Patents
Literature
137 results about "Photoconductive switch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
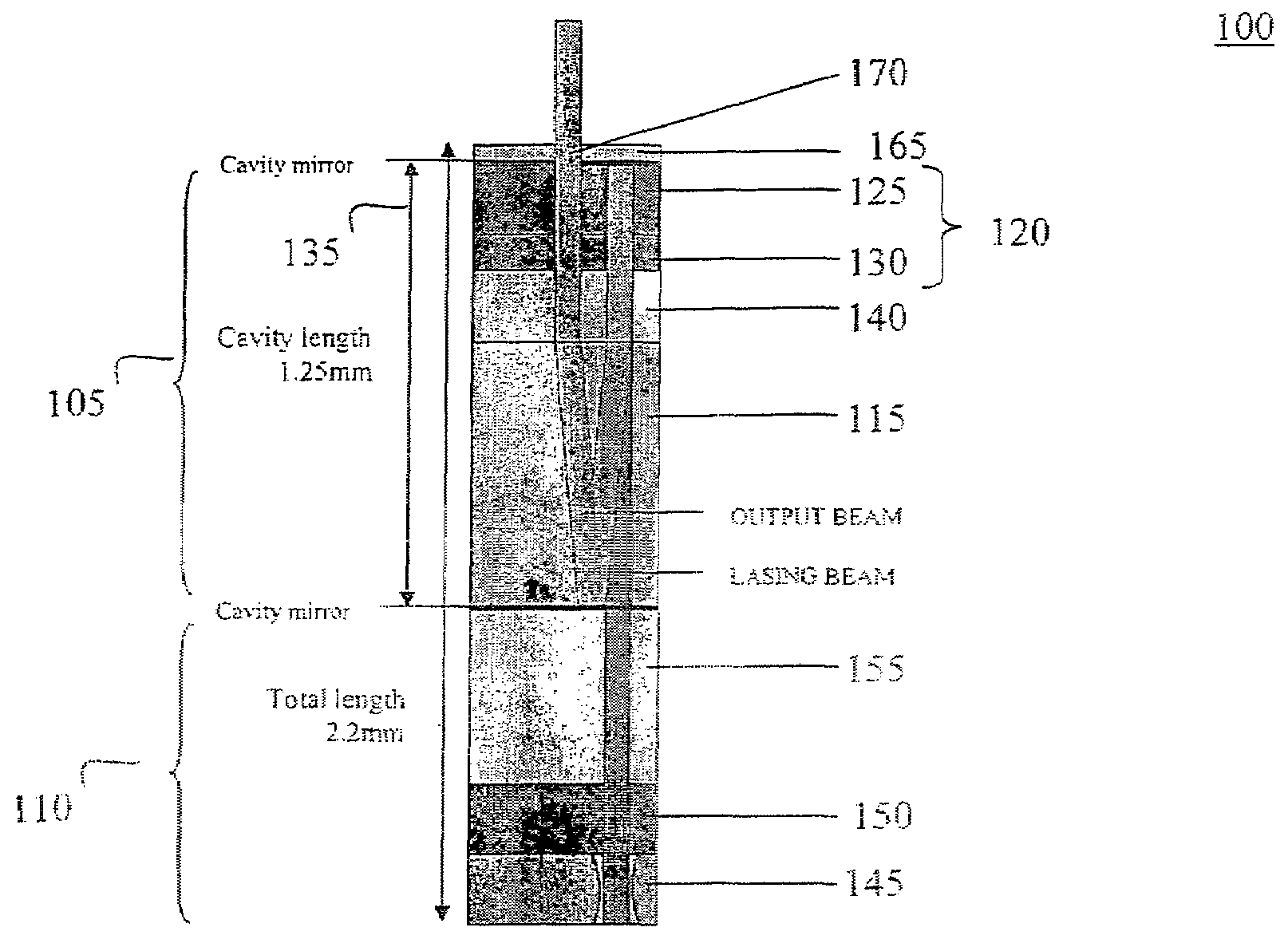
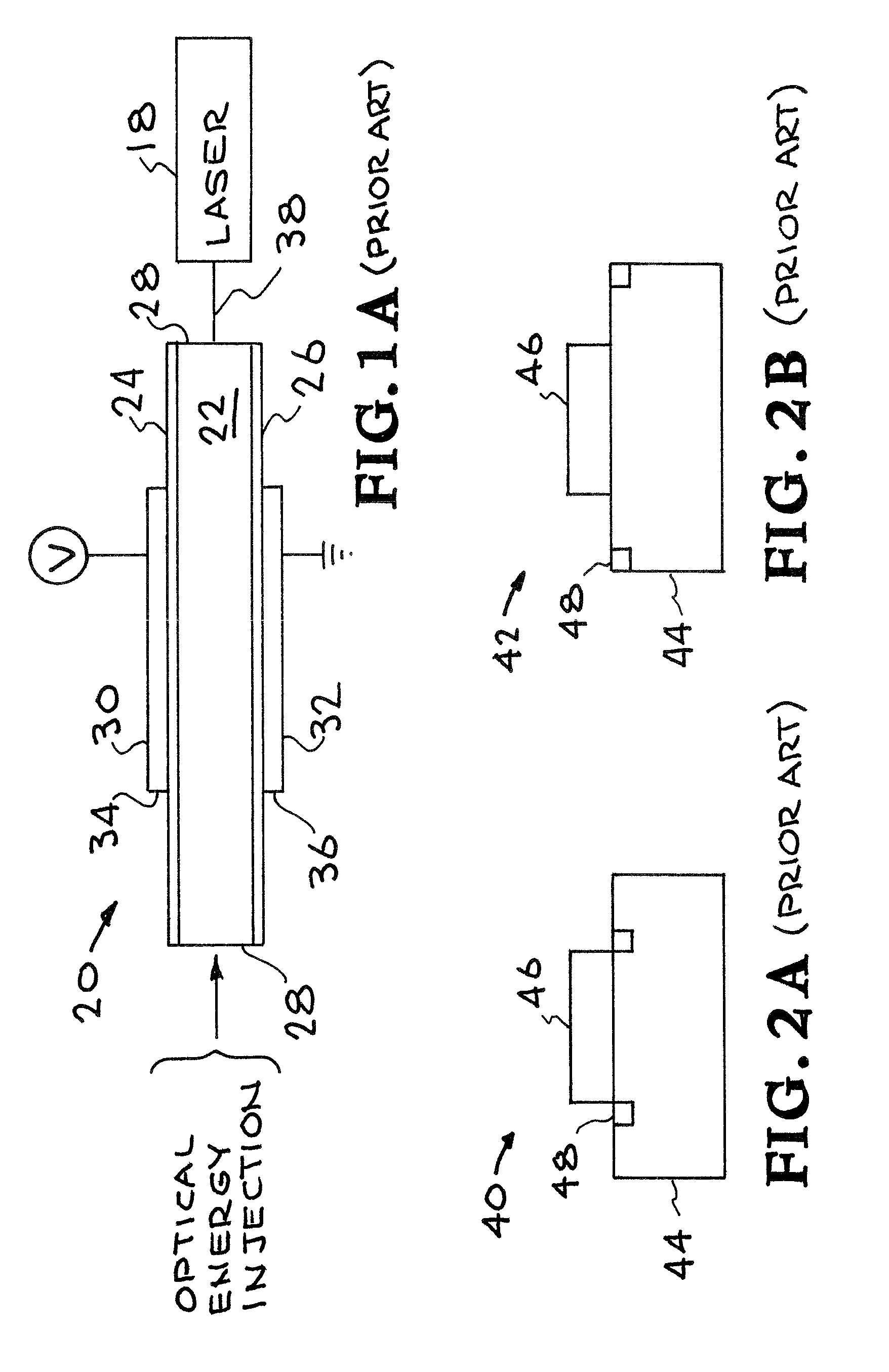
Optically initiated silicon carbide high voltage switch
InactiveUS20070092812A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectric fieldPhotoconductive switch
An improved photoconductive switch having a SiC or other wide band gap substrate material, such as GaAs and field-grading liners composed of preferably SiN formed on the substrate adjacent the electrode perimeters or adjacent the substrate perimeters for grading the electric fields.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
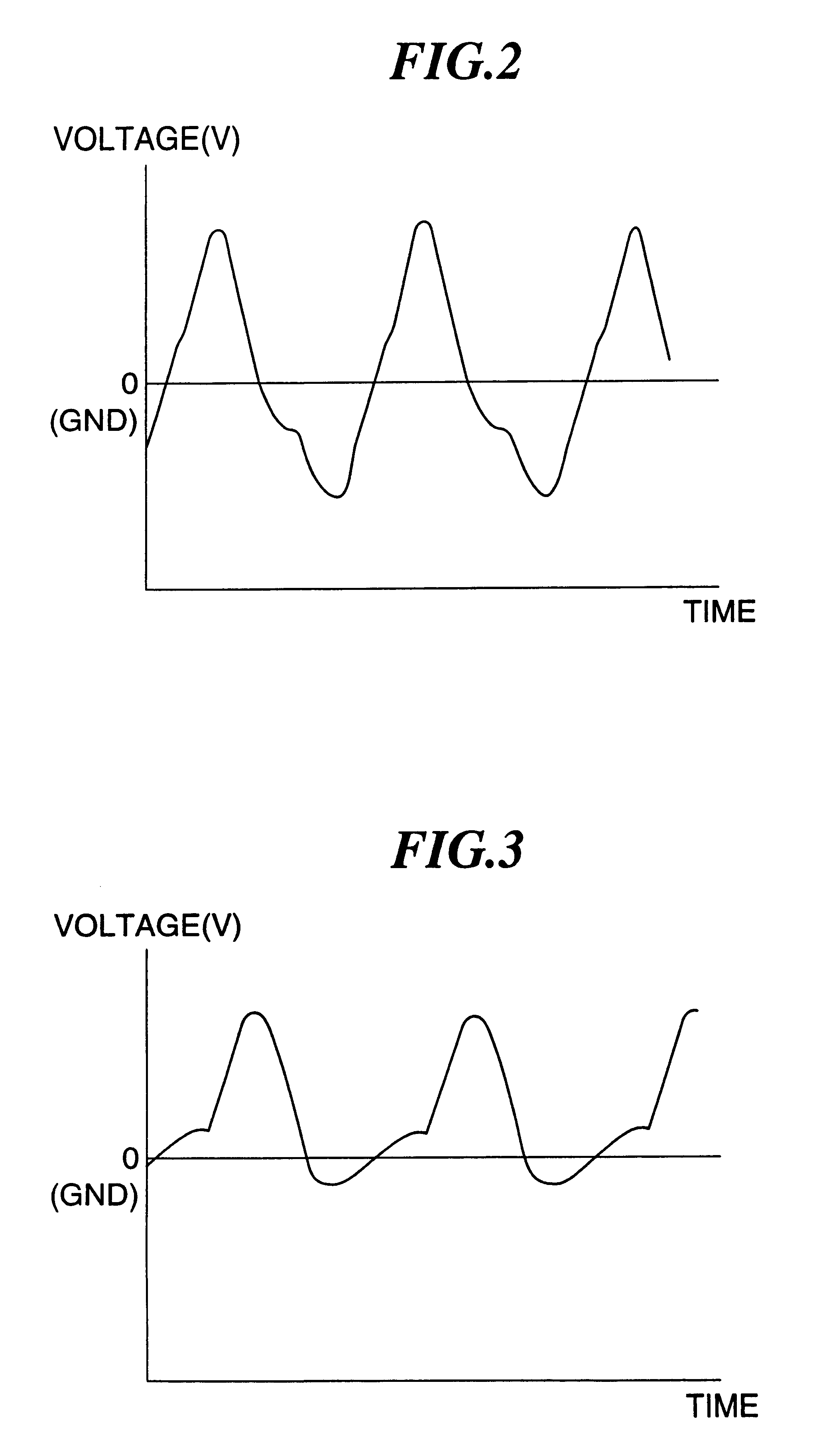
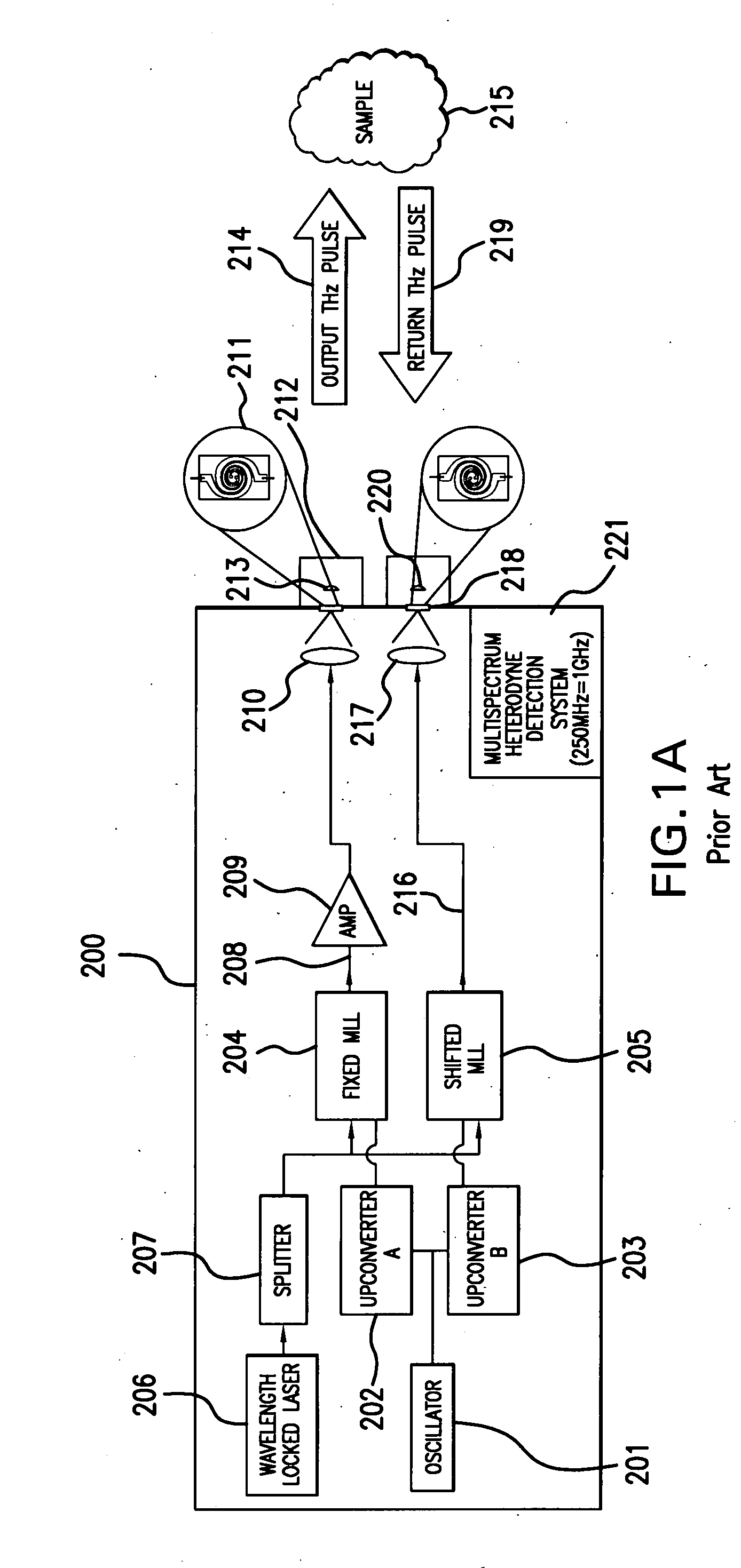
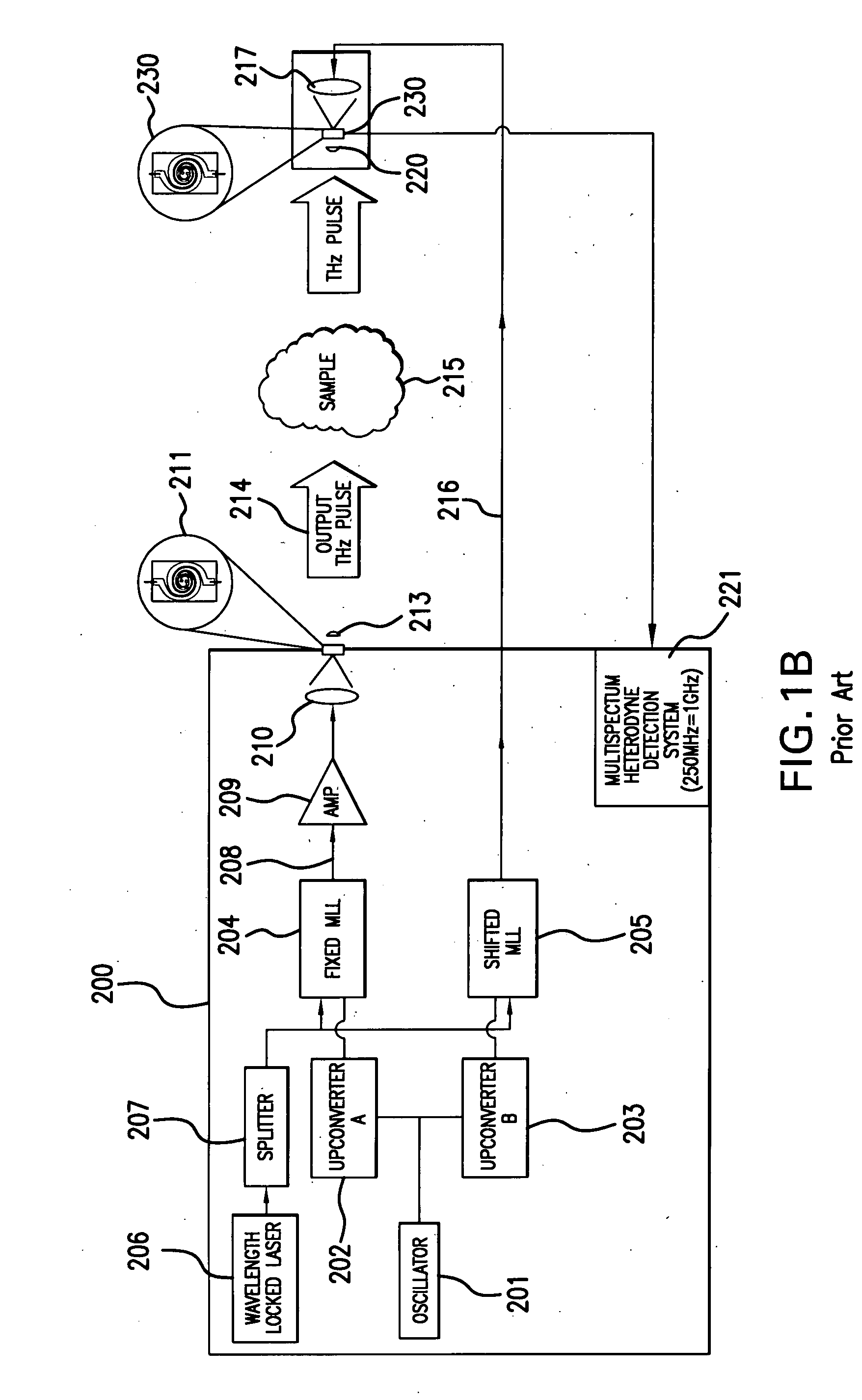
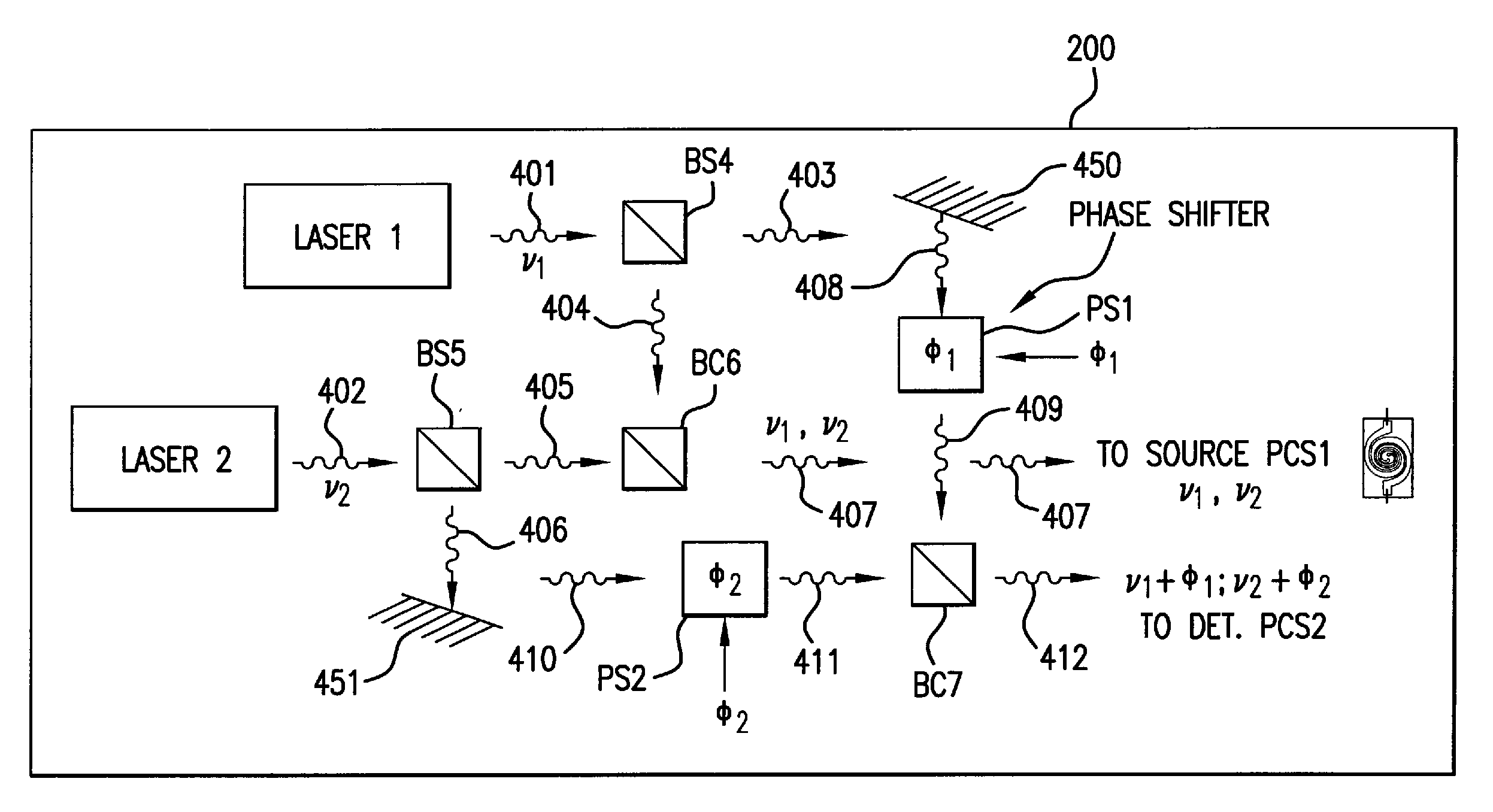
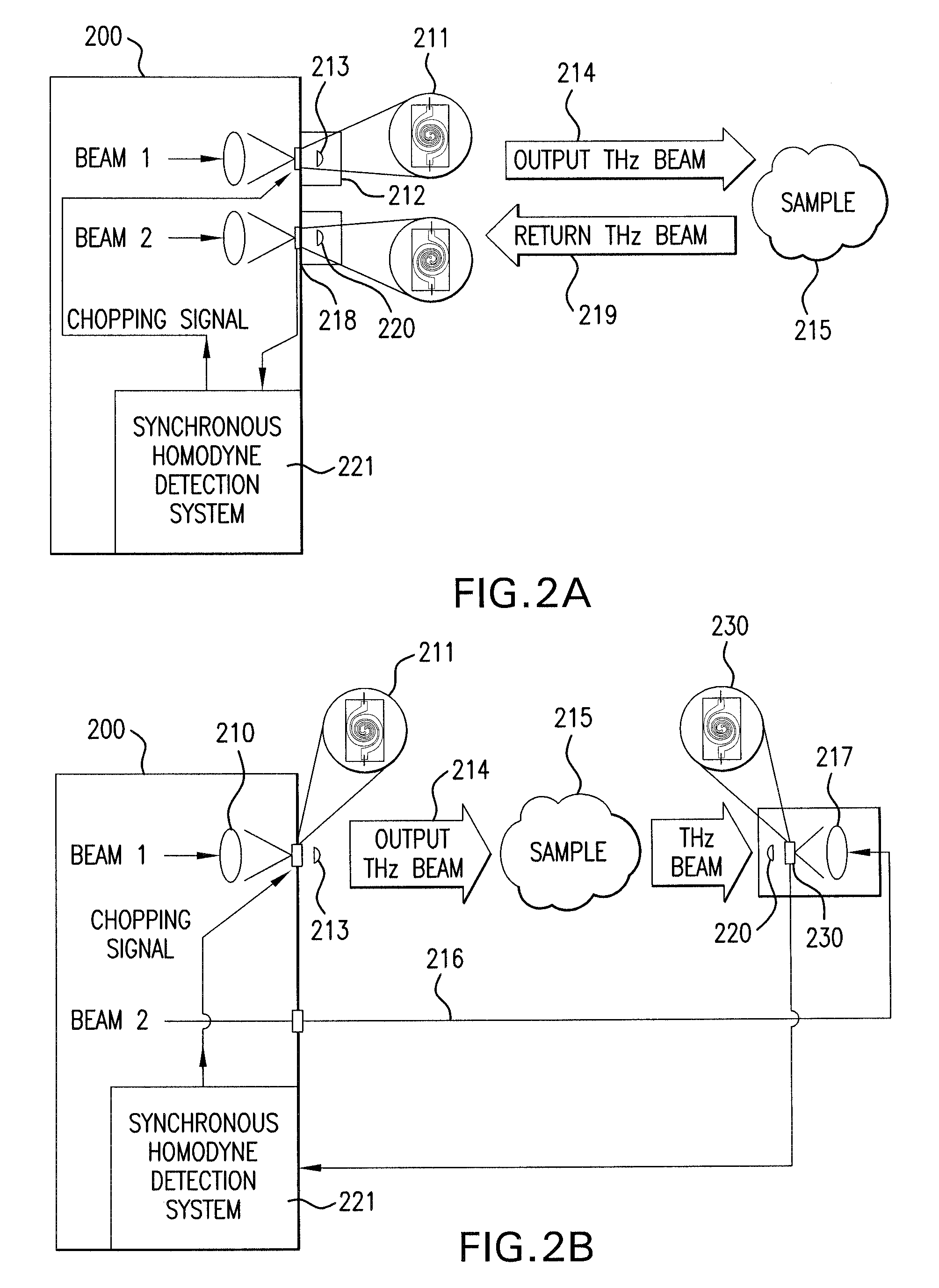
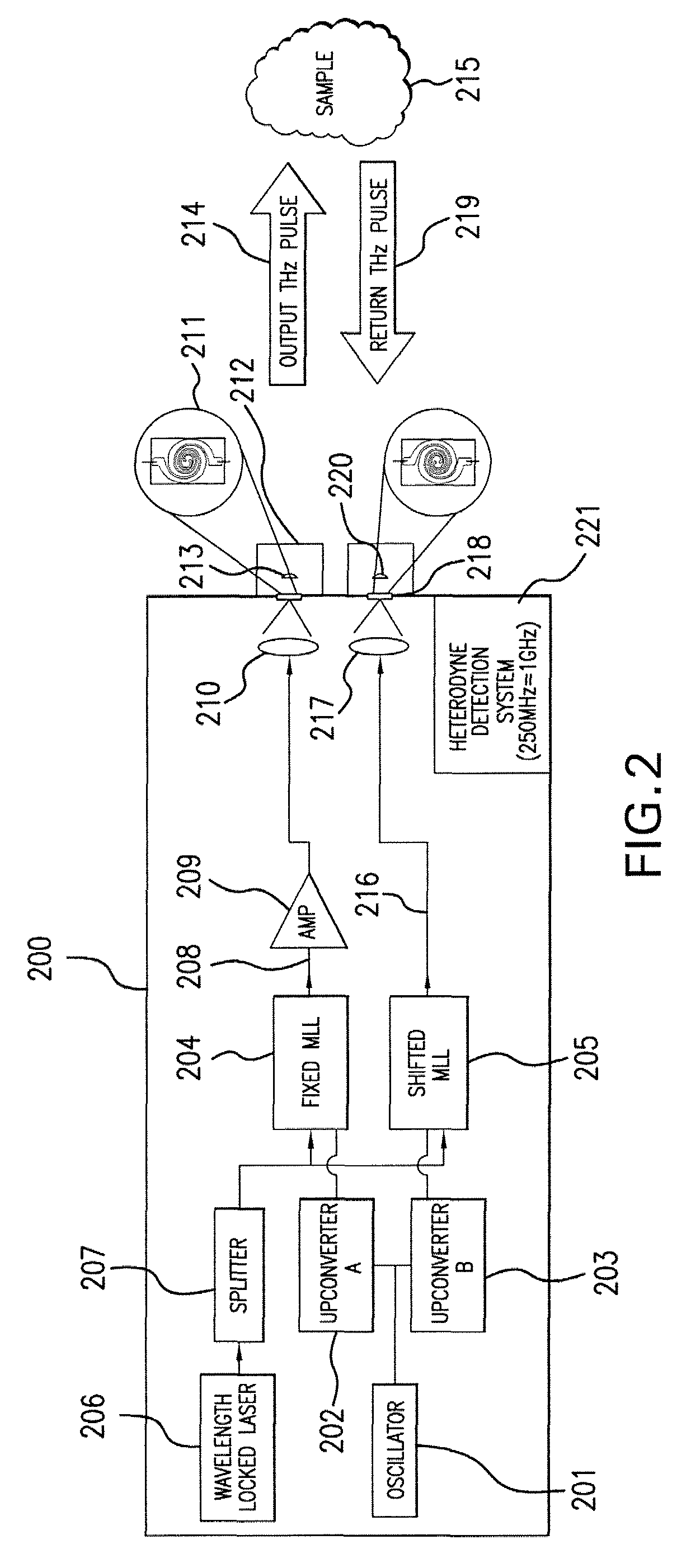
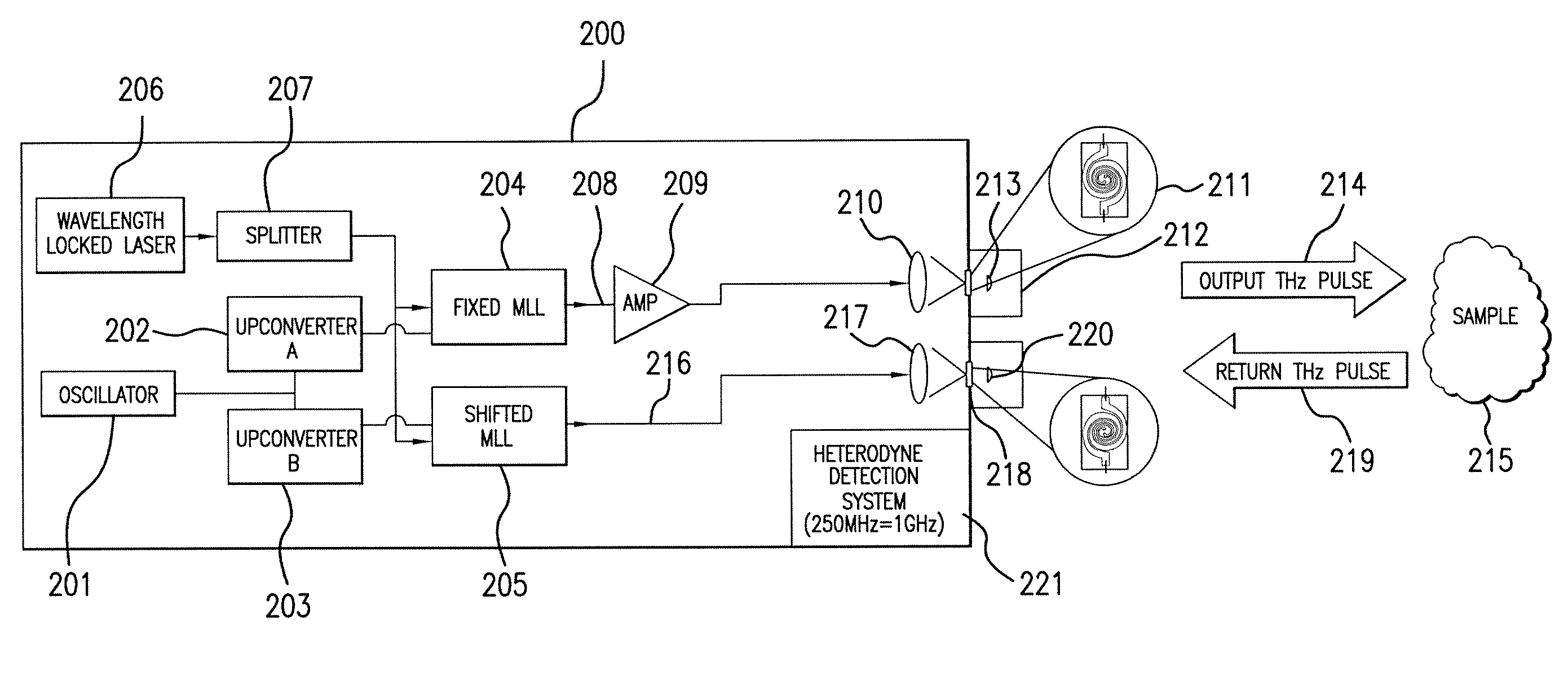
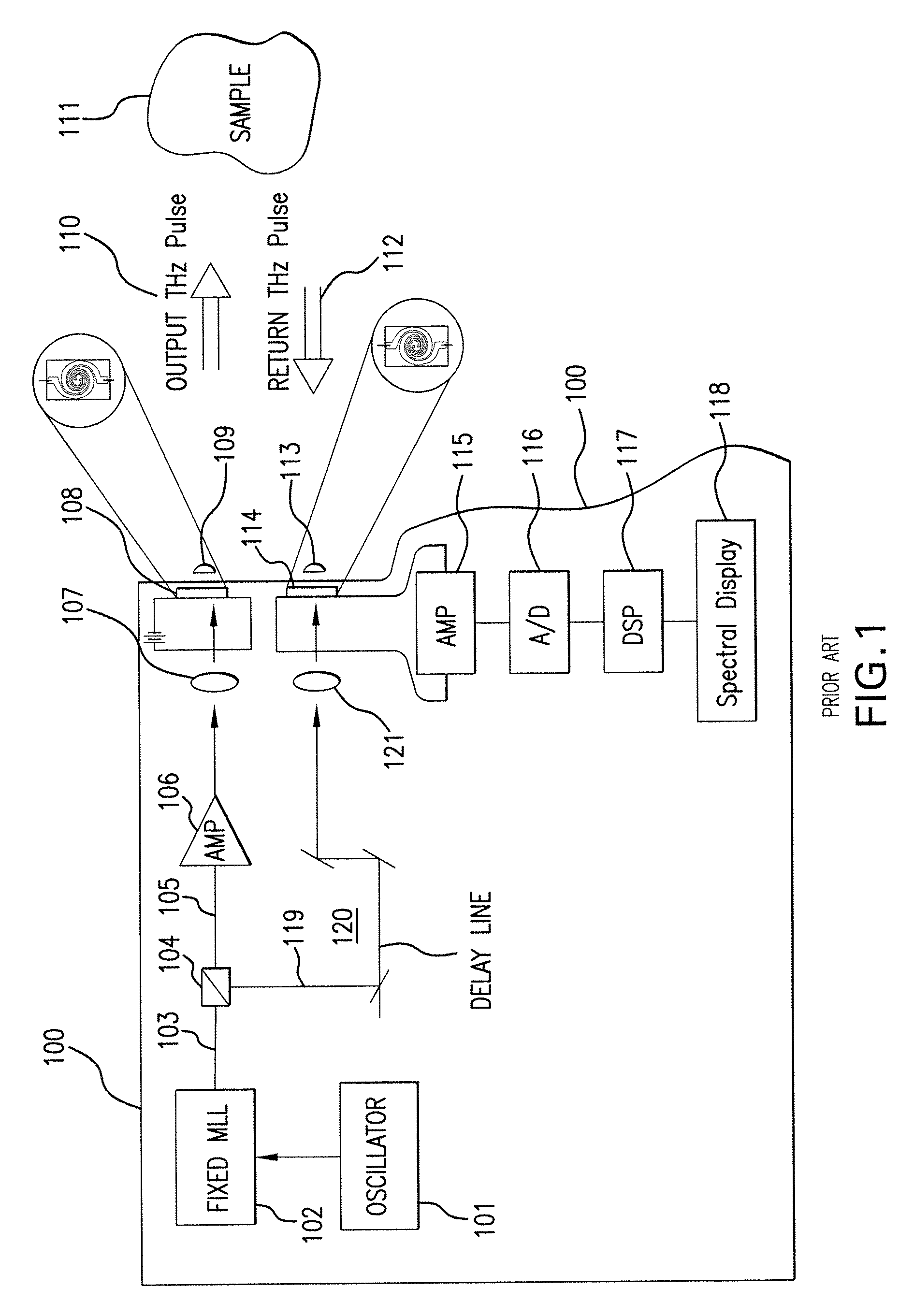
Terahertz Frequency Domain Spectrometer with Controllable Phase Shift
InactiveUS20090283680A1High resolutionHigh detection sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase shiftedPhase difference
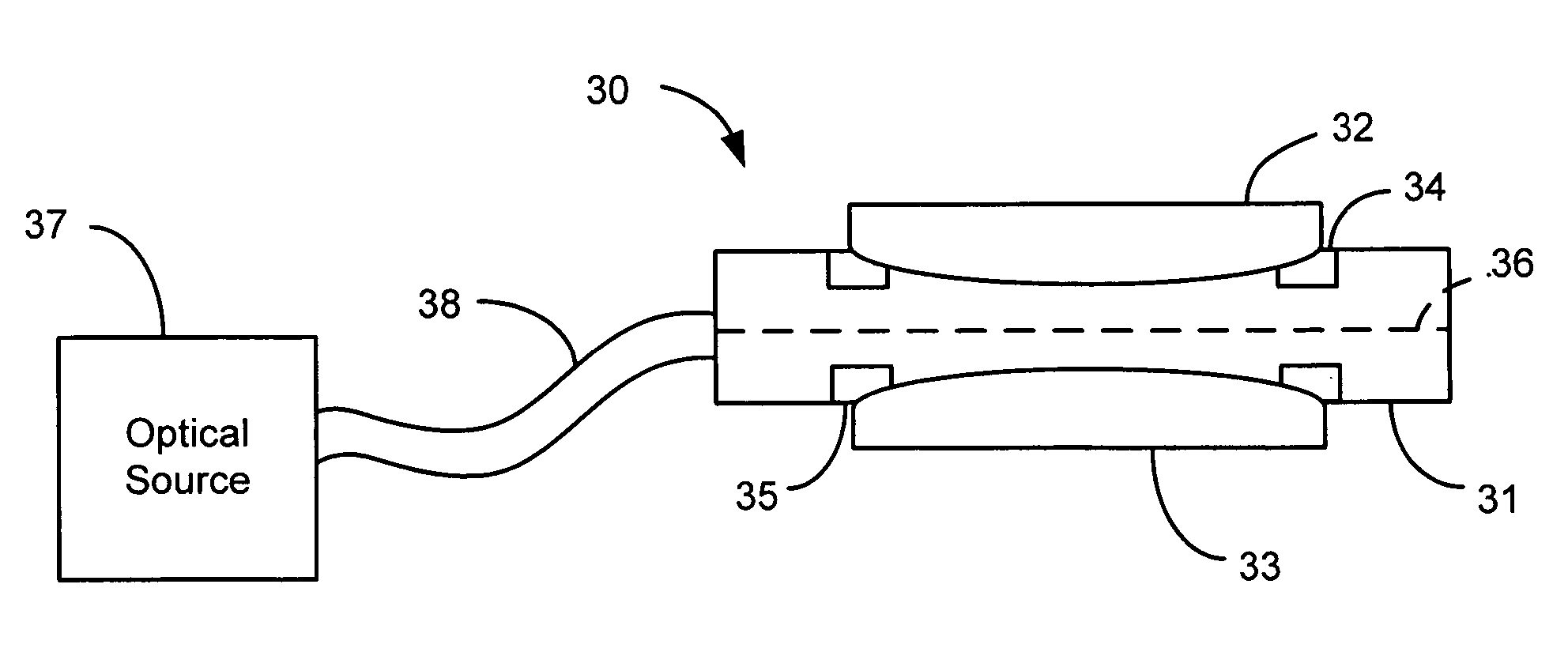
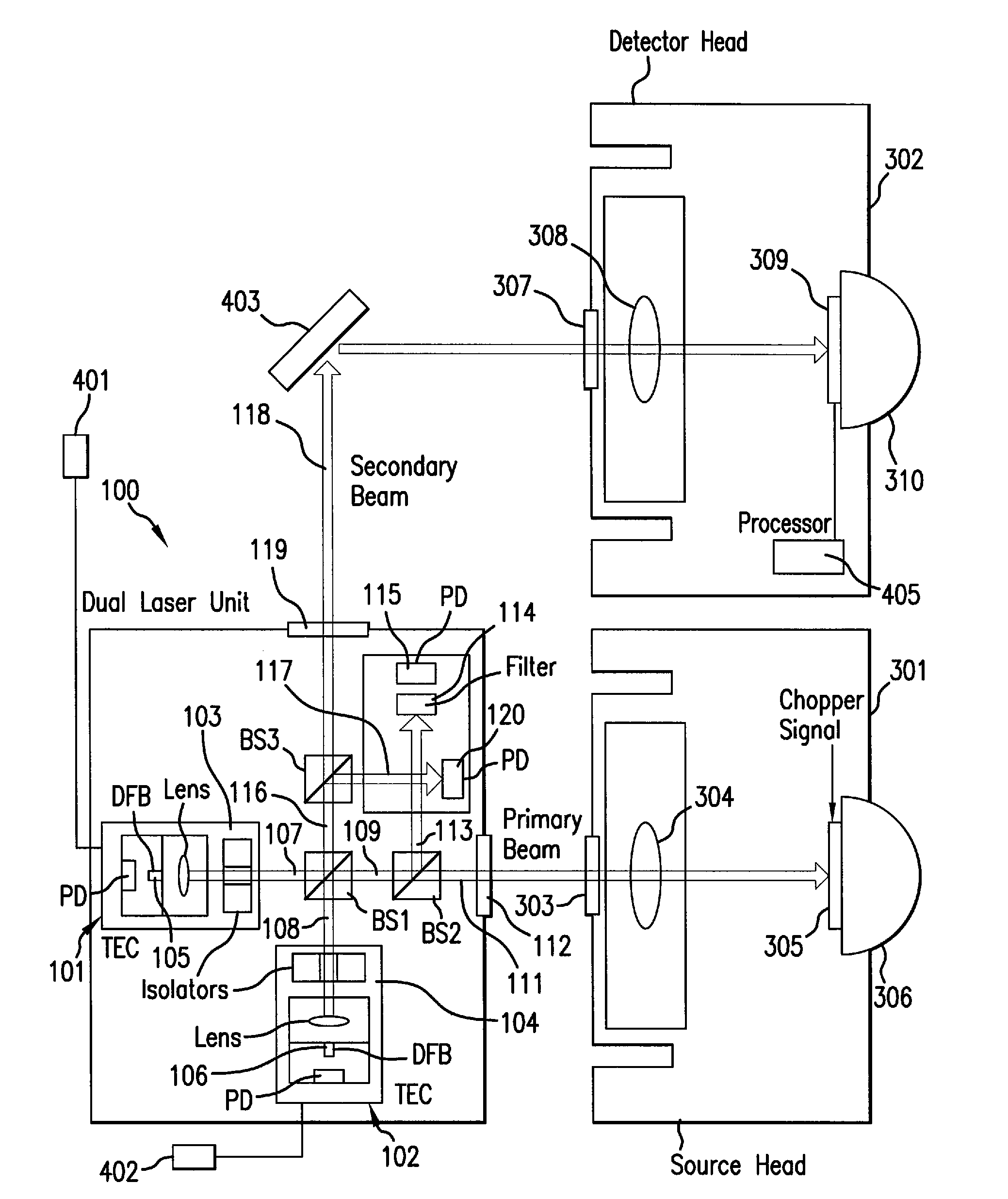
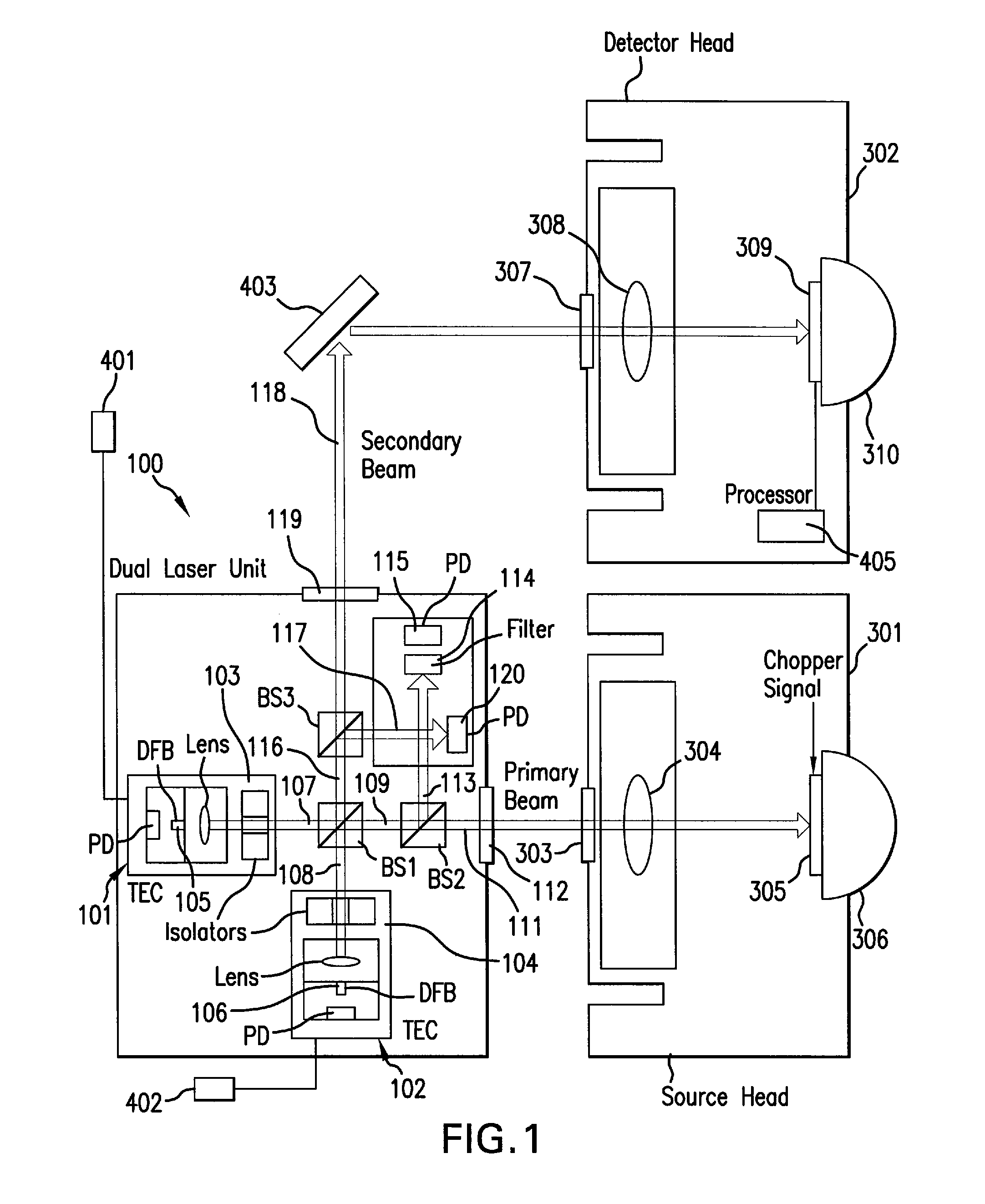
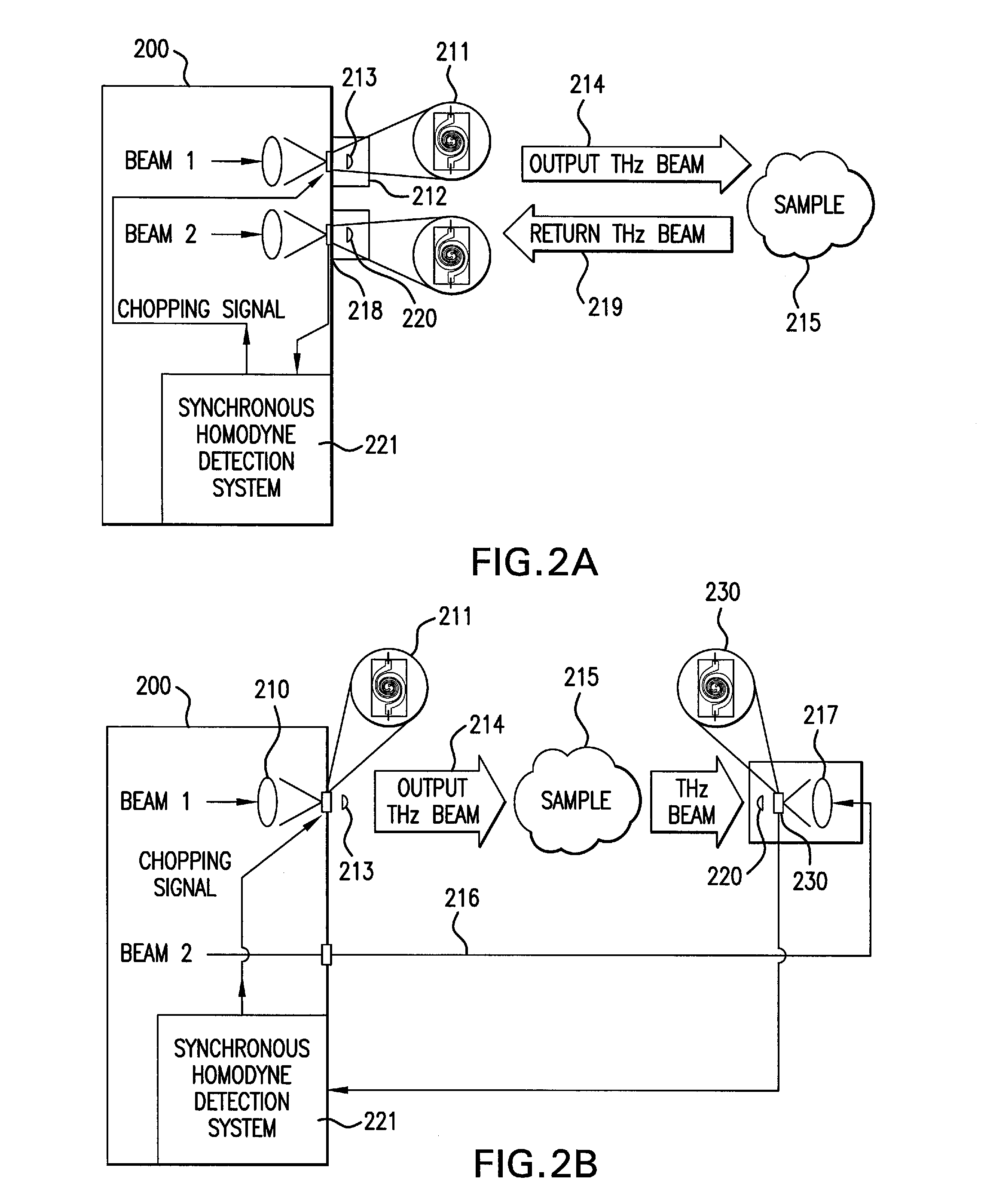
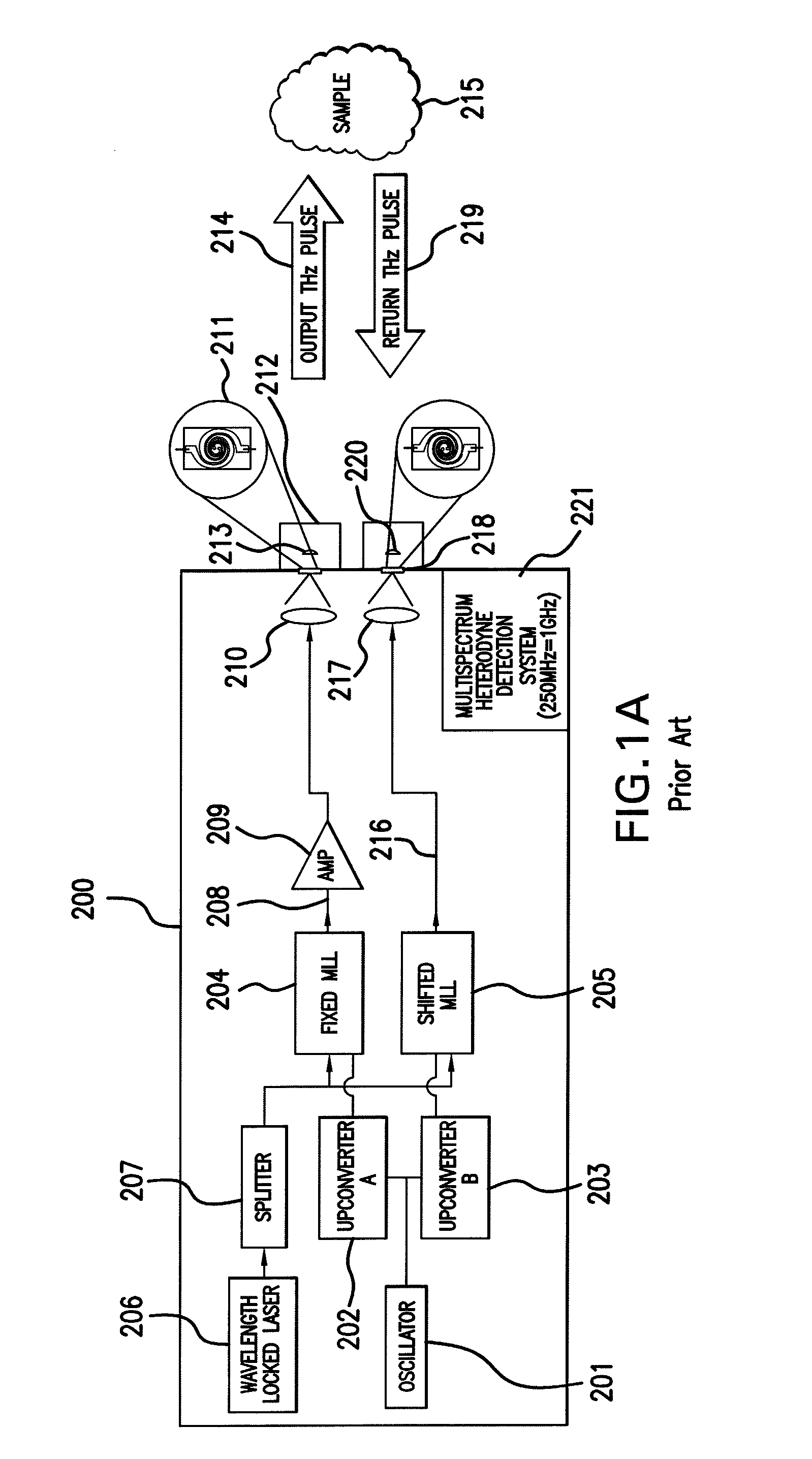
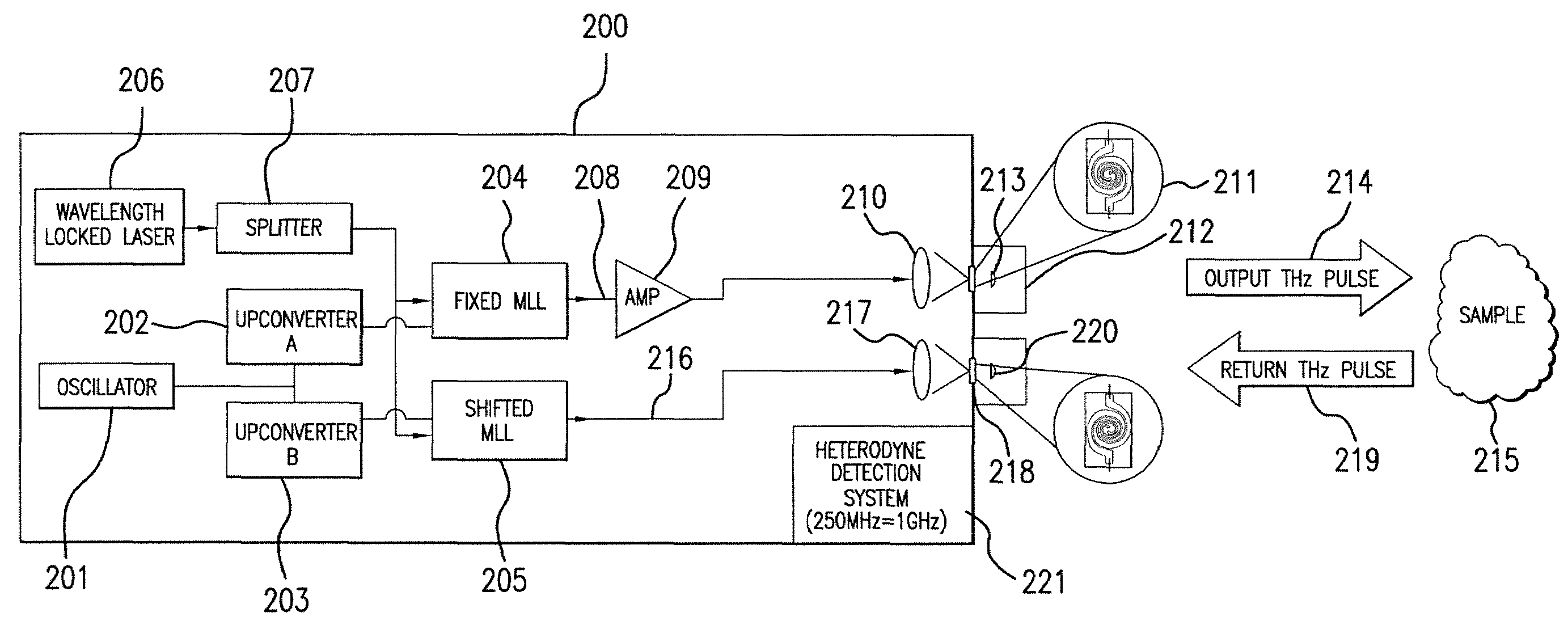
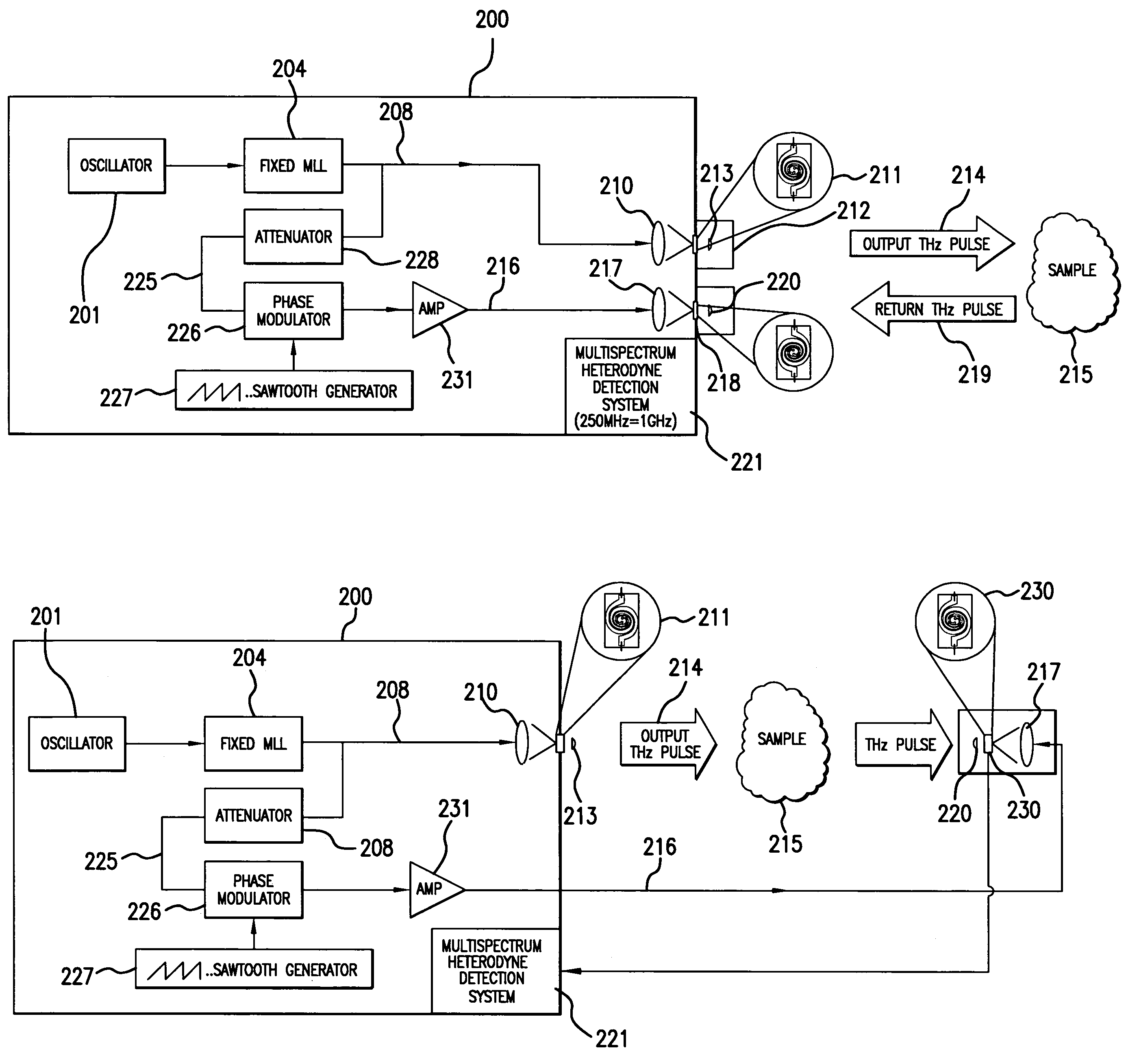
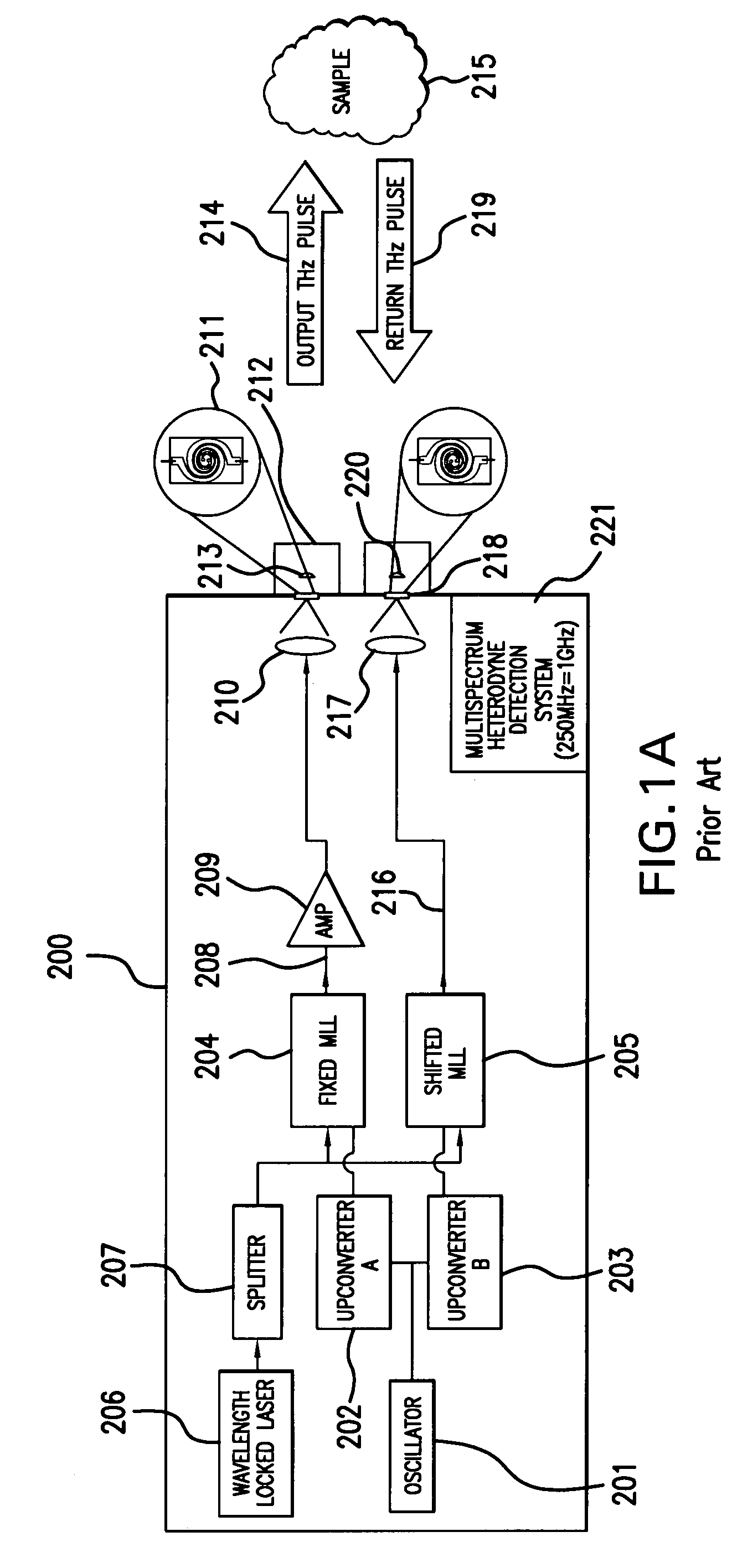
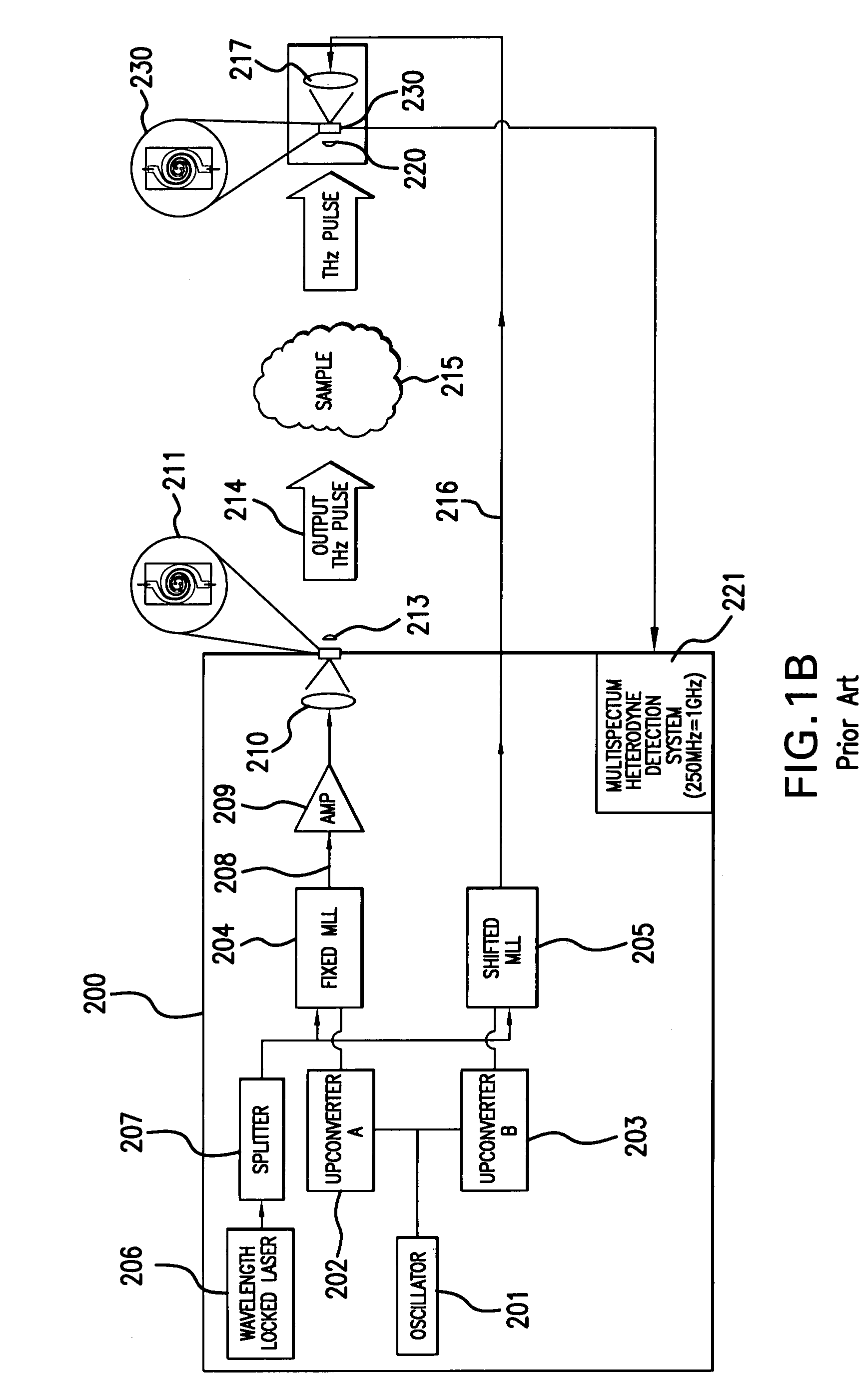
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an target including an integrated dual laser module coupled to a pair of photoconductive switches to produce cw signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on and transmitted through or reflected from the target; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals received from the target and using a multi-spectral homodyne process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the target with resolution less than 250 MHz. The photoconductive switches are activated by laser beams from the dual laser module. The lasers in the module are tuned to different frequencies and a phase shifter in the path of one beam allows the beams to have an adjustable phase difference.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
Photoconductive switching element, device using it, and apparatus, recording apparatus, and recording method in which the device is incorporated
InactiveUS6600473B1Photomechanical apparatusCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
