Composition and method for conferring and/or enhancing tolerance against herbicides by using variants of ppo
An identity, amino acid technology, applied in the field of compositions and methods using PPO variants to confer and/or enhance tolerance to herbicides, capable of solving problems such as pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0187] Example 1. Verification of herbicide tolerance of ApPPO1 and MxPPO isolated from prokaryotes
[0188] The PPO gene sequences were obtained from the Genebank database of two strains of Auxenochlorella protothecoides and Myxococcus xanthus, respectively. For encoding a PPO protein from oleaginous microalgae (ApPPO1; SEQ ID NO:1), the PPO gene designated ApPPO1 was isolated from oleaginous microalgae and optimized to have the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:7. For encoding the PPO protein from M. xanthus (MxPPO; SEQ ID NO:3), the PPO gene designated MxPPO was isolated from M. xanthus and optimized to have the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:8. To obtain herbicide-binding structures of PPO proteins, herbicides including Tifenacil, Saflufenacil, Flufenacil, and Sulfentrazone were used, and PPO proteins including ApPPO1 and MxPPO were used. ApPPO1 was constructed from the structure of CyPPO10 (PPO protein derived from Synechococcus elongatus BP-1; SEQ ID NO:5) using ...
Embodiment 2
[0192] Example 2. Construction of PPO variants
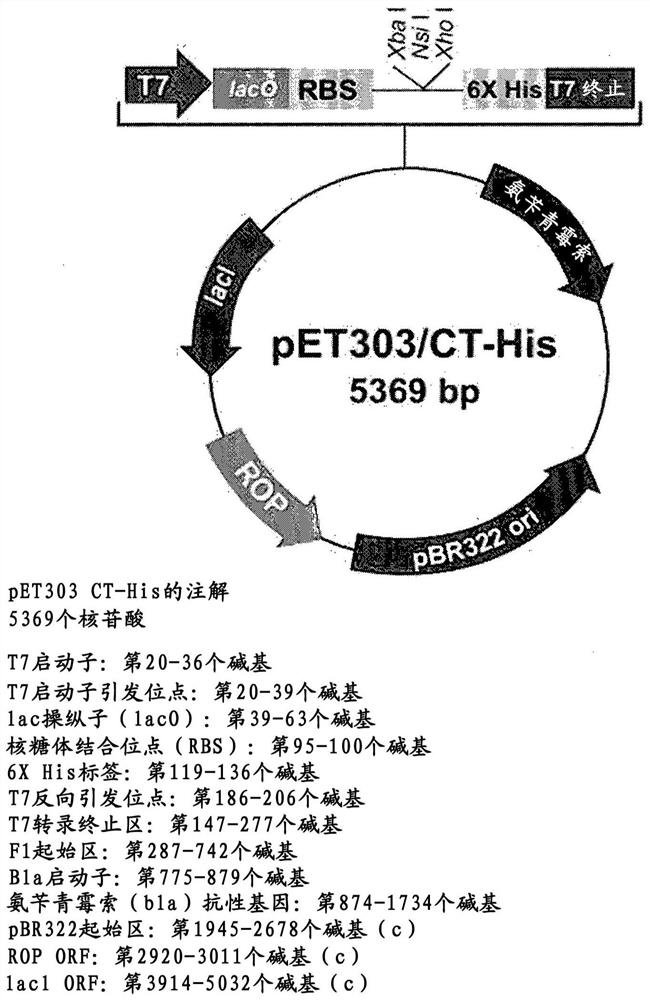
[0193] In order to enhance the PPO-inhibiting herbicide tolerance to ApPPO1 and MxPPO, the mutations at the herbicide-interacting positions obtained in Example 1 were introduced, respectively. Each PPO gene was codon optimized and synthesized (Cosmogenetech Co., Ltd.) for efficient herbicide tolerance testing using PPO-deficient E. coli strain BT3.
[0194] The detailed experimental procedure is as follows:
[0195] Using the primers listed in Table 2, PCR was performed under the following conditions to amplify the PPO gene.
[0196] PCR reaction mix
[0197] Template (synthetic DNA of ApPPO1 and MxPPO) 1 μl
[0198] 5 μl of 10X buffer
[0199] dNTP mix (10 mM each) 1 μl
[0200] Forward primer (10 μM) 1 μl
[0201] Reverse primer (10μM) 1μl
[0202] DDW 40μl
[0203] Pfu-X (Solgent, 2.5 units / μl) 1 μl
[0204] 50 μl total
[0205] [Table 1] PCR reaction conditions
[0206]
[0207] [Table 2] List of primers for ...
