Environment-friendly degradable intelligent card and manufacturing method thereof
A manufacturing method and technology for smart cards, applied in the field of smart cards, can solve problems such as low ink adhesion, delamination of smart cards, and edge bursts, and achieve the effects of improving environmental performance, facilitating degradation, and avoiding scratches
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
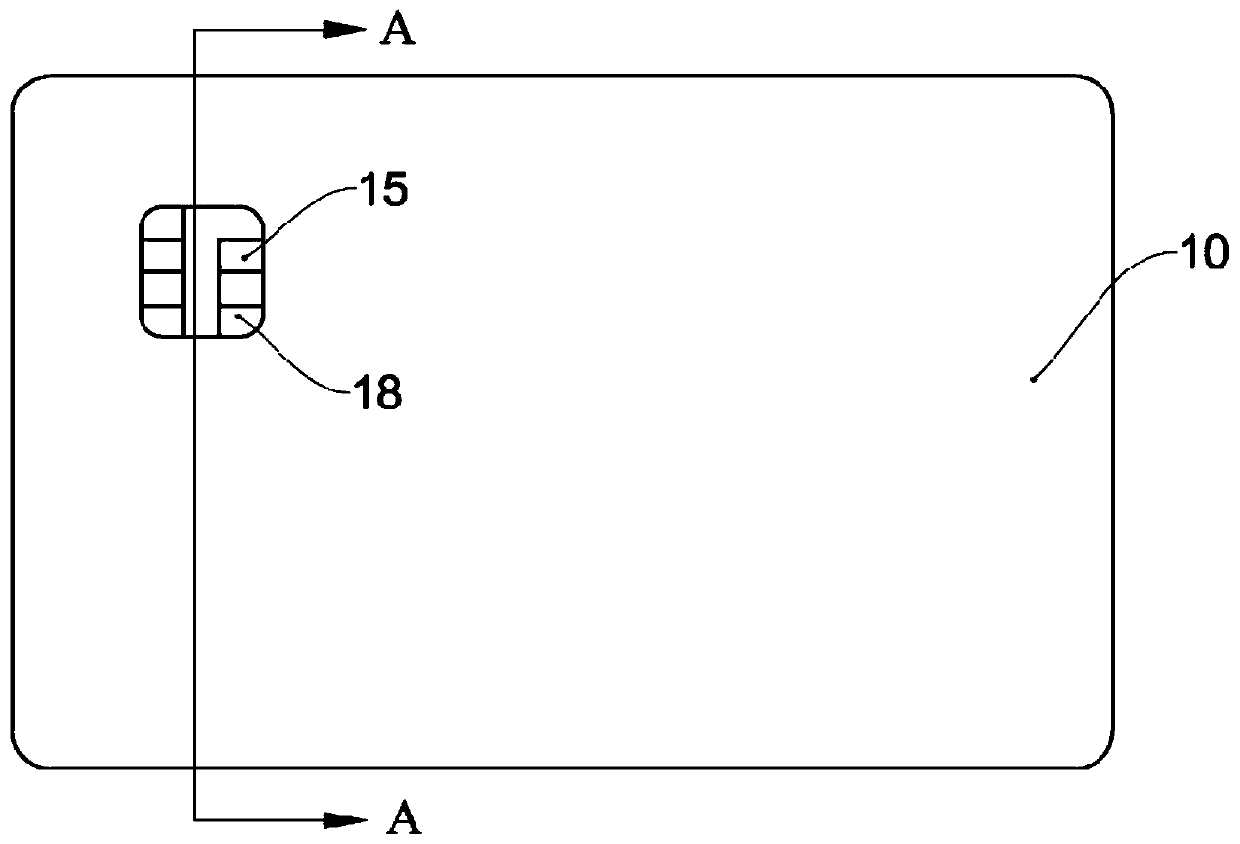
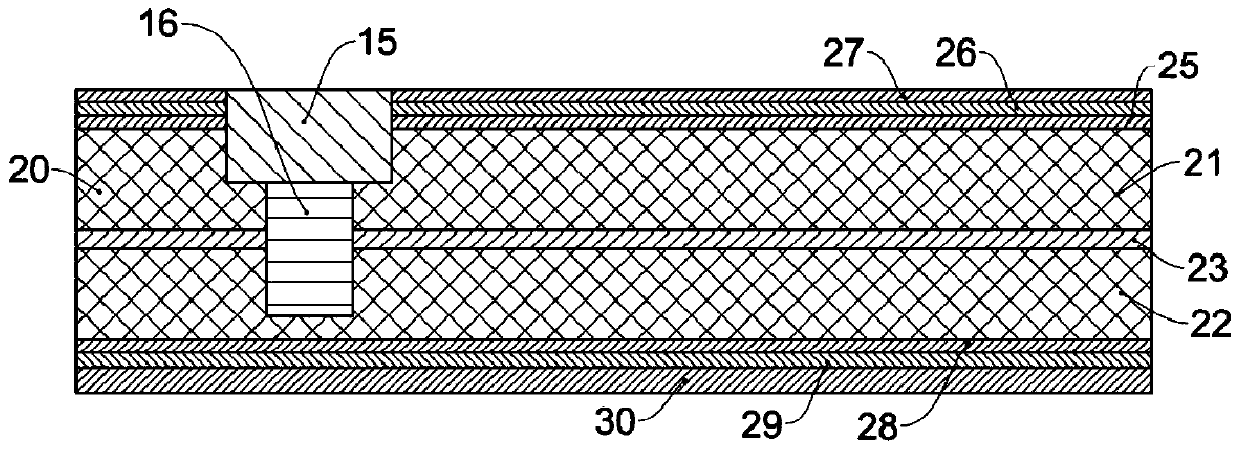
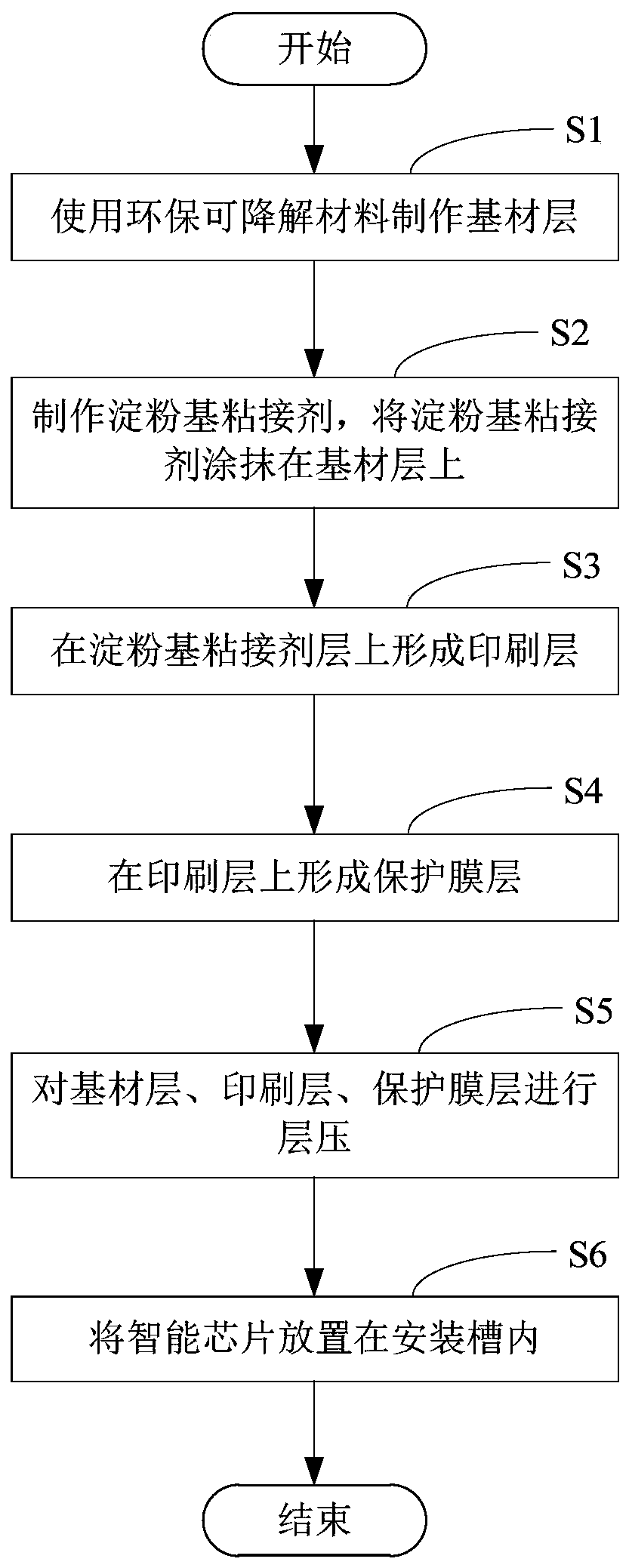
[0052] Combine below image 3 Introduce the manufacturing process of the smart card. First, step S1 is performed to make the base material layer using environmentally friendly and degradable materials. In this embodiment, the base material layer includes a first base material layer and a second base material layer, and an installation cavity needs to be provided on the first base material layer . Specifically, materials such as polylactic acid can be used to make the first base material layer and the second base material layer respectively.
[0053] Then, step S2 is performed to make a starch-based adhesive. In this embodiment, the starch-based adhesive is prepared by cross-linking starch-modified polyvinyl acetate emulsion and polyurethane prepolymer. Specifically, the preparation process of starch-modified polyvinyl acetate emulsion is as follows: starch, Add polyvinyl alcohol and water to a four-necked flask with a nitrogen protection device at the same time, stir and he...
no. 2 example
[0080] The structure of the smart card produced in this embodiment is the same as that of the three smart card embodiments introduced above, and the structure of the smart card will not be introduced here.
[0081] Combine below Figure 6 Introduce the process of this embodiment. First, step S11 is performed to make the base material layer using environmentally friendly and degradable materials. In this embodiment, the base material layer includes a first base material layer and a second base material layer, and an installation cavity needs to be provided on the first base material layer , For example, materials such as polylactic acid can be used to make two substrate sublayers. Since the two base material sub-layers need to be bonded with a synthetic resin adhesive, the step of bonding the two base material sub-layers is performed after the synthetic resin adhesive is prepared. Certainly, the base material layer may also include a first base material layer, an intermediate...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile force | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com