Hydrogel encapsulated bacterial spore self-repairing material with pH responsiveness and cement-based concrete self-repairing method
A technology of self-healing materials and bacterial spores, which is applied in the field of cement-based concrete self-repairing and hydrogel-encapsulated bacterial spore self-repairing materials, which can solve problems such as the influence of cement strength, the effect of cement self-healing results, and the destruction of bacterial spores
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] 1. Materials
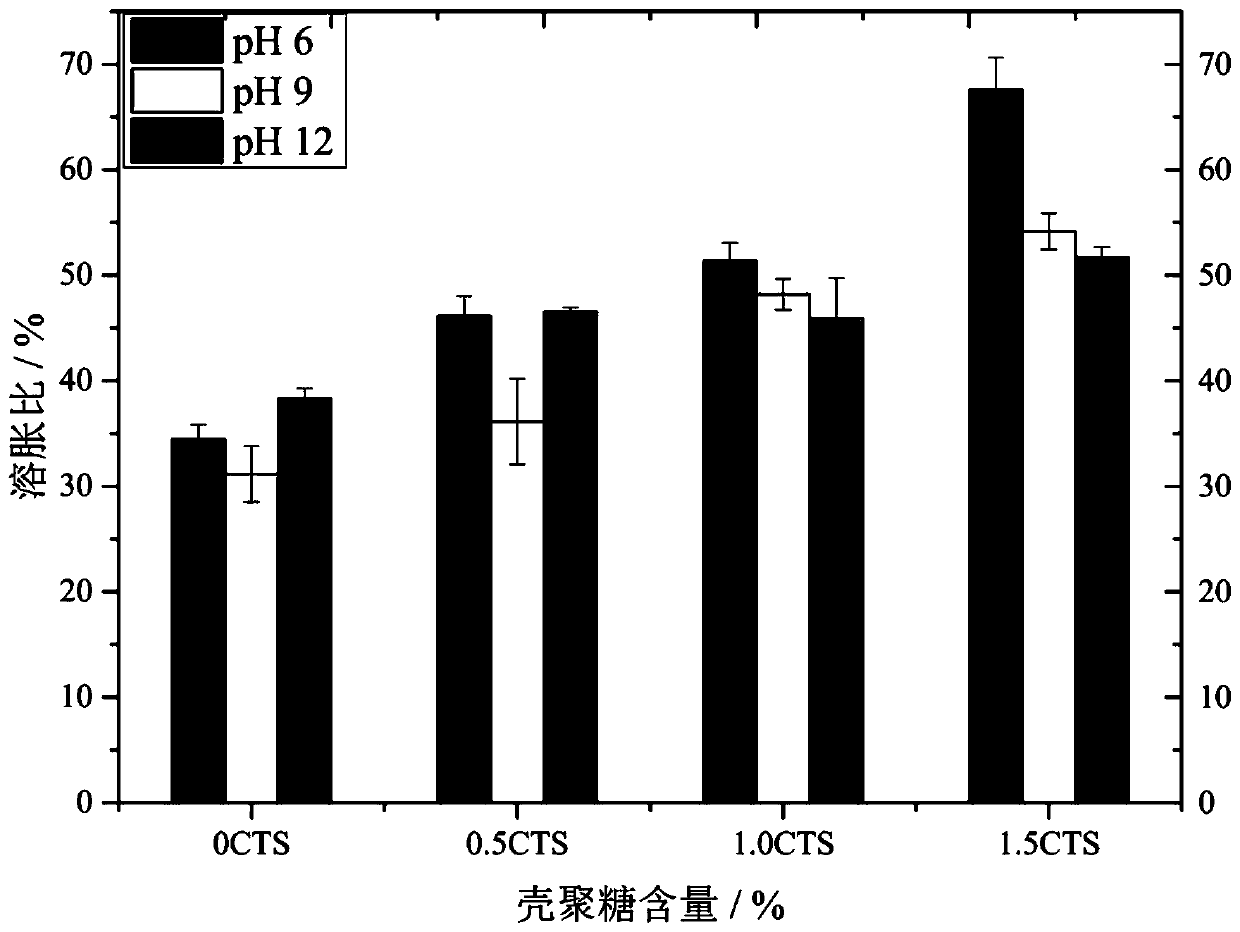
[0067] The bacterial encapsulation materials used in this example are alginate, chitosan, calcium source and aluminum source. The calcium source is composed of calcium chloride and calcium nitrate in a molar ratio of 3:1. The aluminum source is composed of aluminum chloride and aluminum sulfate in a molar ratio of 5:1. The molar ratio of the calcium source (calcium ion) to the aluminum source (aluminum ion) is 6:1. Chitosan calcium alginate hydrogel was used to encapsulate bacterial spores and used for self-healing of cement. Under the condition of external aqueous solution infiltrated into cement cracks, the hydrogel expanded by absorbing water to stimulate the recovery of spores to achieve self-healing. The dosage of hydrogel is 3-5g / 100g cement, and the number of spores contained in each gram of dry hydrogel is 1.0×10 7 ~9.8×10 7 indivual.
[0068] 2. Preparation
[0069] Mix 50 mL of spores of Bacillus alkalophilus (3-7% (w / v), wet weight) with ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] 1. Materials
[0077] The bacterial encapsulation materials used in this example are alginate, polyvinylpyrrolidone and calcium source. The calcium source is composed of calcium chloride and calcium nitrate in a molar ratio of 3:1. The aluminum source is composed of aluminum chloride and aluminum sulfate in a molar ratio of 5:1. The molar ratio of the calcium source (calcium ion) to the aluminum source (aluminum ion) is 6:1. Polyvinylpyrrolidone calcium alginate hydrogel was used to encapsulate bacterial spores and used for self-healing of cement. Under the condition of external aqueous solution infiltrated into cement cracks, the hydrogel expanded by absorbing water to stimulate the recovery of spores to achieve self-healing. The dosage of hydrogel is 3-5g / 100g cement, and the number of spores contained in each gram of dry hydrogel is 1.0×10 7 ~9.8×10 7 indivual.
[0078] 2. Preparation
[0079] Mix 50ml of spores of Bacillus alkalophilus (3-7% (w / v), wet weight)...
Embodiment 3
[0084]1. Materials
[0085] The bacterial encapsulation materials used in this example are polyaspartate, chitosan and calcium source. The calcium source is composed of calcium lactate and calcium acetate in a molar ratio of 3:1. The aluminum source is aluminum chloride. The molar ratio of the calcium source (calcium ion) to the aluminum source (aluminum ion) is 6:1. Chitosan polycalcium aspartate hydrogel was used to encapsulate bacterial spores and used for cement self-healing. Under the condition of external aqueous solution infiltrated into cement cracks, the hydrogel expanded by absorbing water to stimulate the recovery of spores to achieve self-healing. The dosage of hydrogel is 3-5 / 100g cement, and the number of spores contained in each gram of dry hydrogel is 1.0×10 7 ~9.8×10 7 indivual.
[0086] 2. Preparation
[0087] Mix 50ml of alkalophilic Bacillus spores (3-7% (w / v), wet weight) with 350ml of 1.0-9.0% (w / v) polyaspartate solution, and stir evenly. Add the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com