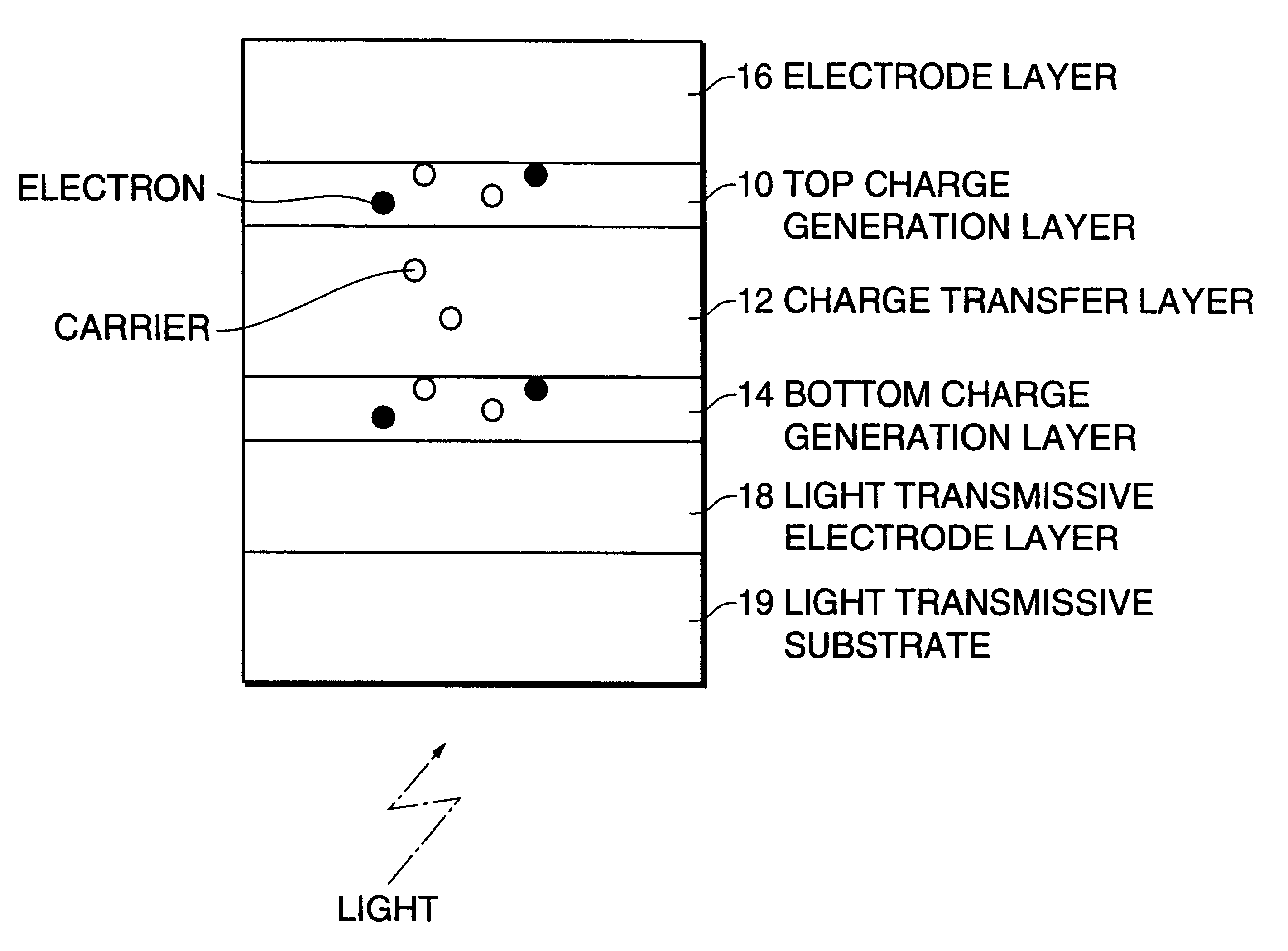
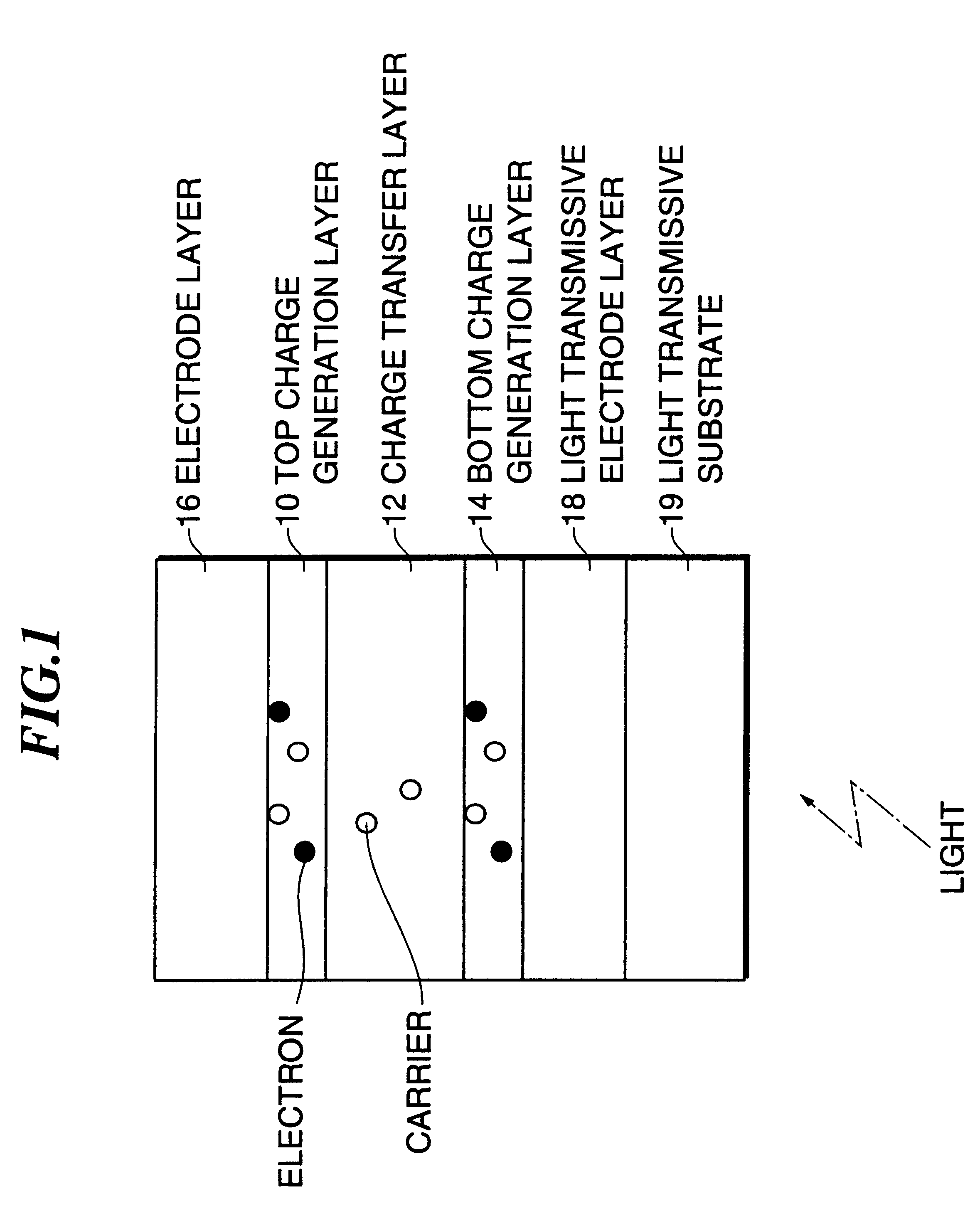
The invention provides a photoconductive switching element used for light switching of a functional element driven by an AC electric field or AC current which are highly functional and inexpensive and provides a device in which such a photoconductive switching element and a functional element such as a liquid display element are combined and incorporated, and an apparatus, a recording apparatus, and a recording method which are provided with the above-mentioned device. The photoconductive switching element has at least a light transmissible electrode layer, a charge generation layer, a charge transfer layer, and a charge generation layer laminated in this order on a light transmissible substrate. The photoconductive switching element is combined with a functional element to form a device of the present invention, and the device is incorporated in an apparatus or a recording apparatus to fabricate an apparatus or a recording apparatus respectively of the present invention. In the recording method of the present invention, such a recording apparatus is used.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
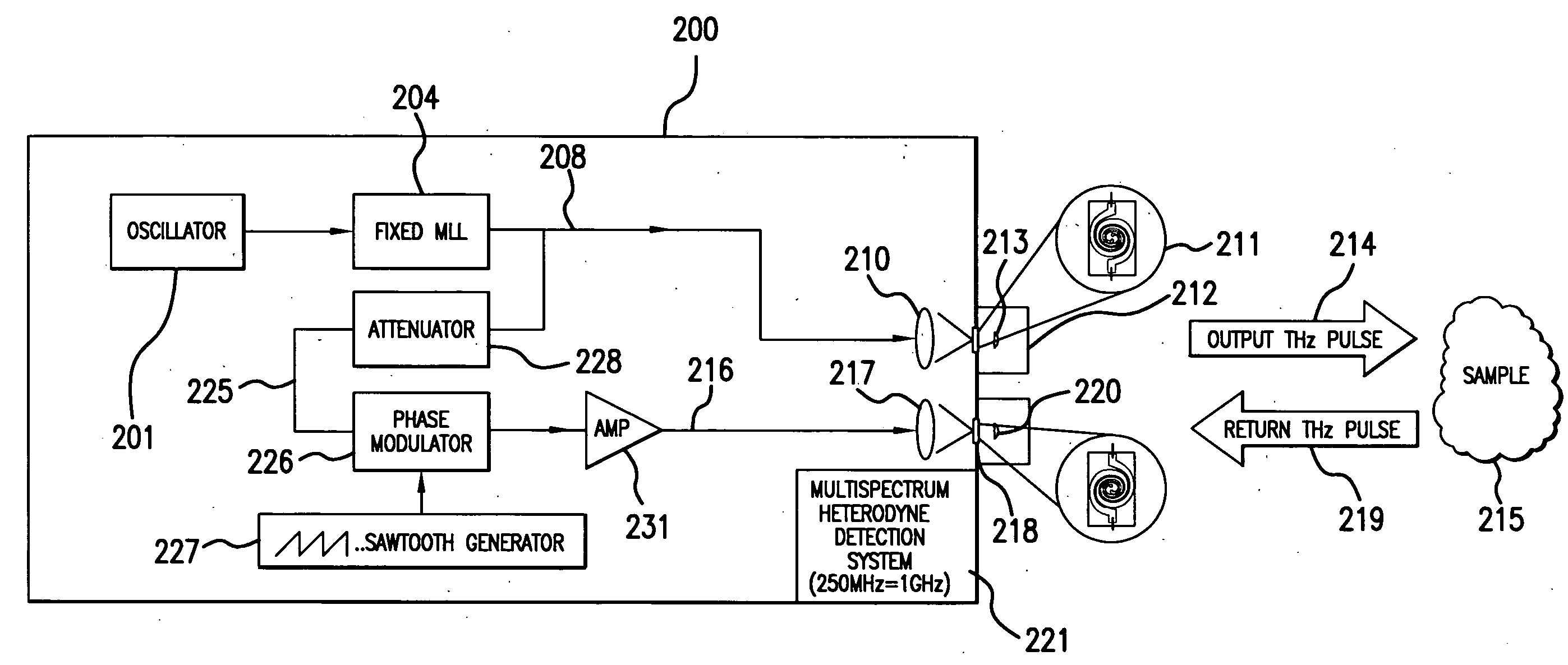
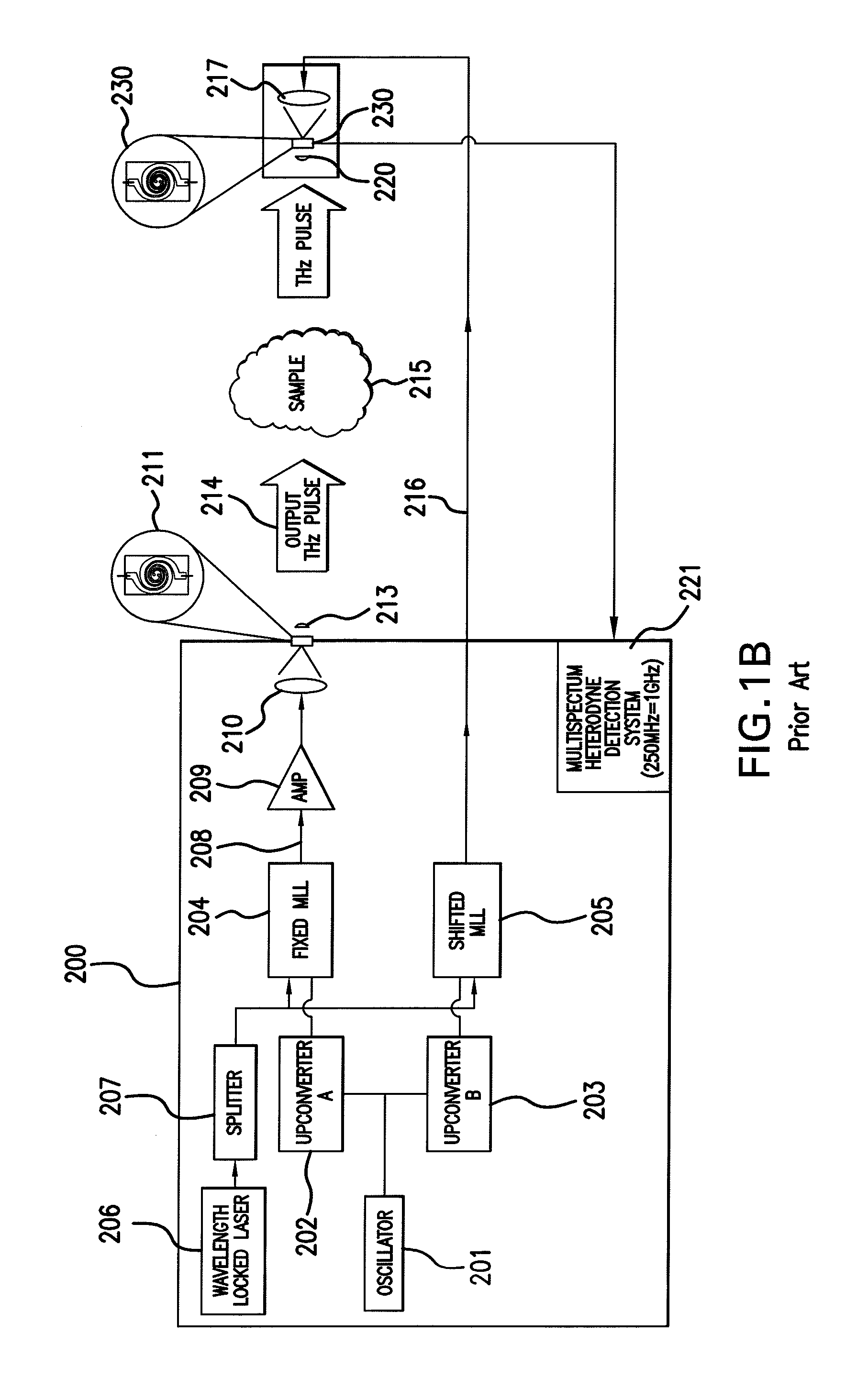
Pulsed terahertz frequency domain spectrometer with single mode-locked laser and dispersive phase modulator
InactiveUS20080179528A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamParticle physics
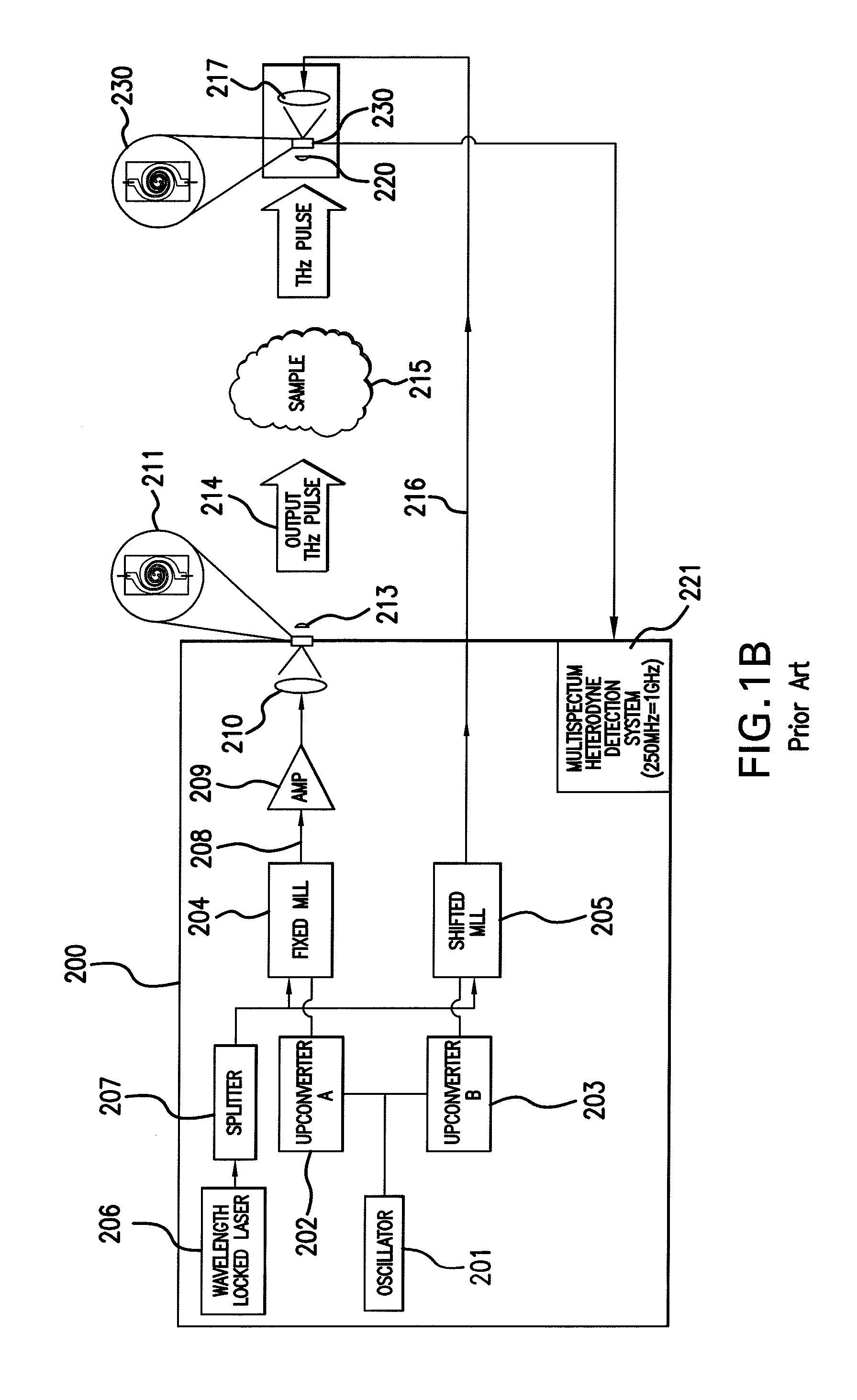
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an target including a source of pulsed signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on or transmitted through the target; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals reflected from the target and using a multi-spectral heterodyning process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the target. The source of pulse signals and the detector are photoconductive switches activated by a pulsed laser beam from a single mode-locked laser.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
Terahertz frequency domain spectrometer with controllable phase shift
InactiveUS7781736B2High resolutionDetection sensitivityRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase shiftedPhase difference
