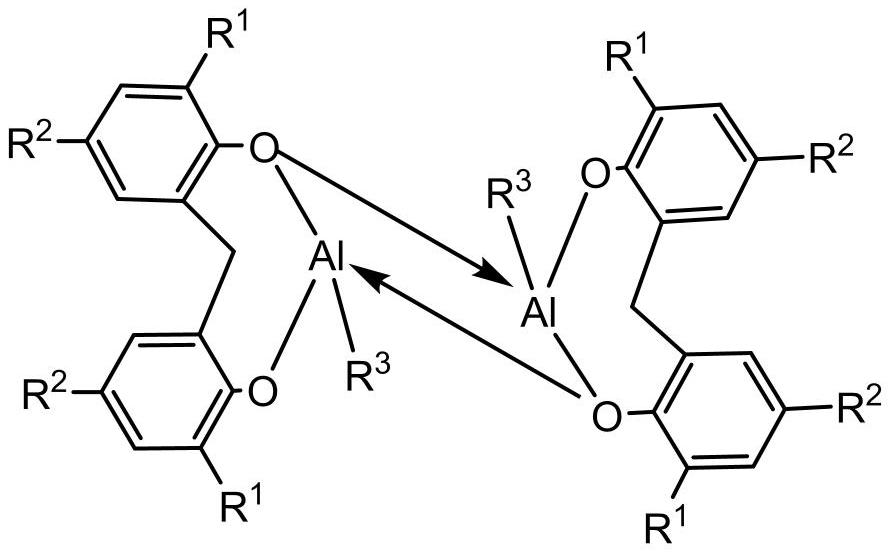
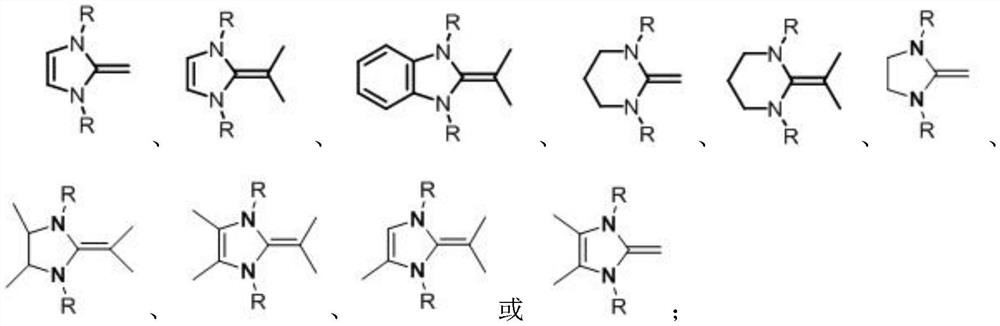
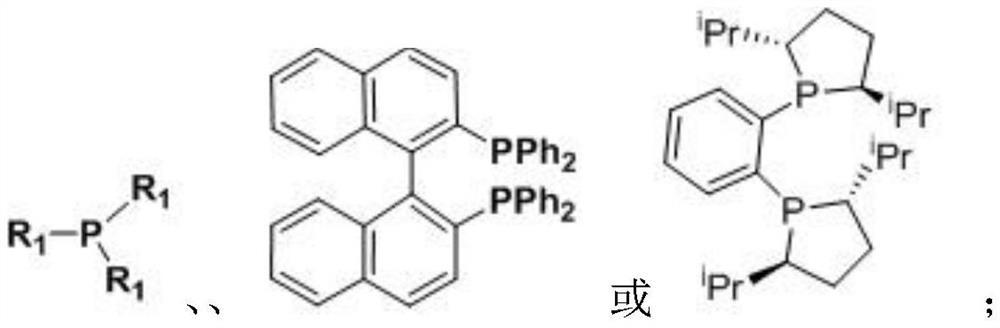
A method for the polymerization of vinyl monomers catalyzed by hindered Lewis acid-base pairs based on binuclear aluminum Lewis acids
A technology of Lewis acid-base pair and Lewis acid, which is applied in the field of polymer synthesis, can solve the problems that polymers cannot be obtained at the same time, monomers cannot be converted, and the initiation efficiency is low, so as to achieve narrow molecular weight distribution, improve catalytic activity, and low price Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] In the glove box, the indicated amount of Lewis acid ([Al(mbmp)Me] 2 ) specified amount of MMA, then add 2mL of toluene solution, stir evenly, then add specified amount of Lewis base ( iPr I m ) feeding is completed, the reaction begins timing, after the reaction, the Schlenk bottle is taken out from the glove box, and quenched by adding methanol solution containing 5% BHT, getting 0.2mL to measure its NMR in deuterated chloroform, then using the remaining liquid A large amount of methanol is extracted, the solid is taken out, dried in a vacuum oven at 40°C to constant weight, the conversion rate is calculated according to the NMR results, and the molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the obtained polymer are measured by gel permeation chromatography. The reaction conditions and test results are as follows:
[0043] Table 1 base ( iPr I m ) as a Lewis base obtained under different reaction conditions, the polymerization results are as follows
[004...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The reaction was carried out in a glove box, and 0.024 mmol of Lewis acid ([Al(mbmp)Me] 2 ), 2mL of toluene and 0.5mL (4.8mmol) of MMA, after stirring evenly, add 0.024mmol of Lewis base. Quenched with methanol solution, take 0.2mL in 0.4mL deuterated chloroform to measure its NMR, then extract the remaining liquid with a large amount of methanol, take out the solid, dry it in a vacuum oven at 40°C to constant weight, and calculate according to the NMR results Conversion rate, molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the obtained polymer were measured by gel permeation chromatography. The reaction conditions and test results are as follows:
[0047] Table 2 [Al(mbmp)Me] 2 Synergistic Catalysis of MMA Polymerization with Different Lewis Bases
[0048]
[0049] Through this group of experiments, it is proved that the initiation efficiency of the MMA monomer based on the binuclear aluminum Lewis acid and the adopted Lewis base is 100%. The superiority of ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The reaction was carried out in a glove box, and the designated Lewis acid ([Al(mbmp)Me] 2 ), 2mL of solvent and quantitative MMA, after stirring evenly, add Lewis base ( iPr I m ), the feeding was completed, and the reaction began to be timed. After the reaction, the schlenk bottle was taken out from the glove box, and the methanol solution containing 5% BHT was added to quench, and 0.2mL was measured in 0.4mL deuterated chloroform to measure its NMR, and then the remaining The liquid was extracted with a large amount of methanol, and the solid was taken out, dried in a vacuum oven at 40°C to constant weight, the conversion rate was calculated according to the NMR results, and the molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the obtained polymer were measured by gel permeation chromatography. The reaction conditions and test results are as follows:
[0052] Table 3 Polymerization of MMA in different solvents
[0053]
[0054] Through the above experiment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com