Method for in-situ revealing anaerobic iron ammonia oxidizing bacteria in river and lake sediment by DNA stable isotope probe
An anaerobic iron ammonium oxidation and isotope technology, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of small bacterial population ratio and difficult analysis, and achieve the effect of improving the identification rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
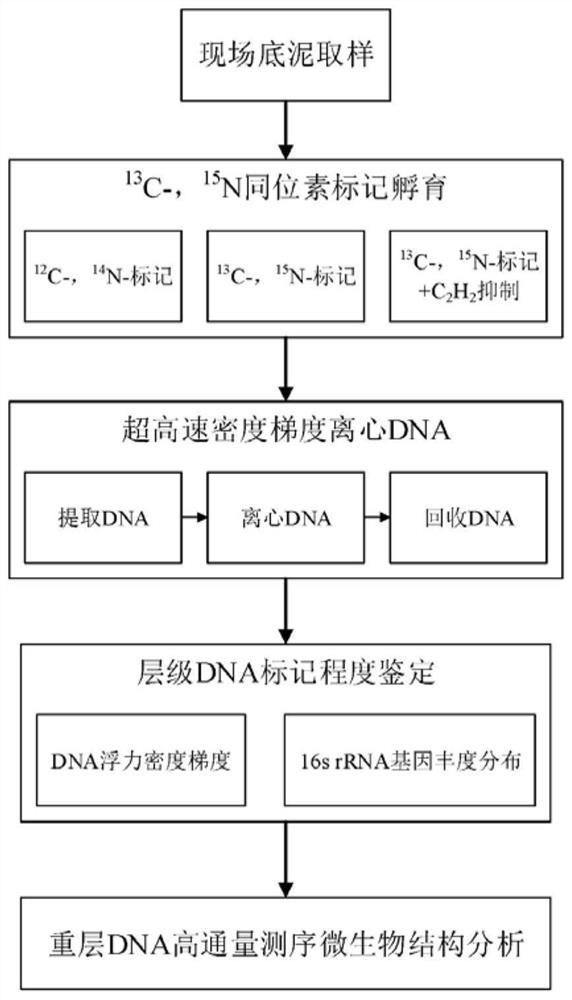
[0044] A method for in situ revealing of anaerobic iron ammonia oxidizing bacteria in sediments of rivers and lakes by DNA stable isotope probes, the process operation is as follows figure 1 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
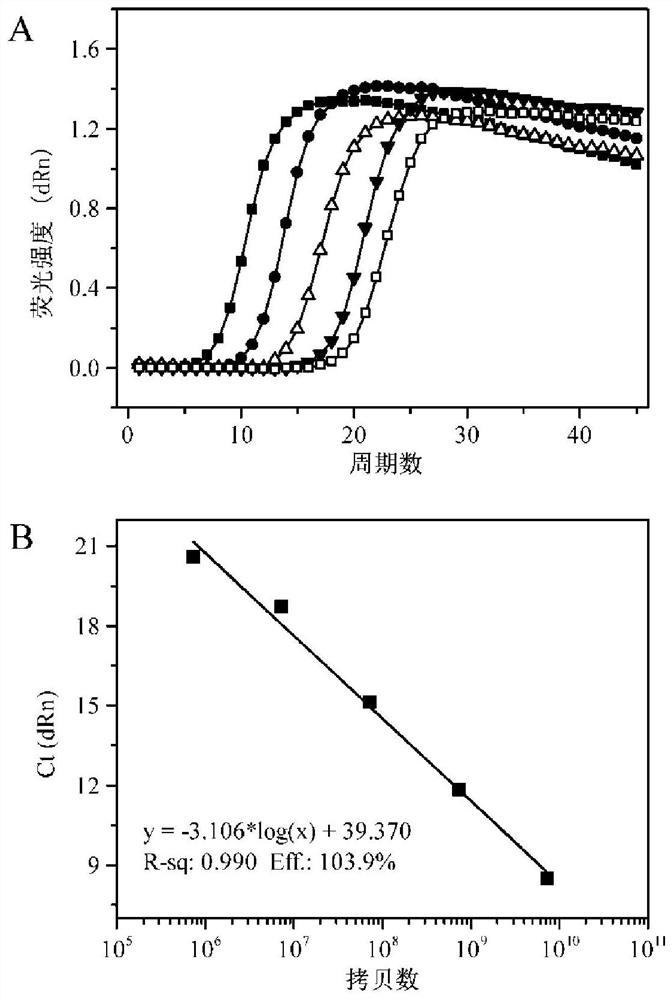
[0045] 1, 13 C, 15 N-SIP incubation and DNA extraction
[0046] (1) On-site sampling: According to the investigation purpose and sampling plan, collect about 2L of biological samples from river (lake) sediment at a depth of 0-20cm at each sampling point, and divide them into two equal parts and place them in sterile plastic sampling bags. Empty the air on the upper part of the sampling bag and seal it, and transport it to the laboratory through a sampling box with built-in ice cubes;
[0047] (2) For each sampling point sample, one of the samples was analyzed according to the method of "Physical and Chemical Analysis of Soil" (China Forestry Press, 2017) to measure water content, pH, particle size distribution, dissolved nitrogen...
