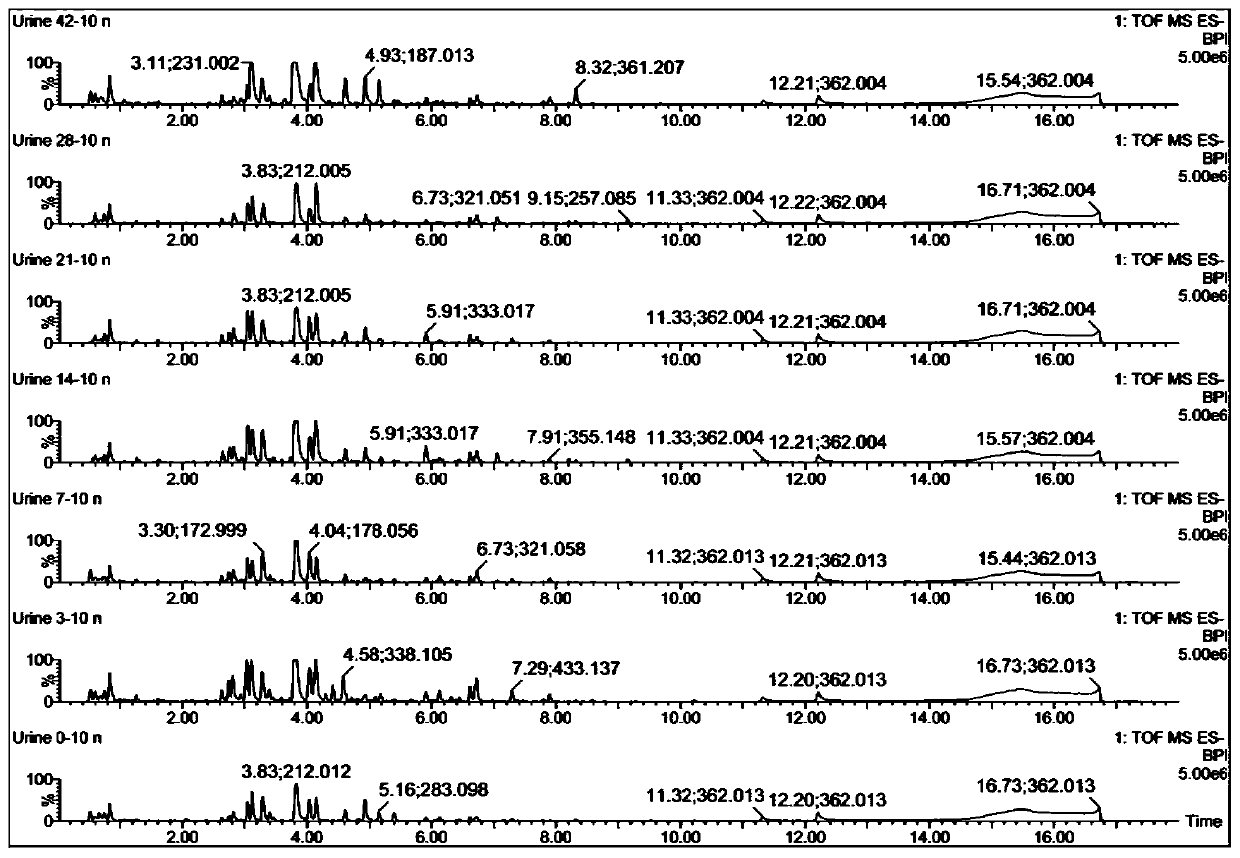
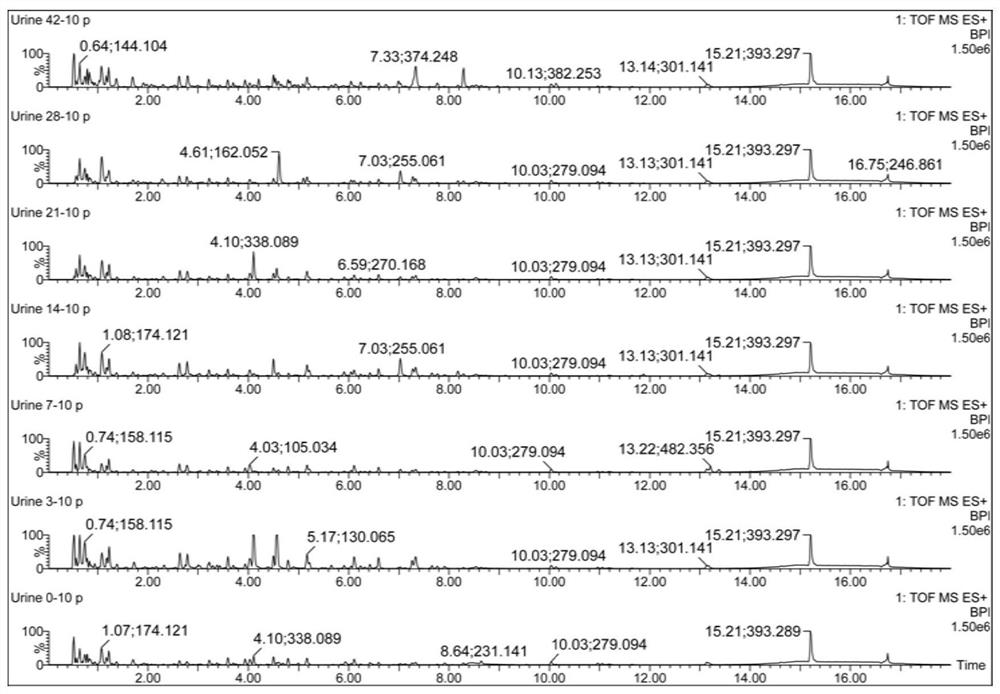
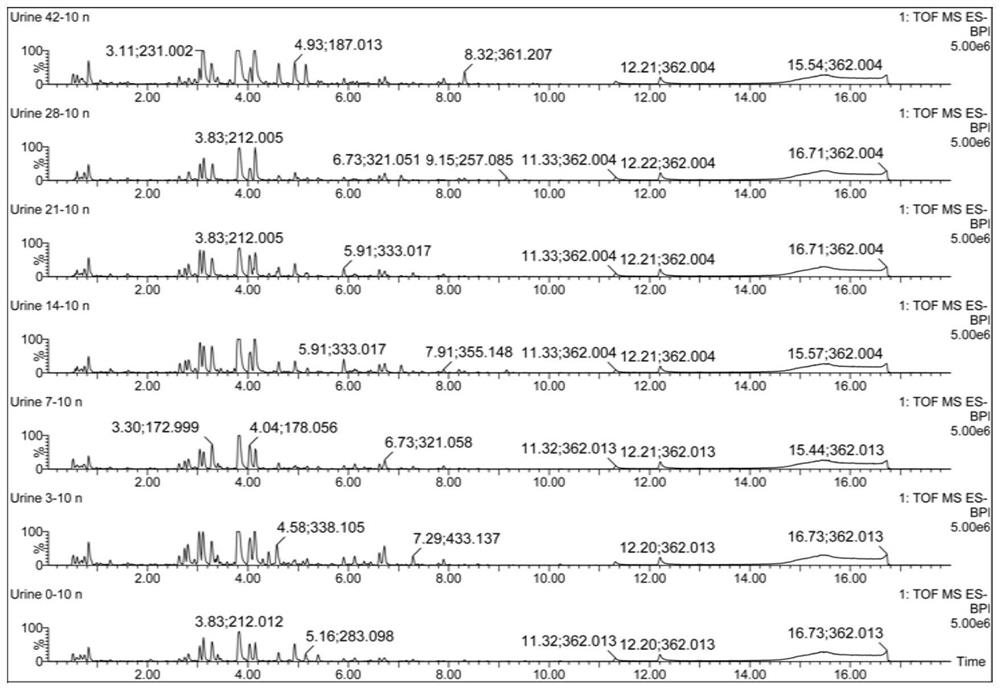
Urine biomarker for Japanese schistosomiasis early diagnosis, screening method, and application
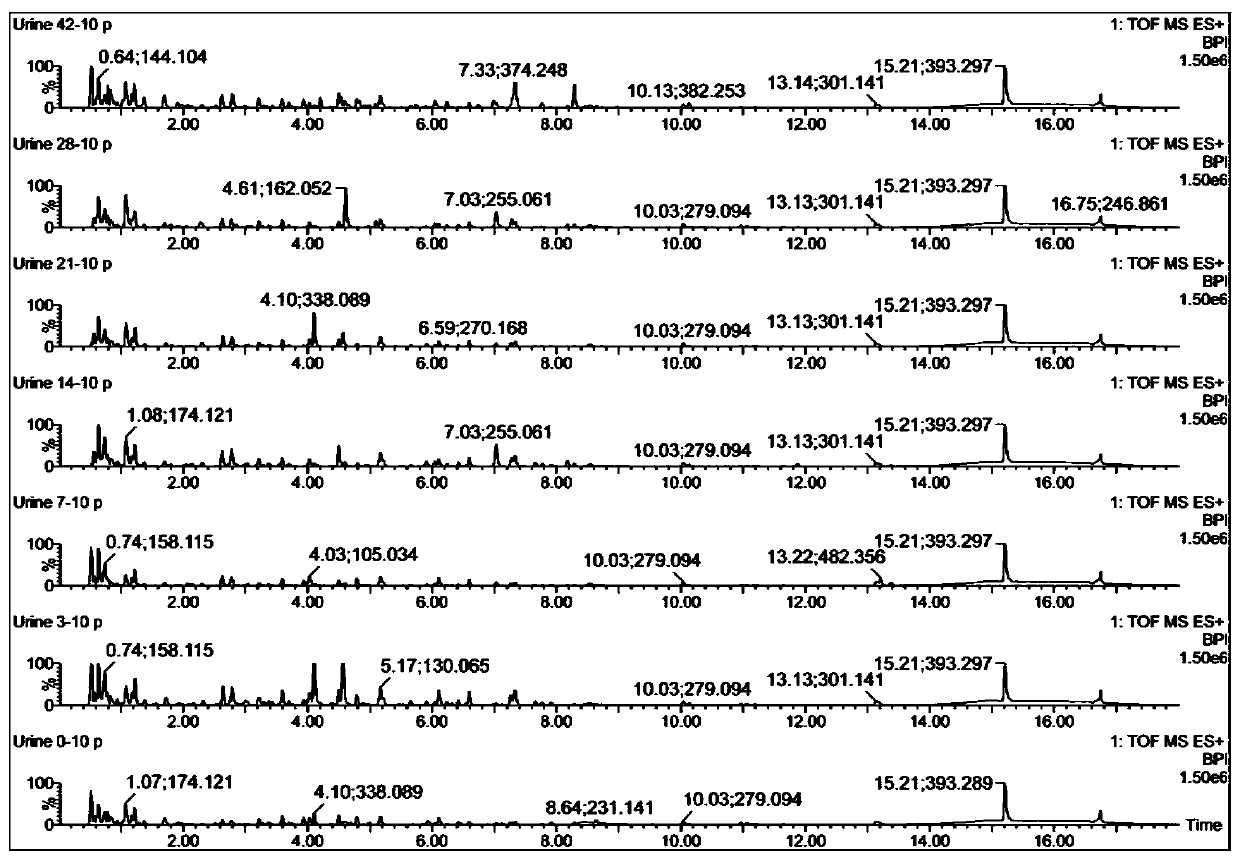
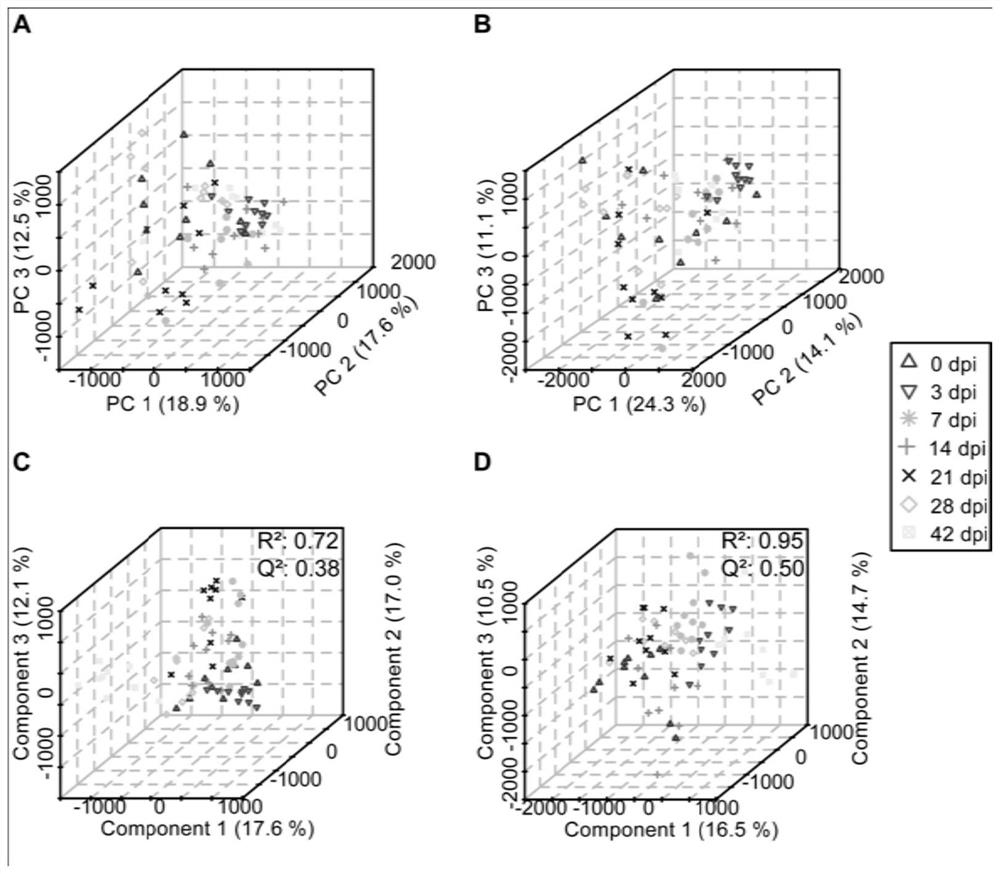
The invention discloses a urine biomarker for Japanese schistosomiasis early diagnosis. The urine biomarker is one or more of a xanthurenic acid, a naphthalenesulfonic acid, or enanthylcarnitine. Sensitivity and specificity of the marker are greater than 0.9, and an area under the curve (AUC) is greater than 0.9, indicating that the three indicators have better predictability and may be used for the Japanese schistosomiasis early diagnosis. The invention further discloses a metabolomics-based screening method for the urine biomarker for the Japanese schistosomiasis early diagnosis. By constructing a mouse Japanese schistosomiasis model, ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry is used to perform metabolomics analysis on mouse urine, and a characteristic differentialmetabolite, that is, the biomarker for the Japanese schistosomiasis early diagnosis, between a normal mouse and a Japanese schistosomiasis-infected mouse is found and analyzed. The screening method is non-invasive, convenient and fast, and can accurately reflect a metabolic spectrum difference between the Japanese schistosomiasis-infected mouse and the normal mouse and have high specificity.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
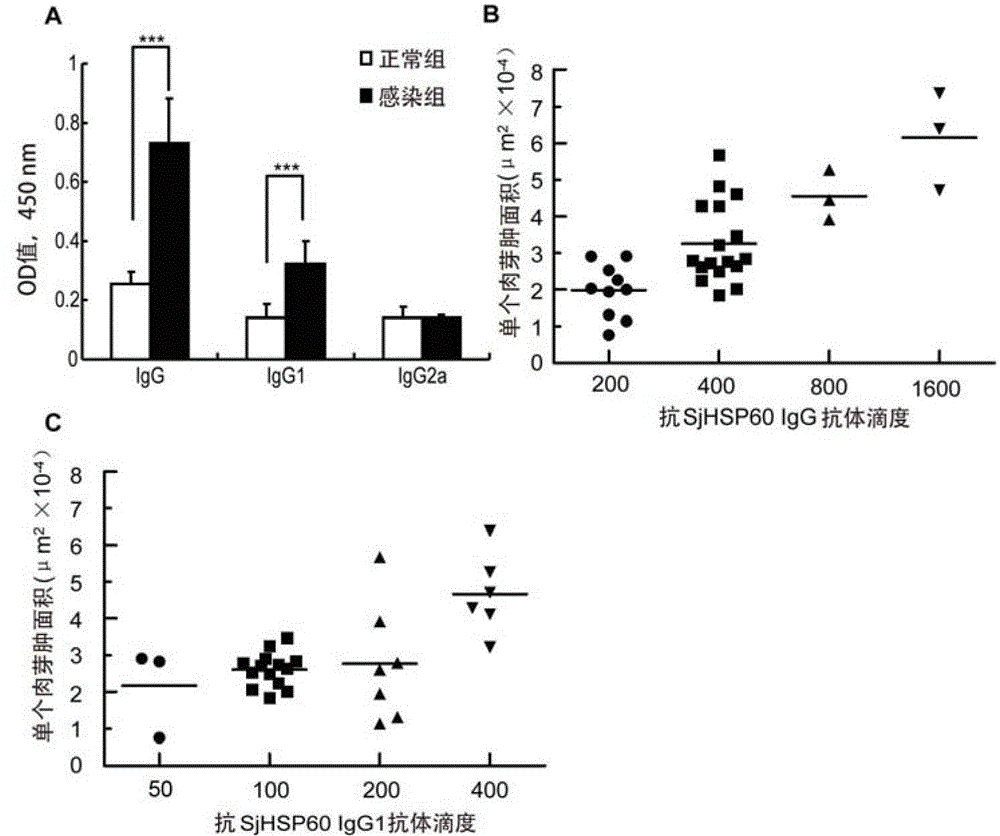
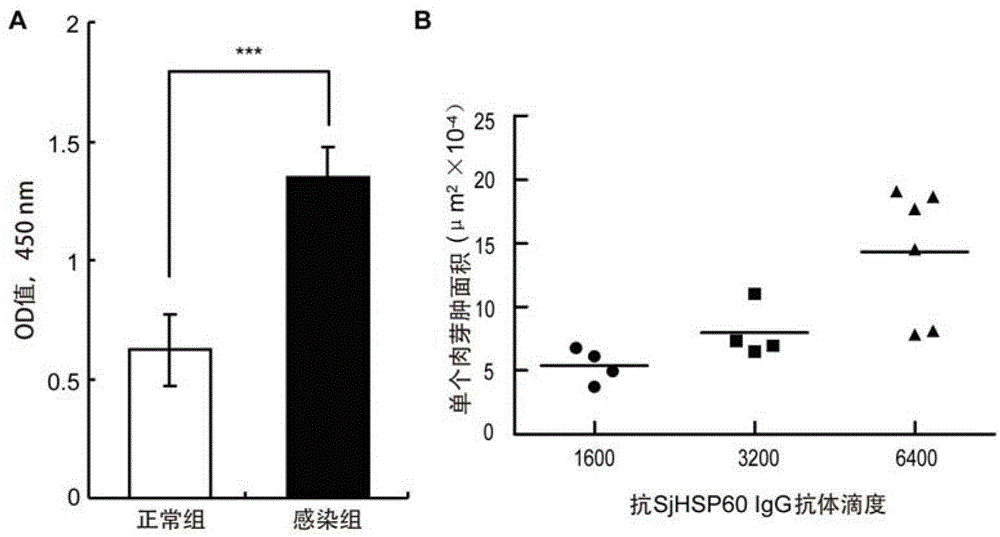
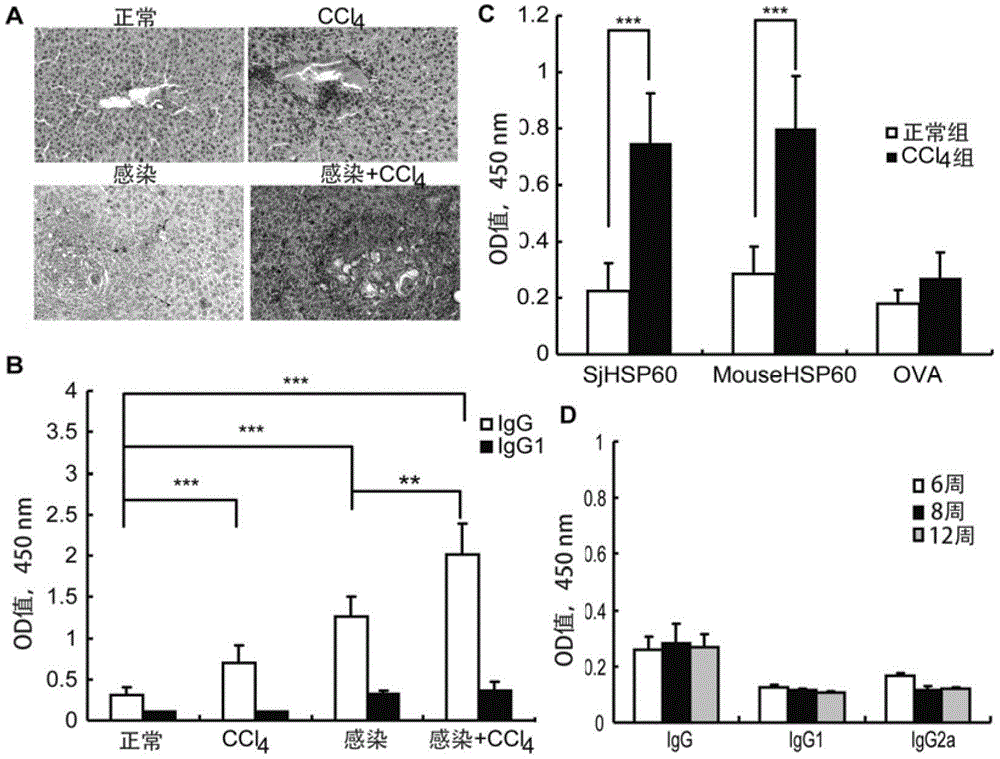
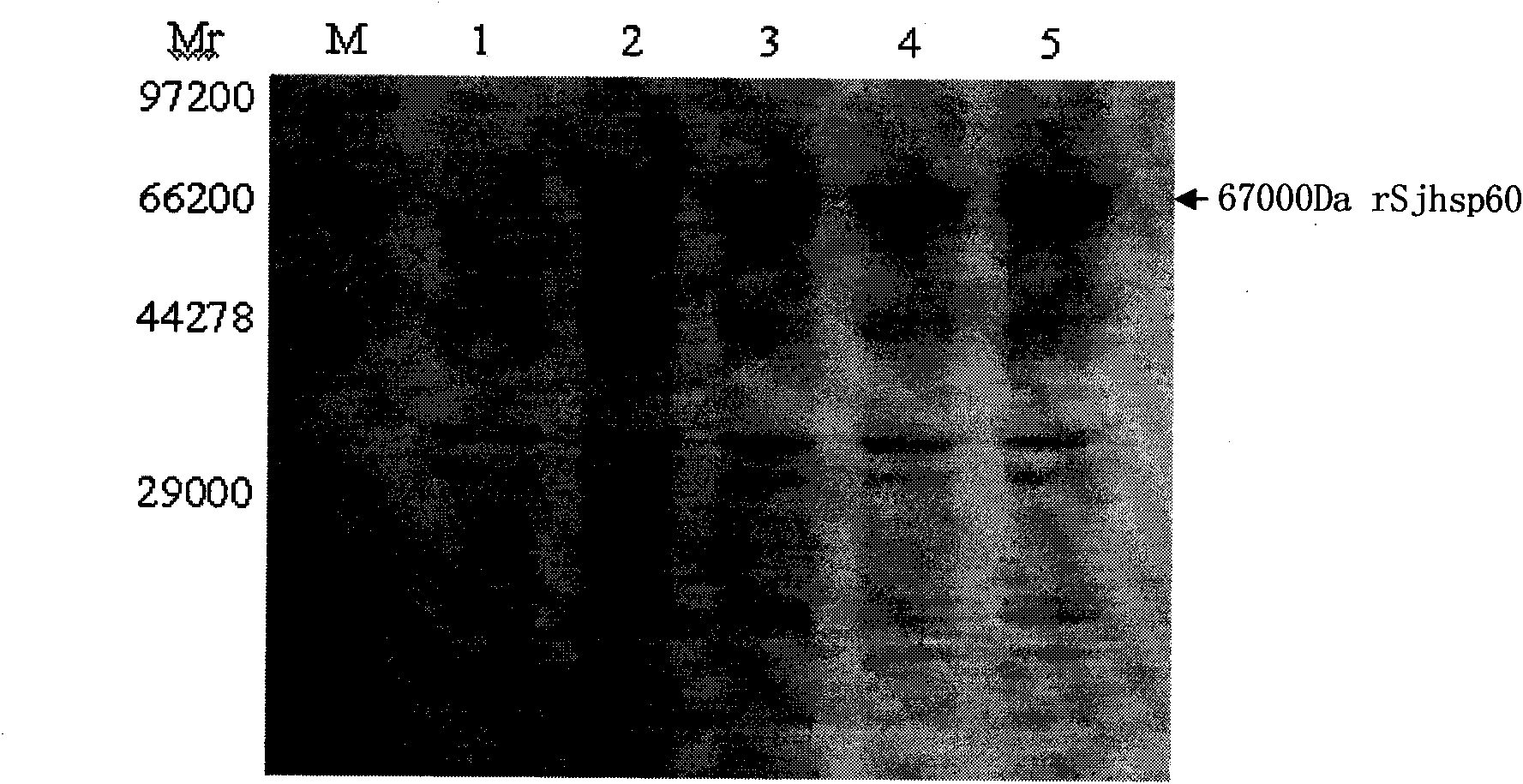
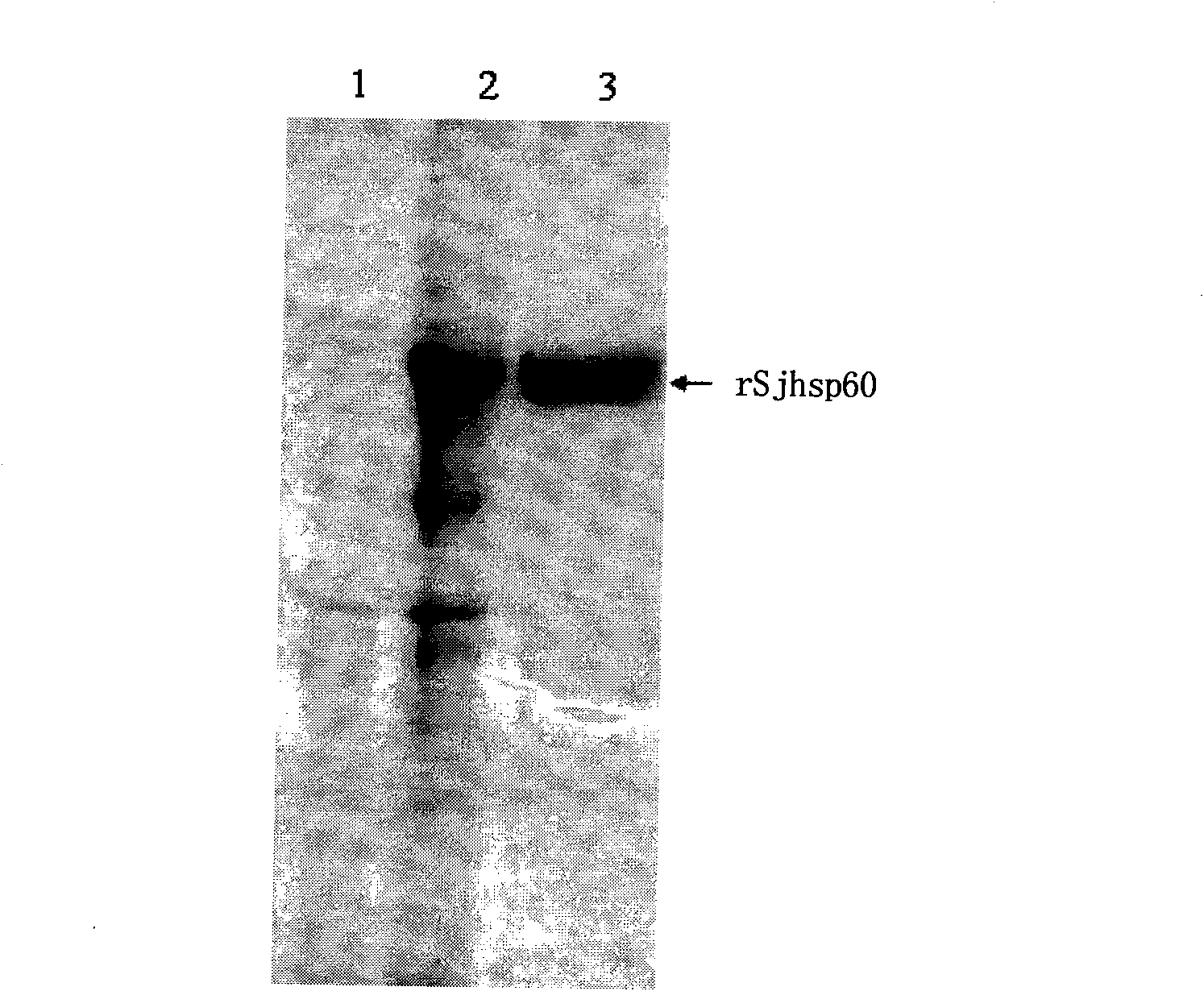
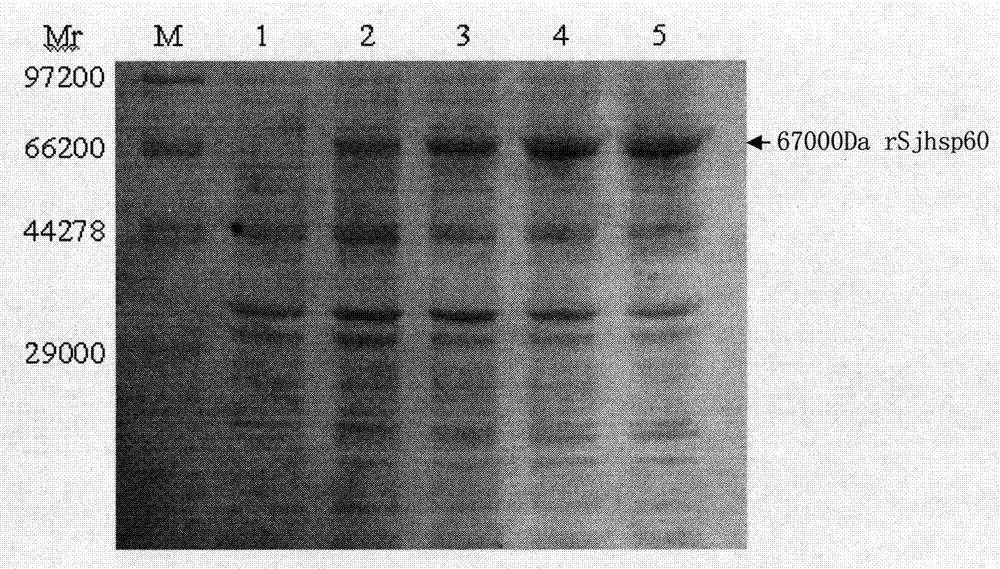
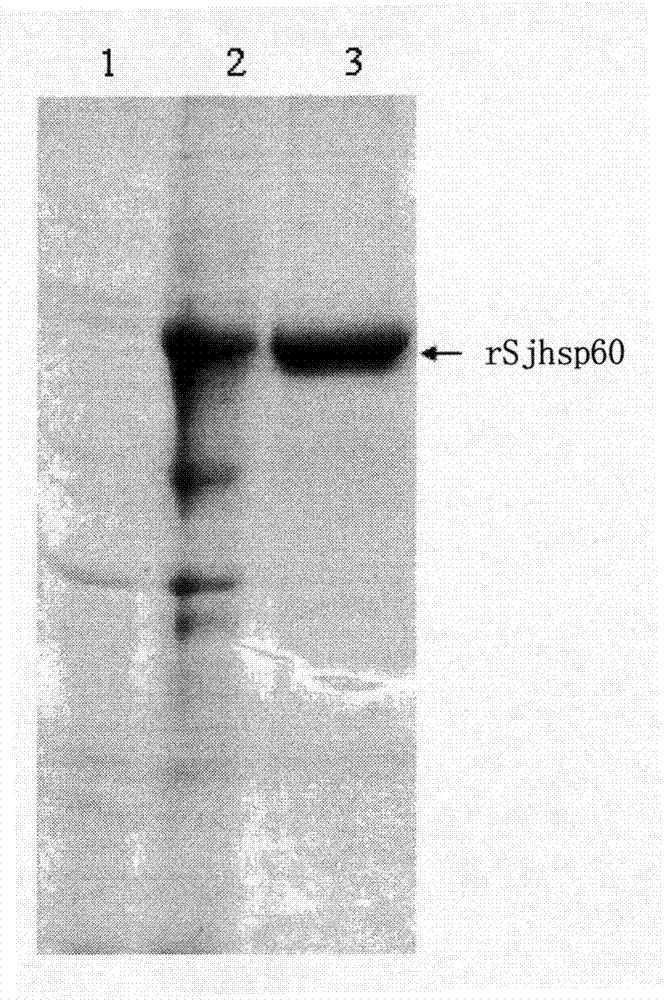
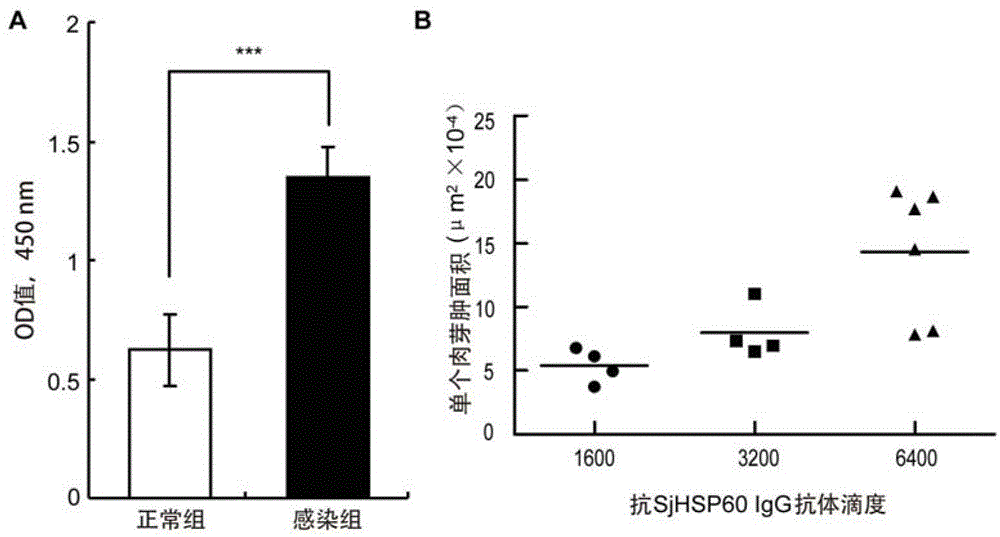
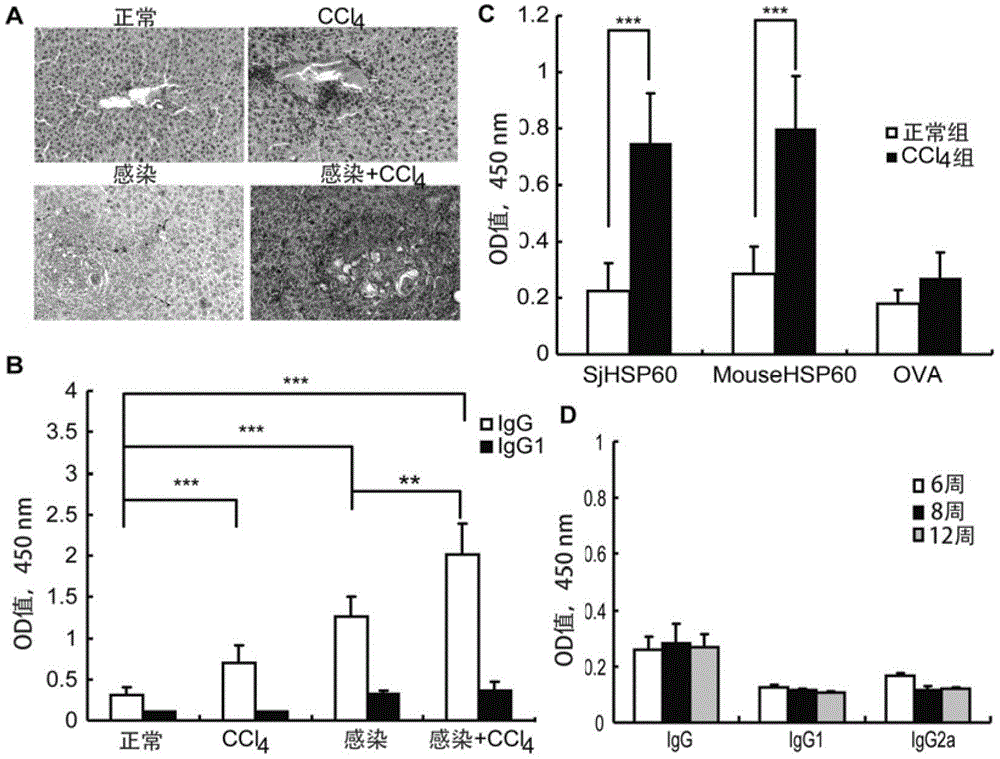
Application of SHSP60 for preparing diagnostic reagent for monitoring comprehensive hepatic pathology injury degree of schistosomiasis patient
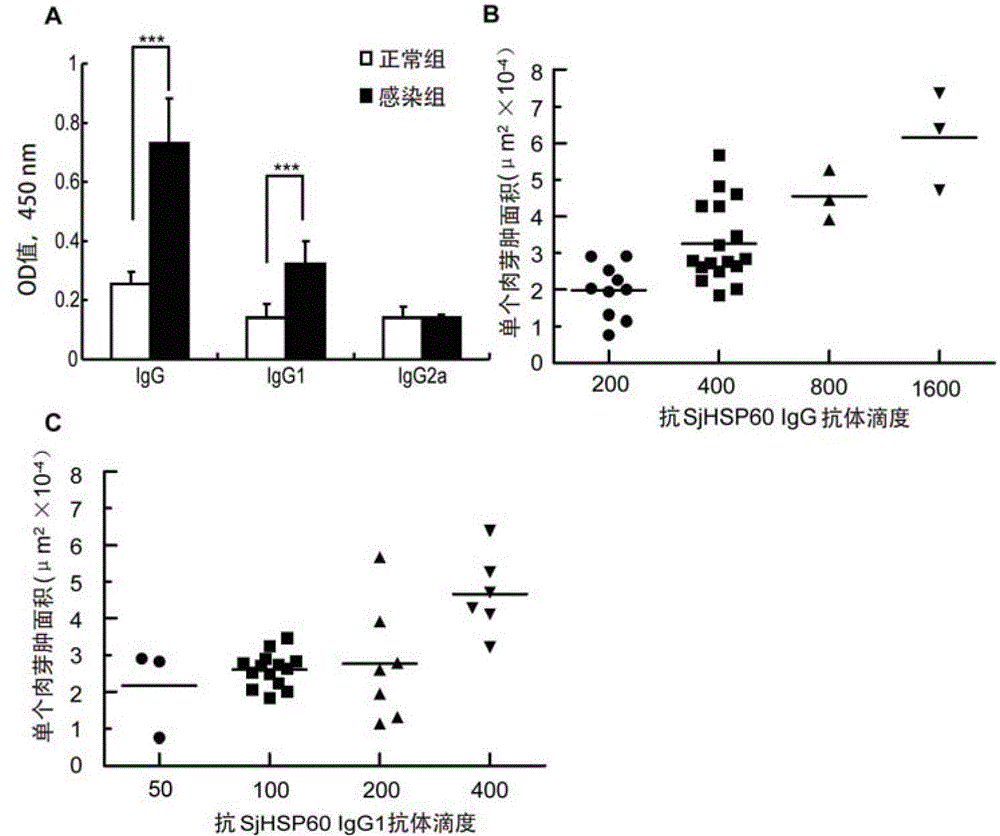
The invention belongs to the field of immunology, and particularly relates to an application of proteantigen molecules from schistosomes such as Japanese schistosome shock proteins 60KDa (SjHSP60), which is the application of Japanese schistosome shock proteins 60KDa for preparing a diagnostic reagent for monitoring comprehensive hepatic pathology injury degree of a schistosomiasis patient. The SjHSP60IgG in blood serum of a Japanese schistosome infected host and subtype IgG1 antibody level thereof are positively correlated to liver granuloma and fibrosis degree, which promotes that the SjHSP60IgG in blood serum and the subtype IgG1 antibody level thereof can be used as an index of evaluating the pathological degree of the liver of the schistosomiasis patient and has potential clinical application value. In the future, the novel diagnostic reagent may be used for monitoring the pathological degree of the liver of the schistosomiasis patient.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
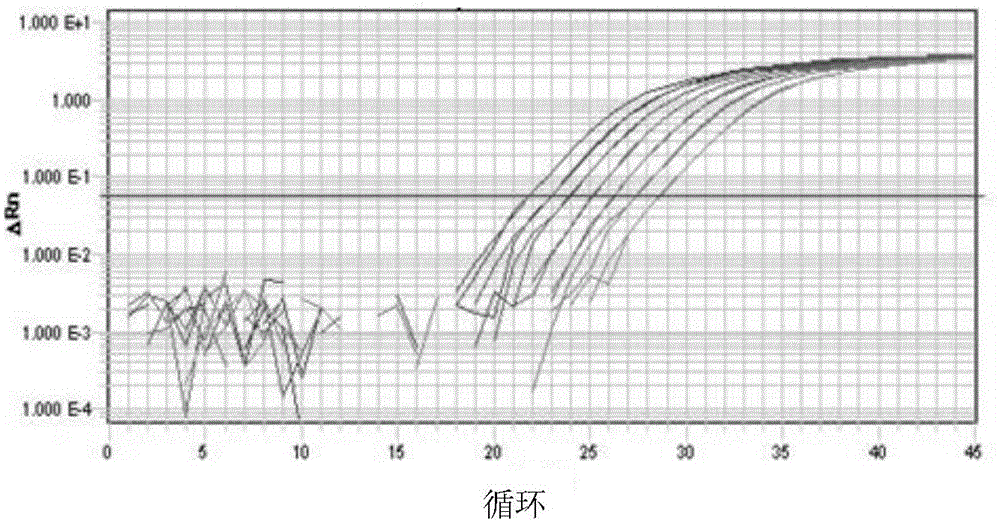
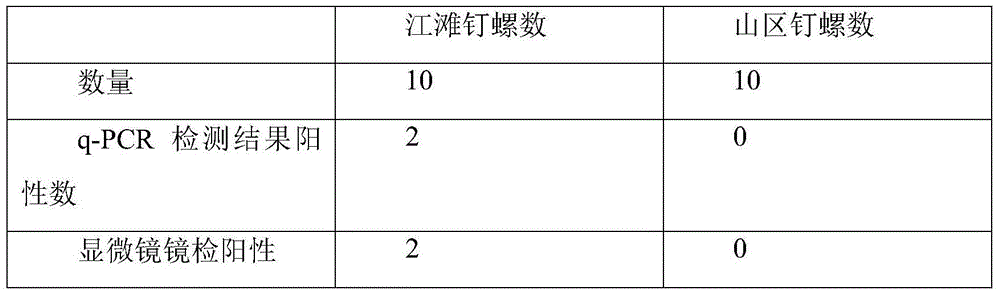
Q-PCR primer, identification method and kit for identifying schistosoma japonicum infected oncomelania
ActiveCN104651489AEasy to operateProgrammatic highMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationOncomelaniaAgricultural science
