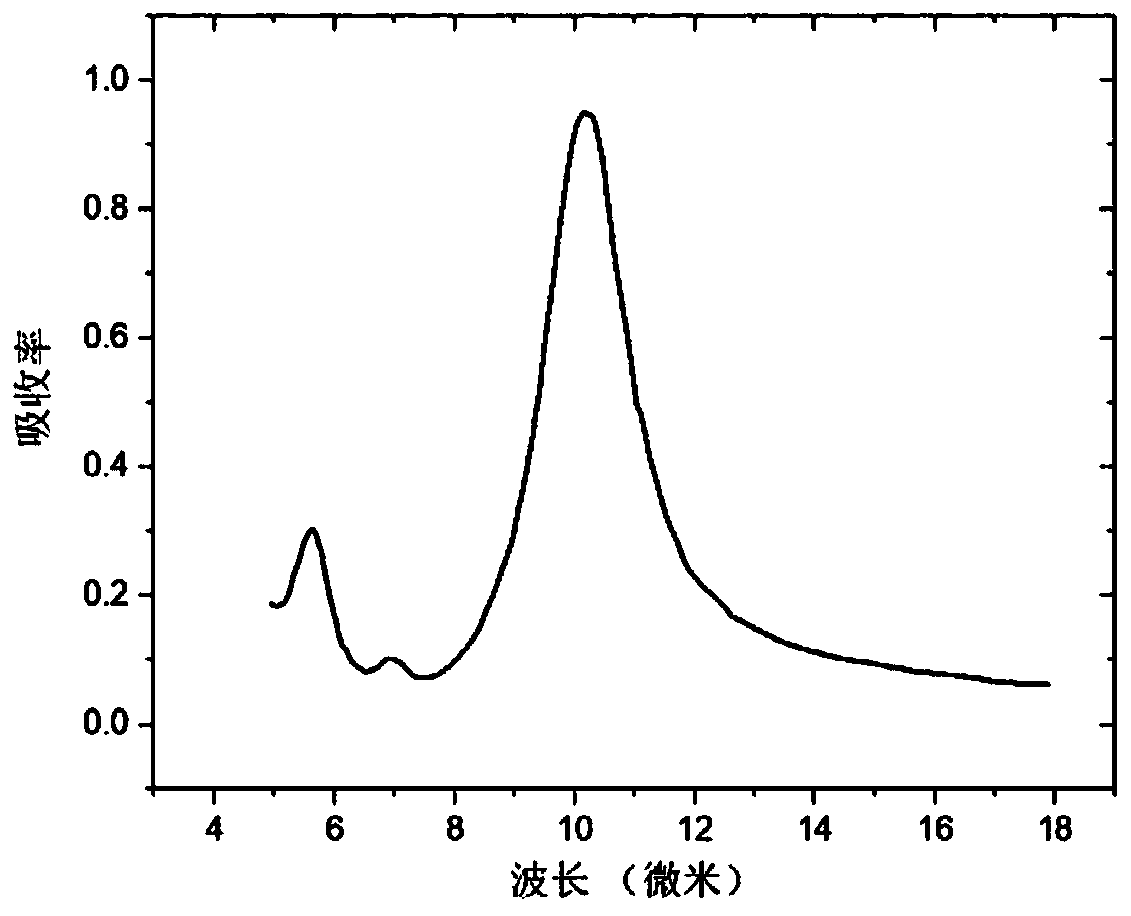
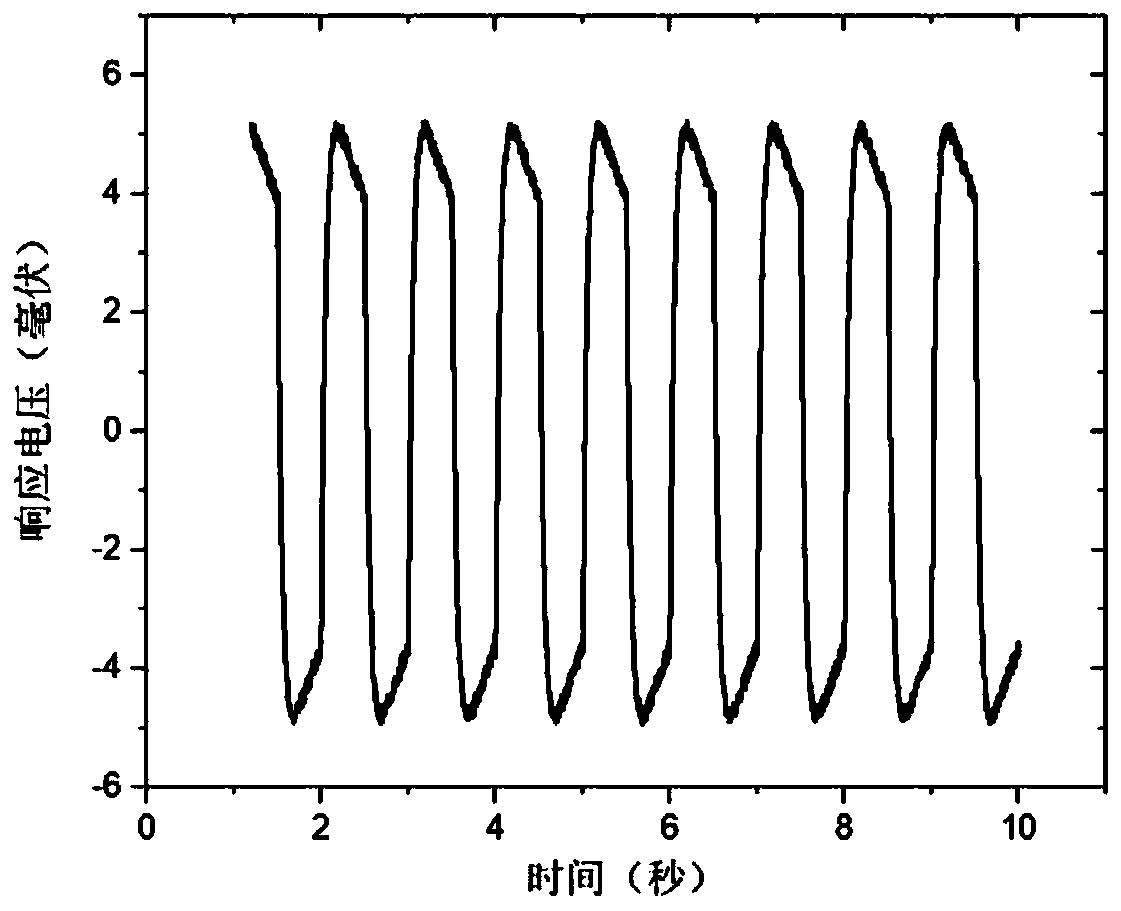
Narrow-band infrared detector and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of infrared detector and manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of photoelectric detection, can solve problems such as high cost, reduced stability, and complex structure, and achieve the effects of low cost, high stability, and improved signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
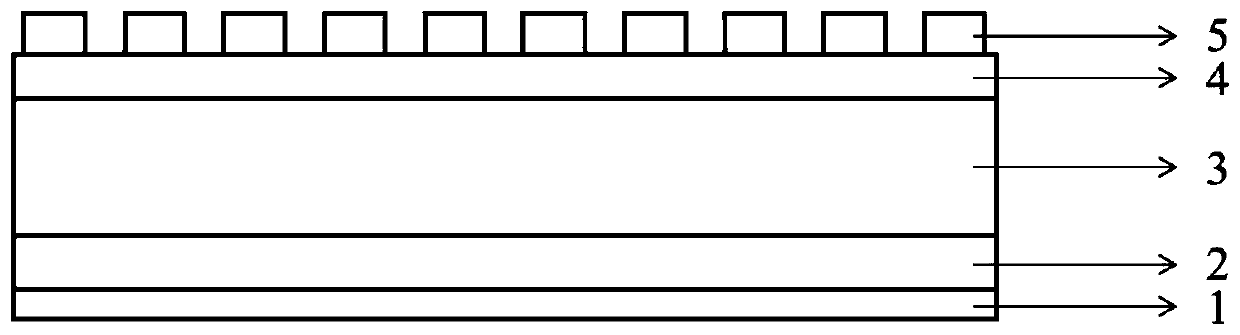
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, a narrow-band infrared detector includes from bottom to top: an insulating substrate 1, a metal lower electrode 2, a ferroelectric functional layer 3, a metal upper electrode 4, and a plasmonic structure 5;
[0044]The insulating substrate 1 can be made of sapphire, quartz sheet or intrinsic silicon, and the upper surface of the insulating substrate 1 is covered with a polyester film, and the thickness of the polyester film is 2-5 microns;
[0045] The lower metal electrode 2 is an aluminum metal film with a thickness of 50-150 nanometers;
[0046] The ferroelectric functional layer 3 is a poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) ferroelectric polymer film (P(VDF-TrFE)), with a thickness of 1-4 microns;
[0047] The metal upper electrode 4 is a nickel-chromium alloy film with a thickness of 10-30 nanometers;
[0048] The plasmonic structure 5 is a lattice structure composed of multiple metal squares with a thickness of 20-100 nanometers. ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] A narrow-band infrared detector, comprising: an insulating substrate, a metal lower electrode, a ferroelectric functional layer, a metal upper electrode, and a plasmonic structure from bottom to top;
