Method for passivating activity of dissolved polyphenol oxidase and membrane-bound polyphenol oxidase
A polyphenol oxidase-membrane-binding technology, applied in the field of food processing, can solve the problems of non-enzymatic and enzymatic browning, product color, flavor, nutrition and other quality loss, achieve passivation activity, and be beneficial to the sensory quality of juice , to maintain the effect of juice flavor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0071] The specific method is as follows: select fresh fruit as a raw material, and process the fresh raw material according to the following method.
[0072] (1) Raw material pretreatment: Wash the fresh fruit and pre-cool it in a 4°C freezer, then cut it into pieces about 8-10cm long.
[0073] (2) Soaking treatment: soak the material obtained in step (2) in 10 mM ascorbic acid solution for 2 min.
[0074] (3) The first ultra-high pressure treatment passivation sPPO: the material obtained in step (2) was vacuum-packed and subjected to ultra-high pressure treatment. The pressure at room temperature was set to 350 MPa, and the pressure holding time was set to 10 minutes.
[0075] (4) Beating and filtering: add appropriate amount of edible water to the material obtained in step (3) to beat, the ratio of liquid to material is 1:2, and the time is 2 minutes. After filtering with 2 layers of 120-mesh gauze, put the juice into a sterile bottle. All the above operations were perform...
Embodiment 1
[0084] Embodiment 1, the influence of different inhibitors on PPO activity
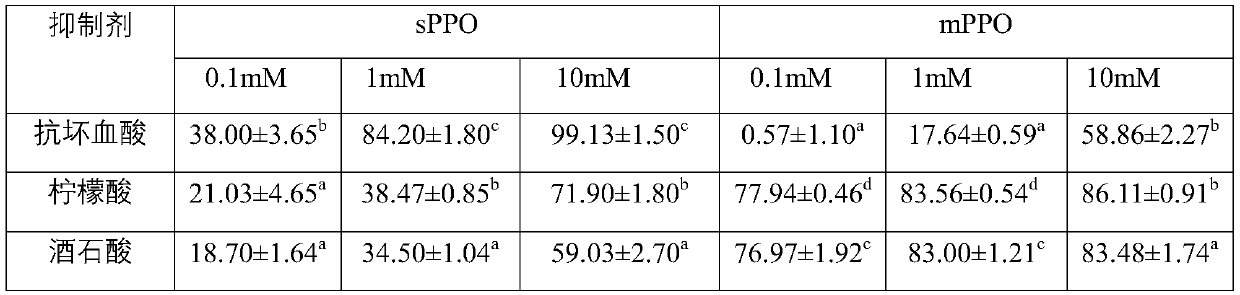
[0085] In order to prevent enzymatic browning of raw materials before beating, which will affect the quality, and to improve the effect of ultra-high pressure inactivation, chemical inhibitors are added to the materials before ultra-high pressure treatment. The inhibitory effects of different concentrations of ascorbic acid, citric acid, and tartaric acid on PPO were determined, and the results are shown in Table 1.
[0086] Table 1. Inhibition rate of sPPO and mPPO by different concentrations of chemical inhibitors
[0087]
[0088] Note: Different lowercase letters in the table indicate significant differences between groups.
[0089] It can be seen from the results that ascorbic acid with a concentration of 10mM has an inhibitory rate of 99.13% to sPPO, but its inhibitory effect on mPPO is not good; the highest inhibitory rate of citric acid with a concentration of 10mM to mPPO is 86.91%, so it...
