Ultra-low-speed high-precision positioning control method of frameless torque motor
A torque motor and positioning control technology, which is applied in motor generator control, AC motor control, electronic commutation motor control, etc., can solve the problems of unable to suppress torque ripple, large flux compensation error, and large computational complexity. Achieve the effect of large self-disturbance rejection moment, small calculation amount and high positioning accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
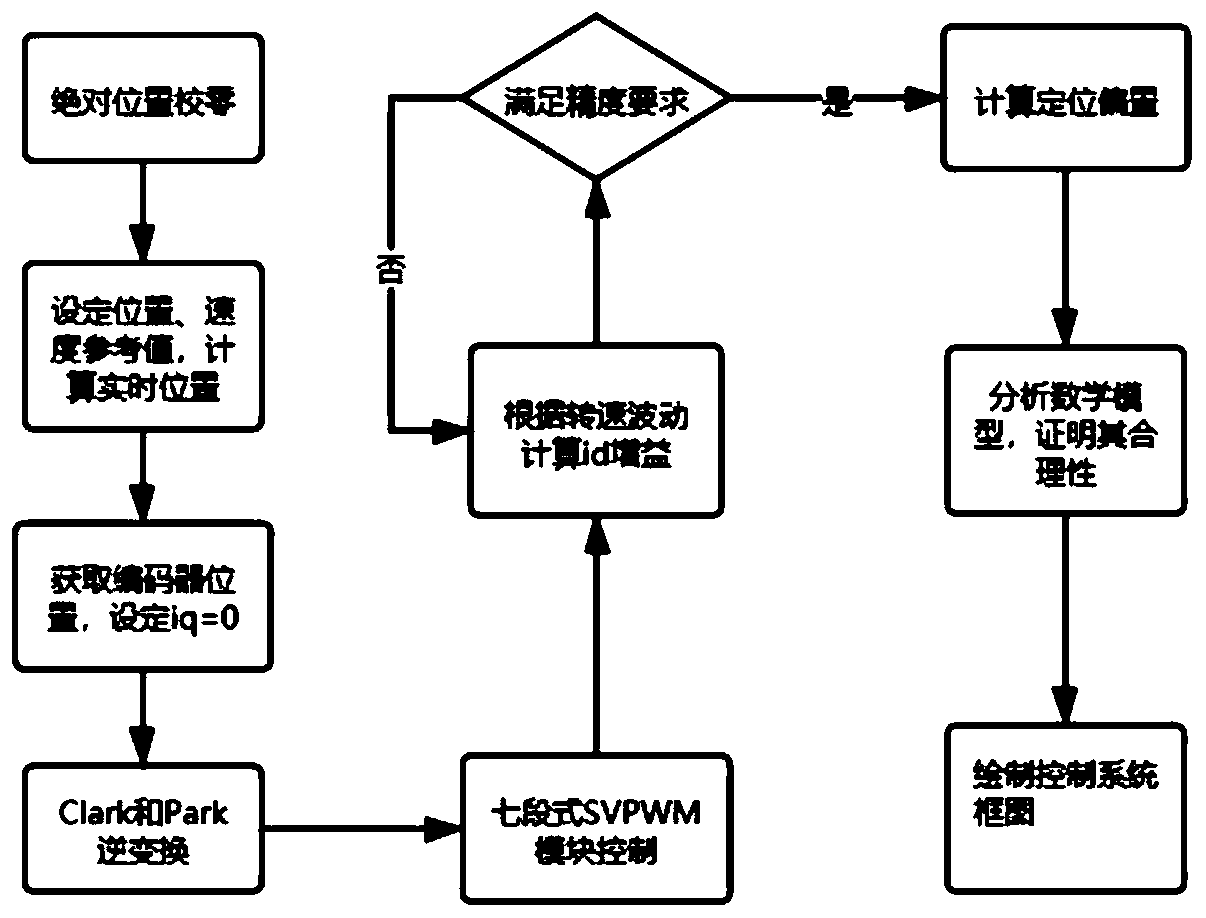
[0057] see Figure 1 to Figure 9 , an ultra-low-speed high-precision positioning control method for a frameless torque motor, mainly comprising the following steps:
[0058] 1) Connect the encoder coaxially with the motor rotor, and adjust the absolute position of the motor to zero.
[0059] The absolute position of the motor is zero calibration time t 0 The encoder angle read when the inner motor rotates to a position where the electrical angle is 0°.
[0060] 2) Set the reference value θ of the target position of the motor rotation tar and the reference value of rotation speed x tar , and calculate the mechanical angle θ the motor should rotate m , the electrical angle θ that should be rotated e , Motor real-time position θ real and motor real-time speed ω r .
