Optical structure for improving photoelectric conversion efficiency of silicon carbide photoconductive switch
A technology of photoelectric conversion efficiency and photoconductive switching, which is applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing the optical distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
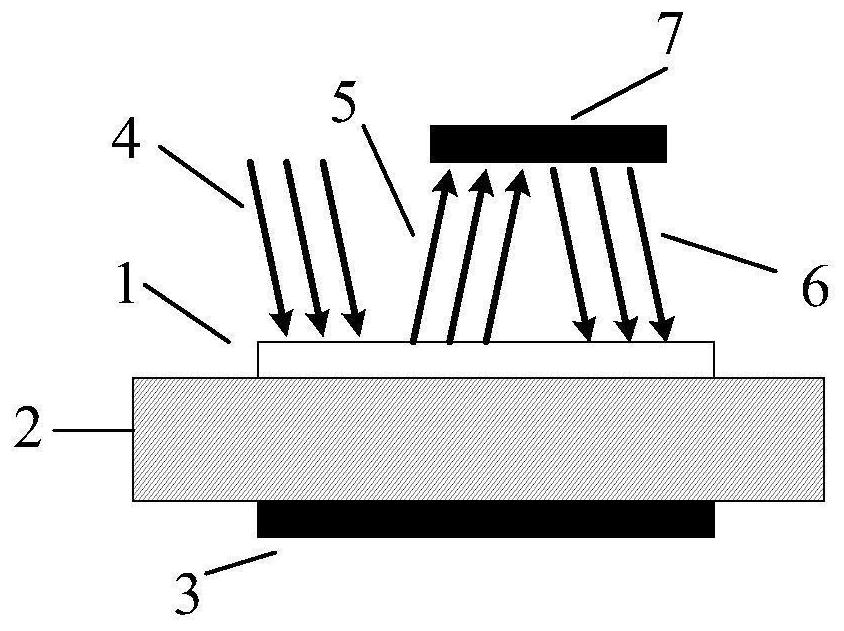
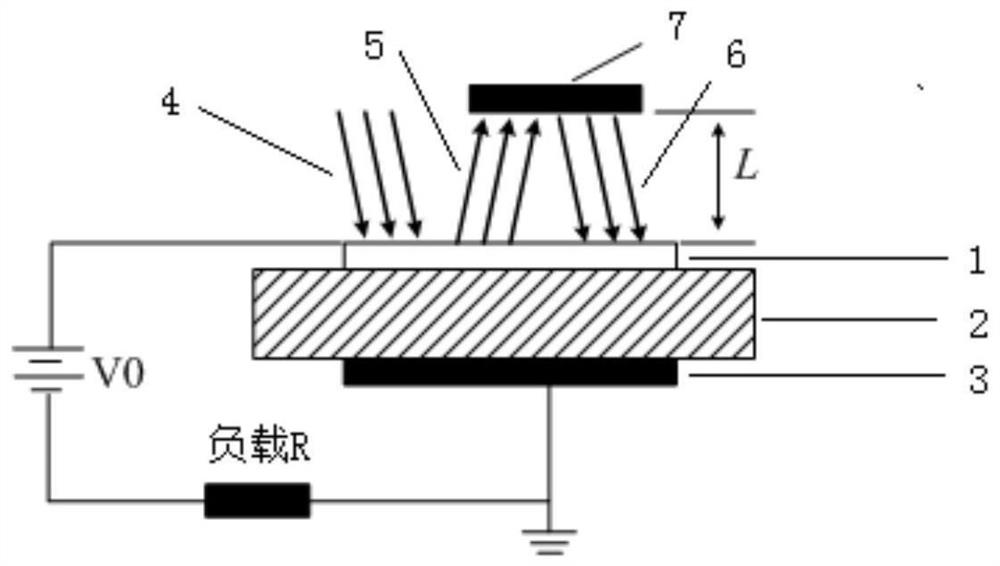
[0029] refer to figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides an optical structure for improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of a silicon carbide photoconductive switch, including: a silicon carbide photoconductive switch and a reflective structure 7; the silicon carbide photoconductive switch includes a transparent electrode 1 and a SiC material substrate 2 , the back-counter electrode 3 ; the transparent electrode 1 , the SiC material substrate 2 , and the back-counter electrode 3 are arranged sequentially from top to bottom; the reflective structure is located above the transparent electrode 1 .
