Application of gastrodin in the use of titanium metal in traditional Chinese medicine in diabetic environment
A technology of diabetes and gastrodin, applied in the fields of pharmaceutical formula, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as poor osseointegration of titanium metal implants, affect cell biological functions, oxidative stress damage, etc., and achieve enhanced osteogenic differentiation ability, increased proliferation level, and improved biological function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
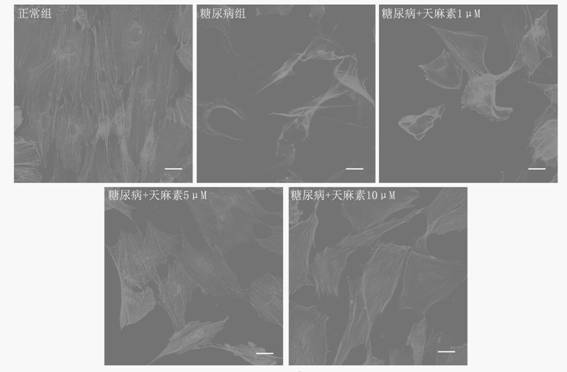
[0041] This example shows the application of gastrodin in the preparation of drugs for improving the adhesion function of osteoblasts at the "titanium-bone" interface in a diabetic environment, that is, the application of gastrodin in improving the adhesion state of osteoblasts on the titanium metal surface in a diabetic environment effect.
[0042] Experimental method: cutting and processing medical titanium metal into titanium sheets, grinding and polishing the surface, cleaning and disinfecting for later use. Use trypsin to isolate and culture the primary osteoblasts from the calvaria of SD rat suckling rats and pass them down, and press 1×10 4 Cells per milliliter were seeded on the surface of titanium metal with the same number to establish an in vitro "titanium-bone" interface model.
[0043] Divided into 5 groups:
[0044] 1) normal serum group (normal group);
[0045] 2) diabetes serogroup (diabetes group);
[0046] 3) Diabetes + gastrodin 1 μM;
[0047] 4) Diabet...
Embodiment 2
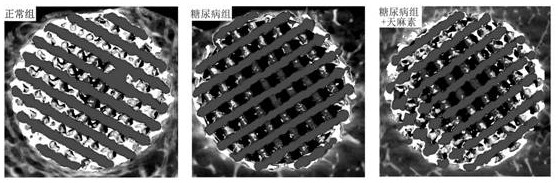
[0053] This example gives the application of gastrodin in the preparation of drugs that improve the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts at the "titanium-bone" interface in the diabetic environment, that is, the effect of gastrodin on the osteoblasts in the diabetic environment on the titanium metal surface is given. Improvement of proliferation ability and osteogenic differentiation level.
[0054] Experimental method: Osteoblasts were seeded on the surface of the titanium sheet for culture, and the grouping was the same as in Example 1. On the 4th and 7th days of culture, the cells on the surface of the titanium sheet were detected by MTT, and on the 7th day of culture, the cells on the surface of the titanium sheet were detected by ALP.
[0055] Result: if Figure 4 , Figure 5 As shown, compared with the normal control group, the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in diabetic patients were significantly inhibited, and after adding gastrodin to d...
Embodiment 3
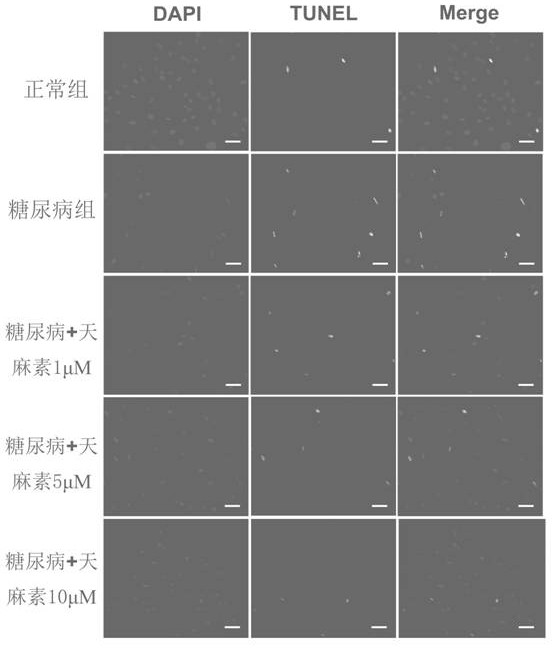
[0058] This example shows the application of gastrodin in the preparation of drugs for inhibiting the pathological apoptosis of osteoblasts at the "titanium-bone" interface in a diabetic environment, that is, it shows that gastrodin can reduce the apoptotic damage of osteoblasts on the titanium metal surface in a diabetic environment protective effect.
[0059] Experimental method: Osteoblasts were seeded on the surface of titanium metal for culture, and the grouping was the same as in Example 1. On the 7th day of culture, TUNEL and DAPI were used for double-labeled staining, and confocal microscope was used for observation; Caspase-3 kit was used to detect the activity of apoptosis pathway protein Caspase-3, and the effect of gastrodin on osteoblast apoptosis in diabetic environment was evaluated Impact.
[0060] result: Figure 6 The staining results of apoptotic cells in each group are shown, and the green image is the apoptotic cell nucleus marked by TUNEL. Figure 7 Fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com