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an target including an integrated dual laser module coupled to a pair of photoconductive switches to produce cw signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on and transmitted through or reflected from the target; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals received from the target and using a multi-spectral homodyne process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the target with resolution less than 250 MHz. The photoconductive switches are activated by laser beams from the dual laser module. The lasers in the module are tuned to different frequencies and a phase shifter in the path of one beam allows the beams to have an adjustable phase difference.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
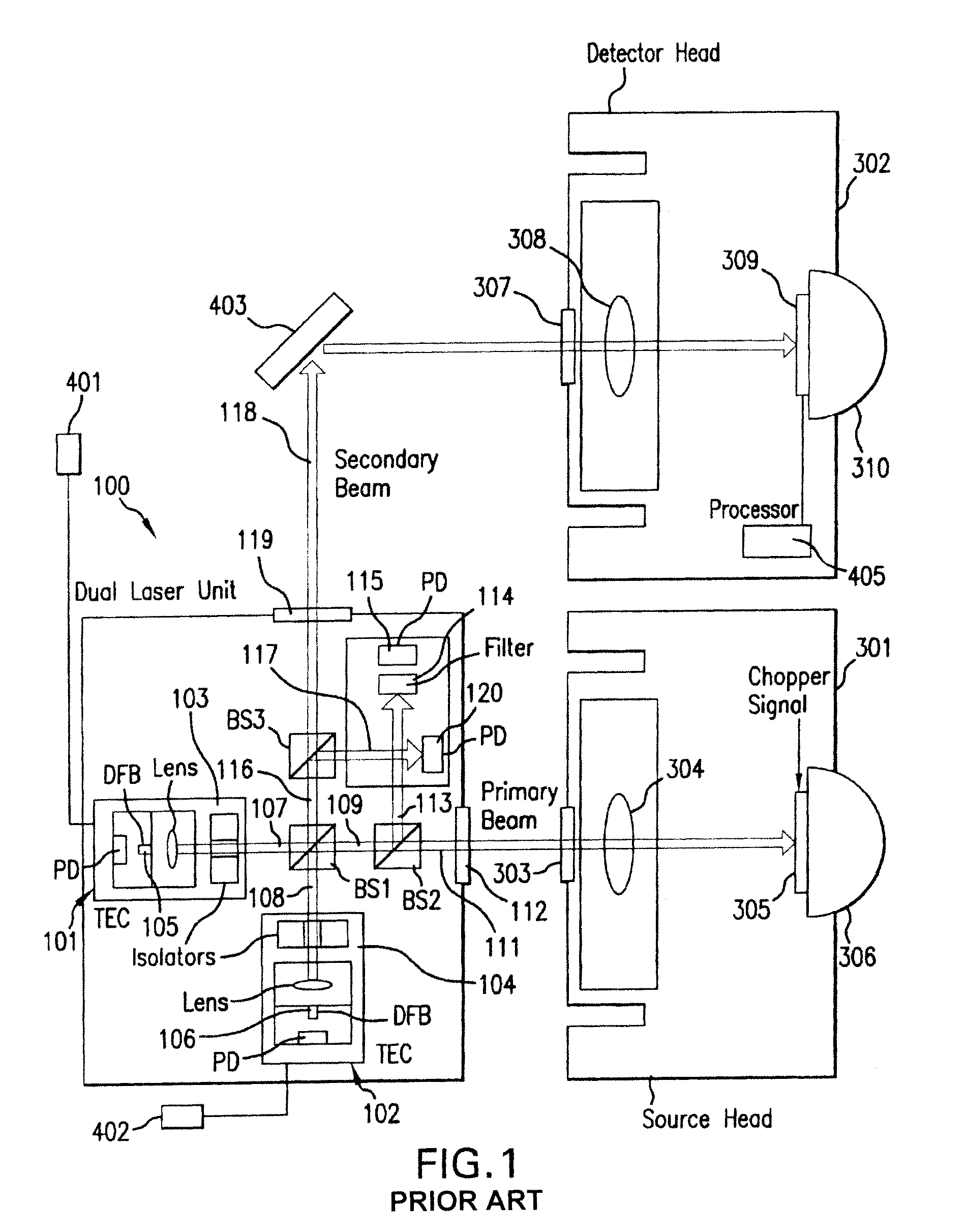
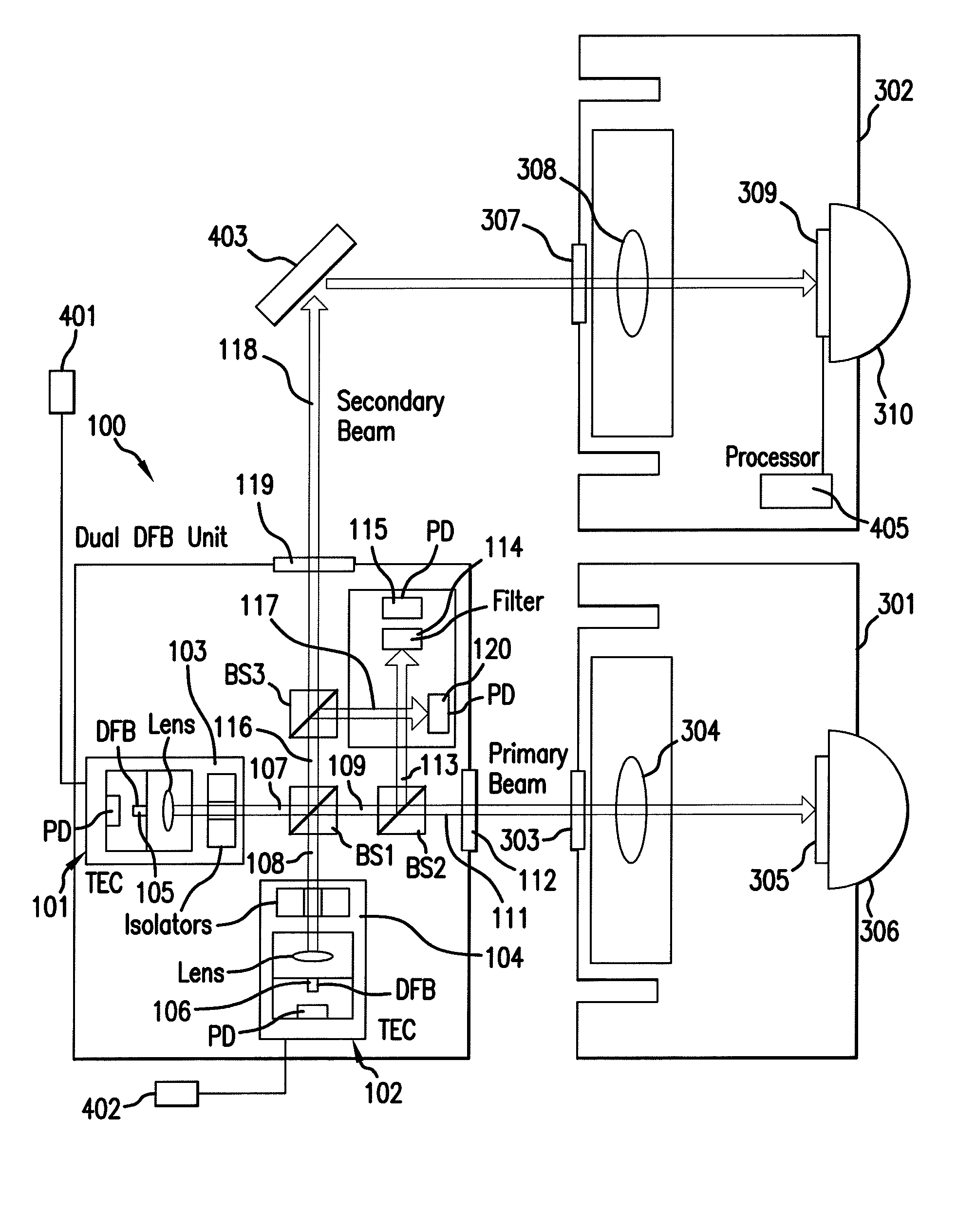
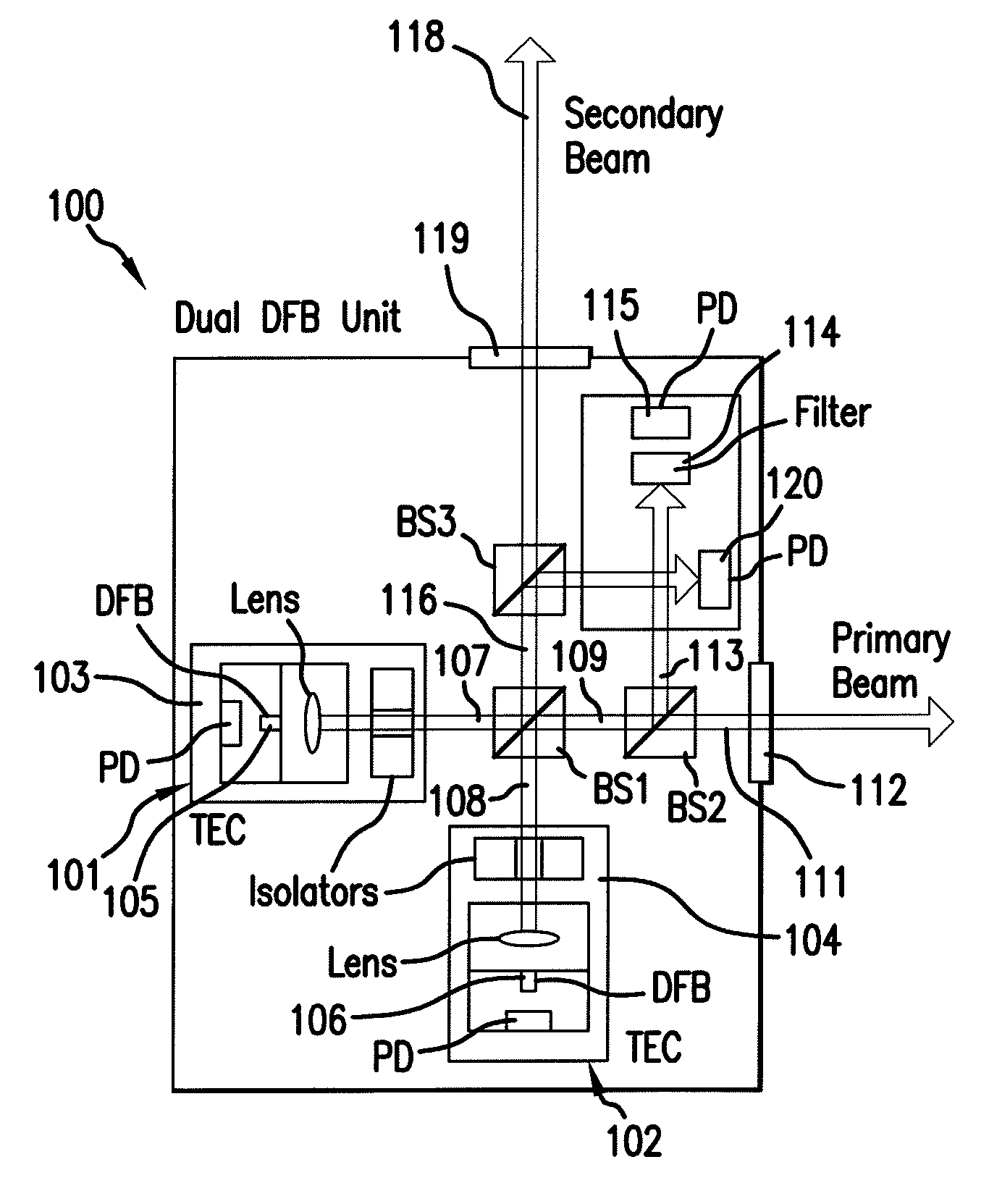
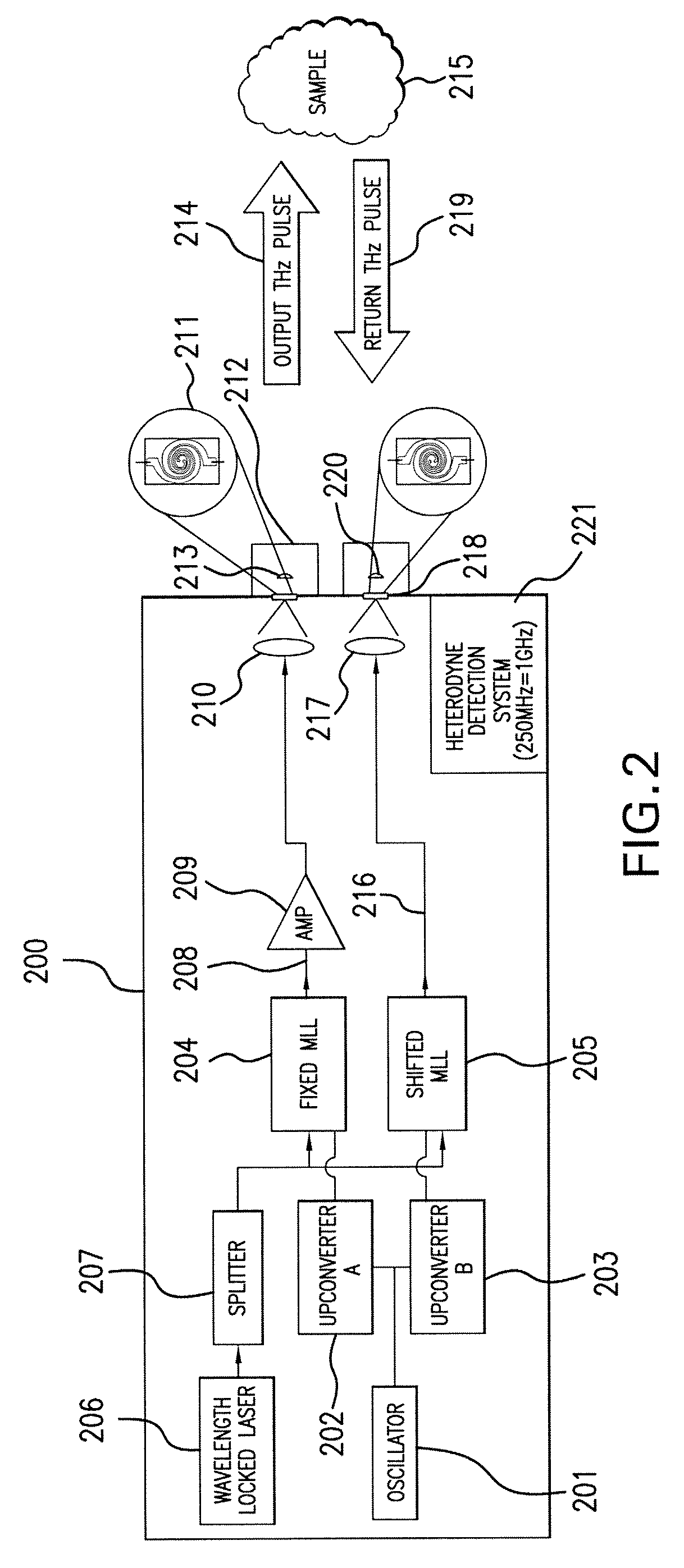
Terahertz Frequency Domain Spectrometer with Integrated Dual Laser Module
InactiveUS20100277726A1High resolutionLow costRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoconductive switchLaser beams
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an target including an integrated dual laser module coupled to a pair of photoconductive switches to produce cw signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on and transmitted through or reflected from the target; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals received from the target and using a multi-spectral homodyne process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the target with resolution less than 250 MHz. The photoconductive switches are activated by laser beams from the dual laser module. The lasers in the module are tuned to different frequencies and have two distinct low frequency identification tones respectively that are used in conjunction with a stable optical filter element to permit precise determination of the offset frequency of the lasers.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
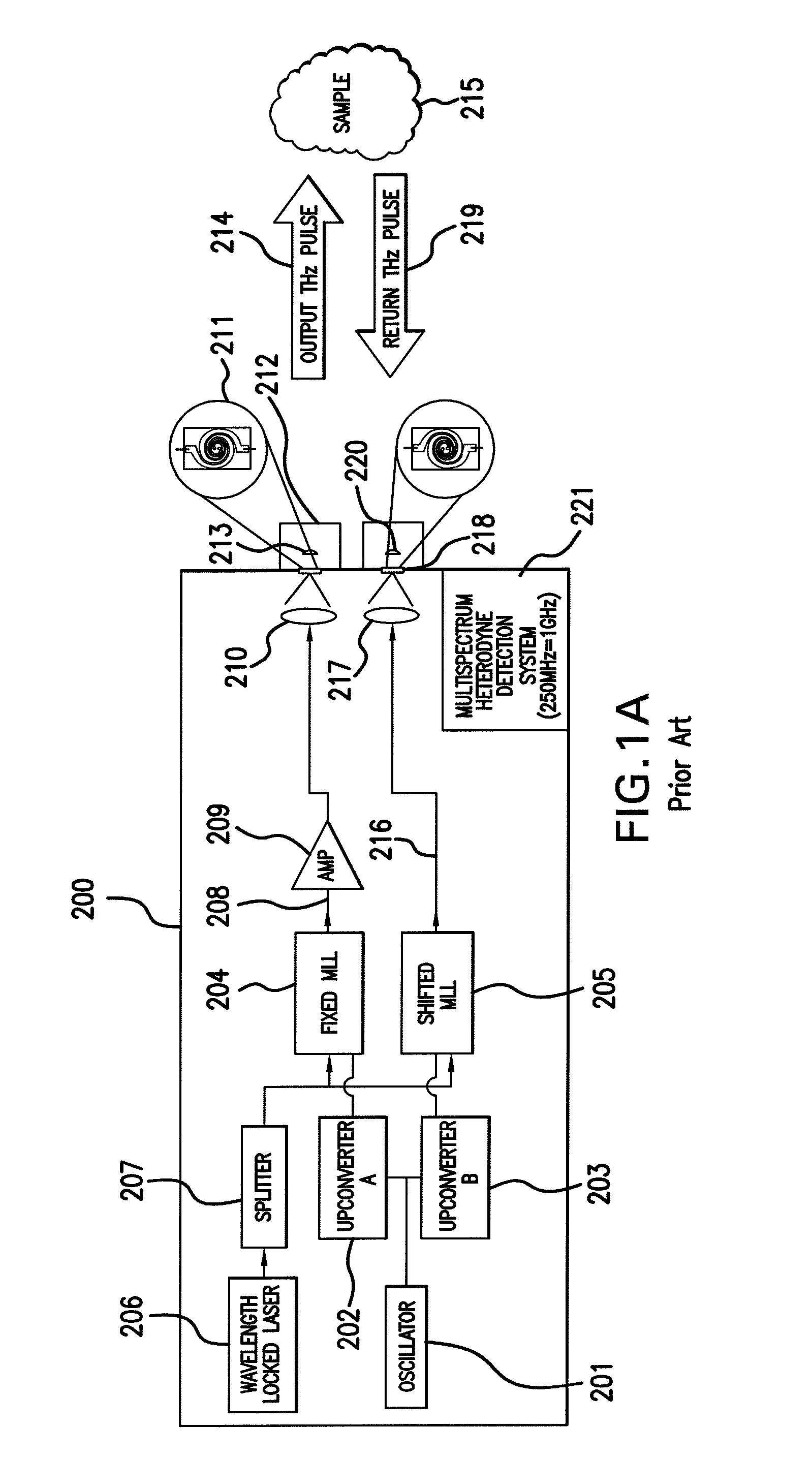
Pulsed terahertz spectrometer
InactiveUS7535005B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle physicsPulsed laser beam
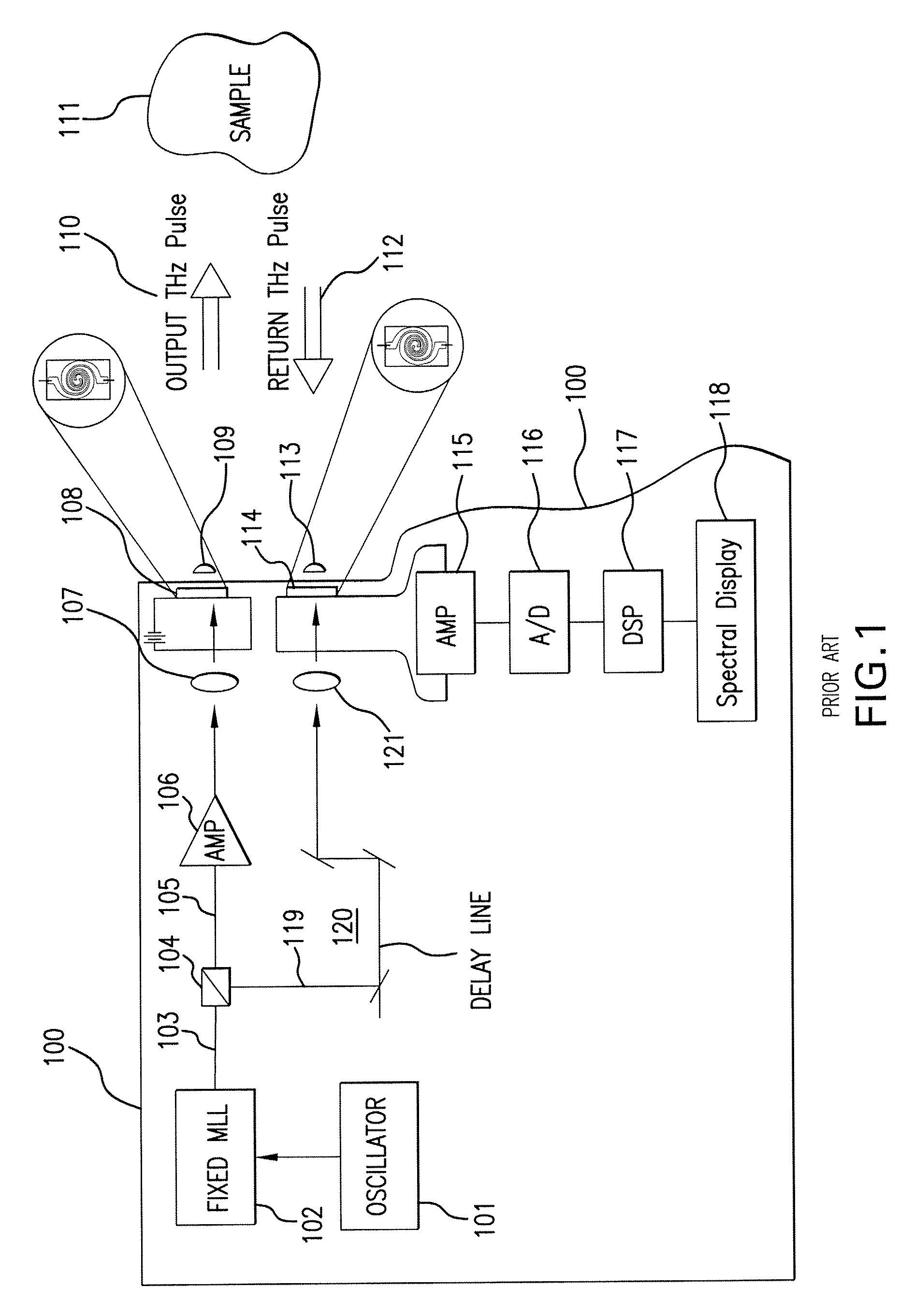
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an object including a source of pulsed signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on the object; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals reflected from the object and using a heterodyning process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the object. The source of pulse signals and the detector is a photoconductive switch activated by a pulsed laser beam.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
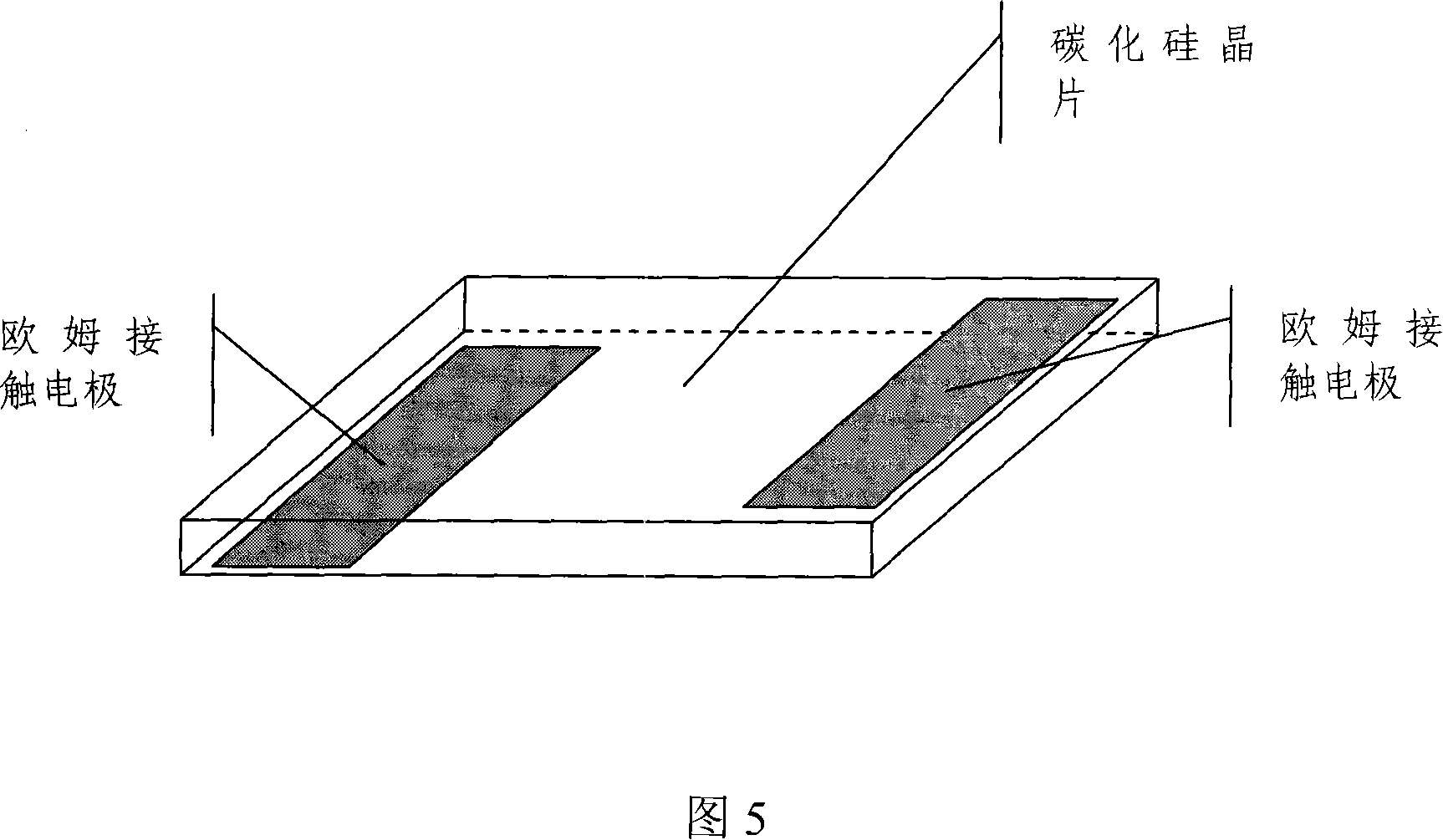
High-pressure resistant silicon carbide light guide switch
ActiveCN101132030AHigh compressive strengthImprove pressure resistanceSemiconductor devicesLight guideOhmic contact
