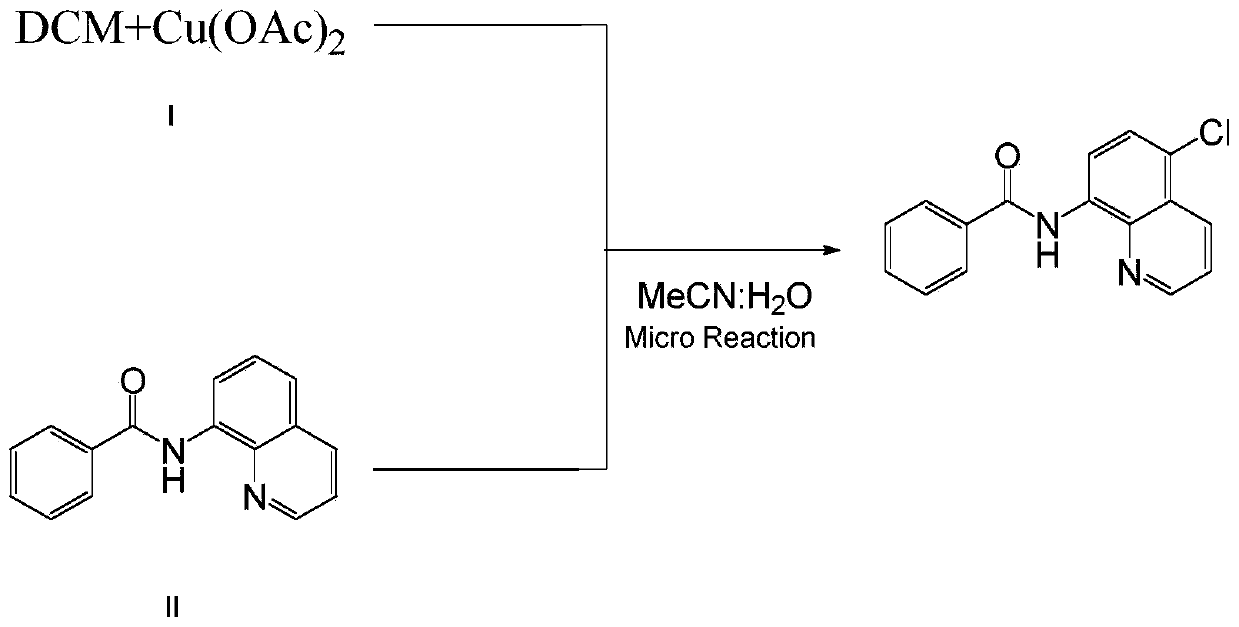
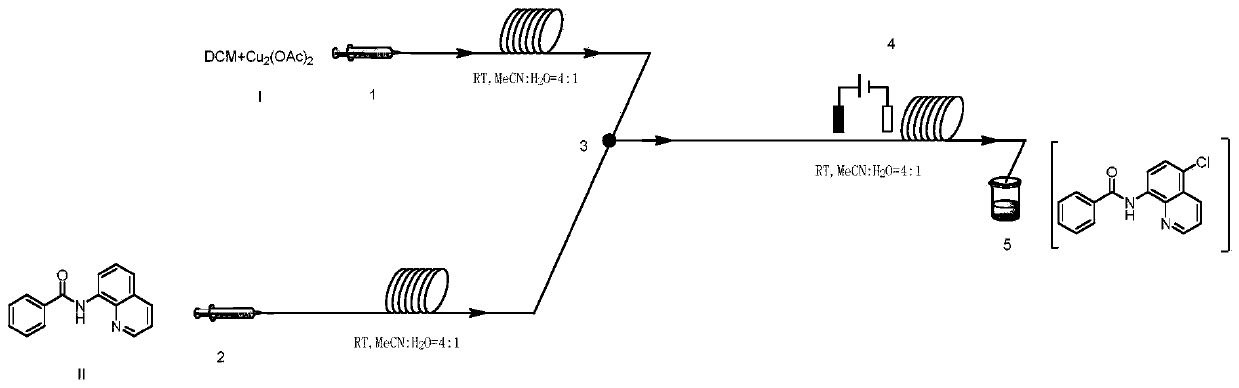
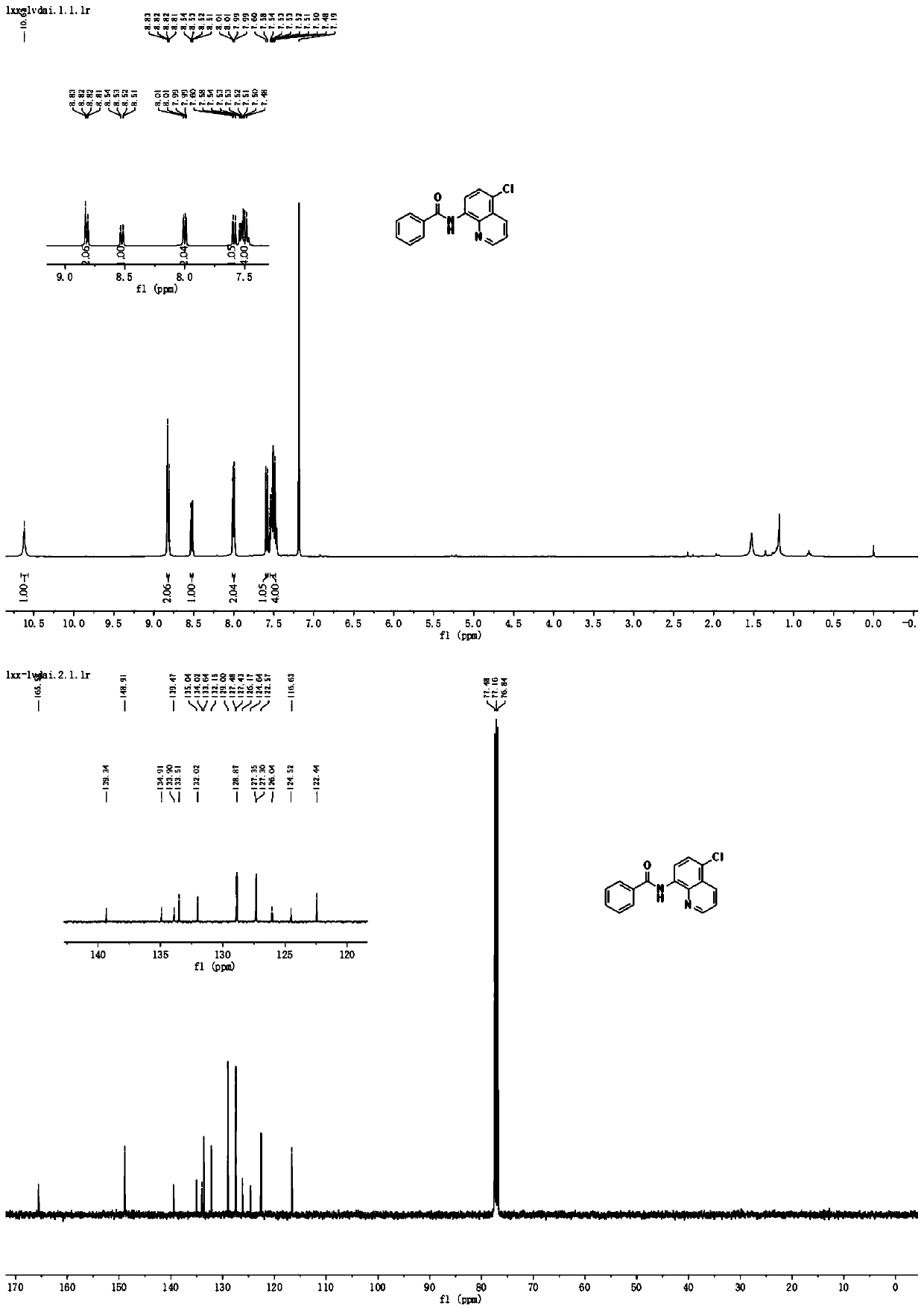
Method for preparing N-(5-chloro-8-quinolyl)benzamide compound by adopting electrochemical micro-channel reaction device
A technology of microchannel reaction and benzamide, which is applied in electrolysis process, electrolysis components, electrolysis organic production and other directions, can solve the problems of complicated steps and long reaction time, and achieves the effects of simple operation, shortened reaction time and improved yield.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Mix 24mmol (1.99g) of dichloromethane and 0.3mmol (0.06g) of copper acetate with 10mL of acetonitrile and water in a mixed solution (acetonitrile: water = 4:1, that is, 8mL of acetonitrile and 2mL of water) to obtain a homogeneous Solution I was added to syringe pump 1; 2.0 mmol (0.50 g) of N-(quinolin-8-yl) benzamide was dissolved in 10 mL of acetonitrile and water mixed solution (acetonitrile: water = 4: 1, ie 8mL of acetonitrile and 2mL of water) to obtain a homogeneous solution II, which was added to the syringe pump 2; the syringe pump 1 and the syringe pump 2 were used to inject solution I and solution II at a