Method for remedying tidal flat plants and recycling organic pollutions
A technology of organic pollution and phytoremediation, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, water pollutants, land preparation methods, etc., can solve the problem of difficult plant treatment, underutilization, no harmless recycling of papermaking wastewater, soil improvement, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of promoting plant growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
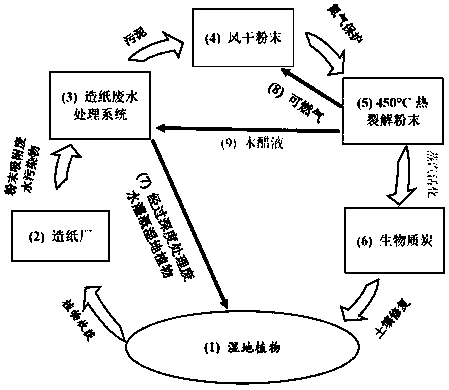
[0041] A method for phytoremediation and recycling of organic pollution in tidal flats, such as figure 1 As shown, including the following steps:
[0042] The first step: From 2001 to 2013, the papermaking wastewater from the papermaking wastewater treatment plant was used to irrigate the saline-alkali soils in the wetland with the papermaking wastewater. For 13 years, the refractory pollutants in the papermaking wastewater were left in the soil and were not discharged into the irrigated wetland; One or more of Spartina or Suaeda;
[0043] The second step: Collect the tidal flat plants growing in the contaminated soil of the first step, air-dry until the moisture content is less than 20%, and crush them into powder with a particle size of 0.125-0.250 mm;
[0044] The third step: 60-80% of the tidal flat plants in the second step are used for papermaking, and 20-40% is put into the papermaking wastewater to absorb the pollutants in the papermaking wastewater, kept at 21-29℃ for 2 hour...
Embodiment 2
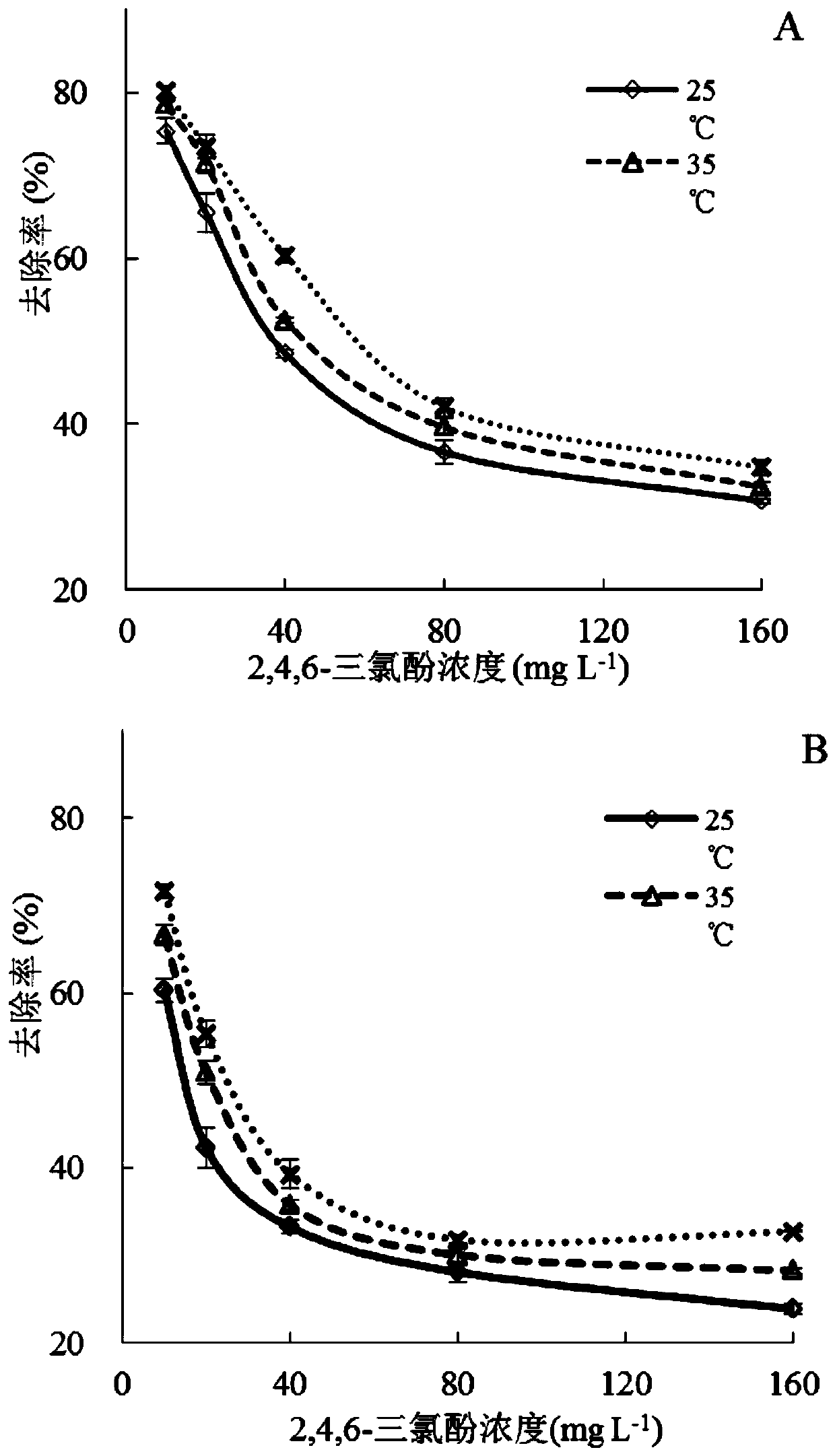
[0051] Such as figure 2 As shown, the powder of reed A and Spartina alterniflora B adsorbed different concentrations of organic pollution in the solution, such as the removal rate graph of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol.