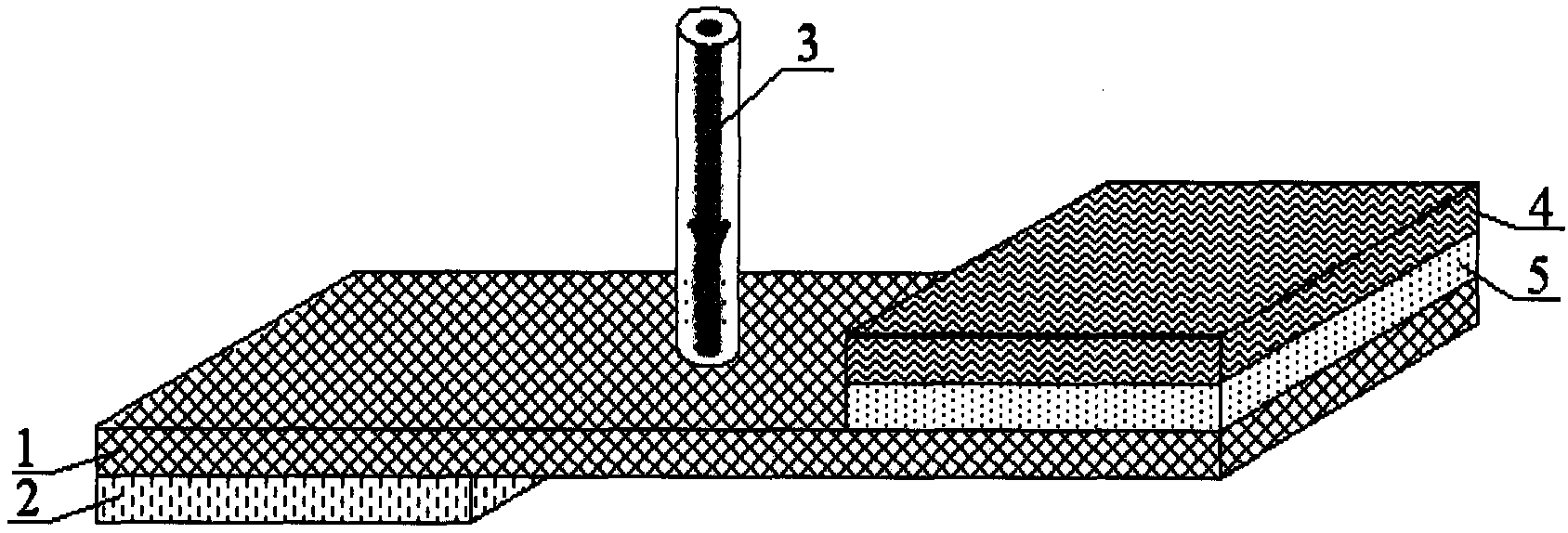
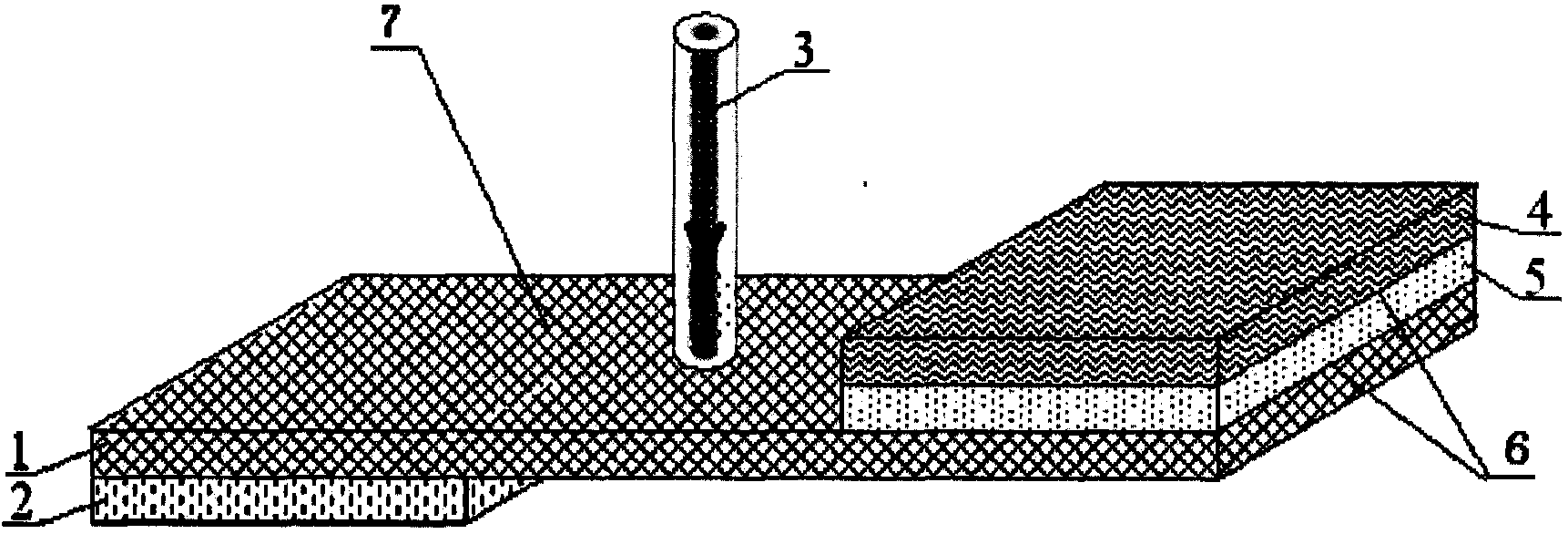
The present invention relates to a high-pressure-resisted, silicon-carbide, photoconductive switch, and belongs to field of semiconductor device processing technology. The photoconductive switch takes relative-surface-shape design; the processed silicon-carbide polished wafer is form with ohmic contacts on its two surfaces, and the electrodes are formed. The relative-surface-shape, silicon-carbide, photoconductive switch can increase duplicate times of pressure resistance of the switch, and minimize volume of the photoconductive switch. The present invention creates conditions for integrating photoconductive switches, and can be used in field of semiconductor switches.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photoconductive switch package
ActiveUS20100282949A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringPhotoconductive switch
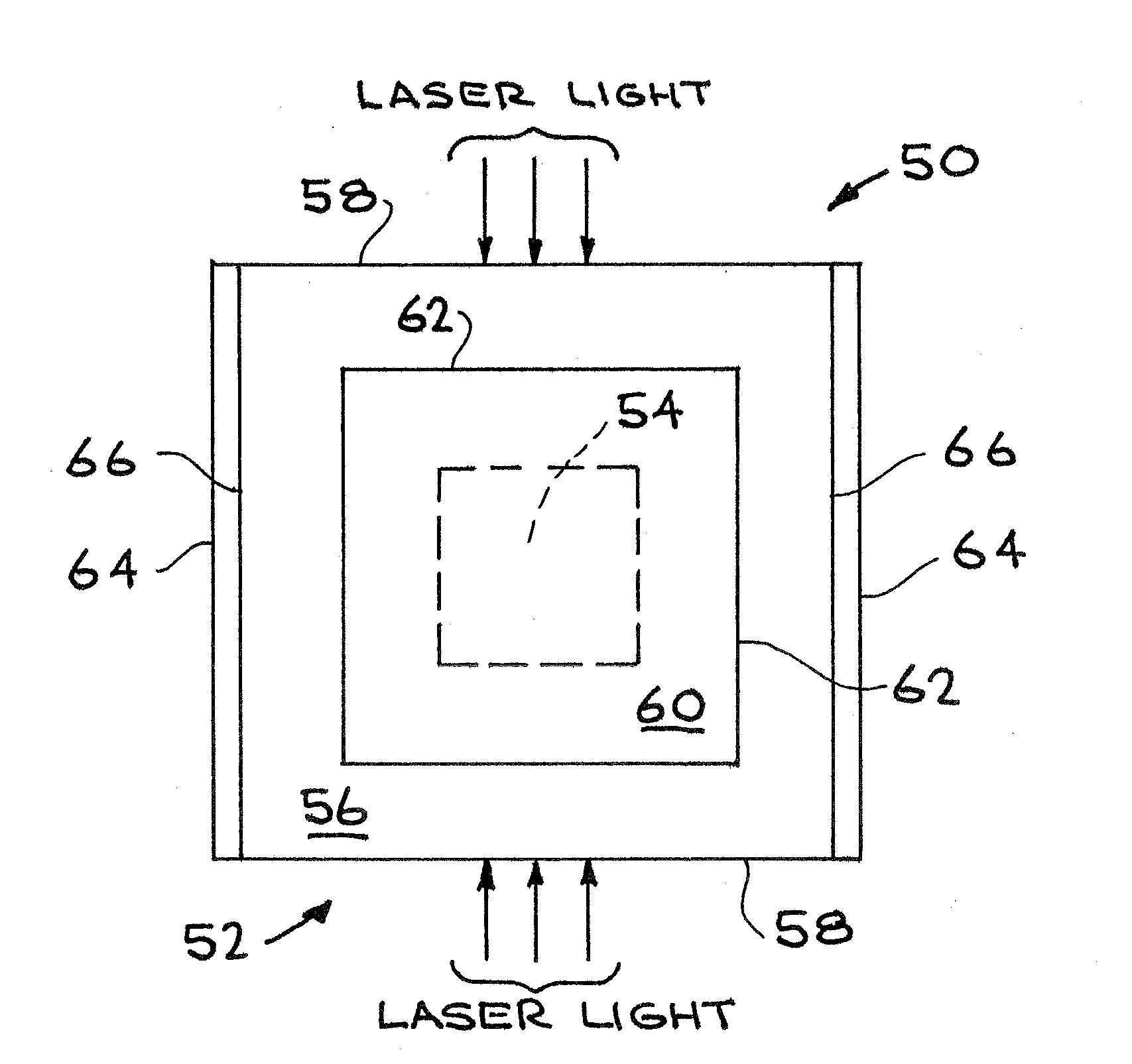
A photoconductive switch is formed of a substrate that has a central portion of SiC or other photoconductive material and an outer portion of cvd-diamond or other suitable material surrounding the central portion. Conducting electrodes are formed on opposed sides of the substrate, with the electrodes extending beyond the central portion and the edges of the electrodes lying over the outer portion. Thus any high electric fields produced at the edges of the electrodes lie outside of and do not affect the central portion, which is the active switching element. Light is transmitted through the outer portion to the central portion to actuate the switch.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Optically-initiated silicon carbide high voltage switch with contoured-profile electrode interfaces
An improved photoconductive switch having a SiC or other wide band gap substrate material with opposing contoured profile cavities which have a contoured profile selected from one of Rogowski, Bruce, Chang, Harrison, and Ernst profiles, and two electrodes with matching contoured-profile convex interface surfaces.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Pulsed terahertz frequency domain spectrometer with single mode-locked laser and dispersive phase modulator
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an target including a source of pulsed signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on or transmitted through the target; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals reflected from the target and using a multi-spectral heterodyning process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the target. The source of pulse signals and the detector are photoconductive switches activated by a pulsed laser beam from a single mode-locked laser.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