The invention a Q.PCR primer for identifying schistosoma japonicum infected oncomelania, and also provides a method for identifying the schistosoma japonicum infected oncomelania by use of the primer. The PCR primer is reasonably designed according to the special A gene sequence of the schistosoma japonicum, and the PCR primer is combined with reverse transcription, PCR amplification and amplification curve interpretation to identify whether the oncomelania is of positive infection of the schistosoma japonicum; the identification method has the advantages of simple operation, high sequencing, quick identification, accurate result and the like; the defects of high time and labor consumption, poor repeatability, large man-made interference factor and the like of a traditional microscopic dissection and identification method are avoided.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF PARASITIC DISEASES
Method for detecting insecticide resistance of schistosoma japonicum eggs to praziquantel in vitro
InactiveCN102608306AResolve detectionSolve technical problems of monitoringBiological testingIodine lugolFeces
The invention relates to a method for detecting insecticide resistance of schistosoma japonicum eggs to praziquantel in vitro, belonging to the technical field of antiparasitic drugs. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting 1,000-2,000 eggs from the feces of schistosoma japonicum infected hosts, respectively immigrating the 1,000-2,000 eggs in a flask of 50mL of normal saline containing praziquantel of 5*10-6mol / L and single control normal saline, and placing the eggs in the dark environment for 24h; then immigrating the eggs in fresh dechlorinated tap water, and hatching miracidia under irradiation of an incandescent bulb of 28 DEG C; after hatching starts, collecting tap water containing the miracidia for one time with a centrifuge tube of 50mL every 30 min; centrifuging after adding few drops of Lugol's iodine solution; collecting the miracidia, observing the miracidia under a microscope, counting, and calculating the hatching rate of eggs; setting normal saline control, and repeating for 3 times; detecting the insecticide resistance of the schistosoma japonicum eggs to praziquantel by observing the hatching rate of eggs. The method is fast, simple, convenient, sensitive and reliable and is suitable for fast detecting and monitoring the insecticide resistance of the schistosoma japonicum to praziquantel on site.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF PARASITIC DISEASES
Hybridoma for secreting anti-recombinant schistosoma japonica enolase specific monoclonal antibody as well as preparation method and application of hybridoma
InactiveCN104611296AImprove accuracyIncrease positive rateTissue cultureVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismElisa method
The invention relates to a hybridoma for secreting an anti-recombinant schistosoma japonica enolase specific monoclonal antibody as well as a preparation method and application of the hybridoma, and belongs to the technical fields of gene engineering, preparation of monoclonal antibodies and immunologic diagnosis. The hybridoma JYG-1 capable of secreting the anti-recombinant schistosoma japonica enolase (Sj Enolase protein) specific monoclonal antibody is preserved in the Common Microbiology Center of CCCCM (China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms) and has the preservation number of CGMCC NO. 9910. The hybridoma JYG-1 can secrete the anti-recombinant schistosoma japonica enolase (Sj Enolase) specific monoclonal antibody JYGENmb-1. The monoclonal antibody JYGENmb-1 can be combined with Sj Enolase protein specificity of schistosoma japonica, a sandwich ELISA method for detecting Sj Enolase protein is provided, and the monoclonal antibody can be applied to establishing various immunological methods for detecting Sj Enolase protein in schistosoma japonica infected human and animal blood and excreting secretion.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF PARASITIC DISEASES
Serum biomarker for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonica and screening method and application
ActiveCN110763795AIndicators are predictiveGood forecastComponent separationSchistosomiasesMetabolite
