Four-dimensional ultra-fast photographing device
A photographic device, ultra-fast technology, used in measuring devices, optical radiometry, instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
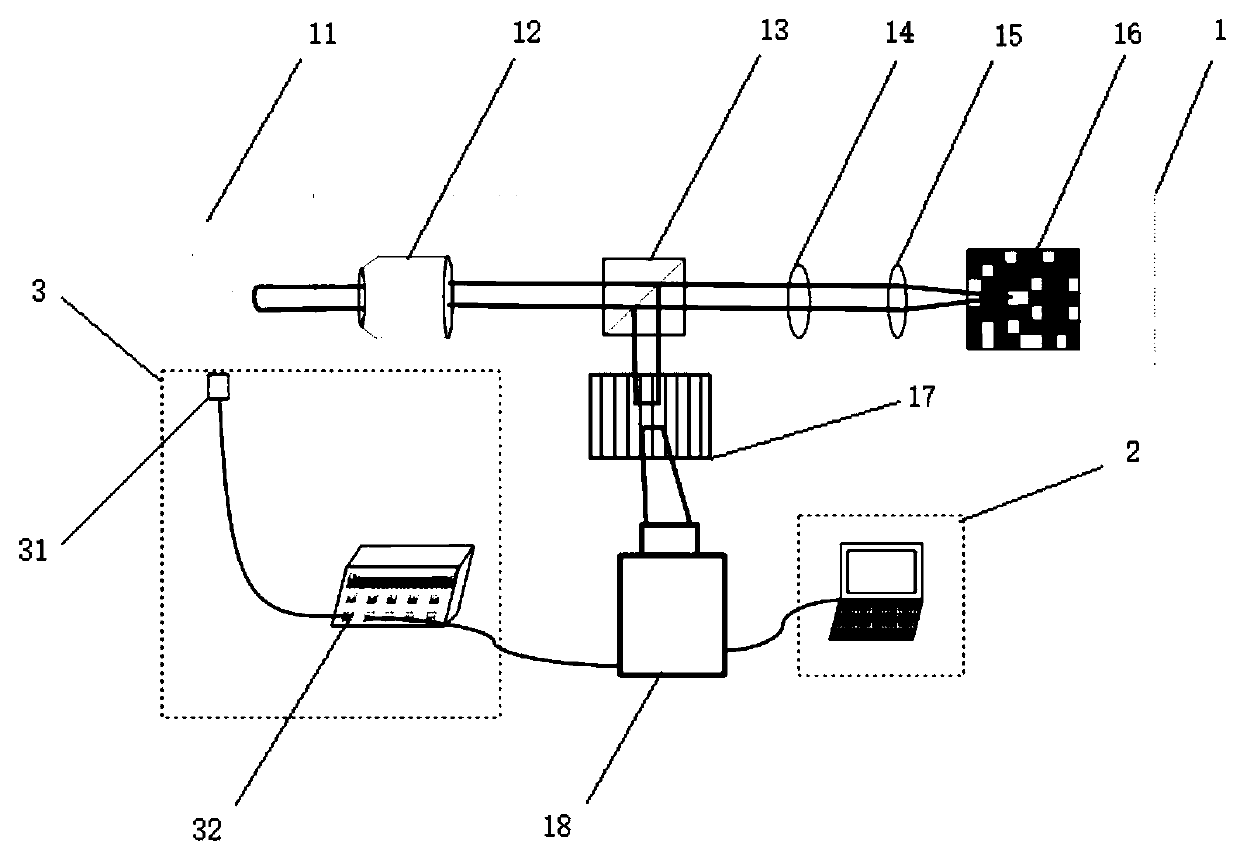
[0046] refer to figure 1 , in the present embodiment, digital delay pulse generator 32 selects DG645 digital delay pulse generator for use; Streak camera 18 selects CMOS industrial camera for use; The scale of grating 17 is 300lp / mm;
[0047] The data acquisition system 1 works, first selects the dynamic scene 11 to be measured, and the dynamic image enters the focusable lens 12, the beam splitter cube 13, the first lens 14, and the second lens 15 to reach the digital micromirror device 16, and the digital micromirror The device 16 performs a pseudo-random encoding, and the encoded image is reflected by the small unit on the digital micromirror device 16 back to the original 4f system and then back to the beam splitter cube 13, and then reflected into the grating 17 after beam splitting by the beam splitter cube 13 , the spectral offset is performed by the grating 17, and finally enters the streak camera 18 for time offset and compression.
[0048] The data reconstruction sys...
Embodiment 2
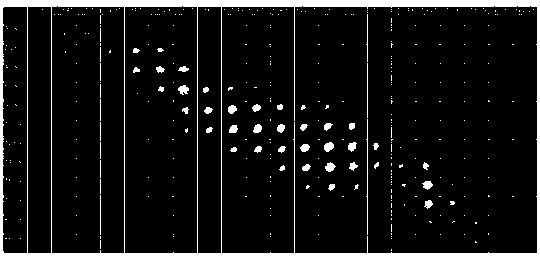
[0051] refer to figure 1 , figure 2 , the selected dynamic scene 11 to be tested is a chirped picosecond pulse signal, and the whole single pulse signal is captured by the present invention.
[0052] When the data acquisition system 1 works, the dynamic scene 11 to be measured is first selected as a chirped picosecond pulse signal, and the dynamic image enters the adjustable focus lens 12, the beam splitter cube 13, the first lens 14, and the second lens 15 to reach the digital microscope. Mirror device 16, a pseudo-random encoding is carried out by digital micromirror device 16, and the encoded image is reflected back to the original 4f system by the small unit on digital micromirror device 16 and returns to beam splitter cube 13 again, through beam splitter cube 13 After beam splitting, the reflection enters the grating 17, and the spectrum shift is performed by the grating 17, and finally enters the streak camera 18 for time shifting and compression.
[0053] The data reco...
Embodiment 3
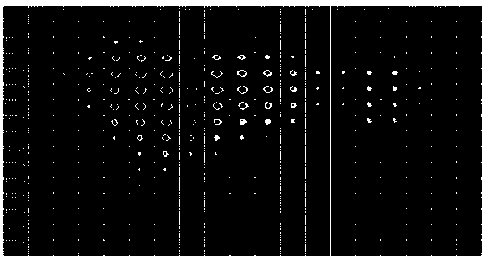
[0056] refer to figure 1 , image 3 , the selected dynamic scene 11 to be tested is a dynamic process of fluorescence decay generated by using 50 fs laser pulses in Rhodamine B solution, and the dynamic process of the entire fluorescence decay is photographed by the present invention.
[0057] When the data acquisition system 1 works, the dynamic scene 11 to be tested is first selected as a dynamic process in which the laser pulse of 50 fs is used to hit the rhodamine B solution to produce its fluorescence decay, and the dynamic image enters the adjustable focus lens 12 and the beam splitter cube 13 in turn. , the first lens 14 and the second lens 15 arrive at the digital micromirror device 16, and a pseudo-random encoding is carried out by the digital micromirror device 16, and the encoded image is reflected back to the original 4f system by the small unit on the digital micromirror device 16 Returning to the beam splitting cube 13 again, the beam is split by the beam splitt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com