Terahertz frequency domain spectrometer with integrated dual laser module
InactiveUS7936453B2High resolutionLow costRadiation pyrometryPolarisation-affecting propertiesImage resolutionCombined use
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
Virtual gap dielectric wall accelerator
ActiveUS20110101891A1Shorten speedSlow electromagnetic wave speedLinear acceleratorsMachines/enginesSurface conductivityDielectric wall accelerator
A virtual, moving accelerating gap is formed along an insulating tube in a dielectric wall accelerator (DWA) by locally controlling the conductivity of the tube. Localized voltage concentration is thus achieved by sequential activation of a variable resistive tube or stalk down the axis of an inductive voltage adder, producing a “virtual” traveling wave along the tube. The tube conductivity can be controlled at a desired location, which can be moved at a desired rate, by light illumination, or by photoconductive switches, or by other means. As a result, an impressed voltage along the tube appears predominantly over a local region, the virtual gap. By making the length of the tube large in comparison to the virtual gap length, the effective gain of the accelerator can be made very large.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
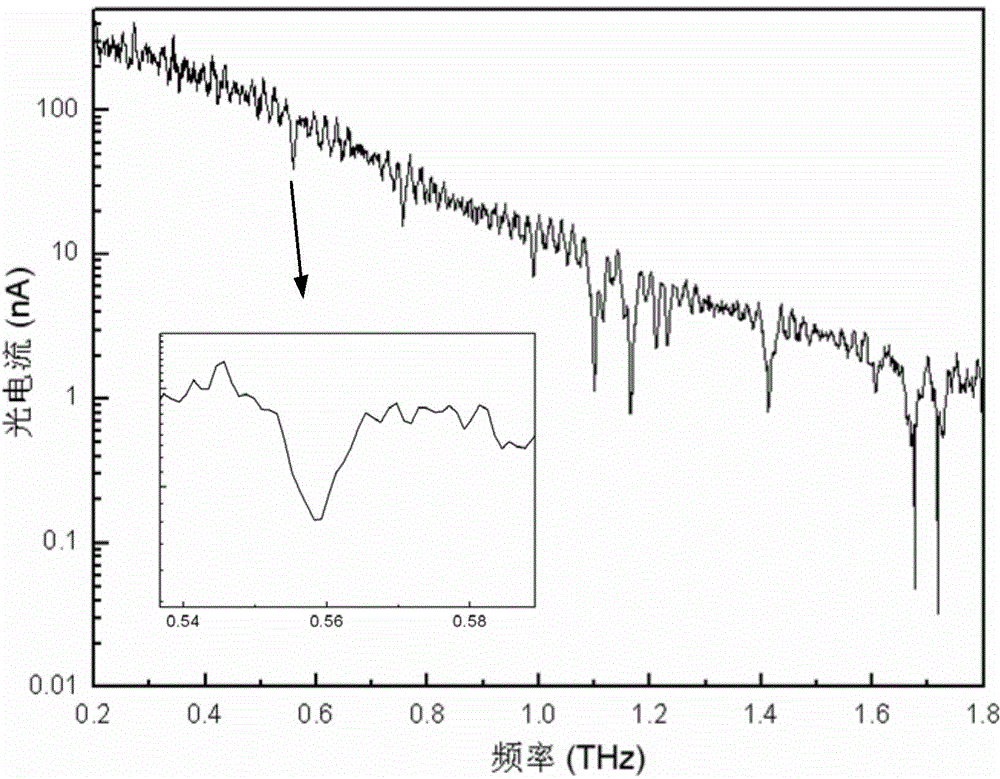
Method and system for realizing continuous terahertz spectrum detection
InactiveCN104458645AAchieving Phase ModulationAverage signal-to-noise ratioMaterial analysis by optical meansExternal biasTerahertz radiation
The invention provides a method and a system for realizing continuous terahertz spectrum detection. A pair of high-stability single longitudinal mode near-infrared lasers serve as seed light sources, a laser signal is modulated by utilizing optical fibers, and continuous terahertz waves are radiated outwards under external bias potential by virtue of an optical mixer; and the terahertz waves are subjected to coherent detection at a signal receiving end by adopting a photoconductive switch and an antenna. The temperature modulation is performed on the lasers, and wide bandwidth difference frequency continuous terahertz radiation output is realized. Compared with a common terahertz time-domain impulse spectral system, the system has the advantages that the spectral resolution acquired by the technology is greatly improved, and the system has an excellent effect of promoting the development of terahertz spectroscopy and related fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
