A kind of high concentration solution and its application and preparation method
A high-concentration, solution-based technology, used in electrical components, electrochemical generators, aqueous electrolytes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
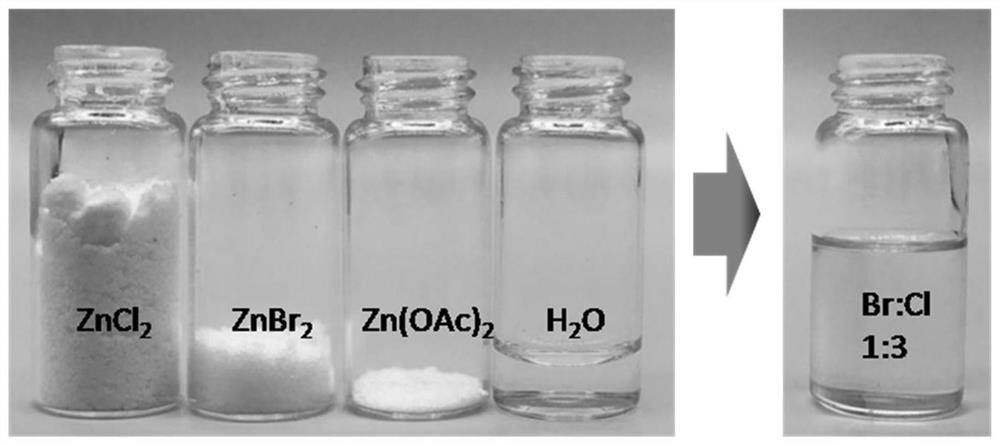
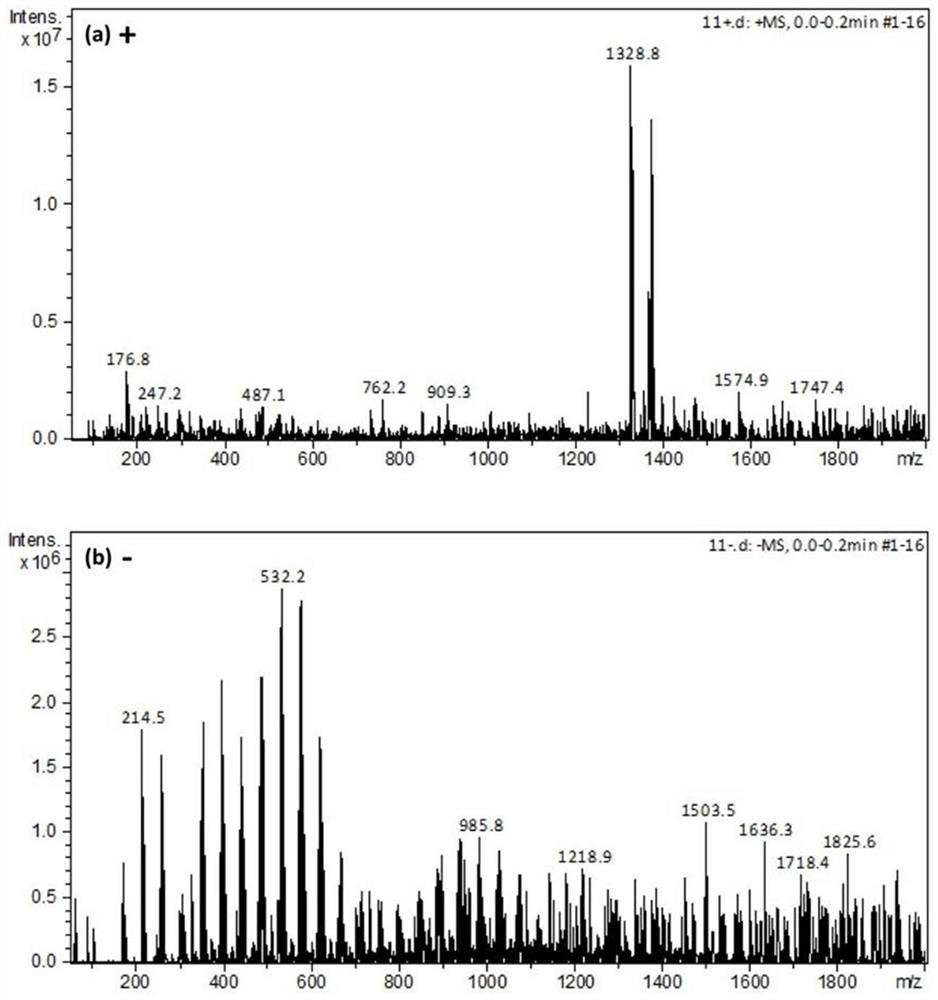
[0028](1) Add 0.3375 mol of zinc chloride and 0.1125 mol of zinc bromide to 10 g of deionized water in sequence, and then heat at 60°C for 2 hours to obtain ZnCl 2 , ZnBr 2 White turbid liquid composed of water. Add 0.01mol zinc acetate, continue heating in an oven at 120°C for 2 hours, and cool naturally to obtain a total concentration of 46mol kg -1 Zinc chloride-zinc bromide-zinc acetate salt-water "copolymer" solution in which the molar ratio of bromide ions to chloride ions is 1:3, see figure 2 .
