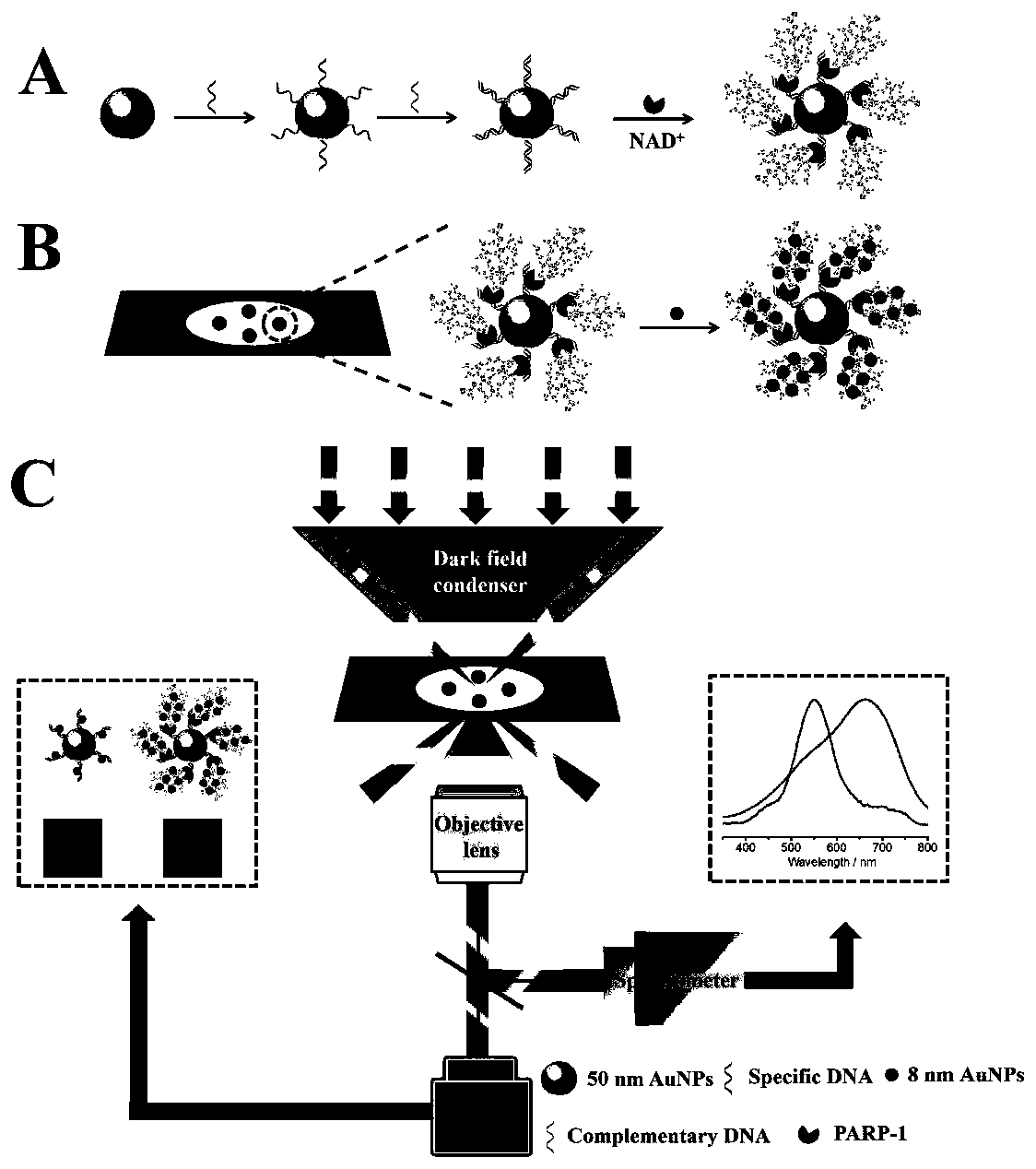
PARP-1 single particle detection method based on dark field scattering imaging
A PARP-1, scattering imaging technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of complex operation, long experimental process, and inability to detect PARP-1 activity, etc., and achieve the effect of high detection sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Embodiment 1 diameter is the gold nanoparticle (Au 50 )Synthesis
[0060] First, gold nanoparticles (Au 13 ): Trisodium citrate solution (38.8mM, 5mL) was quickly added to stirring and boiling chloroauric acid solution (1mM, 50mL), the color of the mixed solution changed from yellow to colorless within 2min, and then turned into black and purple , finally turned into wine red, continue to stir and keep boiling for 15 minutes, after naturally cooling to room temperature, store in a 4°C refrigerator for later use;
[0061] Secondly, gold nanoparticles (Au 50 ): Mix 25mL ultrapure water, 1mL freshly prepared Au 13 , NH 2 OH·HCl solution (0.2M, 360 μL) and polyvinylpyrrolidone solution (PVP, 1% w / v, 300 μL) were sequentially added to a 50 mL round bottom flask, and then 8 mL of 0.1 wt% chloroauric acid was added dropwise to the above mixture at room temperature solution and vigorously stirred for 30min, and left at room temperature for 30min after the stirring was stoppe...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2 diameter is the electropositive gold nanoparticle (Au 8 )Synthesis
[0064] First, chloroauric acid solution (1mM, 15mL) and CTAB (10mM, 2mL) were continuously stirred at room temperature for 15min; secondly, NaBH 4 (10mM, 2mL), the color of the solution changed from saffron yellow to orange red, and did not change within 15min, indicating that Au 8 , the obtained Au 8 Store in a brown glass bottle and store in a refrigerator at 4°C until use.