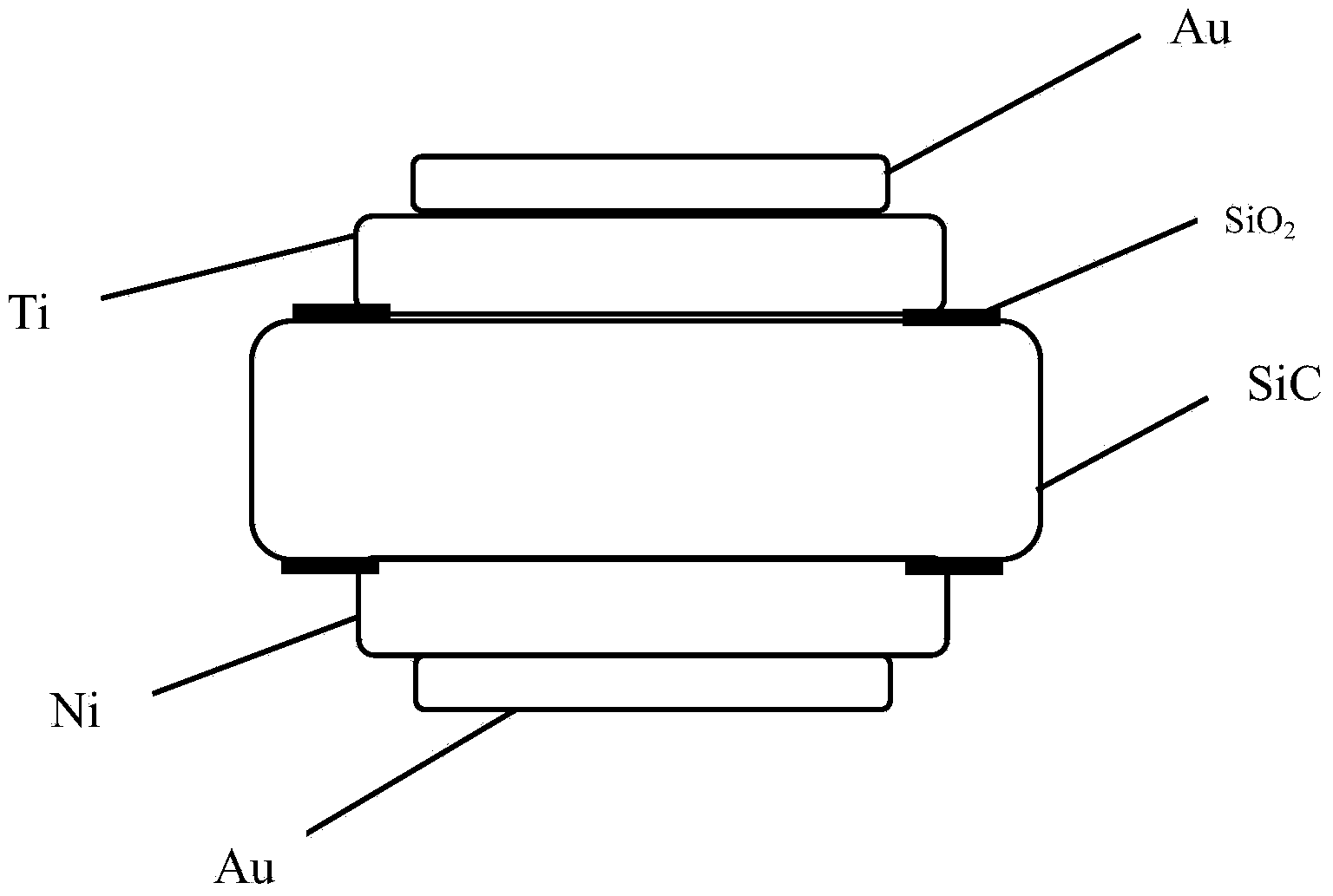
Photoconductive switch manufacturing method based on SiC substrate
InactiveCN103681969AShort processImprove yieldFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsCopper electrode
The invention provides a photoconductive switch manufacturing method based on a SiC substrate, and relates to the technical field of wide bandgap semiconductor material photoelectronic devices. SiC with the thickness of 400 micrometers after polishing serves as a substrate in the photoconductive switch manufacturing method based on the SiC substrate. The photoconductive switch manufacturing method based on the SiC substrate comprises the steps that the SiC substrate is prepared; a SiO2 insulation protective layer is generated through thermal oxidation, and a window is formed through photoetching; in high vacuum low temperature Ar atmosphere, a Ti electrode is deposited on the carbon surface, and a Ni electrode is deposited on the silicon surface; after high temperature rapid thermal processing in the Ar atmosphere, a Au protective film is deposited through a small-size ion sputtering instrument, and a photoconductive switch of a Au / Ti / SiC / Ni / Au different-surface opposite-electrode structure is formed by being encapsulated through transparent Si3N4 after a copper electrode is bonded. According to the photoconductive switch manufacturing method based on the SiC substrate, due to the fact that epitaxy of an n-type or p-type SiC epitaxial layer with high doping concentration is not carried out through devices such as CVDs, the technological process of semiconductors is reduced, the rate of finished products is improved, and production cost is lowered. Technical assurance is provided for the production of devices having hash requirements for large power, high frequency and high temperature resistance in future.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Pulsed terahertz spectrometer
InactiveUS20080179527A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle physicsPulsed laser beam
An apparatus for analyzing, identifying or imaging an object including a source of pulsed signals in the range of frequencies from 100 GHz to over 2 THz focused on the object; and a detector for acquiring spectral information from signals reflected from the object and using a heterodyning process to generate an electrical signal representative of some characteristics of the object. The source of pulse signals and the detector is a photoconductive switch activated by a pulsed laser beam.