Embodiment 2
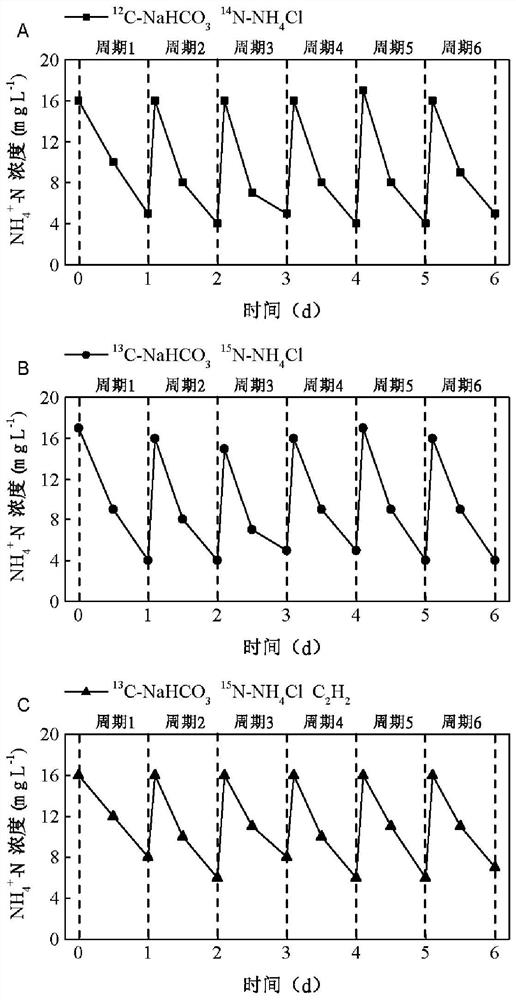
[0079] A DNA stable isotope probe in situ reveals the method for anaerobic iron ammonia oxidizing bacteria in river and lake sediments, the specific steps are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that in the formal cultivation of step 1-(6), Fe (III) The ion concentration is 20mg-Fe / L, 12 C-NaHCO 3 with 14 N-NH 4 The amount of Cl added is 30 mg-C / L and 15 mg-N / L respectively; step 3-(2) ultra-high speed centrifugation, the temperature is 18°C, 180000×g, ultra-high speed centrifugation for 44 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0081] A DNA stable isotope probe in situ reveals the method for anaerobic iron ammonia oxidizing bacteria in river and lake sediments, the specific steps are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that in the formal cultivation of step 1-(6), Fe (III) The ion concentration is 23mg-Fe / L, 12 C-NaHCO 3 with 14 N-NH 4 The amount of Cl added is 33 mg-C / L and 17 mg-N / L respectively; step 3-(2) ultra-high speed centrifugation, the temperature is 22° C., 200,000×g, ultra-high speed centrifugation for 46 hours.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com