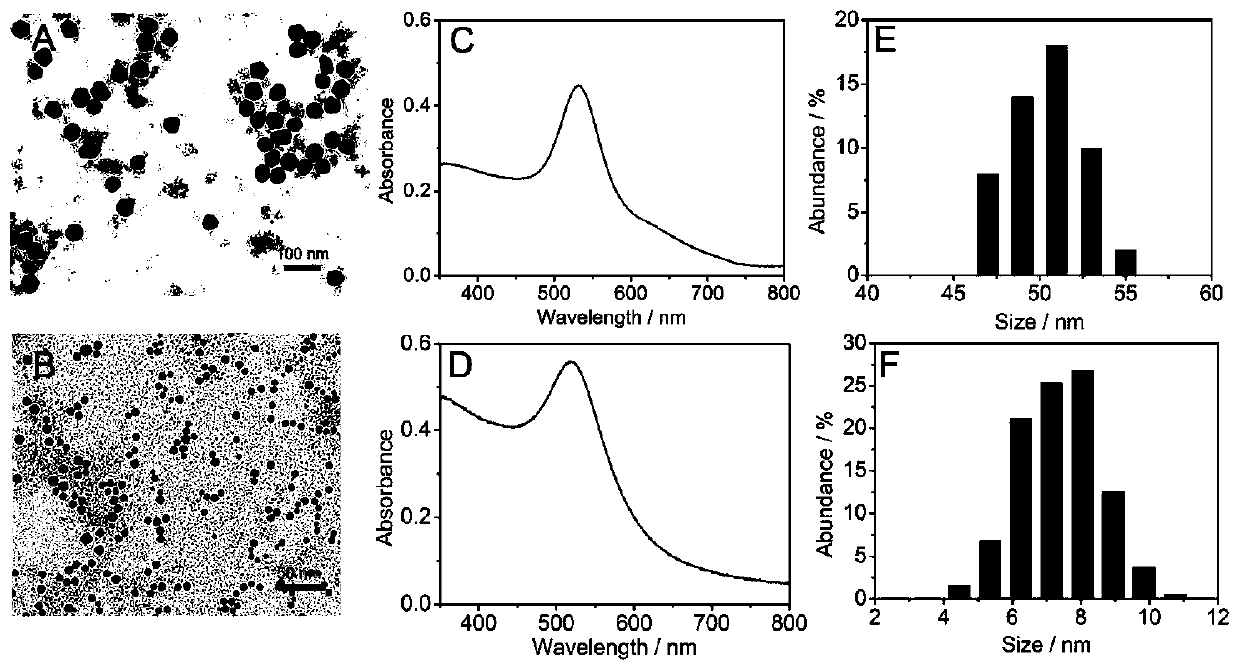
[0065] figure 2 Au is shown 8 sign of figure 2 B is Au 8 The TEM image is a uniform spherical shape with good monodispersity in solution; figure 2 D is Au 8 UV-Vis spectrum, the peak is concentrated at 518nm; figure 2 F is Au 8 The particle size distribution data, mainly distributed in 8nm. The above results indicate the successful synthesis of Au 8 .