[0061] The mechanical angle θ that the motor should rotate at the current moment t m and electrical angle θ e As follows:
[0062]
[0063] In the formula, n is the number of pole pairs of the motor.
...
Embodiment 2
[0109] An ultra-low-speed and high-precision positioning control method for a frameless torque motor, mainly comprising the following steps:
[0110] 1) Connect the encoder coaxially with the motor rotor, and adjust the absolute position of the motor to zero.
[0111] 2) Set the reference value θ of the target position of the motor rotation tar and the reference value of rotation speed x tar , and calculate the mechanical angle θ the motor should rotate m , the electrical angle θ that should be rotated e , Motor real-time position θ real and motor real-time speed ω r .
[0112] 3) Given the excitation current i of the motor d , and maintain the torque current i q =0. Through the coordinate inverse conversion and the seven-segment voltage space vector PWM control module, the switch state changes of the three sets of bridge arms of the inverter are controlled to form a vector rotating magnetic field, thereby adjusting the angle of the rotor to θ e .
[0113] 4) Accordi...
Embodiment 3
[0115] An ultra-low-speed and high-precision positioning control method for a frameless torque motor, the main steps of which are shown in Embodiment 2, wherein the main steps of forming a vector rotating magnetic field are as follows:
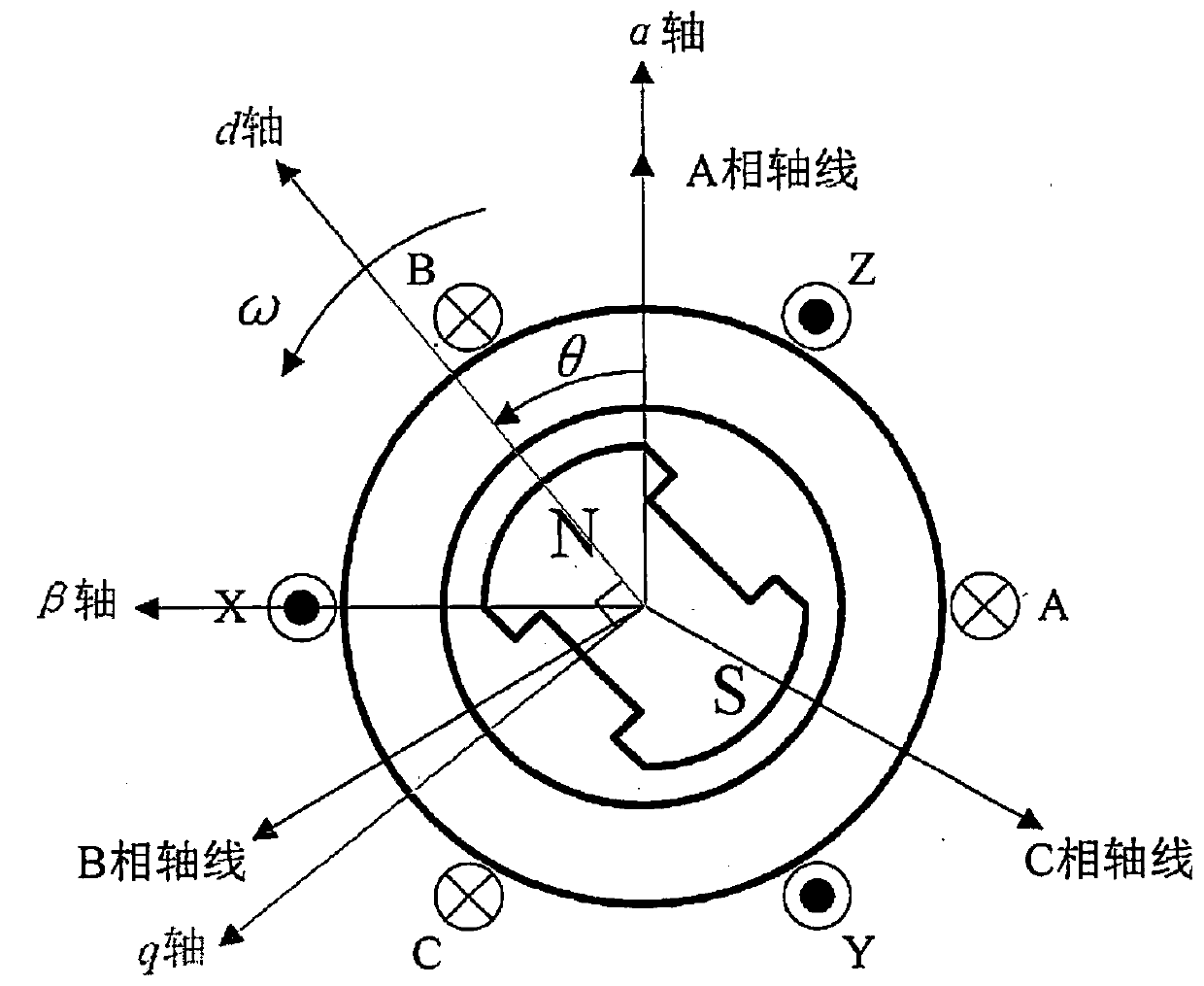
[0116] 3.1) Establish the three-phase coordinate system of the motor stator, where the axes of the motor stator windings are denoted as A, B and C respectively. There is an electrical angle difference of 120° between every two motor stator winding axes.
