Targeting vector and nucleic acid composition for constructing liver injury mouse model, and construction method
A targeting vector, mouse model technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering and genetic modification, can solve the problems of being unsuitable for hepatitis virus infection research, affecting the adenovirus infection rate, reducing the expression of uPA, etc., so as to facilitate large-scale breeding and transplantation. The effect of simplified procedures and low mortality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
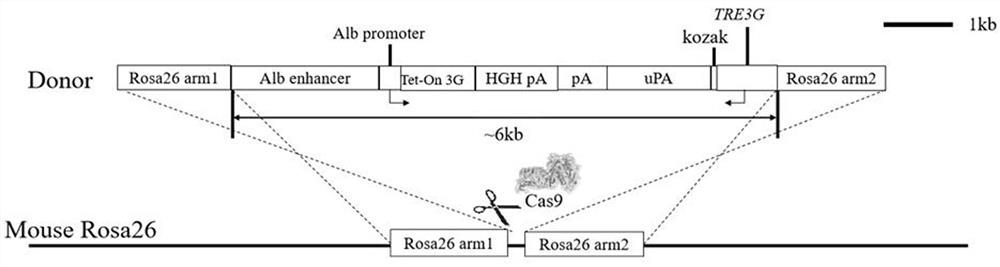
[0076] The targeting vector provided in this example for the construction of a mouse model of liver injury includes: a target sequence and a 5' homology arm sequence (Rosa26 arm1) used to mediate the insertion of the target sequence into the target site (Rosa26) in the mouse genome ) and the 3' homology arm sequence (Rosa26 arm2) (for the positional relationship of each element, see figure 1 ).
[0077] Wherein, the target sequence sequentially includes a first expression cassette and a second expression cassette located downstream of the first expression cassette from upstream to downstream;
[0078] The first expression cassette includes the following elements in series: albumin enhancer (Alb enhancer), albumin promoter (Alb Promoter), tetracycline transcriptional activation regulator (Tet-On 3G) and the first polyA (HGH polyA); At figure 1 In the middle direction, expression is driven from left (upstream) to right (downstream).
[0079] The second expression cassette com...
Embodiment 2
[0084] This embodiment provides the method for constructing the targeting vector of Embodiment 1, including the following steps:
[0085] 1.1 Alb enhancer-Alb promoter fragment preparation
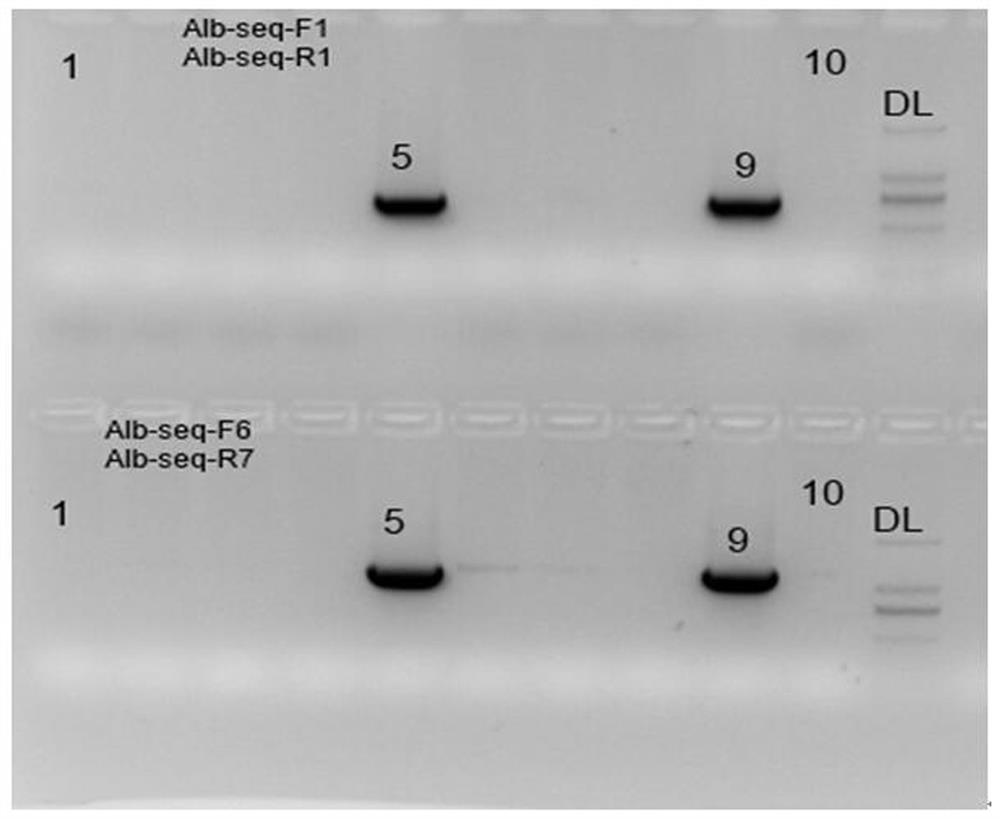
[0086] Use the primers in Table 1 to amplify the Alb enhancer-Alb promoter target fragment and recover it for future use. Conditions for PCR amplification are set according to common knowledge in the field.