[0029] (2) The zinc negative electrode, the glass fiber separator soaked in the electrolyte solution in (1) and the graphene film positive electrode are sequentially stacked into the battery mold and heat-sealed under pressure.
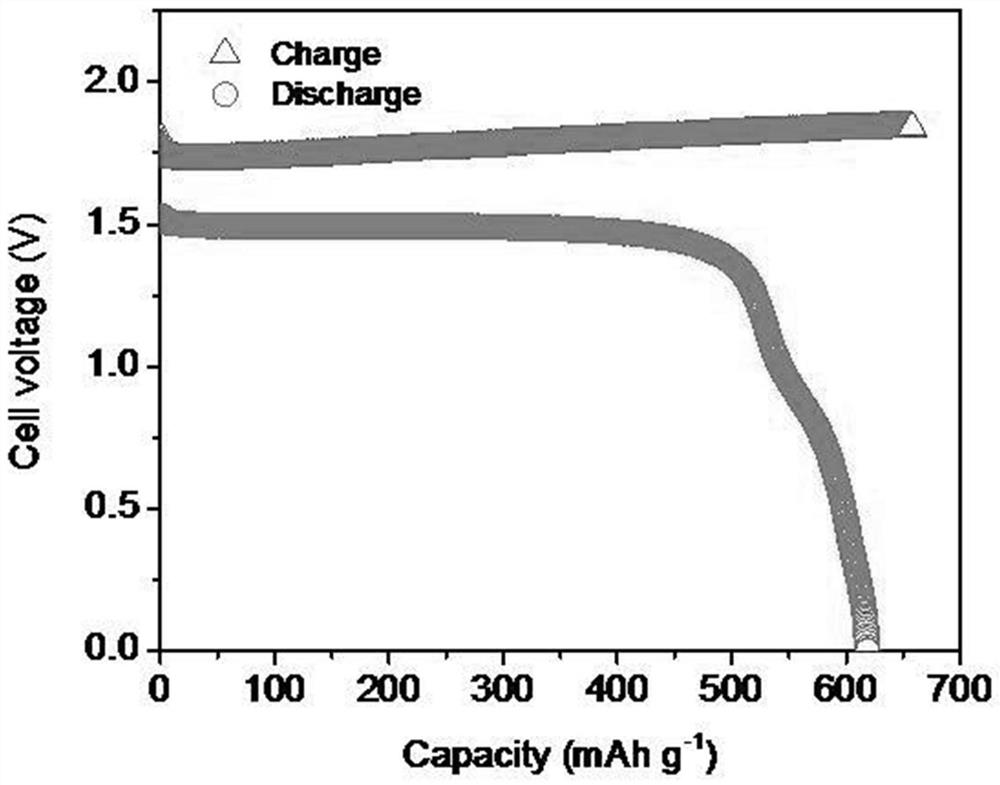
[0030] The battery cell obtained through the above steps, at 1A g -1 Under the current density, its discharge specific capacity is 607.5mAhg -1 (Based on the calculation of the positive active material, see image 3 ), and has excellent cycle st...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Add 0.28 mol of zinc chloride and 0.14 mol of zinc bromide to 10 g of deionized water in sequence, and then heat at 40°C for 24 hours to obtain ZnCl 2 , ZnBr 2 White turbid liquid composed of water. Add 0.01mol zinc acetate, continue heating in an oven at 100°C for 10h, and cool naturally to obtain a total concentration of 43mol kg -1 Zinc chloride-zinc bromide-zinc acetate salt-water "copolymer" solution in which the molar ratio of bromide ions to chloride ions is 1:2, see Figure 5 .
[0040] (2) The graphene fiber non-woven fabric negative electrode substrate, the glass fiber separator soaked in the electrolyte solution in (1) and the expanded graphite positive electrode are sequentially stacked into the battery mold and heat-sealed under pressure.
[0041] The battery cell obtained through the above steps, at 1A g -1 Under the current density, its discharge specific capacity is 632mAhg -1 (calculated based on the positive active material), and has good cycl...
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) Add 0.245mol of zinc chloride and 0.245mol of zinc bromide to 10g of deionized water in sequence, and then heat at 100°C for 2h to obtain ZnCl 2 , ZnBr 2 White turbid liquid composed of water. Add 0.05mol zinc acetate, continue heating in an oven at 120°C for 72 hours, and cool naturally to obtain a total concentration of 50mol kg -1 Zinc chloride-zinc bromide-zinc acetate salt-water "copolymer" solution in which the molar ratio of bromide ions to chloride ions is 1:1, see Figure 6 .
[0045] (2) The carbon cloth negative electrode substrate, the glass fiber separator soaked in the electrolyte in (1), and the mesophase microsphere graphite positive electrode are sequentially stacked into the battery mold and sealed under pressure.
[0046] The battery cell obtained through the above steps, at 1A g -1 Under the current density, its discharge specific capacity is 637mAhg -1 (calculated based on the positive active material), and has good cycle stability, and the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com