Experimental method for photoelectrocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A by polypyridine ruthenium complex
A technology of photoelectric catalysis and experimental methods, applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete removal of phenolic pollutants, secondary pollution, slow process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] An experimental method for the photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A by a polypyridine ruthenium complex, the experimental method for degrading bisphenol A comprises the following steps:
[0037] S1. A three-electrode system is adopted: the working electrode is an indium tin oxide electrode, the counter electrode is a platinum electrode, the reference electrode is an Ag / AgCl electrode, and the electrolyte is a NaCl solution;
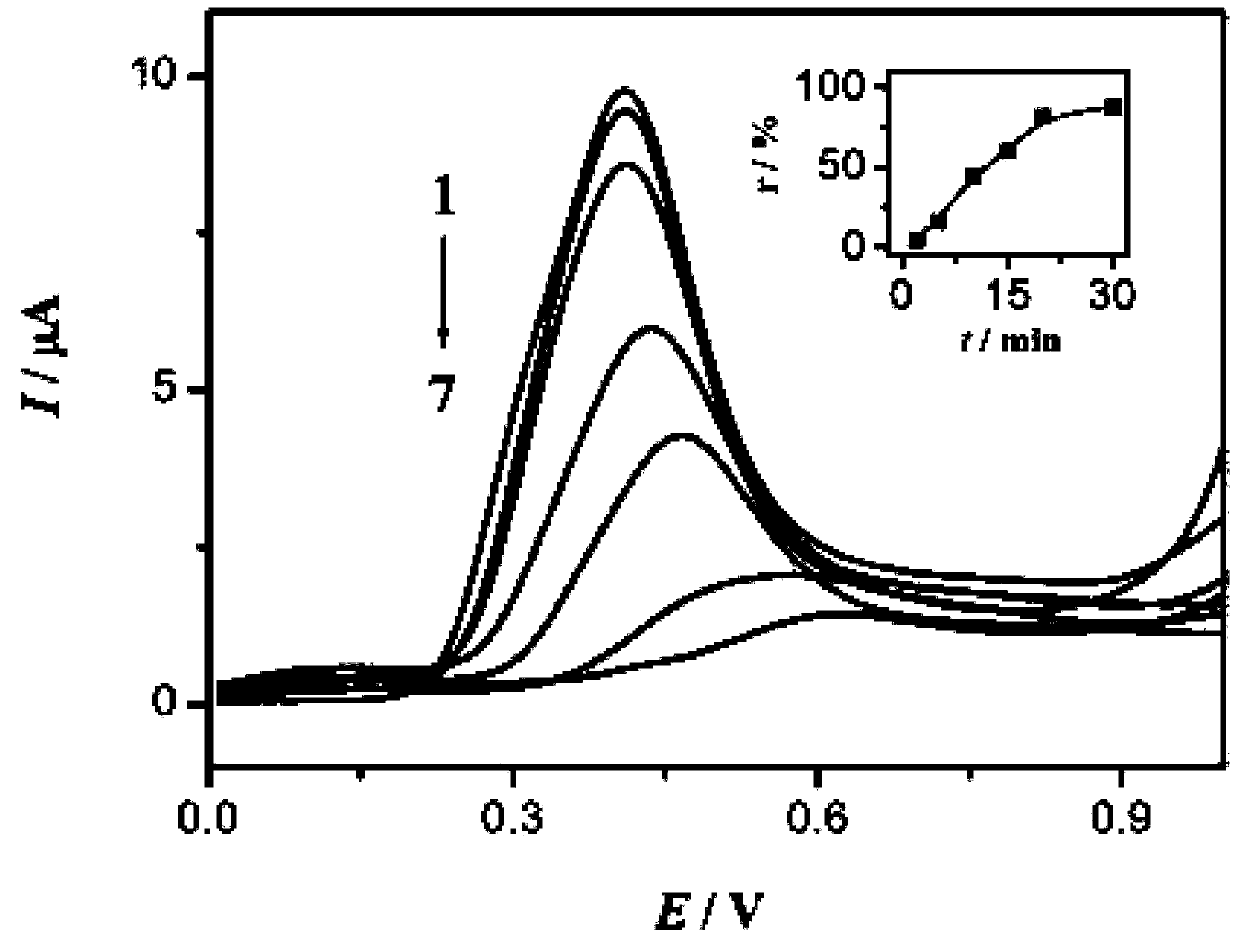
