Method for analyzing and testing urea content in raw milk
A technology for urea content, analysis and testing, applied in the field of raw milk testing, can solve problems such as cumbersome operation and long time-consuming, and achieve the effects of simple testing operation, low environmental requirements, and low testing cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
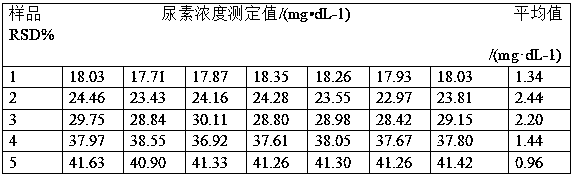
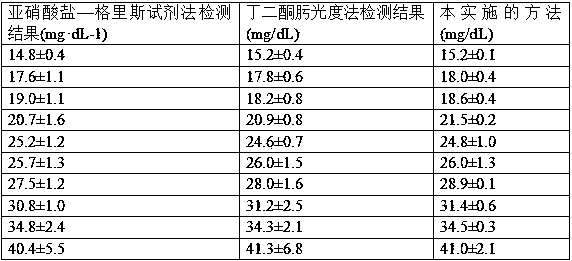
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Embodiment 1 This embodiment is carried out according to the following steps:
[0014] (1) Preparation of reaction reagents: Weigh 10.0 g of potassium hydrogen sulfate, dissolve it in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly; weigh 1.0 g of p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, dissolve it in acetone and dilute to 100 mL, mix Uniform; Weigh 0.1 g of potassium sodium tartrate, dissolve in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly; weigh 0.1 g ascorbic acid, dissolve in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly.
[0015] (2) Production and use of test paper: Soak medium-thickness acid-resistant absorbent paper in the 10% potassium bisulfate solution prepared in step (1) for 10 minutes, heat and dry in a drying oven at 65°C after completely soaking, and dry it for 20 minutes. Take it out after 10 minutes, and immediately soak the taken out absorbent paper in 1% p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution for 20 minutes, then place it in a drying oven at 65°C...
Embodiment 2
[0016] Embodiment 2 This implementation mode is carried out according to the following steps:
[0017] (1) Preparation of reaction reagents: Weigh 10.0 g of potassium bisulfate, dissolve it in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly; weigh 2.0 g of p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, dissolve it in acetone and dilute to 100 mL, mix Uniform; Weigh 0.1 g of potassium sodium tartrate, dissolve in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly; weigh 0.1 g ascorbic acid, dissolve in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly.
[0018] (2) Production and use of test paper: Soak medium-thickness acid-resistant water-absorbing paper in the 10% potassium bisulfate solution prepared in step (1) for 10 minutes, heat and dry in a drying oven at 65°C after fully soaking, Take it out after 10 minutes, then immediately immerse the taken out absorbent paper in 2% p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution for 20 minutes, place it in a drying oven at 65°C, and take it out after 1...
Embodiment 3
[0019] Embodiment 3 This implementation mode is carried out according to the following steps:
[0020] (1) Preparation of reaction reagents: Weigh 10.0 g of potassium hydrogen sulfate, dissolve it in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly; weigh 1.0 g of p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, dissolve it in acetone and dilute to 100 mL, mix Uniform; Weigh 0.1 g of potassium sodium tartrate, dissolve in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly; weigh 0.1 g ascorbic acid, dissolve in deionized water and dilute to 100 mL and mix evenly.
[0021] (2) Production and use of test paper: Soak medium-thickness acid-resistant absorbent paper in the 10% potassium bisulfate solution prepared in step (1) for 10 minutes, heat and dry in a drying oven at 65°C after completely soaking, and dry it for 20 minutes. Take it out after 10 minutes, and immediately soak the taken out absorbent paper in 1% p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde solution for 20 minutes, then place it in a drying ove...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com