Benzoxazine resin based on apigenin biology base and preparation method thereof
A technology of oxazine resin and apigenin, applied in the field of apigenin-based bio-based benzoxazine resin and preparation thereof, can solve problems such as difficulty in forming a dense cross-linked network structure, poor thermal stability, and increased processing difficulty , to achieve the effect of being suitable for large-scale production, improving cross-linking density, and low equipment requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Use 2-furylmethylamine as the amine source; add 2.70g (0.01mol) of apigenin, 1.94g (0.02mol) of 2-furylmethylamine, 1.32g (0.044mol) of paraformaldehyde into the flask, and then add 50mL of toluene solution , connected to a condenser, stirred at 110°C and reacted for 8 hours; after the reaction was stopped, the reaction solution was washed with water, and the organic solvent was removed by rotary evaporation, and dried in a vacuum oven at 50°C for one day to obtain 4.30g of benzoxazine monomer. Yield 84%. The chemical reaction equation is as follows:
[0032]
[0033] In the present embodiment, the obtained oxazine product structure is:
[0034]
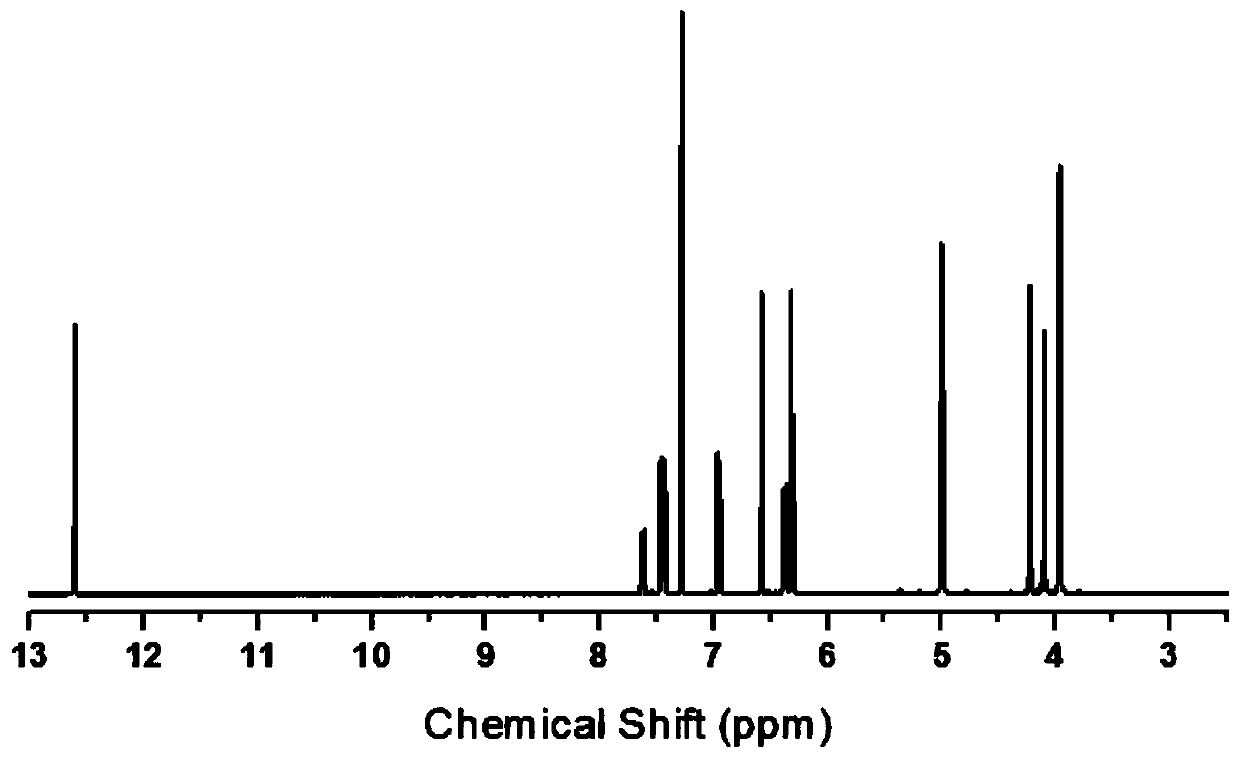
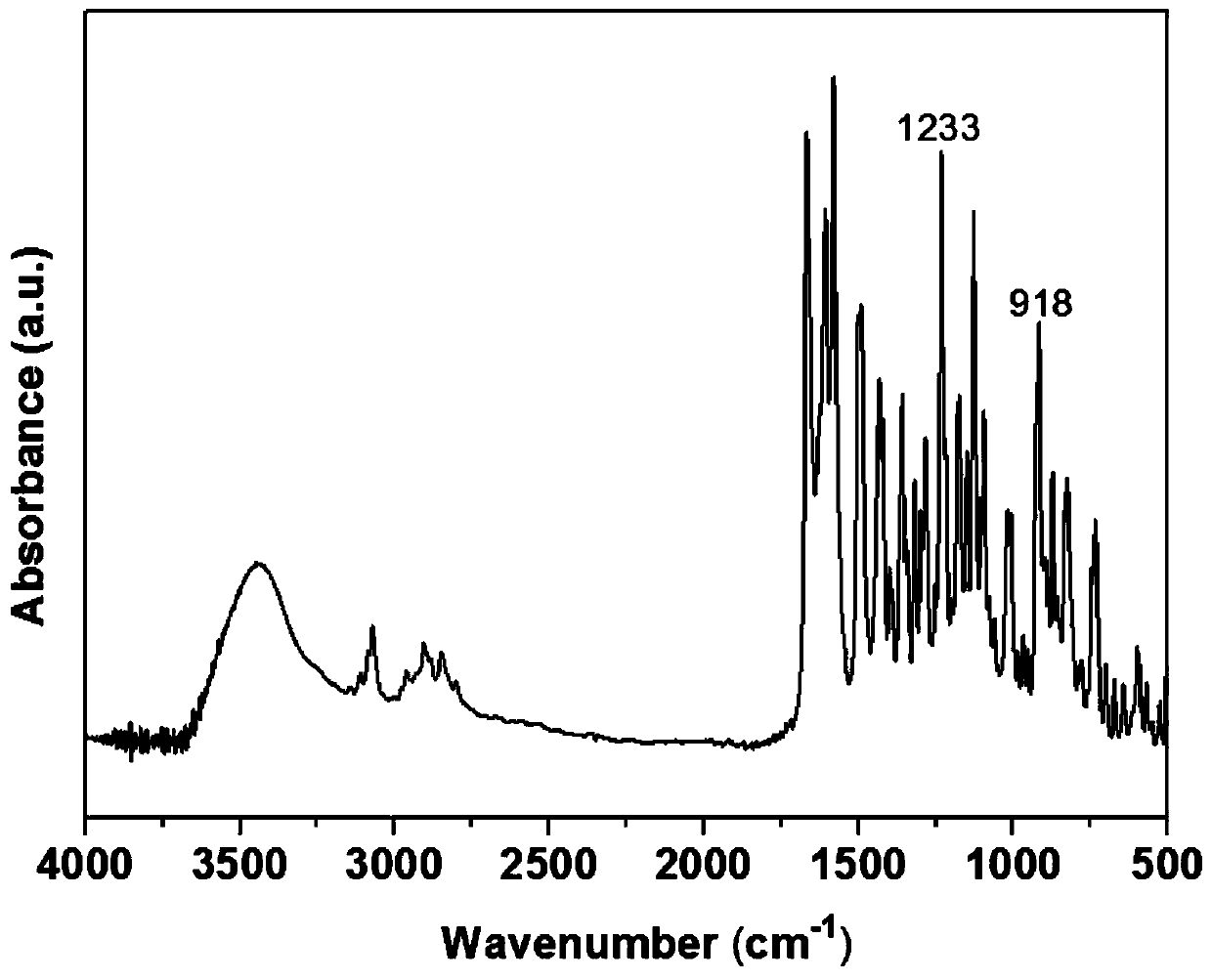
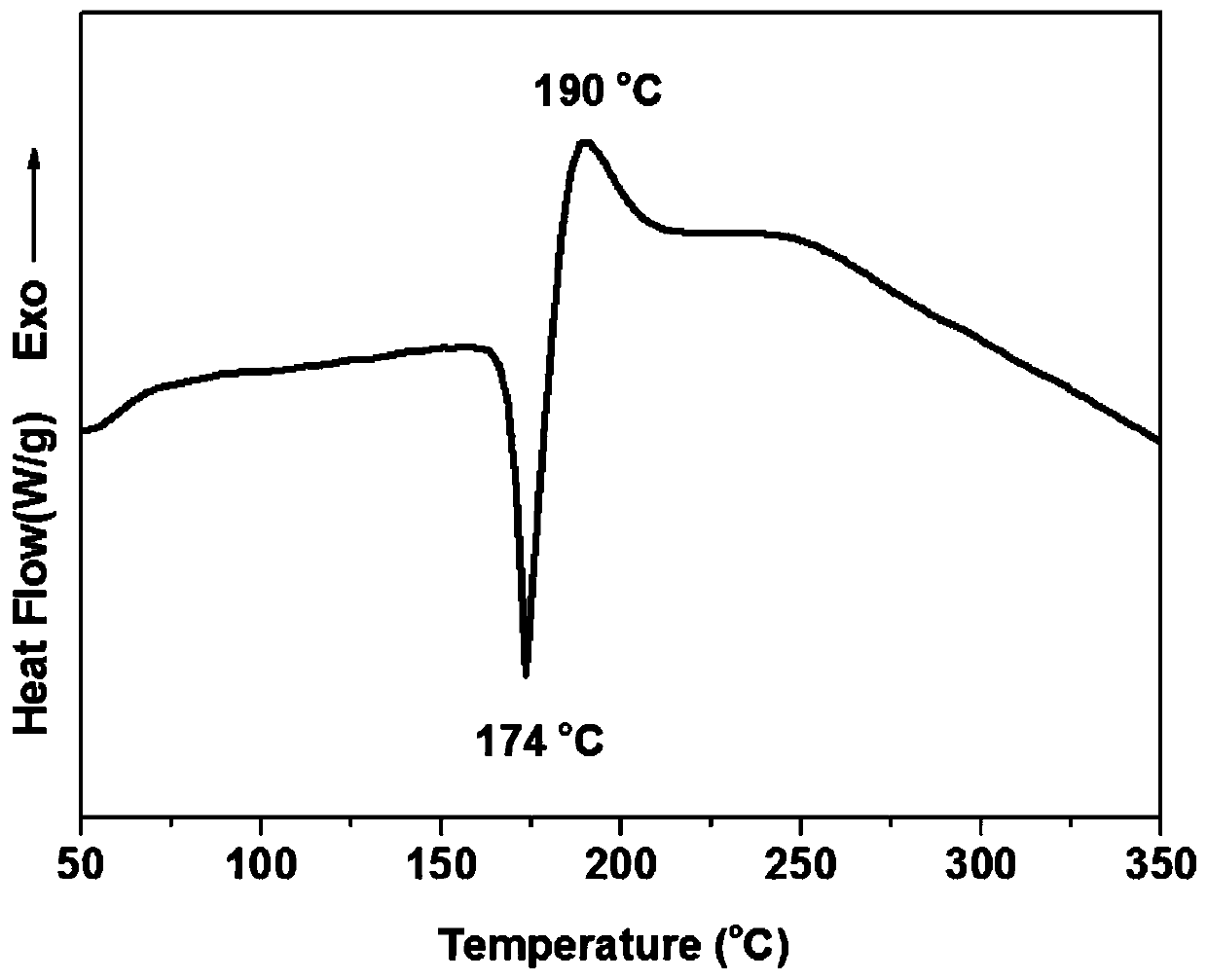
[0035] The product's proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum, Fourier transform infrared transform spectrum, DSC curve and thermogravimetric curve are as follows figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 with Figure 4 shown.
[0036] figure 1 It is a hydrogen nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum, and it can be seen from ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The amine source compound 2-furylmethylamine in Example 1 was replaced by aniline. Other steps are the same as those in Example 1.
[0042] Wherein the specific chemical structural formula of aniline is: The amount of reactants was changed to: weigh 2.70 g (0.01 mol) of apigenin, 1.86 g (0.02 mol) of aniline, and 1.32 g (0.044 mol) of paraformaldehyde, with a yield of 88%.
[0043]
[0044] The curing exothermic peak temperature of the latent curing type benzoxazine resin monomer obtained in this example is 168°C. After further curing and crosslinking, the temperature of the polybenzoxazine resin is 372°C when the thermal weight loss is 5%. At 800°C, the carbon residue rate is 65%.
Embodiment 3
[0046] The amine source compound 2-furylmethylamine in Example 1 was replaced by m-cyanoaniline. Other steps are the same as those in Example 1.
[0047] The specific chemical structural formula of the middle-cyanoaniline is The amount of reactants was changed to: weigh 2.70 g (0.01 mol) of apigenin, 2.36 g (0.02 mol) of m-cyanoaniline, and 1.32 g (0.044 mol) of paraformaldehyde. Yield 80%.
[0048]
[0049] The curing exothermic peak temperature of the latent curing type benzoxazine resin monomer obtained in this example is 195°C. After further curing and crosslinking, the temperature of the polybenzoxazine resin is 386°C when the thermal weight loss is 5%. At 800°C, the carbon residue rate is 66%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| carbon residual rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com