[0087] Table 1. Alb enhancer-Alb promoter amplification primer list
[0088]
[0089] The nucleotide sequence (SEQ ID NO.1) of one strand of the Alb enhancer-Alb promoter target fragment is as follows (5'-3'):
[0090] ggtggttctcctgtcagtttcgaggggggtacagcttgggctgcaggtcgactctagatcgaattcctgcagc ccgggggatcccggggttgataggaaaggtgatctgtgtgcagaaagactcgctctaatatacttctttaaccaat aactgtagatcattaaccatacttacctcgcatttcattggttcctaccccattacaaaatcataccatctttgcc aaaaagttgtttgactaaatcccttgcgtatgtttgccatctggagctgttcccctctaacccccacccccacccccc atgcacaagactttgtccattcattaaagttatgtaaaacagcaaatttt...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Construct a control targeting vector using the H11 site of the mouse genome as the target insertion site. The schematic diagram of its element structure is shown in Figure 6 , compared with the targeting vector of Example 1, the difference is that the sequences of the homology arms at both ends are different.
[0157] The construction method of the control targeting vector is as follows:
[0158] 1. Preparation of carrier skeleton: PMD18T-H11-CAG-FLPo (provided by Jiangsu Jicui Yaokang Biotechnology Co., Ltd., see Figure 19 ) as a template, using the primers in Table 13 to amplify and obtain a fragment of 4965bp and recover it, digest the product with BglII, and use it as a backbone carrier for future use.
[0159] Table 13. Backbone Vector Amplification Primers
[0160]
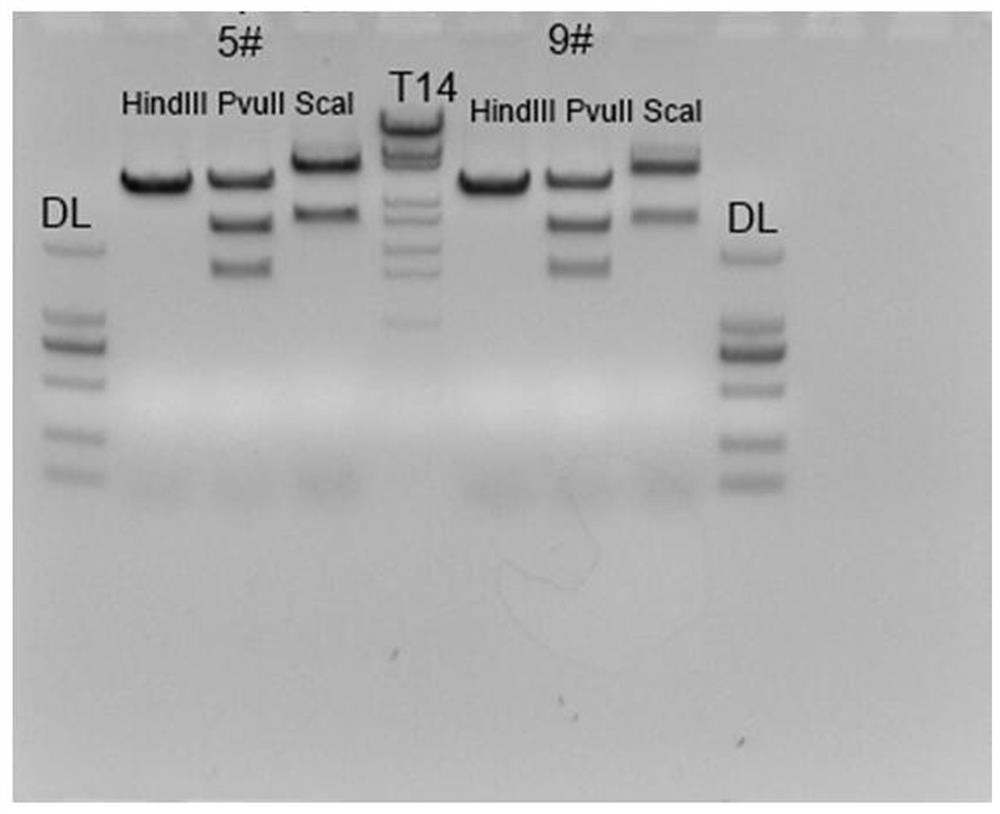
[0161] 2 Digest the correctly sequenced targeting vector of Example 1 with BamHI, the fragment sizes after digestion are 5851bp and 5159bp, and recover the 5851bp fragment.
[0162] 3. Use T4 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com