[0052] The highest percentage of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (2,4,6-TCP) removed by reed and Alternanthera powder in an aqueous solution at 45°C is 80.1% and 71.6%, respectively; at 25°C, reed powder has a low concentration 10 mg L -1 To high concentration 160 mg L -1 , The removal rate dropped from 75.4% to 30.7%, at 35°C, the removal rate dropped from 78.5% to 32.4%, and at 45°C, 80.1% dropped to 34.7%; while the removal rate of Spartina alterniflora powder was At 25°C, it dropped from 60.3% to 23.9%, at 35°C, it dropped from 66.6% to 28.2%, and at 45°C, it dropped from 71.6% to 32.7%.
Embodiment 3
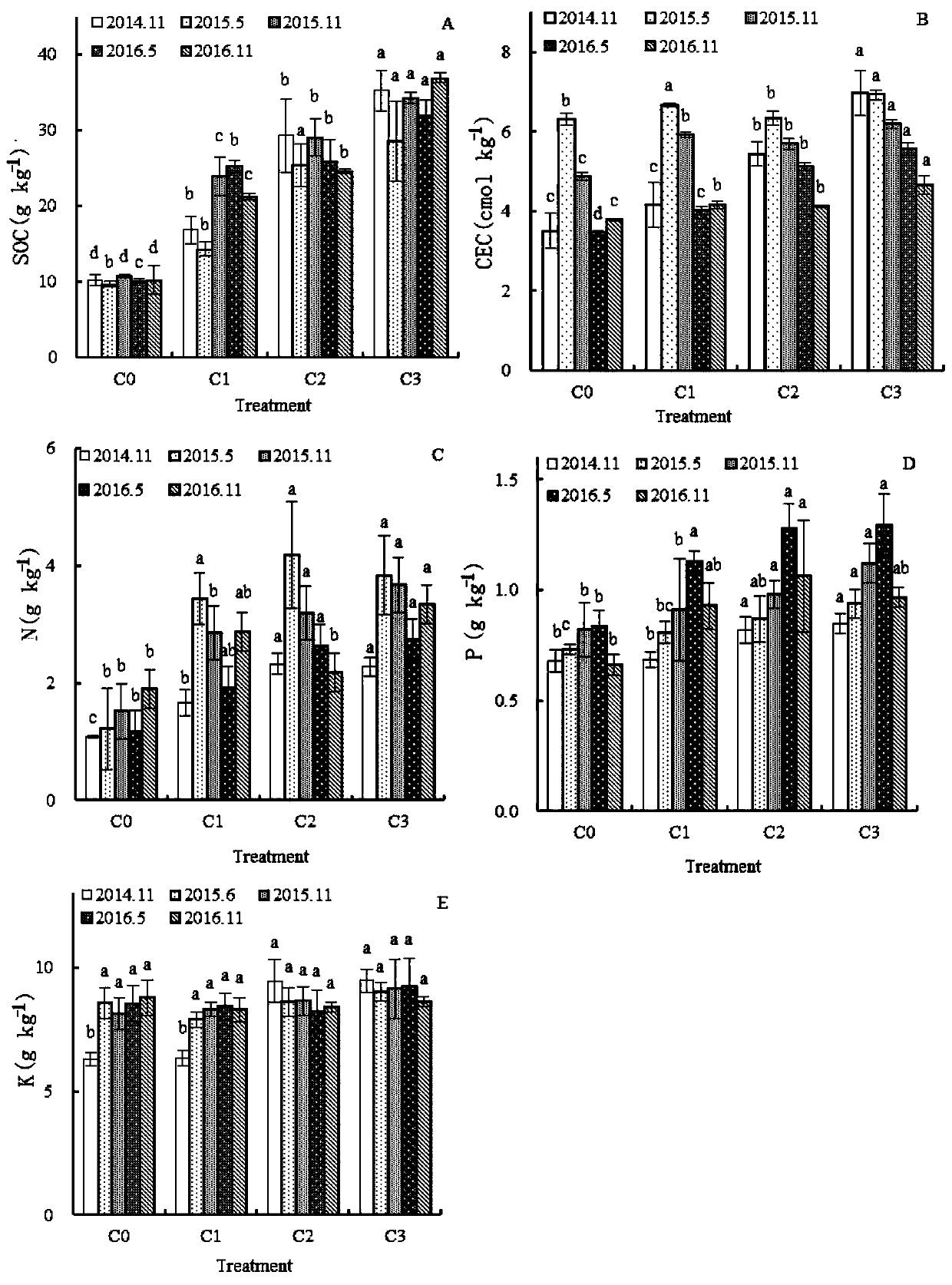
[0054] Such as image 3 Shown are the changes in soil physical and chemical properties such as SOC, CEC, N, P, and K content changes after the application of biomass charcoal.
[0055] Compared with the control, after the application of biomass charcoal, the soil organic carbon content significantly increased by 64%-243.4% (2014.11), 47.9%-194.5% (2015.5), 122.8%-218.8% (2015.11), 151.8%-218.5% (2016.5), 107.6%-260.9% (2016.11) ( image 3 a). With the increase in the amount of biomass charcoal, the content of organic carbon has also increased significantly and remains stable. This is mainly because the carbon element in biomass charcoal is stable and not easily degraded.
[0056] Soil cation exchange capacity (CEC) also increased significantly with the increase in the amount of biomass charcoal application, which is due to the increase in the number of functional groups in the soil by the application of biomass charcoal ( image 3 b). With the increase in the amount of biomass cha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com