Embodiment 3
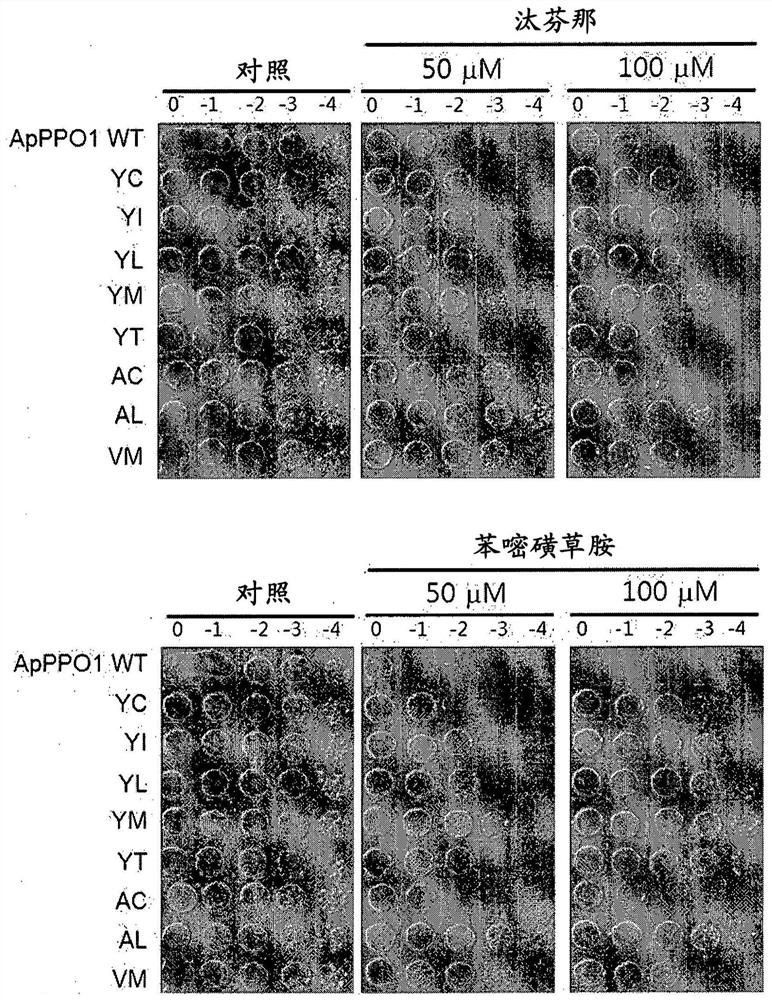
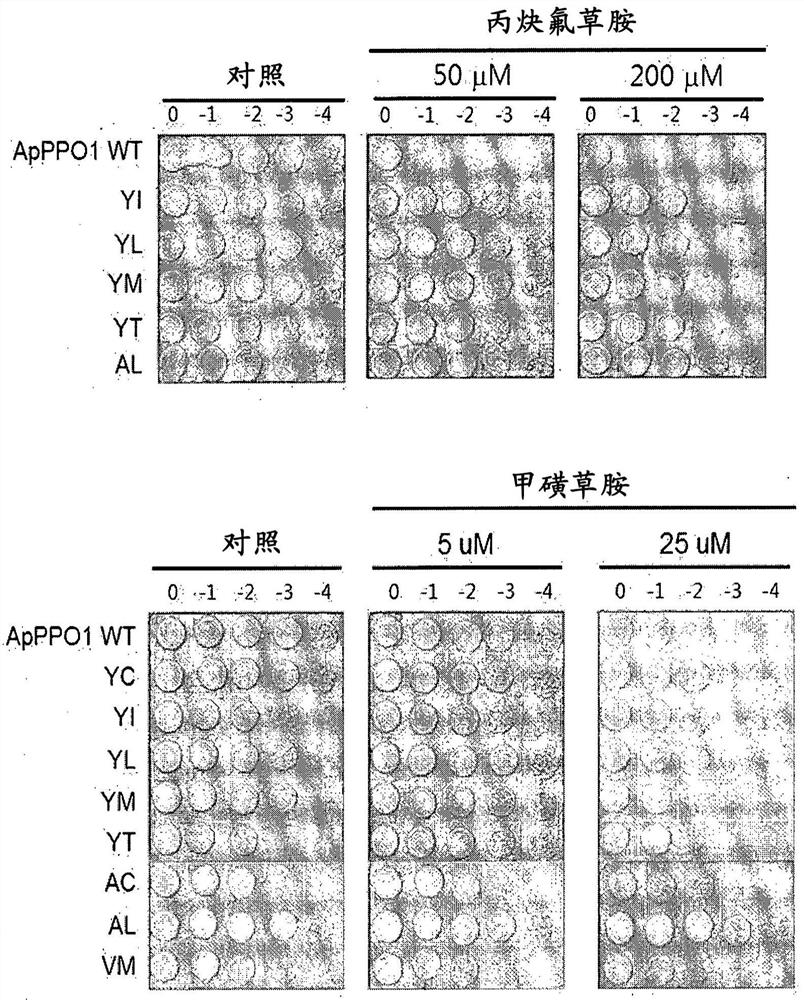
[0229] Example 3. Verification of PPO-inhibiting herbicide tolerance of PPO variants (tested in E. coli)
[0230] The mutated CyPPO gene obtained in Example 2 was transformed into a BT3 (ΔPPO) strain lacking PPO activity, and cultured with a PPO-inhibiting herbicide in LB medium, thereby checking whether the growth of the transformed BT3 was not inhibited.
[0231] The BT3(ΔPPO) strain was provided by Hokkaido University (Japan), which is a hemG-type PPO-deficient and kanamycin-resistant Escherichia coli strain (see "Watanabe N, Che FS, Iwano M, Takayama S, Yoshida S , Isogai A. Dual targeting of spinach protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase II tomitochondria and chloroplasts by alternative use of two in-frame initiationcodons), J.Biol.Chem.276(23):20474-20481, 2001; Che FS, Watanabe N, Iwano M, Inokuchi H, Takayama S, Yoshida S, Isogai A. Protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase in spinach chloroplasts Molecular Characterization and Subcellular Localization of Protoporphyrinogen IX oxidase i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com