Microscopic breeding method for aurelia aurita hydranth in laboratory
A polyp and laboratory technology, which is applied in the field of microscopic feeding of the hydra of the sea moon jellyfish in the laboratory, can solve the problem that the constant temperature control of the water tank does not meet the standard of experimental animal breeding, and the scientific research experiment of accurate quantitative polyp cannot be carried out. , large water body in the breeding tank, etc., to achieve the effects of easy promotion, saving experimental costs, and fast reproduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 6
[0035] The feeding of the moon jellyfish polyp in the six-hole cell culture plate of embodiment 1
[0036] 1. Preparation of artificial seawater suitable for the survival of the polyps of the moon jellyfish
[0037] Prepare artificial seawater with a theoretical salinity of 3.00% according to Table 1:
[0038] Table 1 Preparation table of artificial seawater (salinity is about 3.00%)
[0039]
[0040] After the configuration is complete, turn on the air pump and extend it into the prepared artificial seawater to pump air into the seawater. After 2 hours, take out the air pump. Use a salinity meter to measure the salinity between 2.8 and 3.2 (about 3.00%), add seawater or distilled water appropriately according to the salinity, let it settle for 5 minutes, and take the supernatant for use.
[0041] 2. Preparation of the bait for the polyp of the sea moon jellyfish (brine shrimp Artemia)
[0042] Pour the prepared 1L of artificial seawater and appropriate amount of brine s...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The raising of jellyfish polyp in embodiment 2 petri dish
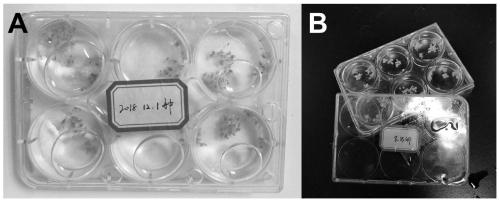
[0065] The difference between this embodiment 2 and embodiment 1 is only in step 3. After the impurities attached to the polyp are removed, the cleaned polyp is sucked into a clean beaker equipped with artificial seawater, and it is left to stand for 30 minutes. To restore the state, select the polyps with stretched tentacles and good vitality and put them into a petri dish filled with artificial seawater. There are 20 to 30 polyps in each culture plate, with the feet down and the tentacles up or sideways. Put the lid on, and put a label on the lid to record the date of planting, such as image 3 As shown, A and B show the polyps of the jellyfish with different planting dates.
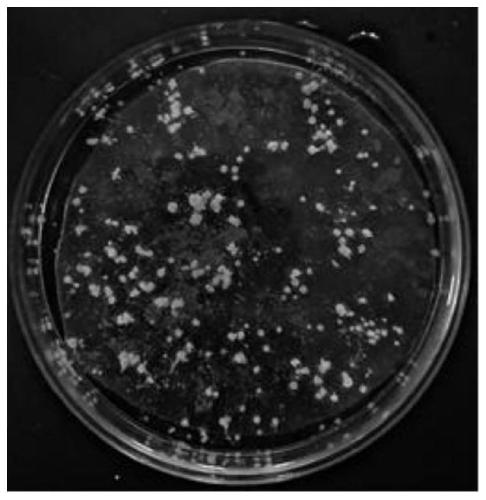
[0066] According to the comparison of the hydra of the jellyfish and the hydra of the jellyfish raised in the embodiment of the present invention 1 and 2 and the traditional feeding method Figure 4 shown, according to Figure 4 , th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com