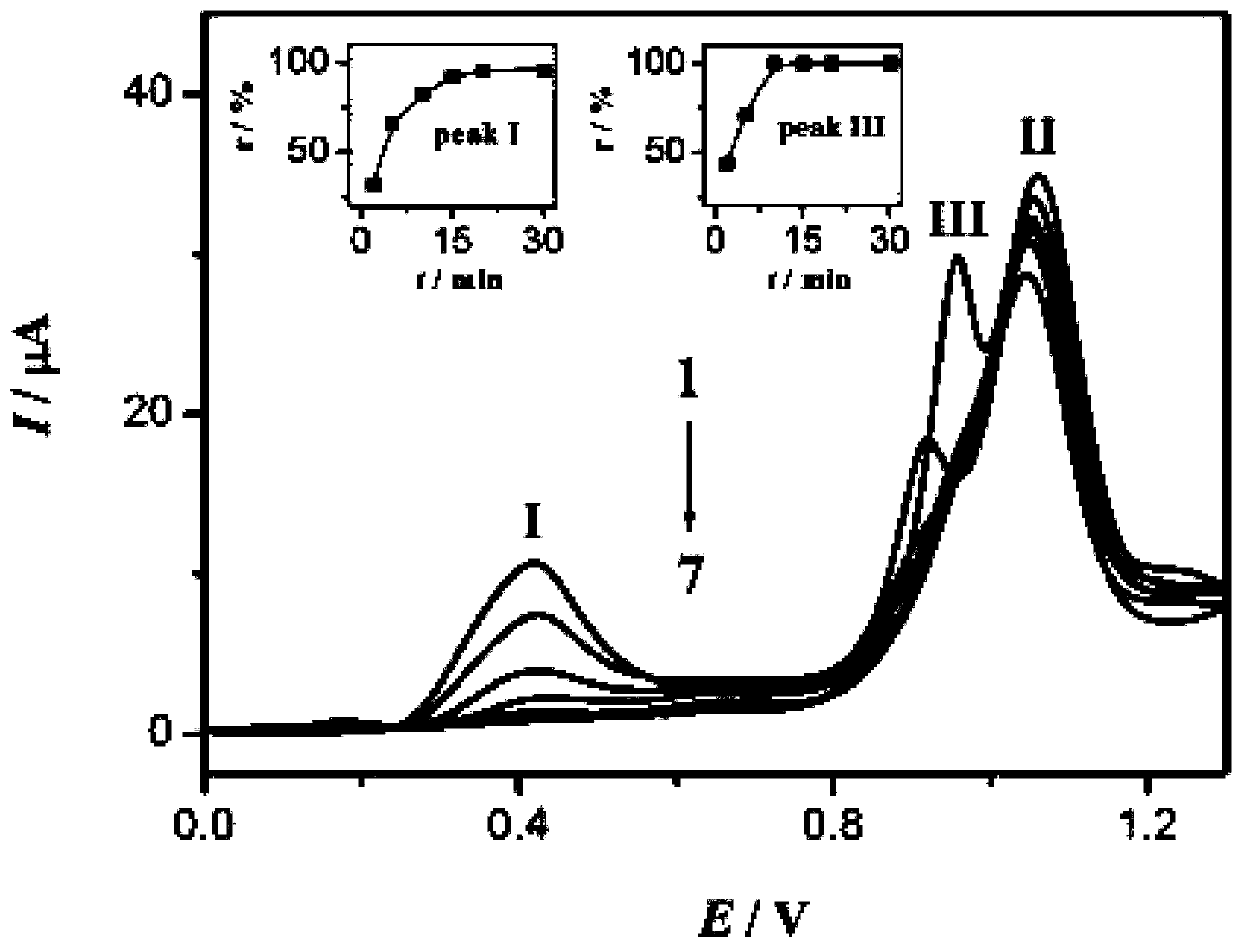
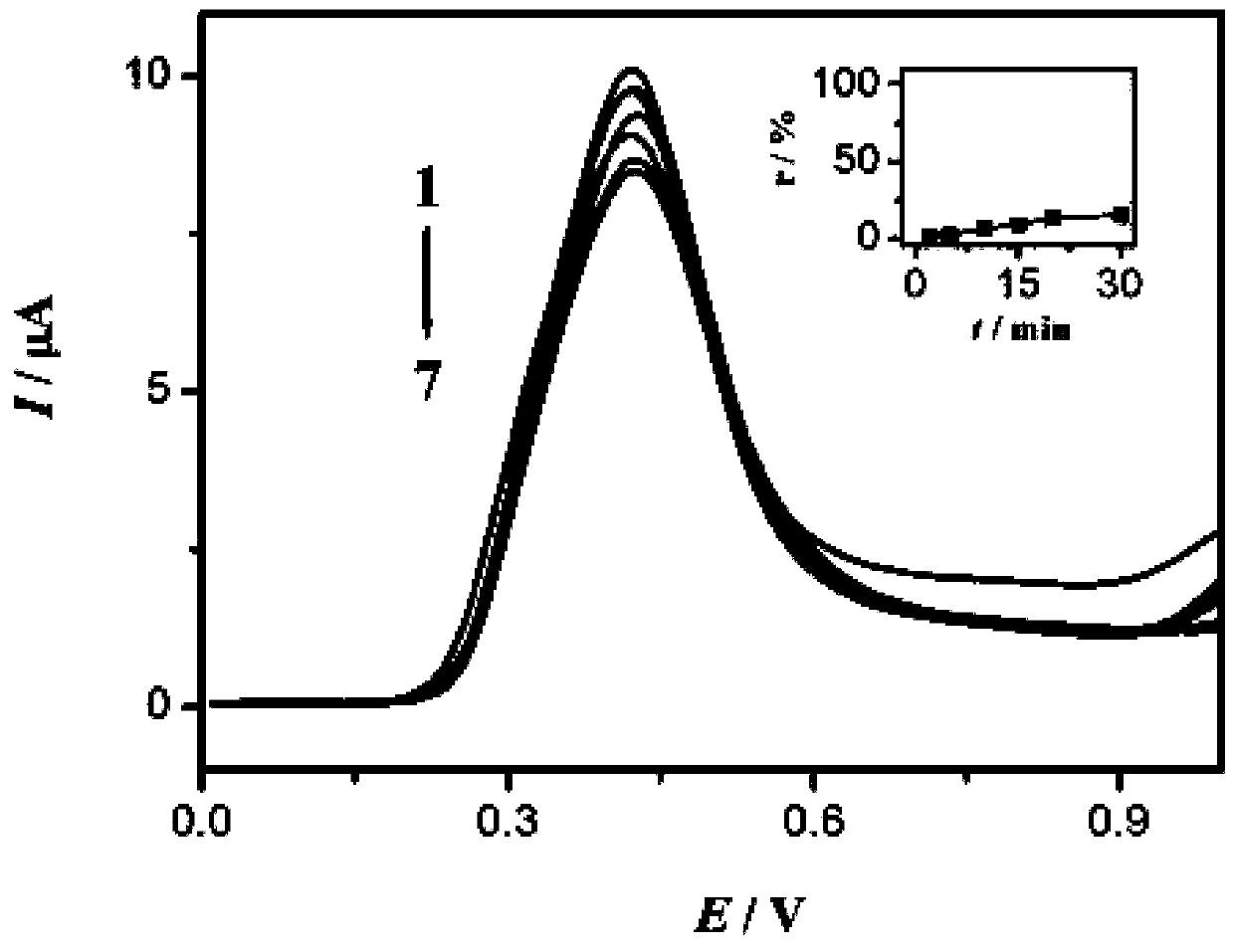
[0038] S2, add 0.5gL -1 TiO 2 / 0.1mMBPA system is irradiated with 365nm ultraviolet light for different times under the condition of oxygen saturation, and the solution obtained is placed in a three-electrode system for scanning and storage;
[0039] S3, add 0.1mM [Ru(bpy) 2 (tatp)] 2+ / 0.1mMBPA system is irradiated with 365nm ultraviolet light for different times under the condition of oxygen saturation, and the solution obtained is placed in a three-electrode system for scanning and storage;
[0040] S4, put BPA in 0.5gL -1 TiO 2 Under ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] According to embodiment 1, with [Ru(bpy) 2 (tatp)] 2+ / TiO 2 As the photoanode, the Ag / AgCl electrode as the cathode, and BPA as the fuel, the fuel cell was assembled under the condition of 8W ultraviolet light irradiation. Figure 7 It can be seen that using [Ru(bpy) 2 (tatp)] 2+ Sensitized TiO 2 The voltage of the battery as the anode in the dark room is -0.040V, and it shifts negatively to -0.468V under the excitation of ultraviolet light, indicating that the light excitation can generate more excited states of Ru(II) complexes, and these excited states can transfer electrons to Inject TiO 2 As a result, the voltage of the battery is shifted negatively. When the resistance is changed from 2000 to 30000Ω, the current and output power of the battery under the excitation of ultraviolet light are as follows: Figure 8 Shown, the fuel cell [Ru(bpy) 2 (tatp)] 2+ Sensitized TiO 2 As photoanode, Ag / AgCl reference electrode as photocathode, when 0.1mMBPA is used as f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com