[0030] Described reflective structure 7 is a kind of in metal film reflector, dielectric film reflector; Can adopt the reflector of the quartz substrate of metallized aluminum film, metal aluminum reflective film is easy to accomplish 90% to 532nm laser reflectivity; Can also The precious metal silver coating is used, and its reflectivity exceeds 95%; while the dielectri...
Embodiment 2
[0038] refer to Figure 4 As shown, according to the optical structure for improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the silicon carbide photoconductive switch described in Embodiment 1, the reflective structure 7 is also provided with a through-hole structure 8 to form a hollow reflective structure;
[0039] The aperture of the through-hole structure 8 is determined by the beam spot radius of the incident laser 4 and the optical damage threshold of the photoconductive switch material. Studies have shown that the SiC material of the transparent electrode 1 can withstand the peak power of light intensity of 10MW / cm 2 . The radius of the circular light spot in this embodiment is about 1 mm, therefore, the aperture used in the experiment of this embodiment is 1 mm; the thickness of the reflective structure 7 should be made thin enough to prevent the light beam from being incident on the surface of the light guide switch. The experiment of this embodiment uses The ref...
Embodiment 3
[0045] refer to Figure 6 As shown, according to the optical structure for improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the silicon carbide photoconductive switch described in the second embodiment, the through-hole structure 8 of the hollow reflection structure is provided with an optical fiber 9 to form an optical fiber fed into the hollow reflection structure. The optical fiber 9 is selected according to the actual application, and it is necessary to select an optical fiber capable of accommodating the pulse peak of the incident laser 4 without being damaged. In this embodiment, a multimode optical fiber is used, and the core diameter of the optical fiber is >100 um.
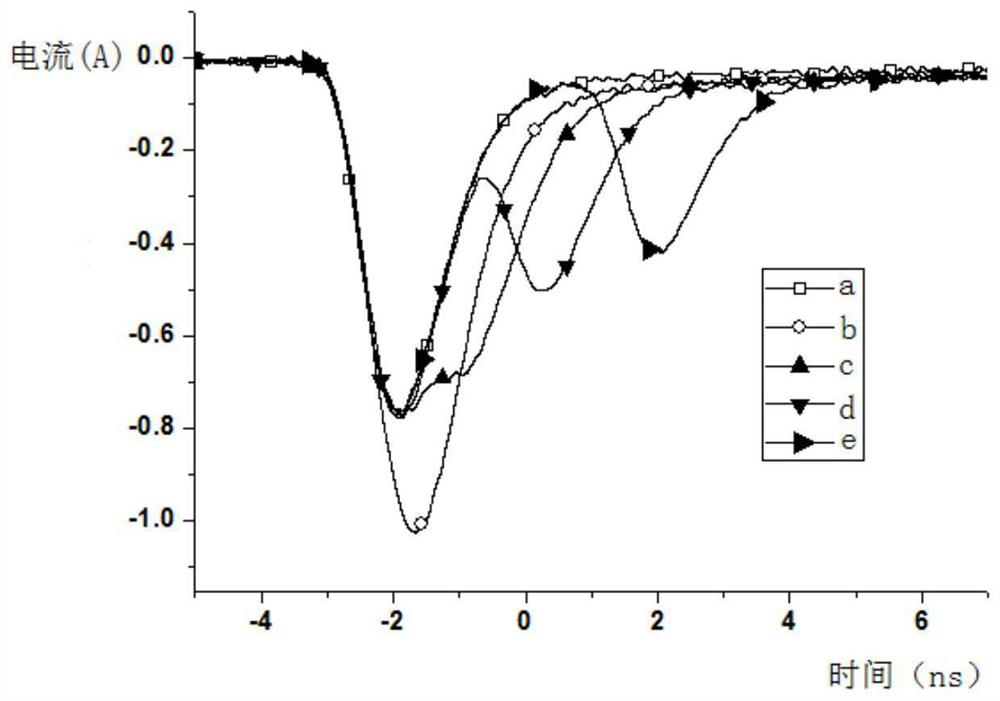
[0046] The specific working principle of the optical structure used to improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the silicon carbide photoconductive switch is:
[0047] The optical fiber 9 passes through the through-hole structure 8, irradiates the high-power laser pulse to the transparent el...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com