The invention discloses a serum biomarker for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonica. The serum biomarker is phosphatidylcholine and / or palmitoyl choline. The sensitivity and specificity of the marker are both greater than 0.9, and the under-curve area (AUC) is greater than 0.9, which indicates that the two indexes have favorable predictability and can be used for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonicum katsurada. The invention further discloses a screening method of the serum biomarker for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonica based on metabonomics. A mouse schistosomiasis japonica model is constructed, and the metabonomics analysis is carried out on mouse serum by utilizing an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry technology, and characteristic differential metabolites between a normal mouse and a schistosomiasis japonica infected mouse are found and analyzed, namely, the schistosomiasis japonica early diagnosis biomarker is obtained. The screening method has the characteristics of convenience and quickness, can accurately reflect the metabolic spectrum difference between a schistosomiasis japonicum infected mouse and a normal mouse, and is high in specificity.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Recombinant expression carrier containing schistosoma japonicum gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant expression carrier containing a schistosoma japonicum gene which is a schistosoma japonicum heat shock protein 60 gene. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the schistosoma japonicum heat shock protein 60 and the application of the recombinant expression carrier. The recombinant expression carrier containing the schistosoma japonicum gene can highly express the schistosoma japonicum heat shock protein 60 gene, and the highly expressed recombinant schistosoma japonicum Hsp60 protein can induce mouse to generate the protection function of resisting the infection of schistosoma japonicum at a certain level.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
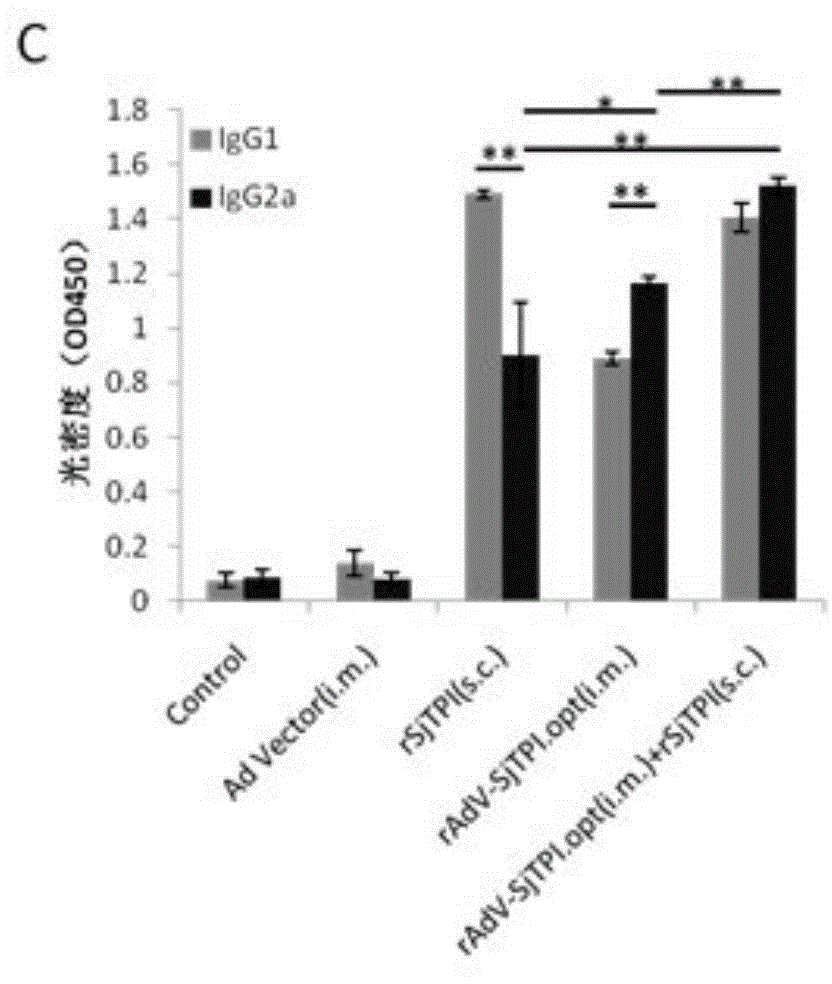
Japanese schistosomiasis vaccine combined immunizing method and application of Japanese schistosomiasis vaccine
InactiveCN104306994AImprove securityEasy to prepareGenetic material ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsTriose-phosphate isomeraseCell immunity
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF PARASITIC DISEASES
Schistosome antigen for inducing short-lived antibody response and schistosomiasis diagnostic kit and detection method for detecting antibody response
InactiveCN103667200AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresBiological material analysisOxidoreductasesSchistosomiasesProtein molecules
The invention relates to a schistosome antigen for inducing short-lived antibody response and a schistosomiasis diagnostic kit and a detection method for detecting the antibody response, belonging to the technical field of schistosomiasis prevention and treatment and immunological diagnosis. Protein molecules such as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (SjGAPDH) and the like capable of inducing short-lived antibody response in a schistosomiasis infected person through an immunoblotting technology and a mass spectrometry method are identified. A recombinant SjGAPD protein is prepared by adopting a genetic engineering technology, and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detection kit and detection method for detecting anti-SjGAPDH protein specific short-lived antibody response in the schistosomiasis infected person by the recombinant SjGAPD protein are established to diagnose the schistosomiasis infected person and estimate the treatment effect.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF PARASITIC DISEASES