Embodiment 2
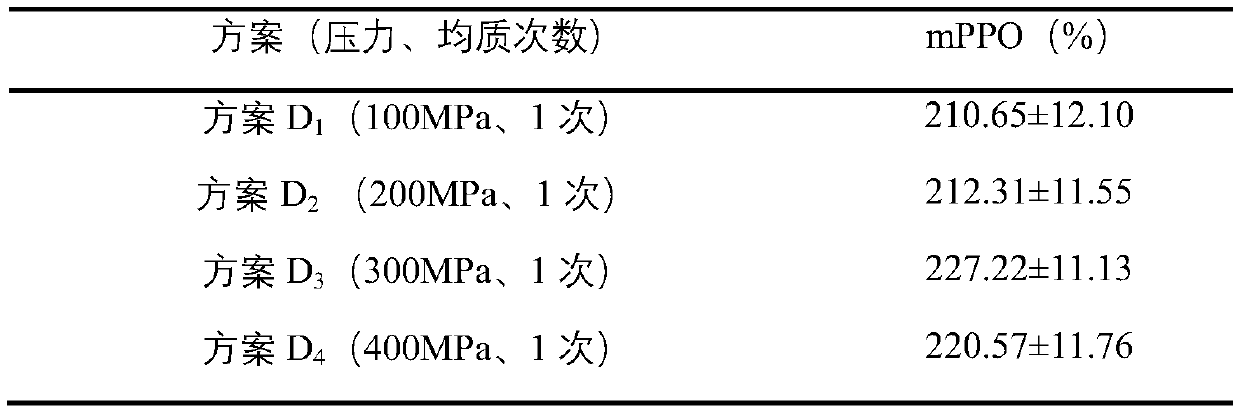
[0090] Embodiment 2, the influence of different ultra-high pressure conditions on sPPO activity
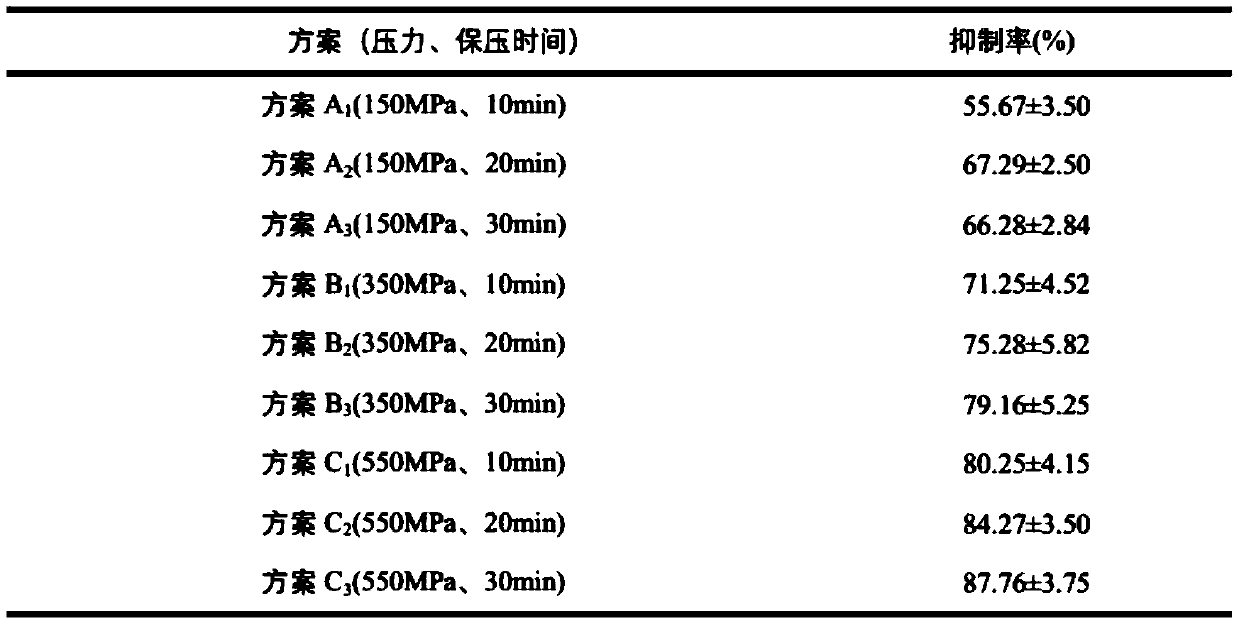
[0091] The purpose of the first ultra-high pressure treatment is to passivate sPPO, and the following treatment schemes are set up to compare the inhibitory effects of different pressure conditions on sPPO:
[0092] Option A 1 : Normal temperature, pressure 150MPa, holding time 10min;
[0093] Option A 2 : Normal temperature, pressure 150MPa, holding time 20min;
[0094] Option A 3 : Normal temperature, pressure 150MPa, holding time 30min;
[0095] Option B 1 : Normal temperature, pressure 350MPa, holding time 10min;
[0096] Option B 2 : Normal temperature, pressure 350MPa, holding time 20min;
[0097] Option B 3 : Normal temperature, pressure 350MPa, holding time 30min;
[0098] Plan C 1 : Normal temperature, pressure 550MPa, holding time 10min;
[0099] Plan C 2 : Normal temperature, pressure 550MPa, holding time 20min;
[0100] Plan C 3 : Normal temperature, pre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com