[0051] The material of the insulating substrate is intrinsic silicon, and the upper surface of the intrinsic silicon wafer is covered with a polyester film, and the thickness of the polyester film is 2 microns;
[0052] The metal lower electrode is an aluminum metal film with a thickness of 100 nanometers;
[0053] The ferroelectric functional layer is a poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) (P(VDF-TrFE)) (70 / 30) ferroelectric polymer film with a thickness of 1 micron;
[0054] The metal upper electrode is a nickel-chromium alloy thin film, the ratio of nickel and chromium is 80:20, and the thickness is 15 nanometers;
[0055] The plasmonic structure is a lattice structure composed of multiple gold squares. The side length of the gold square section is 3.38 microns...
Embodiment 3
[0058] A method of making a narrow-band infrared detector, comprising the following steps:
[0059] S1: substrate preparation: the polyester film is fixed on the insulating substrate, the substrate can be sapphire, quartz plate, intrinsic silicon etc., and the thickness of the polyester film is 2-5 microns;
[0060] S2: preparation of metal lower electrode: adopt vacuum thermal evaporation to grow aluminum metal film on the polyester film in step S1, thickness is 50-150 nanometer;
[0061] S3: Preparation of ferroelectric functional layer: Prepare poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene)P(VDF-TrFE) ferroelectric polymer film on the aluminum metal film in step S2 by solution pulling method, and Anneal at 130°C for 1-2 hours;
[0062] S4: Preparation of metal upper electrode: using ion beam sputtering method to prepare a nickel-chromium alloy film on the ferroelectric polymer film in step S3, the thickness of the nickel-chromium alloy film is 10-30 nanometers;
[0063] S5: ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com