Recombinant expression carrier containing schistosoma japonicum gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101671690ABacteriaGenetic material ingredientsBiotechnologySchistosoma Japonicum Infection
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant expression carrier containing schistosoma japonicum gene and application thereof
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Related gene and protein for preventing and treating Japanese blood fluke infection, and its uses
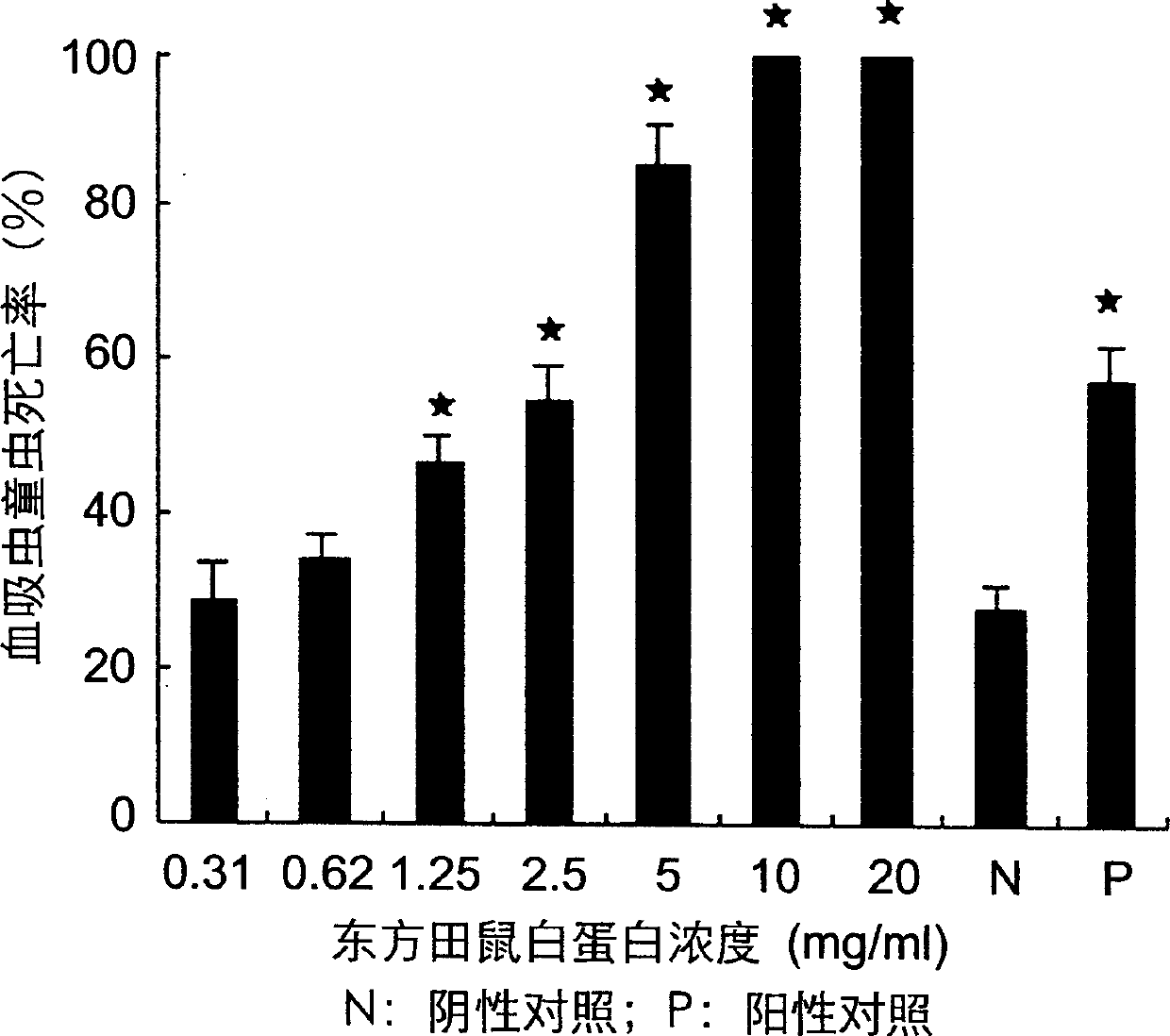
The invention discloses a protein sequence for killing Japanese Schistosoma and preventing and treating Japanese Schistosoma infection and the corresponding gene sequence and its usage. The protein sequence uses affinity chromatography, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; dialysis, freeze drying and protein amino end test sequence to separating obtain the blood serum albumin from oriental hamster unguent. It uses polyase chain reaction technology to obtain oriental hamster blood serum albumin gene sequence. The gene and the decorated mutant insert into the eukaryon expression holder in the animal body, which can be used in preventing and treating the gene of Japanese Schistosoma infection.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
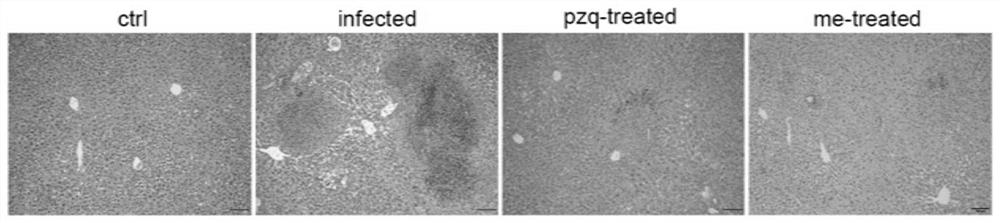
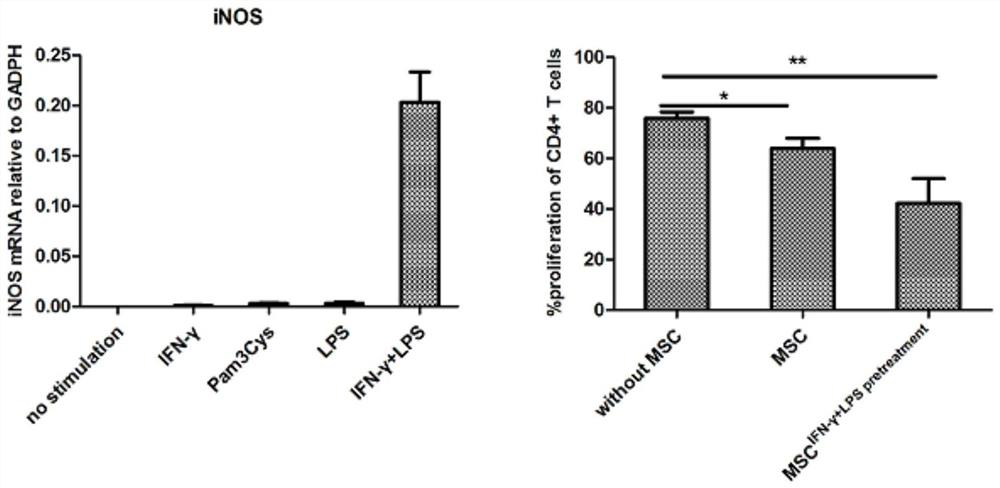
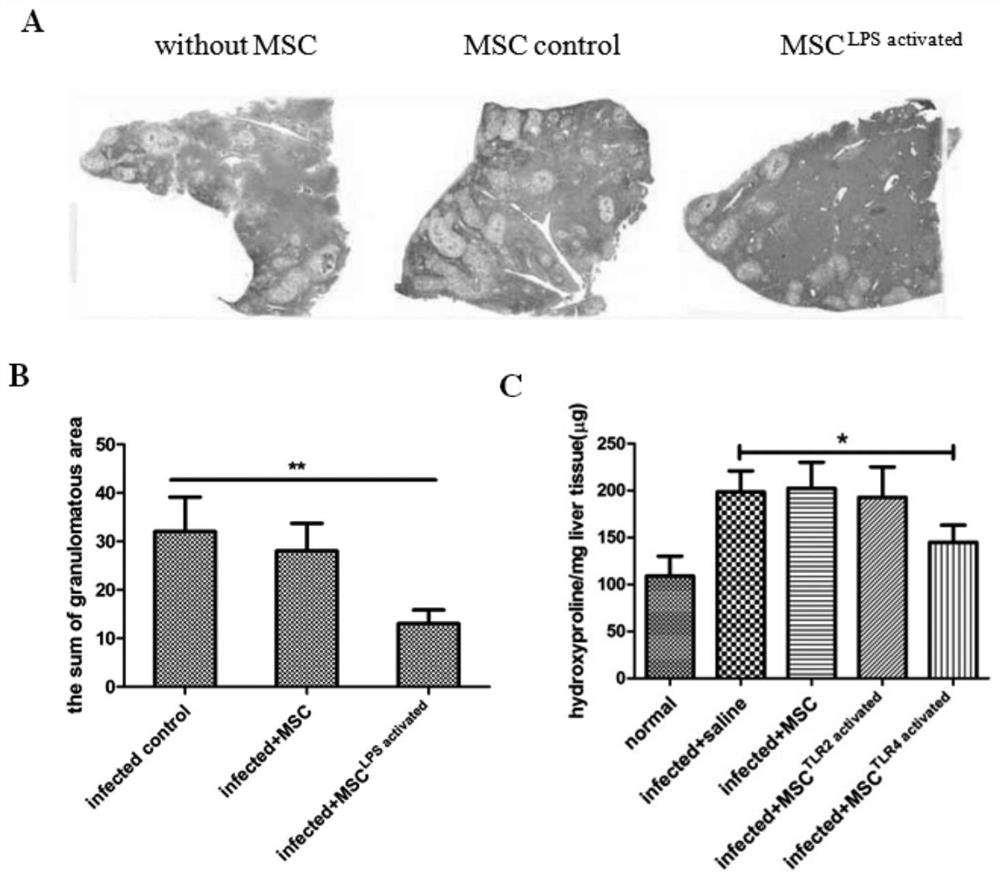
Mesenchymal stem cell treating method for Schistosoma japonicum infection treatment
ActiveCN110777113ANo obvious side effectsReduce fibrosisSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUnknown materialsInfected patientSchistosoma Japonicum Infection
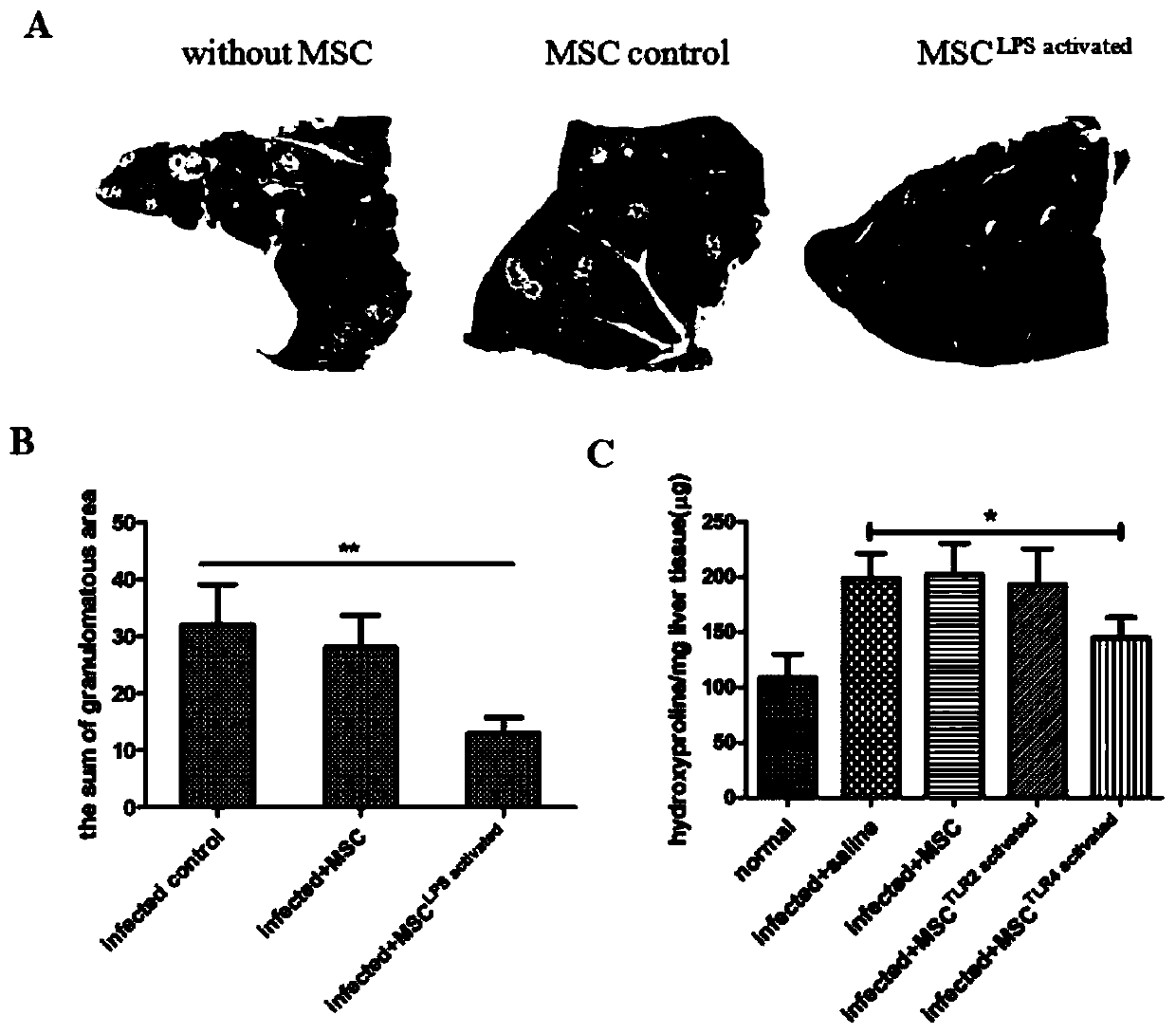
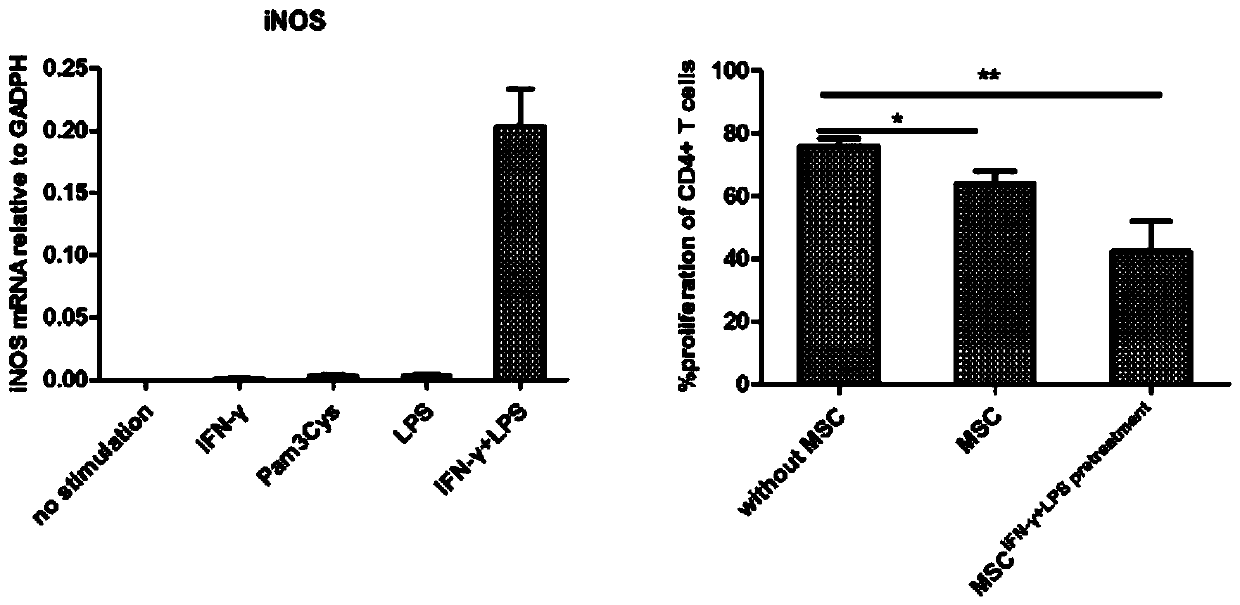
The invention discloses a mesenchymal stem cell treating method for Schistosoma japonicum infection treatment. IFN-gamma and LPS are added into an MSC culture medium to perform cultivation for 24 h at37 DEG C, the final concentration of the IFN-gamma is 5-100 ng / ml, and the final concentration of the LPS is 10-100 ng / ml; and stimulating factors are removed, and therefore, treatment can be realized after full washing. The advantages of the method are mainly manifested as follows: 1, compared with treatment mainly aiming at parasites at present, optimized and induced MSCs can be used for the treatment of the hepatic fibrosis of infected patients and have no obvious toxic and side effects; and 2, compared with the MSCs that are not induced, the optimized and induced MSCs can significantly reduce the hepatic fibrosis caused by schistosome infection by obviously promoting Th1 reaction, so that better curative effect can be obtained.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
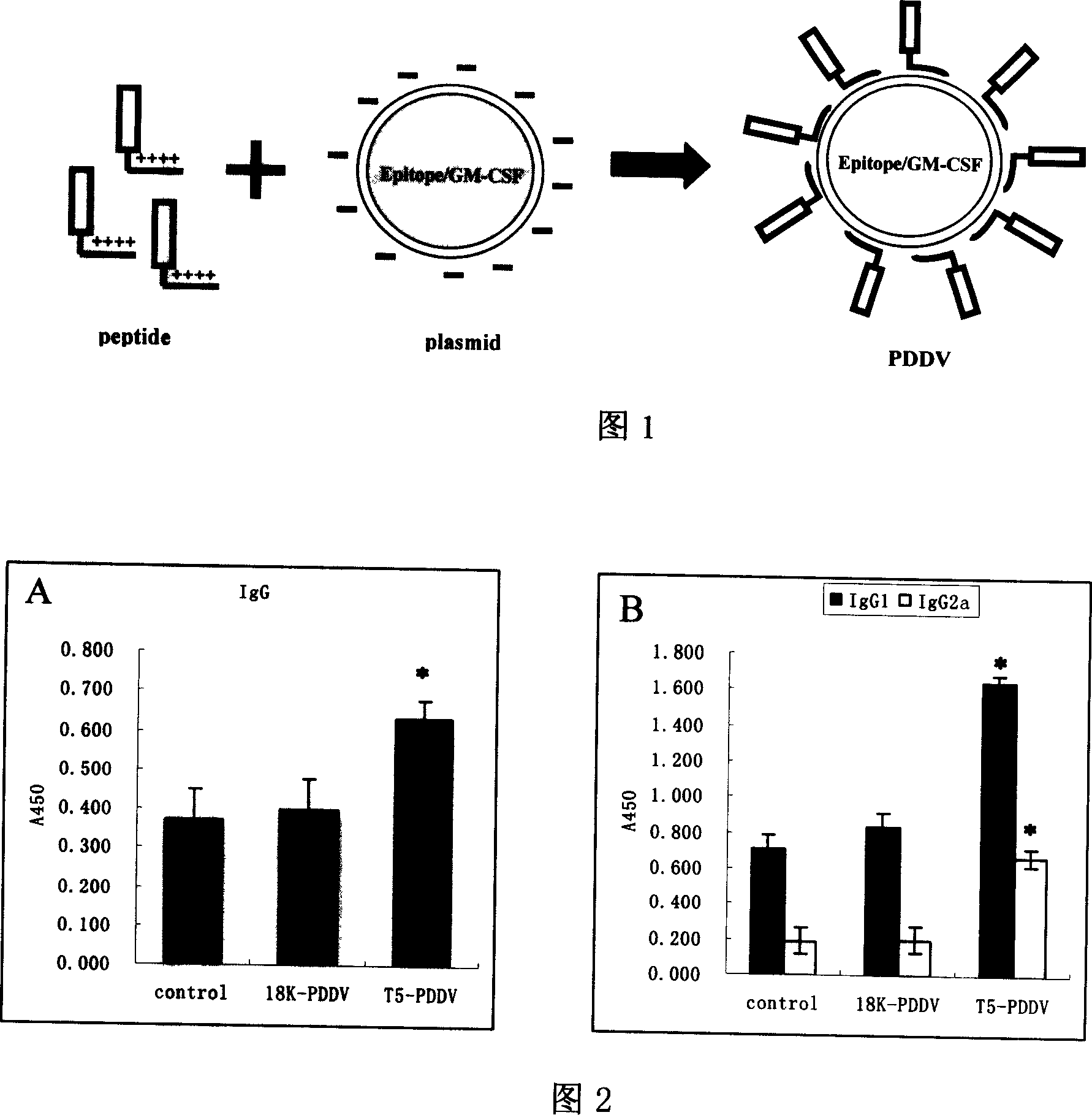
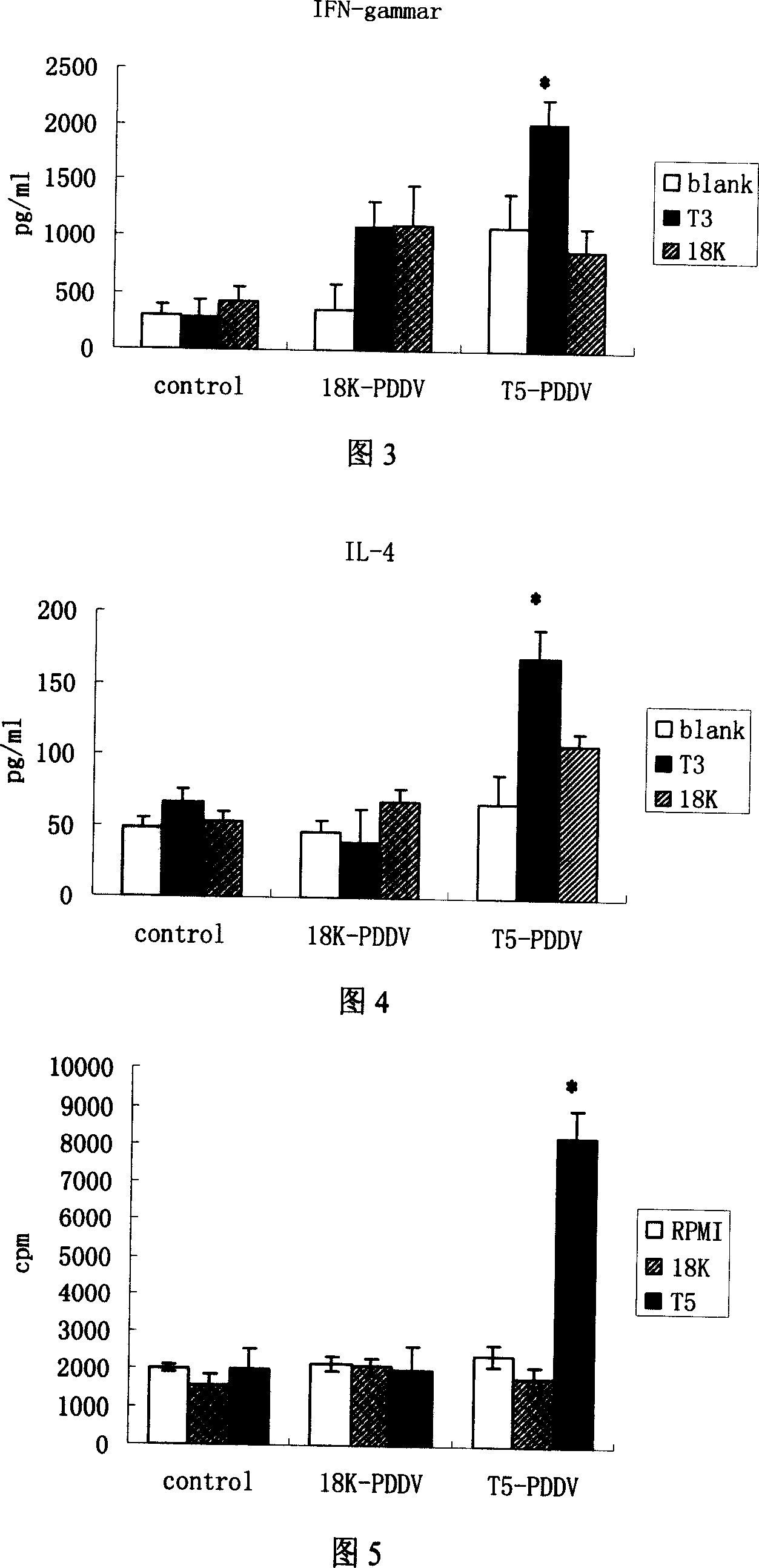
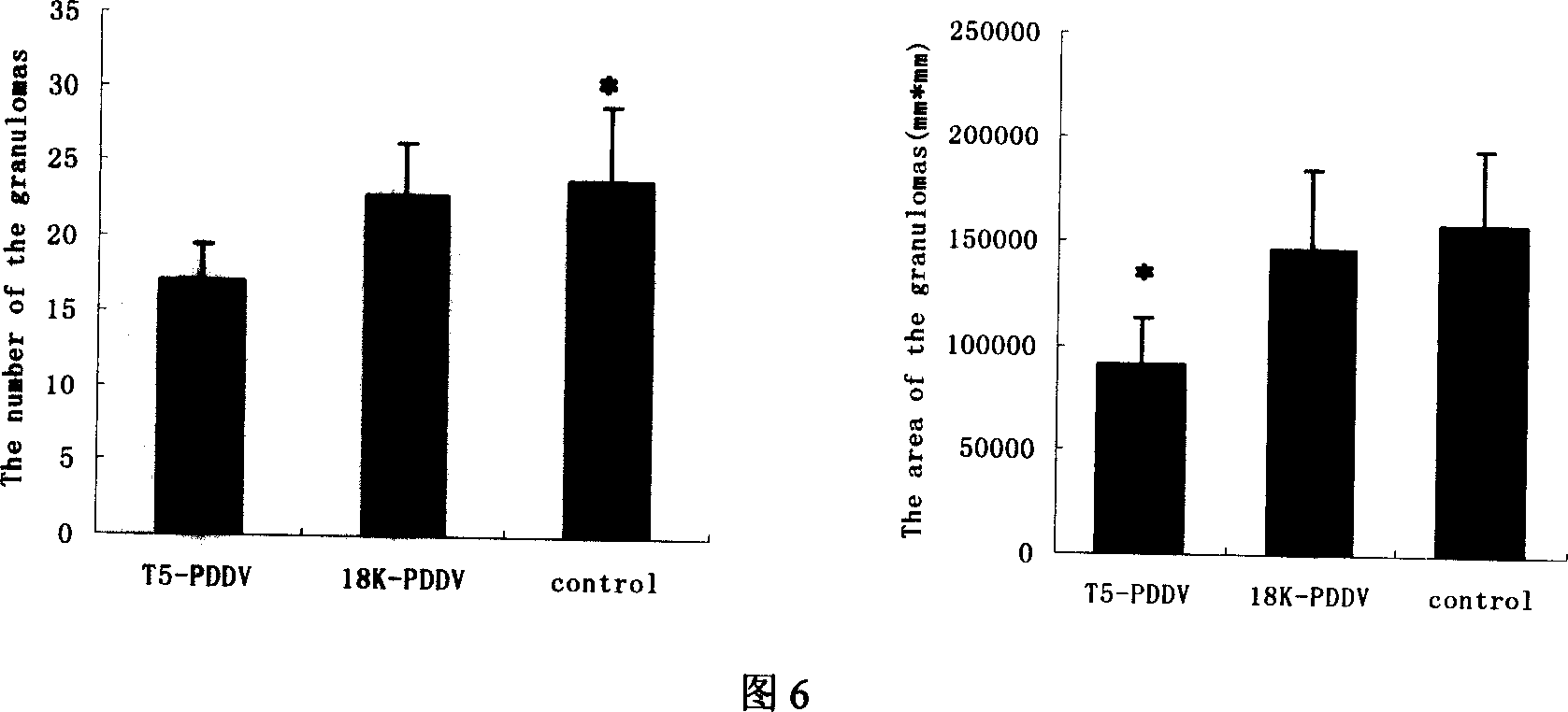
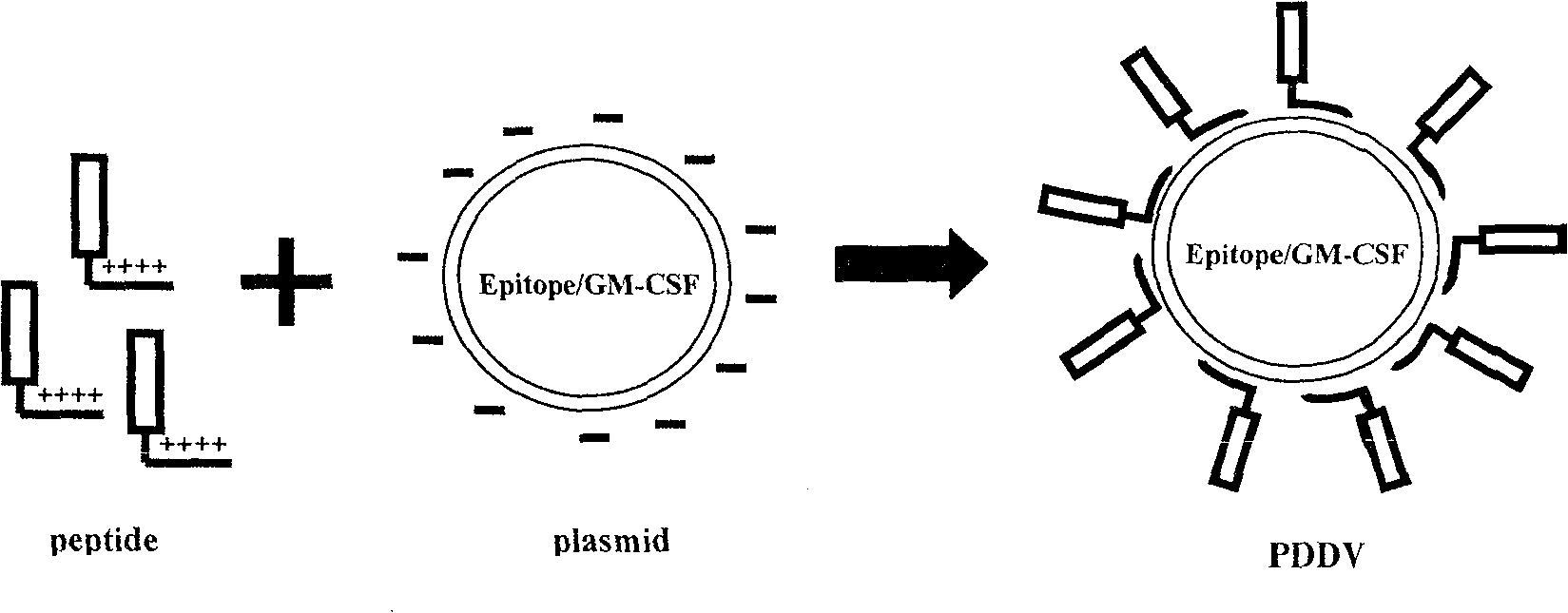
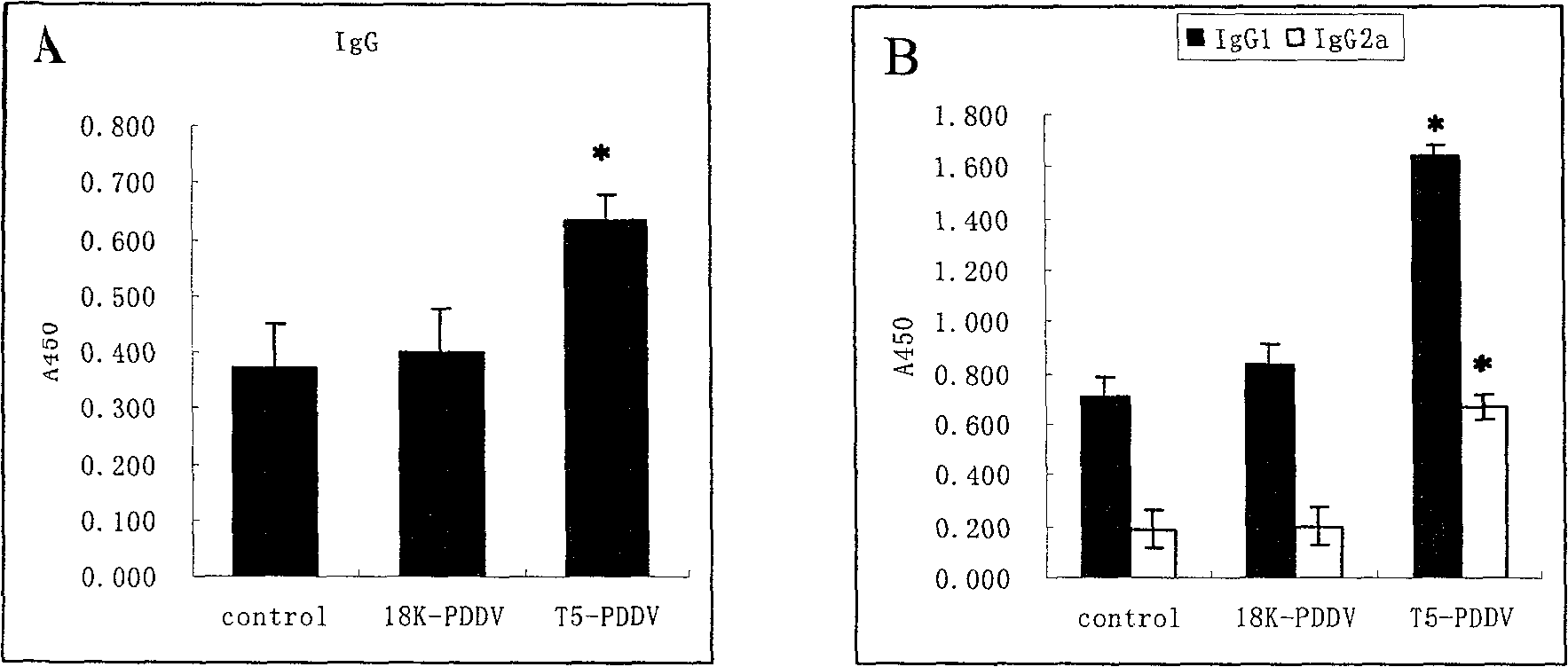
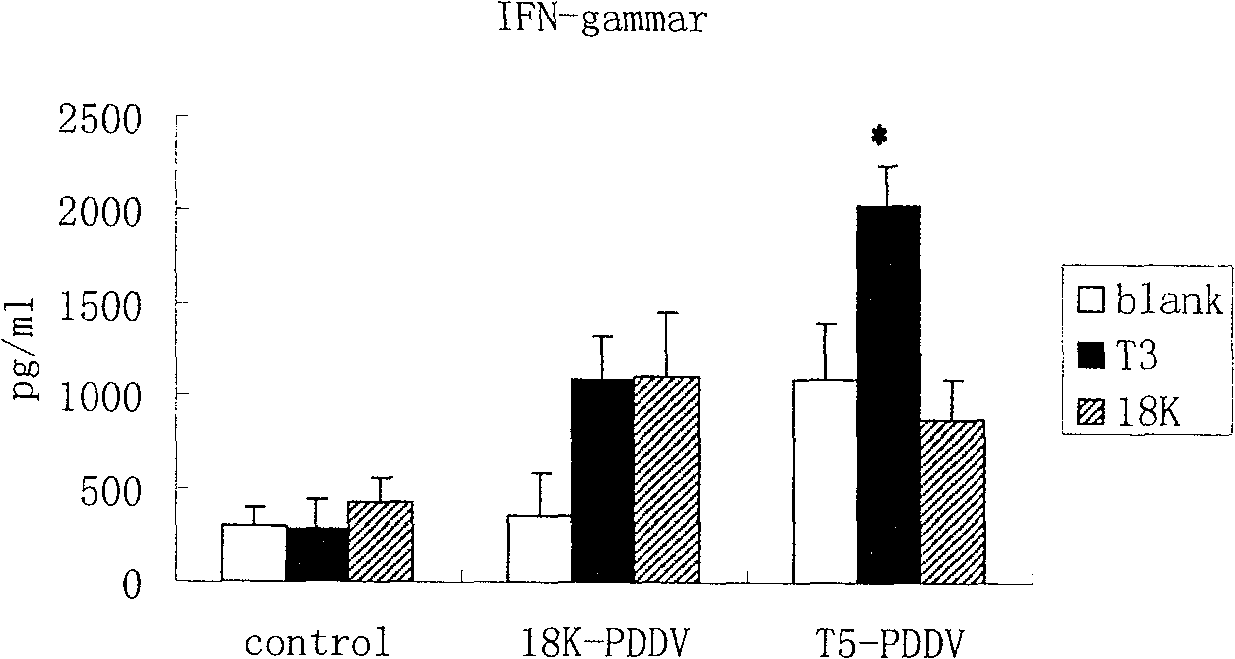
Peptide-DNA double vaccine based on T-cell epitope for anti-Schistosoma japonicum infection
InactiveCN101002948AImprove protectionStrong immunostimulatory abilityGenetic material ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsSchistosoma Japonicum InfectionFhit gene
A double peptide-DNA vaccine based on T-cell epitope for preventing and treating the Japanese schistosome infection features that its eucaryotic expression carrier carrying the epitope peptide coding gene is wrapped by the protein containing the epitope peptide. The amino acid sequence of said T-cell epitope peptide is AKQYNICCKFKELLD. Said vaccine can be prepared by cationic peptide carrying technique.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Method for detecting infection with schistosoma japonicum by using host exosomes miRNA-223-3p
