Method for removing pesticide residues from ginseng extract
A technology for extracting ginseng and pesticide residues, which is applied in the direction of pharmaceutical formulas, plant raw materials, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc. It can solve the problems of high organic solvent residues, large equipment investment, and high operating costs, so as to avoid transfer losses, Ease of operation, effect of reducing layer separation loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
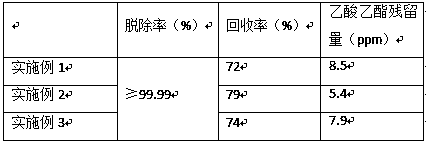
Embodiment 1
[0033] A method for removing pesticide residues from ginseng extracts, comprising the following steps:
[0034] S1. Dissolving: add 35mL water and 65mL 100% ethyl acetate to 100g ginseng crude extract, stir to raise the temperature to above 80°C, keep it warm for 20min, keep stirring during the period, and the stirring speed is 120r / min;
[0035] S2. Extraction: Slowly add 1000mL of 97% ethyl acetate; continue to stir for 2h, and then let it stand for 2h. When the organic layer and the water layer are clearly separated, release the organic layer and continuously extract six times; add 50mL of water to dissolve the bottom layer Extract the extract and stir it evenly, and the organic layer is recycled in the solvent recovery tower to remove high pesticide residue components by distillation;
[0036] S3. Concentration: Use a concentrator to remove the residual organic solvent in the bottom extract. The vacuum degree of concentration is -0.08 mPa, and the concentration temperature...
Embodiment 2
[0040] A method for removing pesticide residues from ginseng extracts, which is basically the same as in Example 1, except that: step S2 extracts each time, when the organic layer is released, a part of the organic layer is kept in the extraction device, subject to the fact that the liquid level of the bottom extract is not exposed; After releasing the organic layer during the last extraction, add water slowly along the inner wall of the extraction device until the thickness of the water layer reaches 1cm, and let it stand for 5 minutes. The retained organic layer moves from the surface of the extract to the surface of the water layer, and then the organic layer can be released, which improves the removal level of the organic layer without causing loss to the extract; then add 50mL to dissolve the bottom extract.
Embodiment 3
[0042] A method for removing pesticide residues from ginseng extracts, which is basically the same as in Example 1, except that in step S4, after the concentrated solution is passed through the macroporous resin, water having the same volume (50 mL) as the concentrated solution is passed through the macroporous resin, and then flows out The liquid is collected together.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com