Owner:DEMERS JOSEPH R
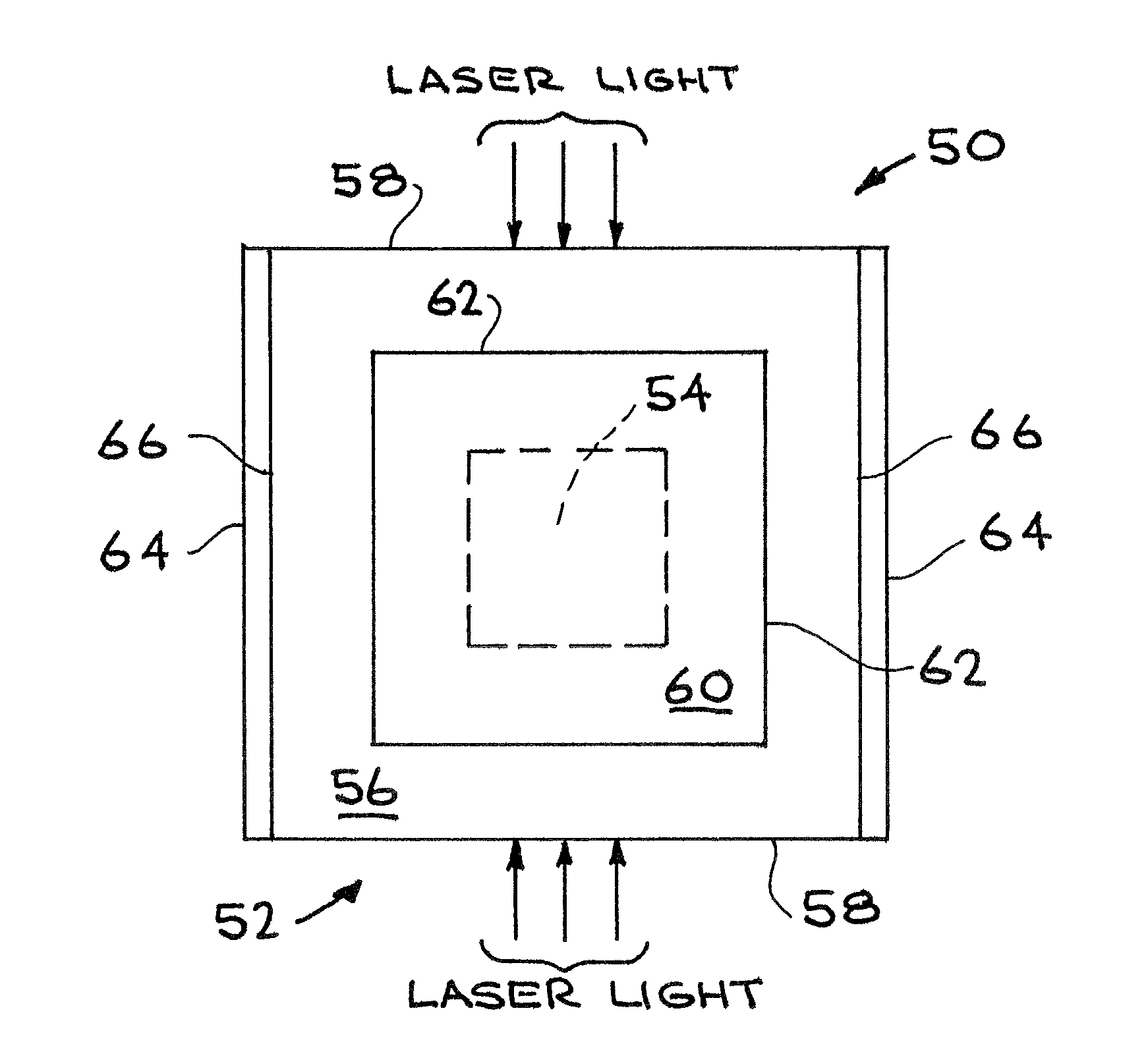
Opposite front light-in high-power photoconductive switch device and making method thereof
ActiveCN107507871AIncrease profitImplement the disconnect functionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides an opposite front light-in high-power photoconductive switch device and a making method thereof. The opposite front light-in high-power photoconductive switch device includes a hollow metal electrode, a metal ring, an antireflection passivation layer, a transparent conductive layer, a high-resistance semiconductor, a high-reflectivity electrode, and a solid metal electrode. The transparent conductive layer and the antireflection passivation layer are arranged in sequence on the high-resistance semiconductor used as a substrate, and the metal ring surrounding and connected around the transparent conductive layer and the antireflection passivation layer is also arranged on the high-resistance semiconductor. The side of the metal ring opposite to the substrate is connected with the hollow metal electrode. The high-reflectivity electrode is arranged on the back of the high-resistance semiconductor. The side of the high-reflectivity electrode opposite to the substrate is connected with the solid metal electrode. The device is packaged with a dielectric material with high breakdown field strength. Edge breakdown caused by uneven carriers can be avoided, and the withstand voltage and light efficiency of the switch can be greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photoconductive switch high in withstand voltage and low in on resistance and method for manufacturing same
ActiveCN103022220ALower on-resistanceReduce field concentrationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhotoconductive switchMetal electrodes
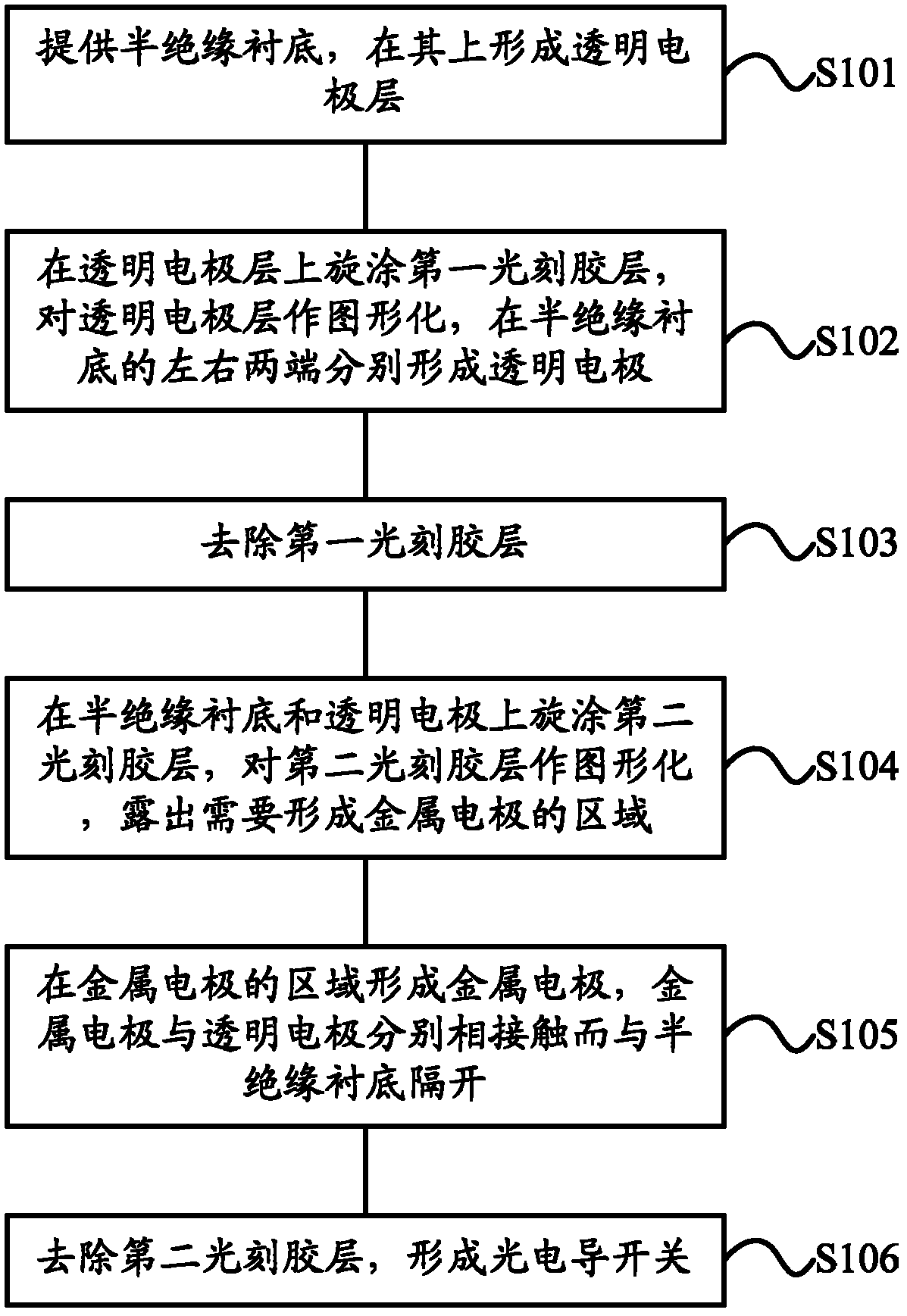
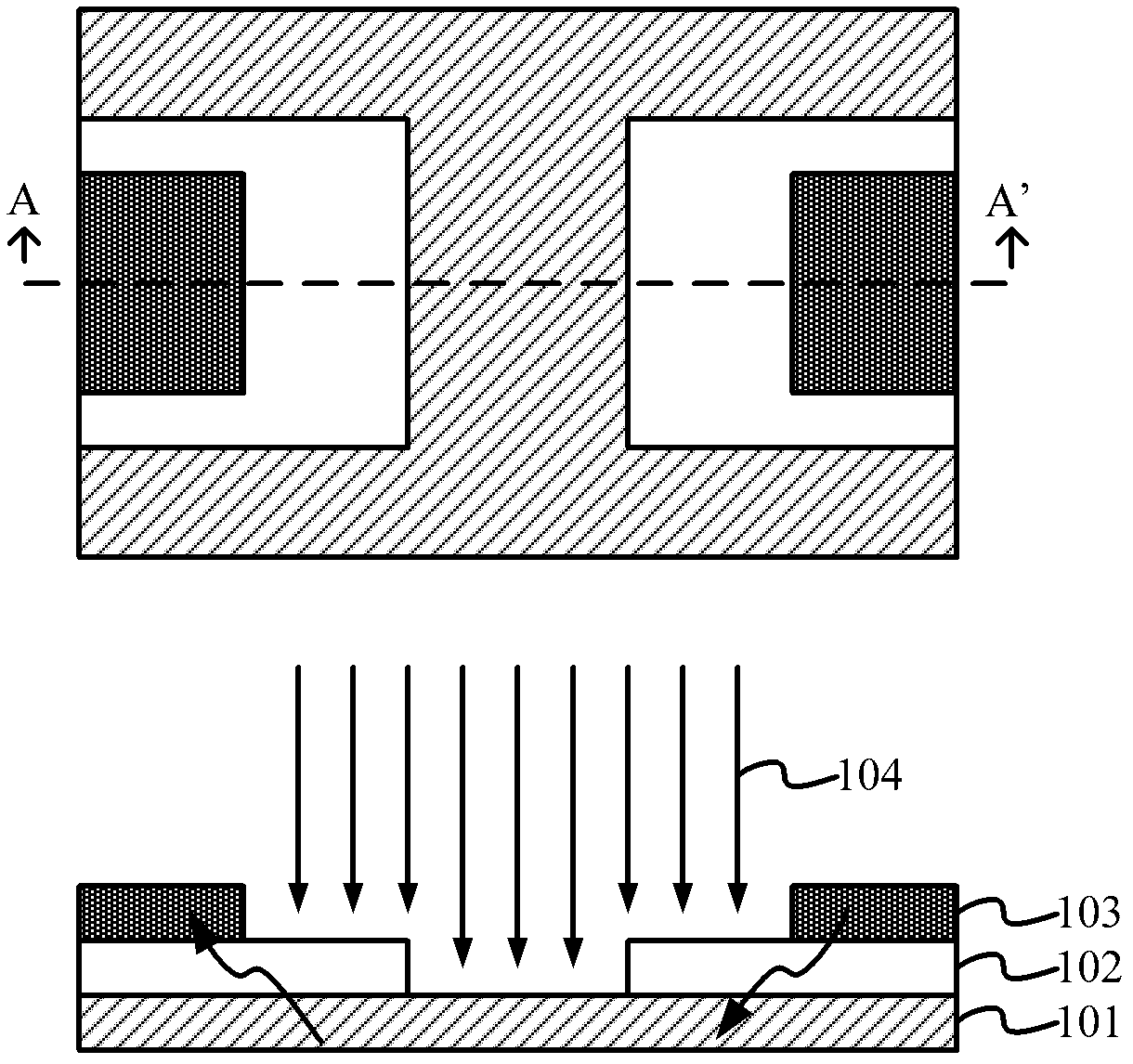
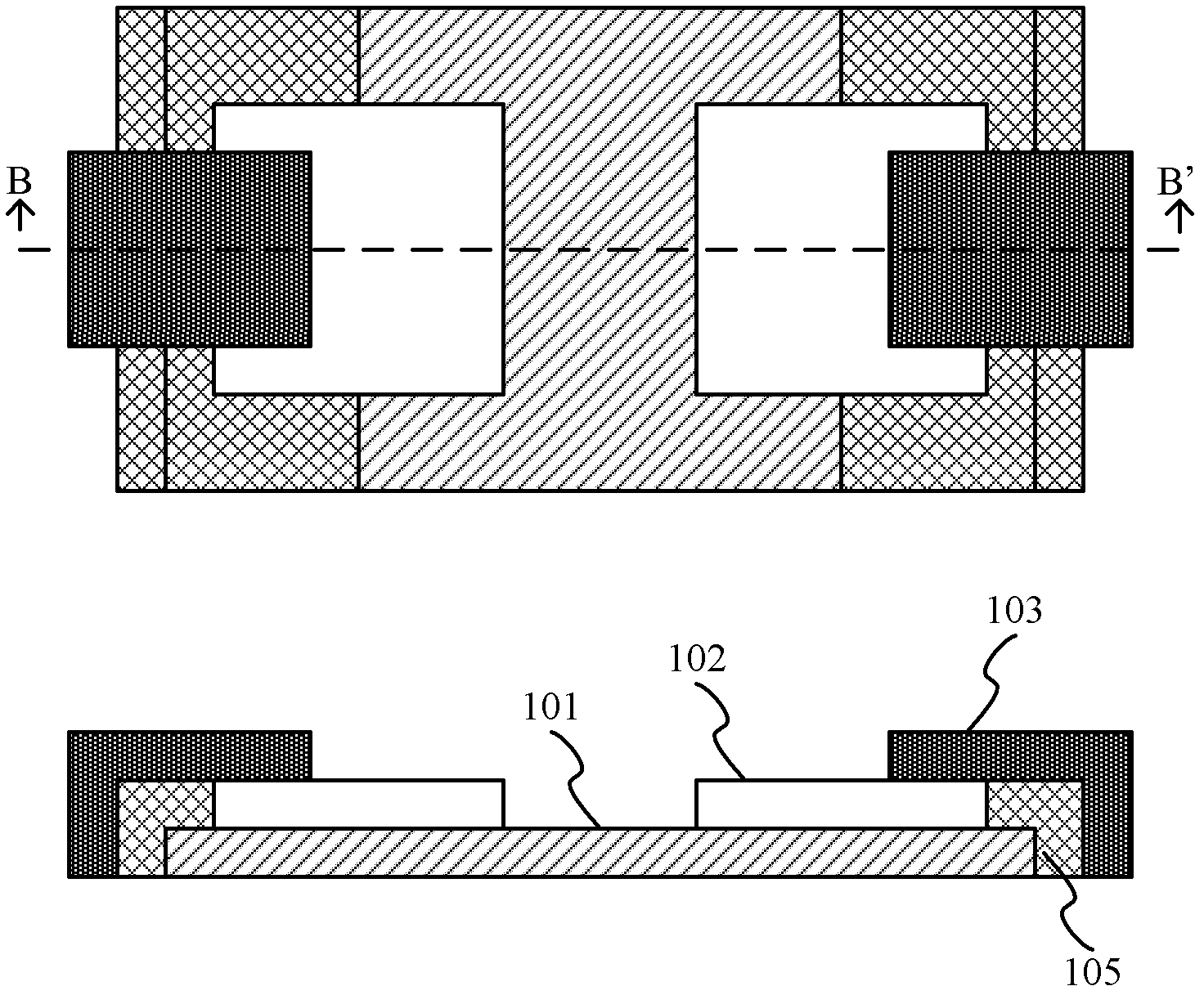
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a photoconductive switch high in withstand voltage and low in on resistance, comprising the steps of: providing a semi-insulating substrate, and forming a transparent electrode layer on the semi-insulating substrate; applying a photoresist layer on the transparent electrode layer through spin coating, patterning the transparent electrode layer and forming transparent electrodes at the left and right two ends of the semi-insulating substrate, respectively; applying second photoresist layers on the semi-insulating substrate and the transparent electrode through spin coating, patterning the second photoresist layer and exposing the region for forming a metal electrode; forming the metal electrode which is in contact with the transparent electrodes, respectively, and isolated from the semi-insulating substrate; and removing the second photoresist layers. Accordingly, the invention also provides a photoconductive switch high in withstand voltage and low in on resistance. The method provided by the invention is capable of improving the current density capacity of the switch and reducing the field intensity concentration while guaranteeing a certain electrode spacing, so that the photoconductive switch has low on resistance and high withstand voltage property at the same time.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
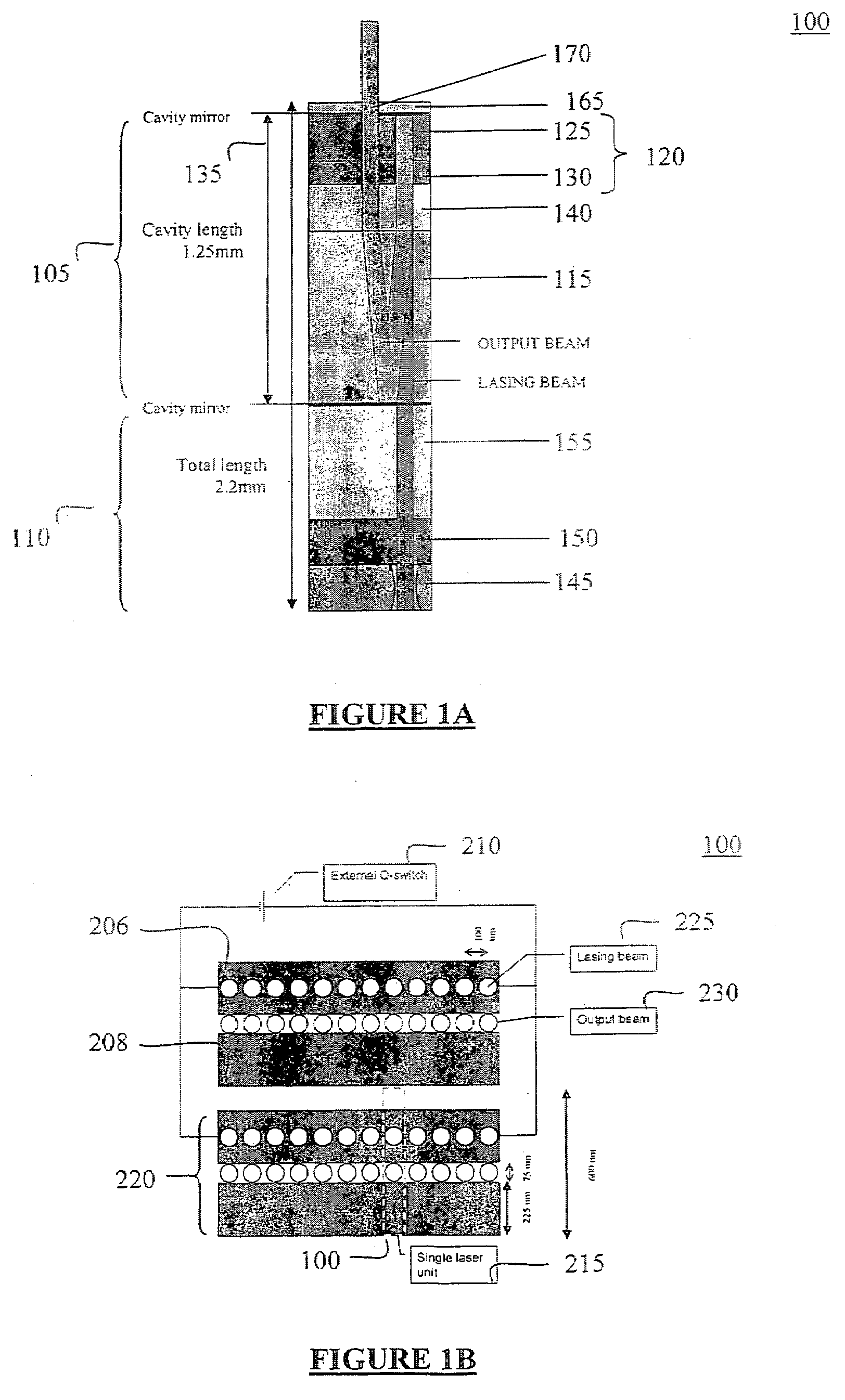
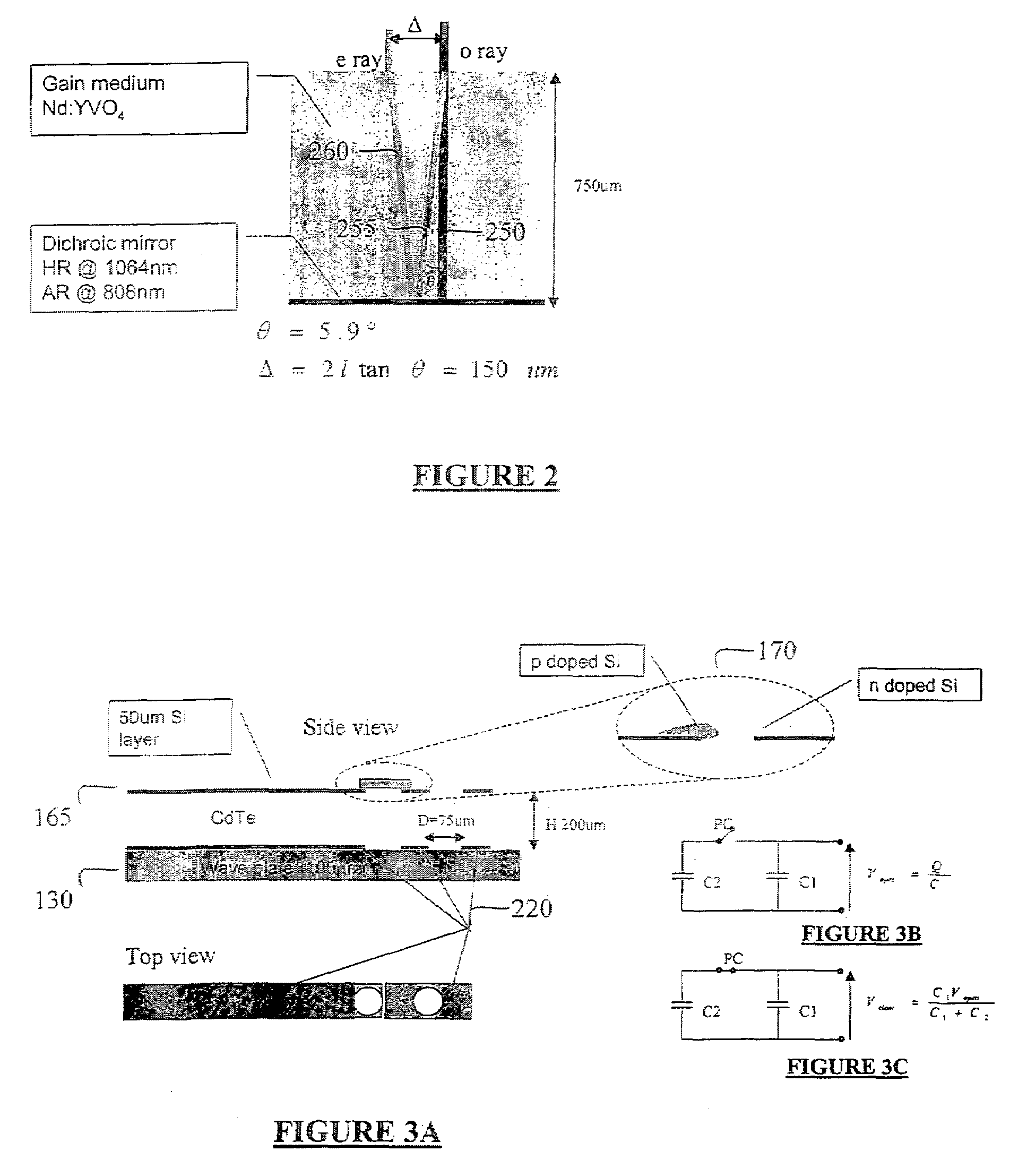
Q-switched cavity dumped laser array
InactiveUS20070280305A1Fast response timeHigh energyLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersHigh densityHigh energy
A microchip, Q-switched, cavity-dumped laser is end-pumped by VCSEL or a laser diode and comprises an electro-optic Q-switch mechanism actively controlled by photoconductive switches. The fast response time of the system and its small dimension produce short pulses (ten pico-second range), with high energy (uJ range). The microchip structure may be built using planar, wafer-like components such that a high-density array of lasers may be manufactured without tight alignment tolerances, providing efficient power or energy scaling.