InactiveCN110760590AReduce traumaTraumaMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMedicine
The invention discloses a method for detecting infection with schistosoma japonicum by using host exosomes. The nucleotide sequence of a serum exosome miR-223-3p is shown as SEQID NO:1, and the methodfor detecting infection with schistosoma japonicum is established according to a primer of which the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQID NO:2. In accordance with the detection method of the schistosoma japonicum, the method is quick, acute, excellent and stable in detection. According to the method, the serum of patients is directly extracted, the wound parts of the patients can be alleviated,and the wound parts are small. A q-PCR detection method is used, so that the sensitivity is high, and the q-PCR detection method is high in sensitivity. An exosome extraction kit being mature exists,and besides, q-PCR detection is a common technique for laboratories, so that the method is simple relatively. Therefore, the method is worth of promotion, and has a good clinical application value.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Application of myricetin in preparation of drug for treating schistosomiasis
ActiveCN111671744AGood anti-schistosomiasis effectImprove liver fibrosisOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemSchistosoma Japonicum InfectionIn vivo experiment
The invention provides application of myricetin in preparation of a drug for treating schistosomiasis. By in-vitro observing an effect of the myricetin for resisting schistosoma japonicum and carryingout in-vivo experiment by establishing a schistosoma japonicum infected mouse model, it is found that the myricetin has good schistosoma japonicum killing effect and an improvement effect on liver fibrosis of schistosoma japonicum infected mice in vivo and in vitro. Moreover, the insecticidal effect of the myricetin is equivalent to that of positive drug praziquantel, the myricetin can replace the application of the positive drug praziquantel to schistosomiasis japonica, possibility is provided for avoiding clinical drug resistance, and the myricetin has a great application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A treatment method of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of Schistosoma japonicum infection
ActiveCN110777113BNo obvious side effectsReduce fibrosisAntimycoticsDigestive systemInfected patientSchistosoma Japonicum Infection
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Method for detecting schistosoma japonicum infection by using host exosome miRNA-142a-3p
InactiveCN110760589AReduce traumaTraumaMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMedicine
The invention discloses a method for detecting schistosoma japonicum infection by using a host exosome miRNA-142a-3p. A nucleotide sequence of the serum exosome miR-142a-3p is as shown in SEQ ID NO 1,and the method for detecting the schistosoma japonicum infection is established based on primers with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO 2. The method for detecting the schistosoma japonicuminfection by using the host exosome miRNA-142a-3p is rapid, sensitive, specific and stable to detect. According to the method, serum of patients is directly extracted so that the trauma of the patients is reduced, and the trauma is small; a q-PCR detection method is used, and the sensitivity is high; and the q-PCR detection method has high sensitivity. At present, a mature exosome extraction kitis provided, meanwhile, q-PCR detection is a commonly used technology in a laboratory and is relatively simple. Therefore, the method is worth popularizing and has a good clinical application value.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Schistosoma japonicum infection, and application of components of schistosoma japonicum to prevention and treatment of human tumors