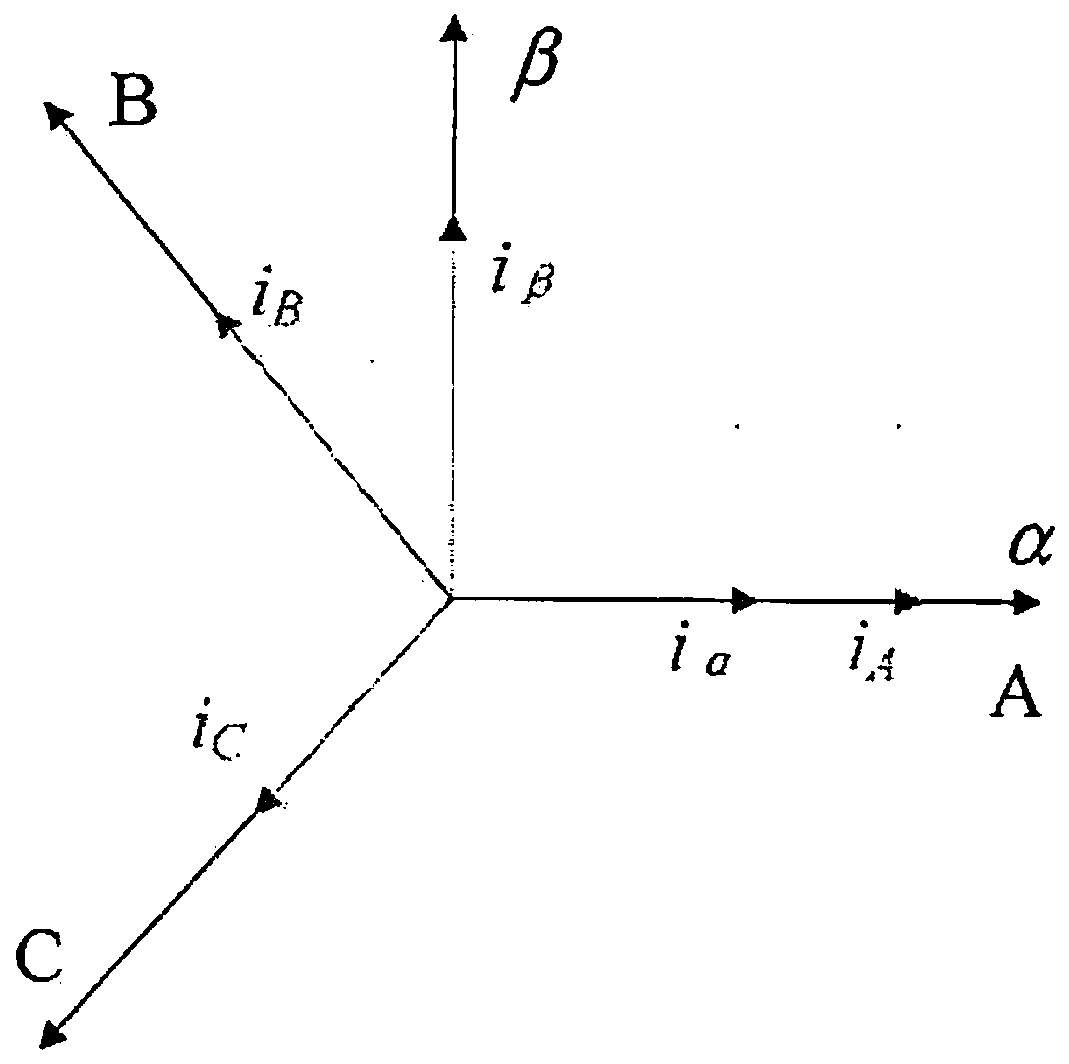
[0117] 3.2) Perform Clark transformation on the three-phase current in the three-phase coordinate system of the motor stator to obtain the two-phase current in the two-phase static coordinate system. Among them, the α-axis of the two-phase static coordinate system coincides with the A-axis of the three-phase coordinate system of the motor stator, and the β-axis leads the α-axis counterclockwise by 90° electrical angle.
[0118] The Clark transformation matrix and inverse transformation matri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com