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 Principle Verification of Poly ADP-ribose Polymerase-1 Single Particle Detection Method Based on Dark Field Scattering Imaging
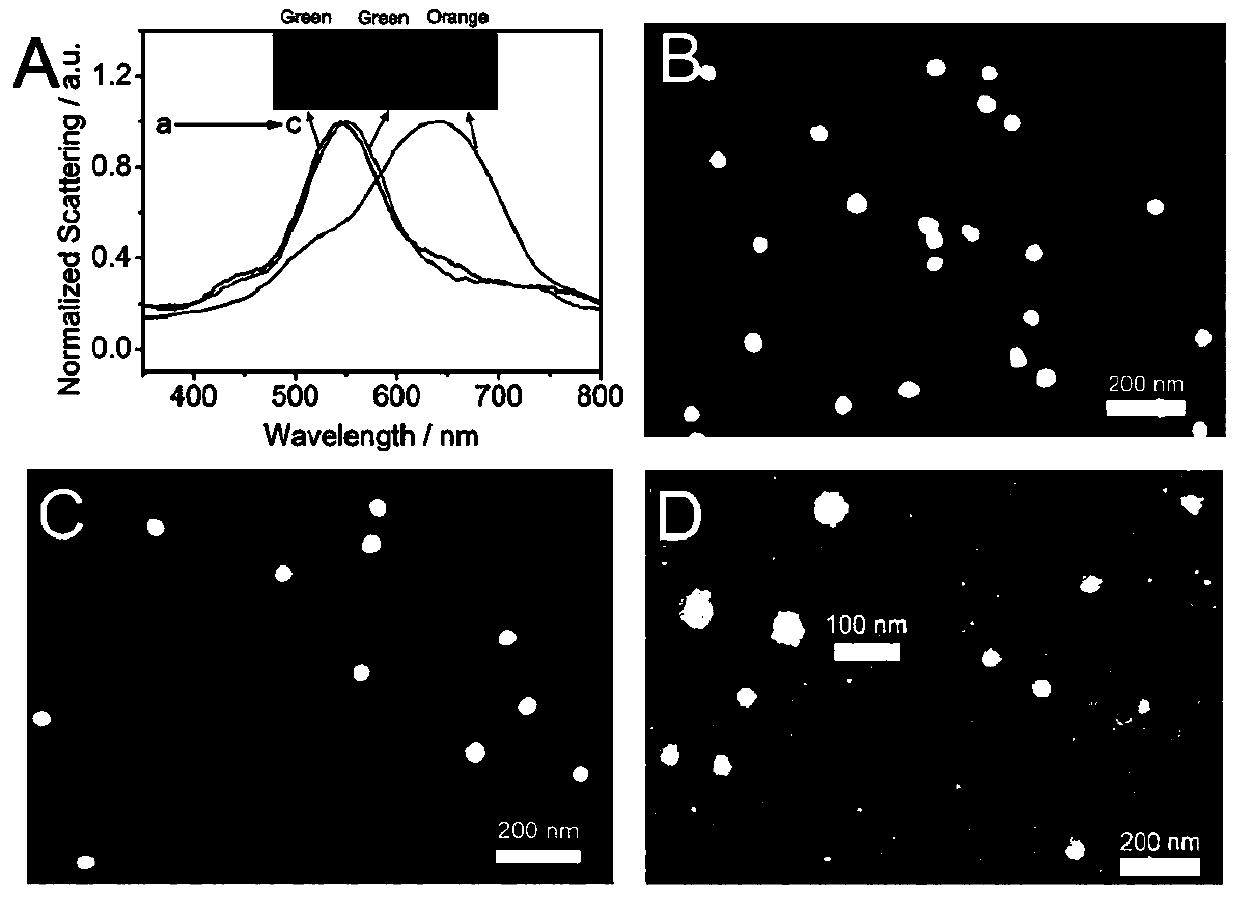
[0067] First, modify the two active DNA strands (s-DNA and c-DNA, see Table 1 for the sequence) to the Au prepared in Example 1 50 Au formed on the surface 50 -dsDNA, then add PARP-1, PARP-1 is Au 50 Active dsDNA on the surface activates the NAD + Cleavage into nicotinamide and ADP ribose, these units are linked to PARP-1 through covalent bonding and polymerized to form hyperbranched poly ADP ribose polymer (PAR), then in order to avoid agglomeration during the adsorption process, Au 50 -dsDNA@PAR is coated on the amino-functionalized glass for electrostatic adsorption for 5 minutes, the unadsorbed liquid is sucked away, and then Au is added 8 to form Au 50 -dsDNA@PAR@Au 8 . Compared with ds-DNA, PAR has more negative charges and can adsorb more Au 8 , so that Au 50 The scattering peaks were significantly red-shifted and exhi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com