InactiveCN109536497AGrowth inhibitionInhibit migrationOrganic active ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsSchistosoma speciesHuman tumor
The invention relates to the use of schistosoma japonicum infection, and an application of components of schistosoma japonicum to the prevention and treatment of human tumors. The schistosoma japonicum components include but are not limited to eggs, miRNAs, exosomes, and proteins. The present invention shows for the first time that the schistosoma japonicum components have an effect of resisting avariety of host tumors including but not limited to liver cancer. The schistosoma japonicum and the components thereof come into play by inducing host-specific and non-specific immune responses, or modulating tumor-associated genes and signaling pathways, or directly killing tumor cells. The schistosoma japonicum and the components thereof have application value in the prevention and treatment ofhuman tumors.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
A detection method for the diagnosis of snail infection, an intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum
ActiveCN110484626BQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInfection diagnosisNucleotide
The invention discloses a detection method for diagnosing the infection of Schistosoma japonicum intermediate host snails. The invention uses a primer combination for detecting Schistosoma japonicum infection with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-6 to establish a Schistosoma japonicum infection testing methods and testing kits. The invention can quickly and accurately detect the schistosomiasis in the inspected snails, and is simultaneously applicable to the detection of the infection of the schistosomiasis in animals and the monitoring of the schistosomiasis in the environment. The detection method has high detection rate, high sensitivity, strong specificity, high accuracy and simple equipment, so it has good application prospect and promotion value.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Young schistosomiasis cell style vaccine for preventing from schistosomiasis disease
InactiveCN1778388AOvercome insecuritiesOvercome practicalityProtozoa antigen ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsDiseaseAdjuvant
A schistosomulum cell type vaccine for preventing schistosomiasis is prepared through collecting the schistosomulums from the rabit infected by Japanese schistosome for 14-24 days, fast cutting in aseptic mode, digestion by pancreatin, taking supernatant, adding Ca or Mg ion type D-Hankí»s liquid to terminate the digestion to obtain living cells, freezing them to obtain the dead cells and using said living cells or dead cells as vaccine.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Peptide-DNA double vaccine based on T-cell epitope for anti-Schistosoma japonicum infection
InactiveCN100553683CImprove protectionStrong immunostimulatory abilityGenetic material ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsPeptide vaccineIn vivo
The invention belongs to the field of immunology, and in particular relates to a mixed vaccine of T cell epitope protein and DNA against Schistosoma japonicum infection. The said anti-Schistosoma japonicum infection peptide-DNA double vaccine is to wrap the protein containing the epitope peptide outside the eukaryotic expression vector with the gene encoding the epitope peptide, the amino acid sequence of the said T cell epitope peptide For AKQYNICCKFKELLD. The peptide-DNA double vaccine can be prepared by cationic peptide loading technology. The anti-Schistosoma japonicum infection peptide-DNA double vaccine of the present invention can effectively resist the degradation of DNase in the body after injection into the body, thereby greatly reducing the dosage of the vaccine; it is easy to enter the antigen-presenting cells and the antigen is efficiently presented; Facilitates simultaneous stimulation of cellular and humoral immune responses.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
