Method for extracting phosphate ester from alga mud by using dimethyl ether
A technology of phosphate ester and dimethyl ether, applied in the field of resources and environment, can solve problems such as no document disclosure, and achieve the effects of improving energy utilization efficiency, saving costs, and being easy to separate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 7
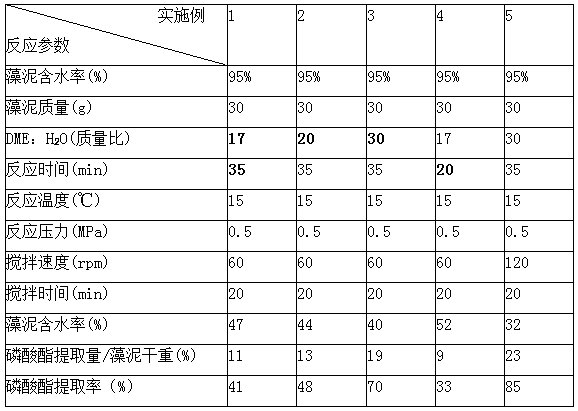
[0033] Embodiment 7 reaction temperature Investigation on Extraction Rate of Phosphate Ester
[0034] Polarity is the key to determining solubility, because Phosphates are polar organic compounds , according to the principle of like dissolves like, need to adjust DME is a polar solvent, and the larger the dielectric constant, the stronger the polarity, and vice versa, the smaller the dielectric constant, the smaller the polarity.
[0035] Dielectric constant between 0-5: non-polar
[0036] Dielectric constant in 5-30: medium (or semi-polar)
[0037] Dielectric constant > 30: strong polarity
[0038]The inventors assessed the parameters (relative dielectric constant of DME) that affect the extraction rate of phosphate esters at different temperatures, as shown in Table 2. It can be seen that as the temperature increases, the dielectric constant decreases, and the extraction rate of phosphate esters decreases. (Phosphate extraction rate in DME: H 2 O mass ratio is mea...