flow rate of 0.10mL / min and 0.15mL / min, respectively. Inject in the micro-mixer 3, enter the electrochemical microchannel reactor 4 after mixing in the micro-mixer 3 to react; the first microchannel reactor reaction volume is 1.25mL, and the reaction residence time is 5.0min; The temperature of the channel reactor is 25° C., and the reaction current is 100 m...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Mix 24mmol (1.99g) of dichloromethane and 0.3mmol (0.06g) of copper acetate with 10mL of acetonitrile and water in a mixed solution (acetonitrile: water = 4:1, that is, 8mL of acetonitrile and 2mL of water) to obtain a homogeneous Solution I was added to syringe pump 1; 2.0 mmol (0.50 g) of N-(quinolin-8-yl) benzamide was dissolved in 10 mL of acetonitrile and water mixed solution (acetonitrile: water = 4: 1, ie 8mL of acetonitrile and 2mL of water) to obtain a homogeneous solution II, which was added to the syringe pump 2; the syringe pump 1 and the syringe pump 2 were injected into the solutions I and II at a flow rate of 0.10mL / min and 0.15mL / min respectively. In the micromixer 3, after mixing in the micromixer 3, enter the electrochemical microchannel reactor 4 to react; the first microchannel reactor reaction volume is 1.25mL, and the reaction residence time is 5.0min; The temperature of the reactor is 25° C., and the reaction current is 80 mA; after the reaction i...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Mix 24mmol (1.99g) of dichloromethane and 0.3mmol (0.06g) of copper acetate with 10mL of acetonitrile and water in a mixed solution (acetonitrile: water = 4:1, that is, 8mL of acetonitrile and 2mL of water) to obtain a homogeneous Solution I was added to syringe pump 1; 2.0 mmol (0.50 g) of N-(quinolin-8-yl) benzamide was dissolved in 10 mL of a mixed solution of nitrile and water (acetonitrile: water = 4: 1, ie 8mL of acetonitrile and 2mL of water) to obtain a homogeneous solution II, which was added to the syringe pump 2; the syringe pump 1 and the syringe pump 2 were injected into the solutions I and II at a flow rate of 0.10mL / min and 0.15mL / min respectively. In the micromixer 3, after mixing in the micromixer 3, enter the electrochemical microchannel reactor 4 to react; the first microchannel reactor reaction volume is 1.25mL, and the reaction residence time is 5.0min; The temperature of the reactor is 25° C., and the reaction current is 120 mA; after the reaction ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com