A urine biomarker for the early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonicum and its screening method and application
The invention discloses a urine biological marker for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonica, wherein the urine biological marker is one or more of xanthonic acid, naphthalenesulfonic acid or heptanoylcarnitine. The sensitivity and specificity of the markers were all greater than 0.9, and the area under the curve (AUC) was greater than 0.9, indicating that the three indicators had good predictive performance and could be used for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonica. The invention also discloses a screening method for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonica urine biomarkers based on metabolomics. By constructing a mouse schistosomiasis japonica model, the ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry technology is used to metabolize mouse urine. The omics analysis found and analyzed the characteristic differential metabolites between normal mice and Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice, which were biomarkers for early diagnosis of Schistosomiasis japonicum. The screening method has the characteristics of non-invasiveness, convenience and quickness, and can accurately reflect the difference of the metabolic profile between the mice infected with schistosomiasis japonicum and the normal mice, and has high specificity.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
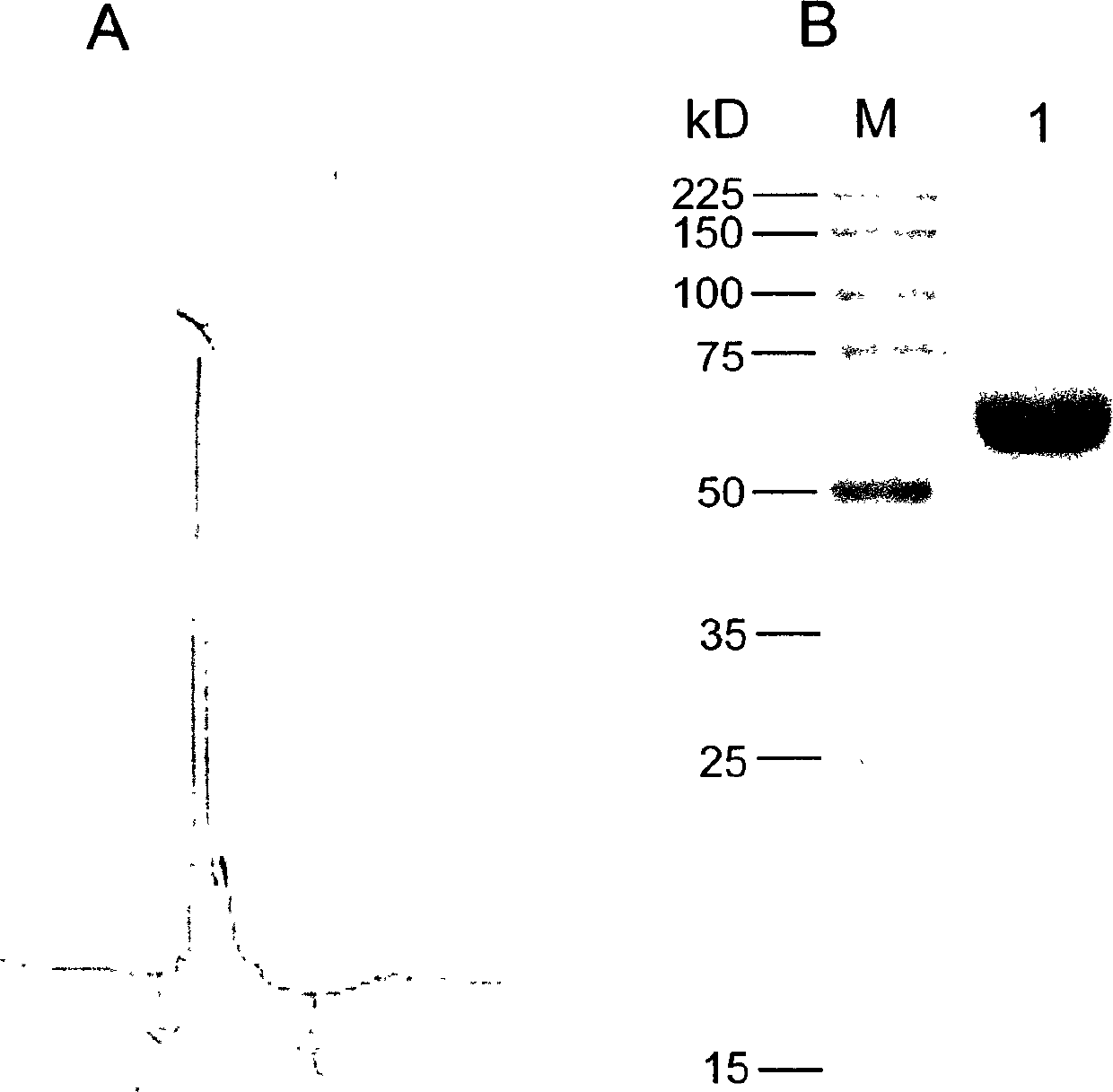
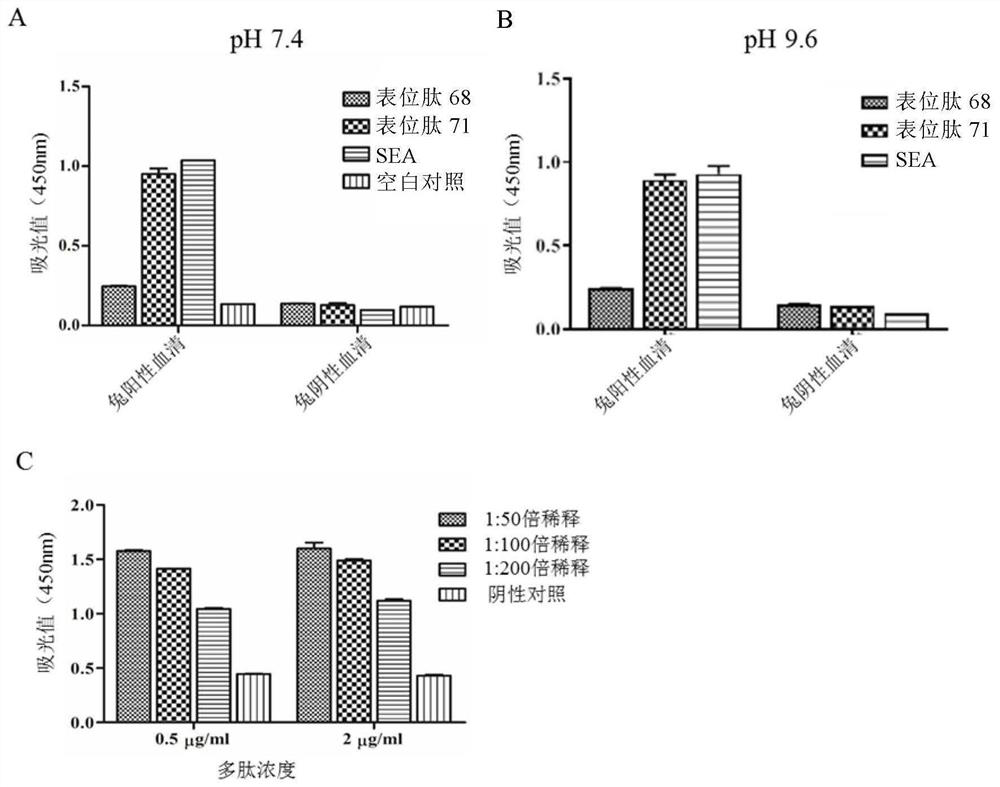
A Schistosoma japonicum immune epitope recombinant protein and its application
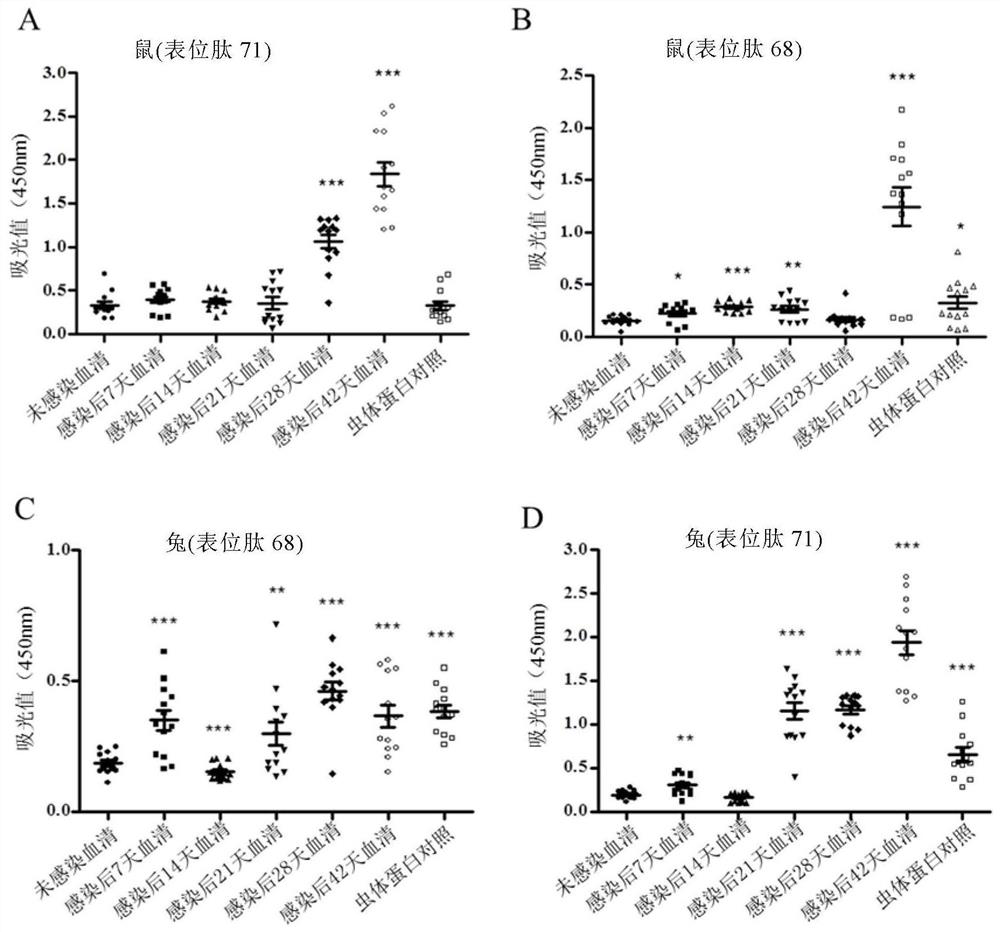
ActiveCN110357951BEfficient detectionQuick checkDisease diagnosisBiological testingEpitopeSchistosoma Japonicum Infection
The invention discloses a Schistosoma japonicum immune epitope recombinant protein, which is represented by epitope peptide 68 shown in SEQ ID NO.1, epitope peptide 71 shown in SEQ ID NO.2 or SEQ ID NO.3. The tandem epitope peptides shown. The invention also discloses the application of the above-mentioned immune epitope recombinant protein of Schistosoma japonicum in the preparation of products for diagnosing Schistosoma japonicum. The Schistosoma japonicum immune epitope recombinant protein of the invention can effectively and rapidly detect the infection of the Schistosoma japonicum, and has good sensitivity in detecting the early infection of the Schistosoma japonicum.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A serum biomarker, screening method and application for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonicum
The invention discloses a serum biomarker for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonicum, and the serum biomarker is phosphatidylcholine and / or palmicholin. The sensitivity and specificity of the markers are both greater than 0.9, and the area under the curve (AUC) is greater than 0.9, indicating that these two indicators have better predictability and can be used for early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonicum. The invention also discloses a metabolomics-based screening method for serum biomarkers for the early diagnosis of schistosomiasis japonicum, by constructing a mouse schistosomiasis model, and using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to perform metabolomics on mouse serum Analyze, discover and analyze the characteristic differential metabolites between normal mice and Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice, which are biomarkers for early diagnosis of Schistosomiasis japonicum. The screening method has the characteristics of convenience and quickness, can accurately reflect the difference in metabolic spectrum between mice infected with schistosomiasis japonicum and normal mice, and has high specificity.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