Embodiment 8
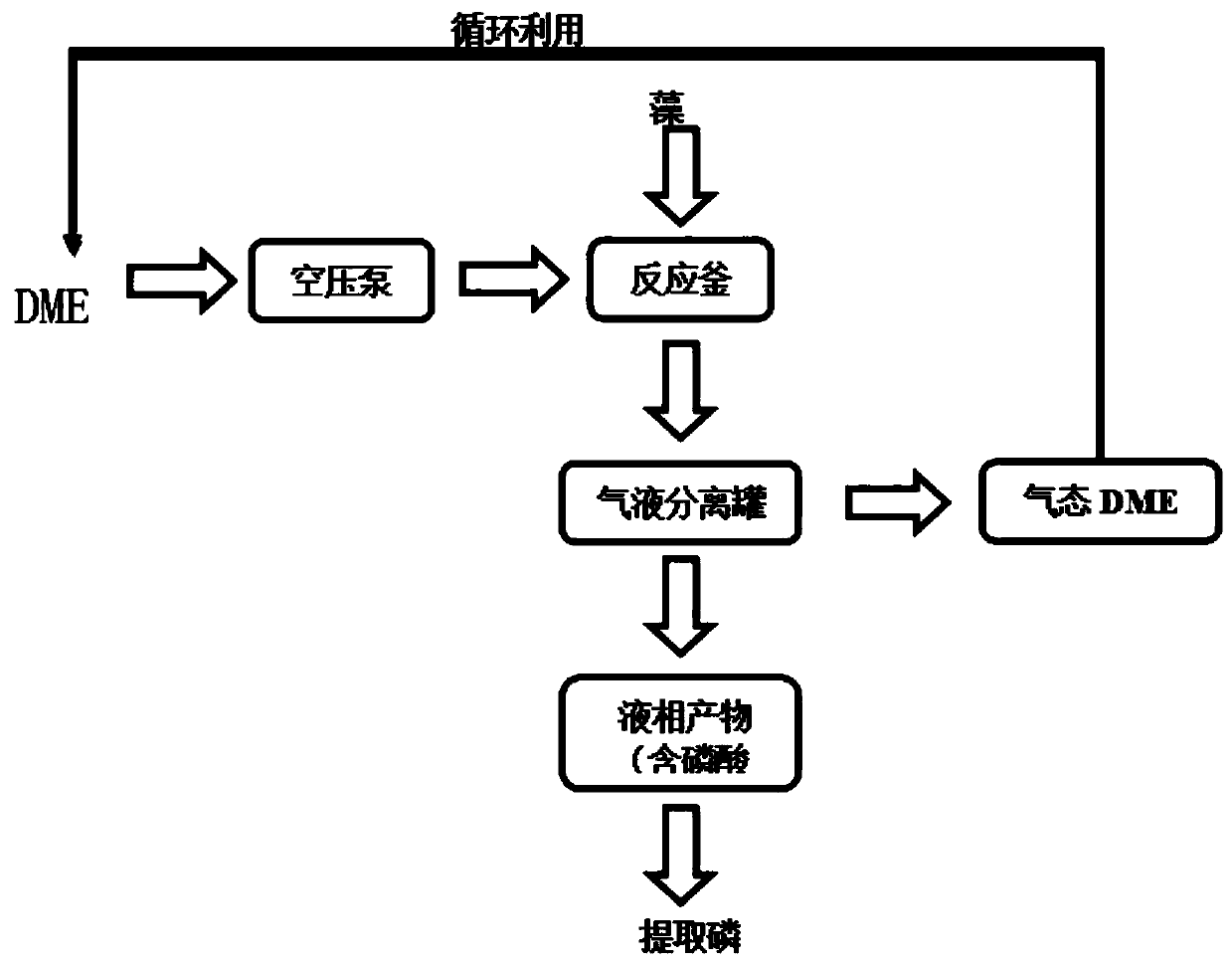
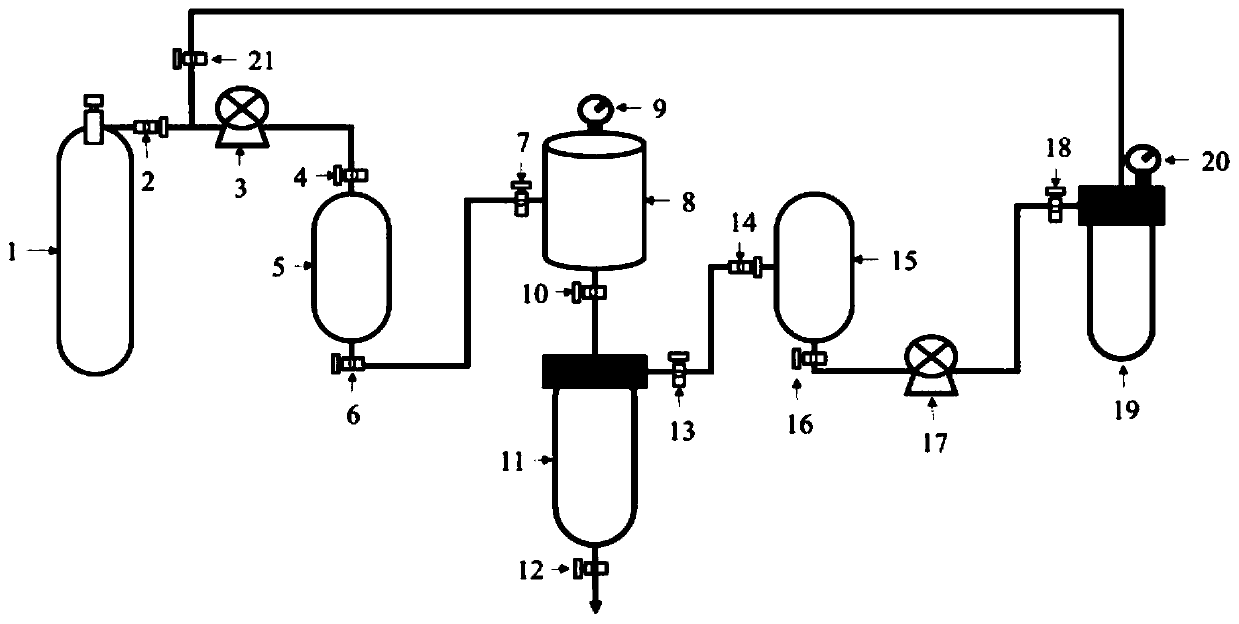
[0042] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the connection relationship of the devices adopted in the present invention. like figure 2 As shown, the output pipeline of the DME gas tank 1 is connected to the liquid DME temporary storage tank 5 through the flow regulating valve 2; the output pipeline of the liquid DME temporary storage tank 5 passes through the storage tank outlet valve 6, the reactor inlet valve 7 and the reactor 8 in sequence Input pipeline links to each other; The output pipeline of reactor 8 links to each other with the input pipeline of gas-liquid separation tank 11 by pressure regulating valve 10; The first output pipeline of gas-liquid separation tank 11 exports the liquid that is rich in phosphoric acid ester through liquid flow valve 12, can A further step is to extract the phosphorus element in it.
[0043] The second output pipeline of the gas-liquid separation tank 11 is connected to the input pipeline of the drying tank 15 through the gas flow ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com