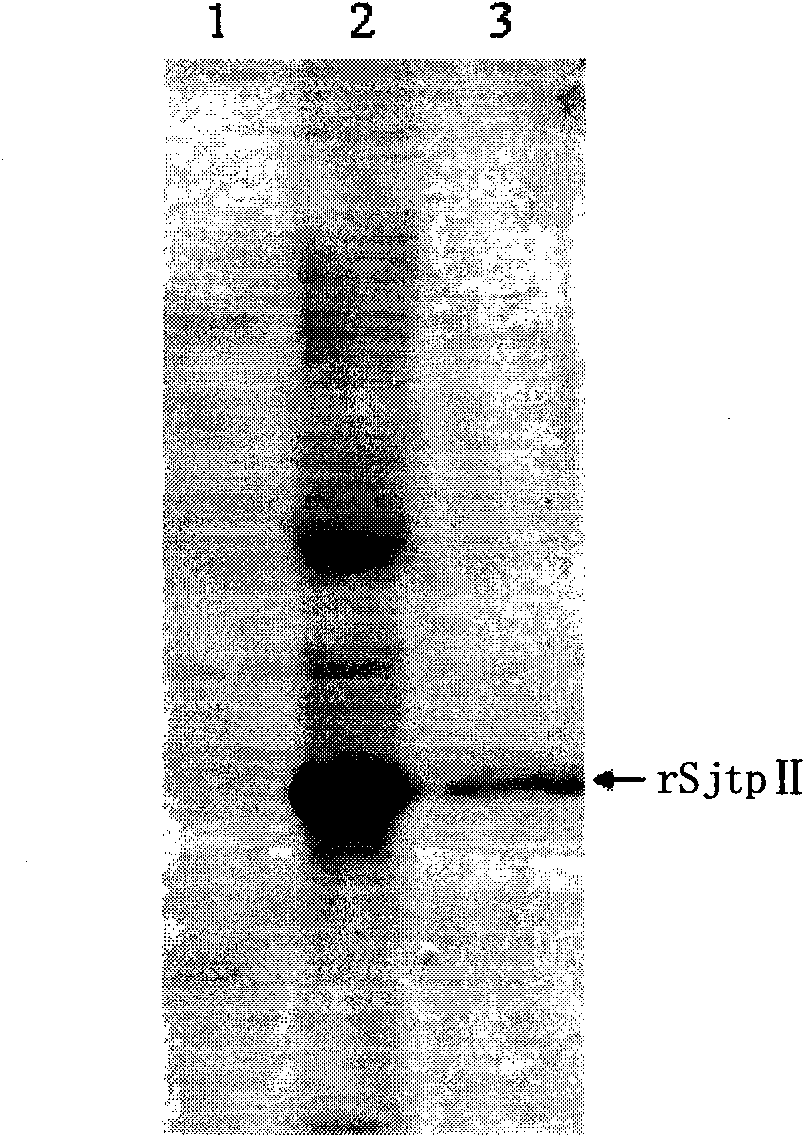
Recombinant expression vector containing Schistosoma japonicum gene and its application
InactiveCN101671690BBacteriaGenetic material ingredientsBiotechnologySchistosoma Japonicum Infection
The invention discloses a recombinant expression carrier containing a schistosoma japonicum gene which is a schistosoma japonicum thioredoxin peroxidase II gene. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the schistosoma japonicum thioredoxin peroxidase II and the application of the recombinant expression carrier. The recombinant expression carrier containing the schistosoma japonicum gene can highly express the schistosoma japonicum thioredoxin peroxidase II, and the highly expressed recombinant schistosoma japonicum thioredoxin peroxidase II can induce mouse to generate the protection function of resisting the infection of schistosoma japonicum at a certain level.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of SHSP60 for preparing diagnostic reagent for monitoring comprehensive hepatic pathology injury degree of schistosomiasis patient
The invention belongs to the field of immunology, and particularly relates to an application of proteantigen molecules from schistosomes such as Japanese schistosome shock proteins 60KDa (SjHSP60), which is the application of Japanese schistosome shock proteins 60KDa for preparing a diagnostic reagent for monitoring comprehensive hepatic pathology injury degree of a schistosomiasis patient. The SjHSP60IgG in blood serum of a Japanese schistosome infected host and subtype IgG1 antibody level thereof are positively correlated to liver granuloma and fibrosis degree, which promotes that the SjHSP60IgG in blood serum and the subtype IgG1 antibody level thereof can be used as an index of evaluating the pathological degree of the liver of the schistosomiasis patient and has potential clinical application value. In the future, the novel diagnostic reagent may be used for monitoring the pathological degree of the liver of the schistosomiasis patient.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Garlic seed aqueous extracts for killing schistosoma japonicum cercariae
InactiveCN101036743AAbundant material sourcesLow priceAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryIrritationSlurry
A garlic seed immersion fluid for killing japaneses schistosomulum, is composed of garlic seed immersion fluid and water. The garlic seed is peeled off the skin, and then squeezed by clear water dechlorinated after airing to become the raw liquor of the garlic seed fluid, at last the garlic seed immersion fluids of various concentrations above 0.79% are prepared by distilled water for killing japaneses schistosomulum. A great variety of emulsion, slurry, aqua and oil are prepared by the garlic seed immersion fluid as protective agents for skin protection against the penetration of the japaneses schistosomulum, namely avoiding the infection of the japaneses schistosomulum. The garlic seed immersion fluid is natural product, the features of which comprise small skin irritation, low price, economy, practicality.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Micro rna and its application in the preparation of preparations against Schistosoma japonicum infection
ActiveCN108531480BOrganic active ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsSchistosoma Japonicum InfectionPharmaceutical drug
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com