Owner:ZUCKER OVED
Optically initiated silicon carbide high voltage switch
InactiveUS7893541B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsHigh pressure
An improved photoconductive switch having a SiC or other wide band gap substrate material, such as GaAs and field-grading liners composed of preferably SiN formed on the substrate adjacent the electrode perimeters or adjacent the substrate perimeters for grading the electric fields.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Photoconductive optical write driver for magnetic recording
InactiveUS20050111129A1Construction of head windingsFilamentary/web carriers operation controlElectrical conductorSwitched current
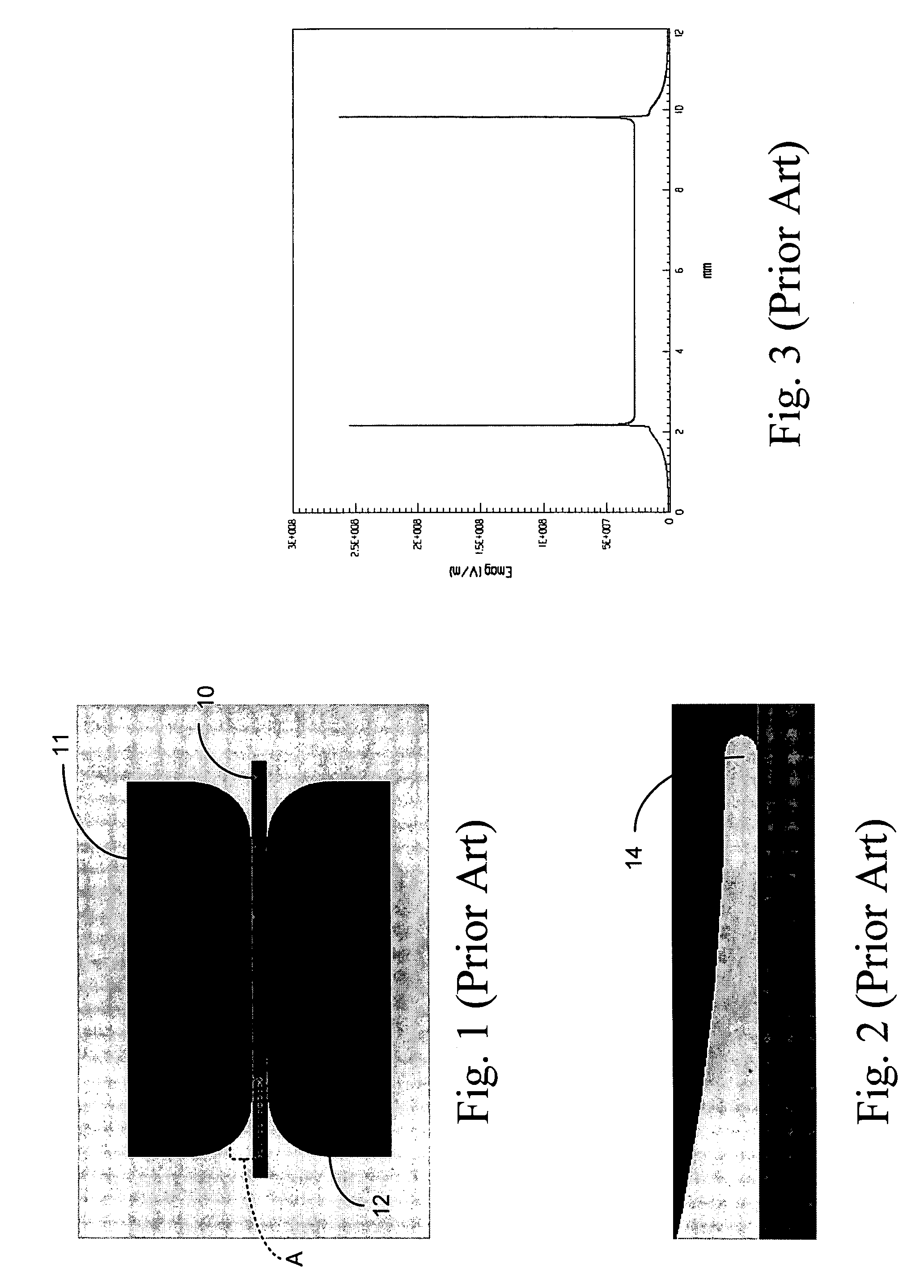
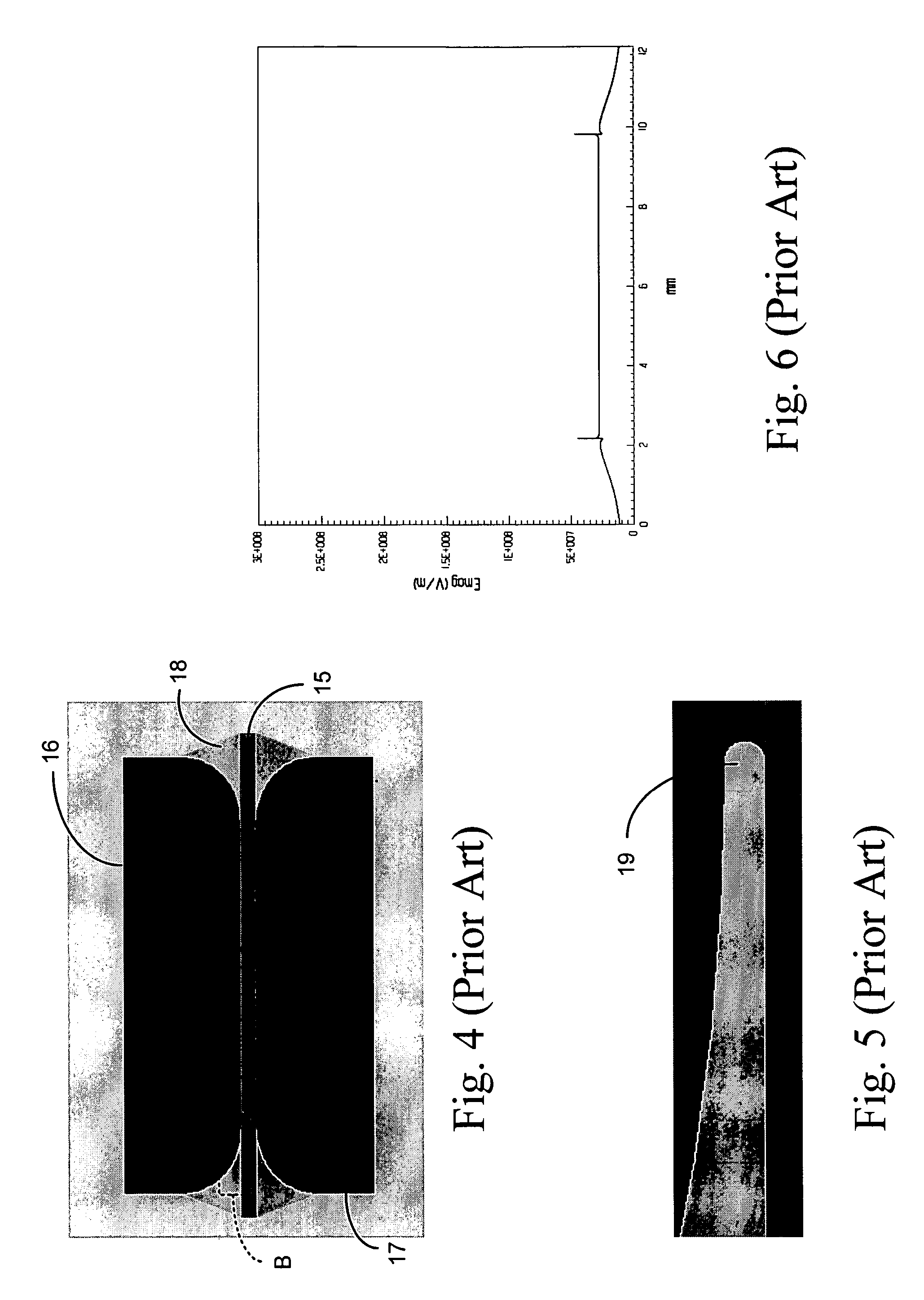
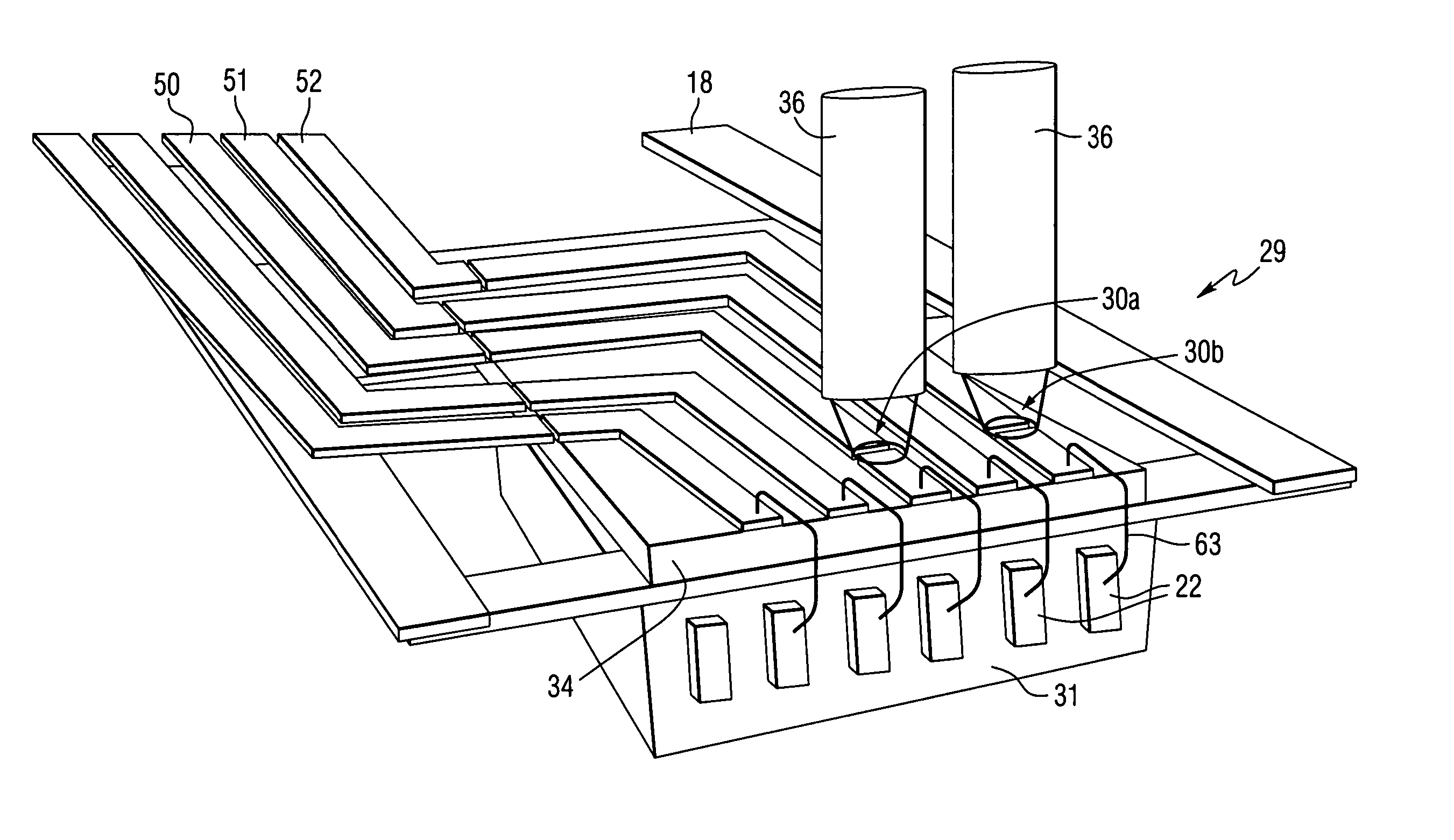
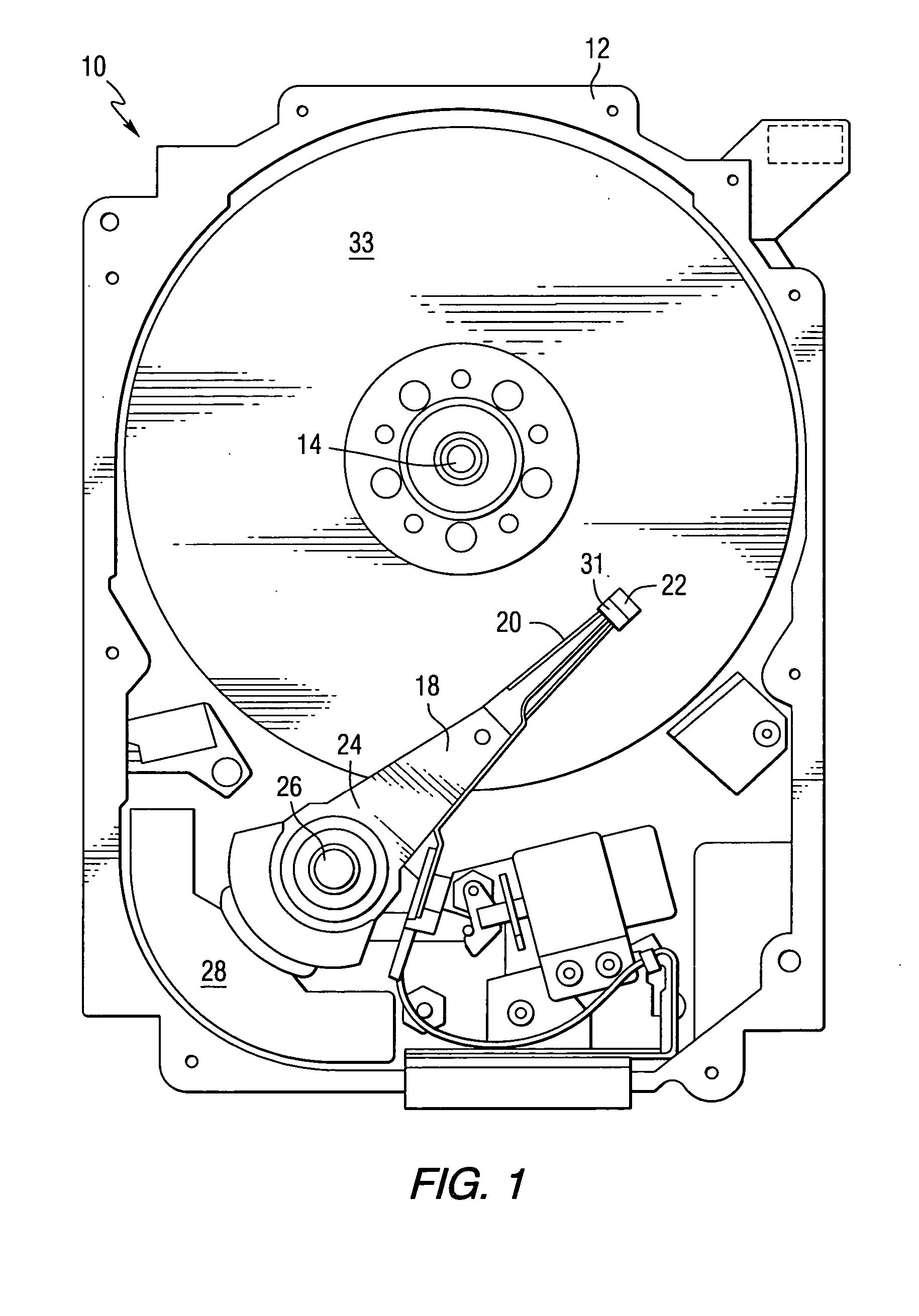
A write driver for use with a magnetic recording head includes a photoconductive switch that is positioned adjacent a magnetic recording head for switching current waveforms. Both light and a DC voltage are applied to the photoconductive switch to switch the applied current waveforms. The write driver further includes means for writing to a storage medium in response to current waveforms switched by the photoconductive switch. The write driver may also include a suspension that supports at least one photoconductive switch, DC conductors for supplying a DC voltage, means for supplying light, and recording head means for writing to a storage medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
High power bipolar pulse generators
InactiveUS20100231278A1Simple structureImprove efficiencyDelay lines pulse generationPulse generation by energy-accumulating elementFiberEngineering
A bipolar pulse generator is implemented in a simple structure while providing a high efficiency design having a relatively low total size, while still allowing access by fibers used to control a photoconductive switch that activates the generator. The bipolar pulse generator includes a stacked Blumlein generator structure with an additional transmission line connected to a load at its near end and short-circuited at its distal end. An extra transmission line is positioned between the Blumlein generator's structure and the load provides specified limited gap between positive and negative sub-pulses. The bipolar pulse generator further includes a bended Blumlein generator structure, in which an existing intrinsic “stray” transmission line is used to provide the bipolar pulse. Still further, bipolar pulse generator includes stepped transmission lines, with additional switches positioned between steps, which are charged by different voltages.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
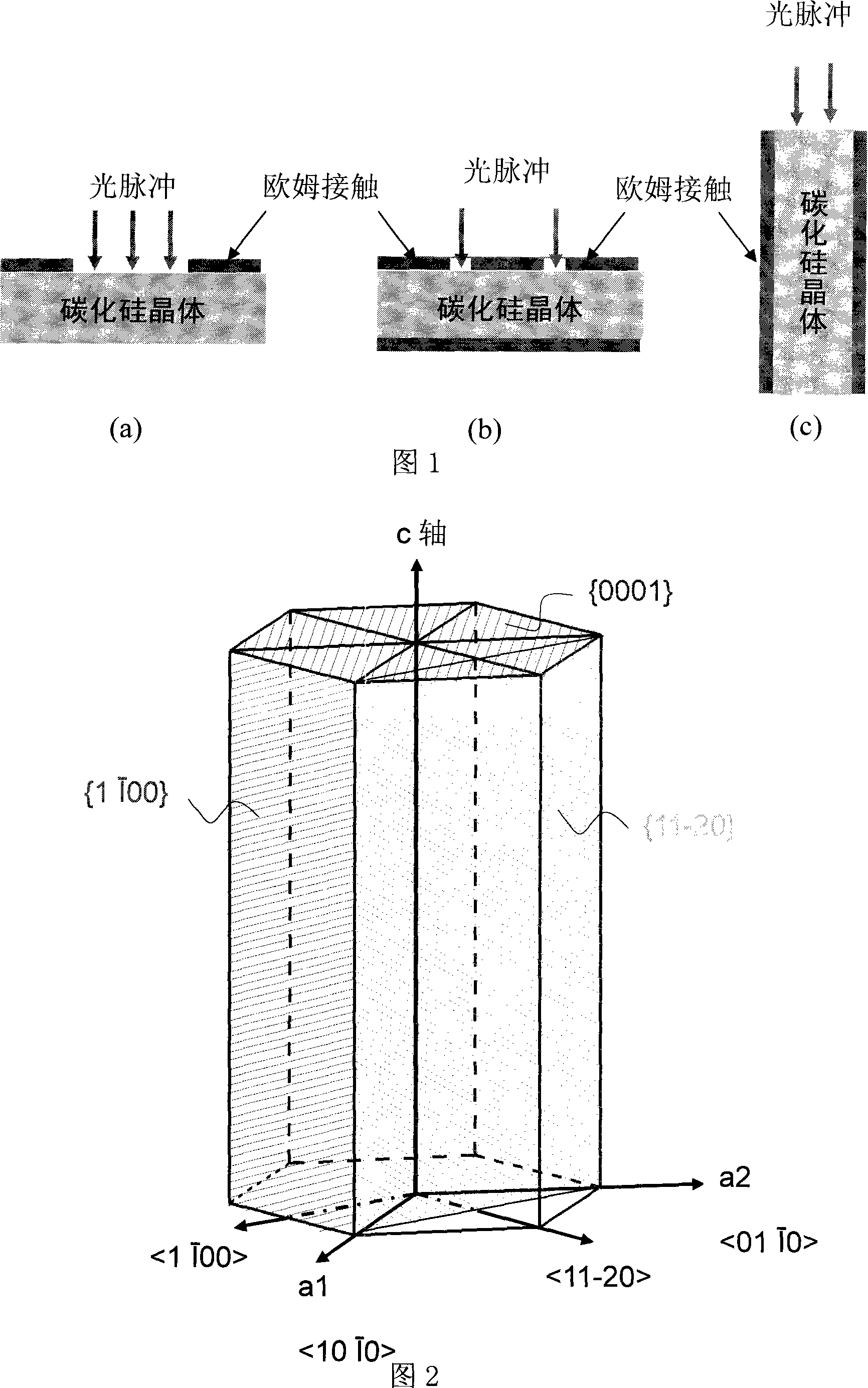
Optical control silicon carbide (SiC) photoconductive switch
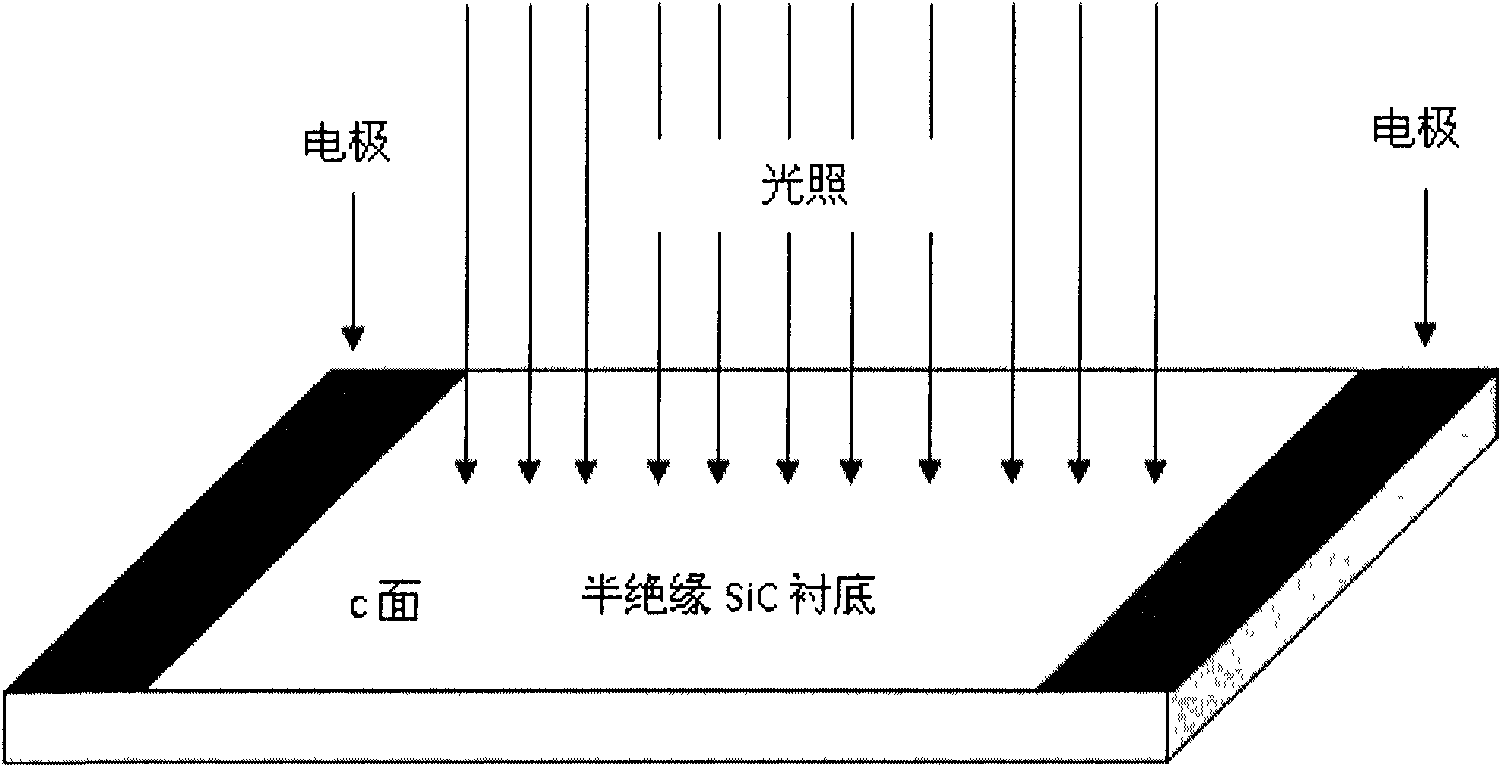
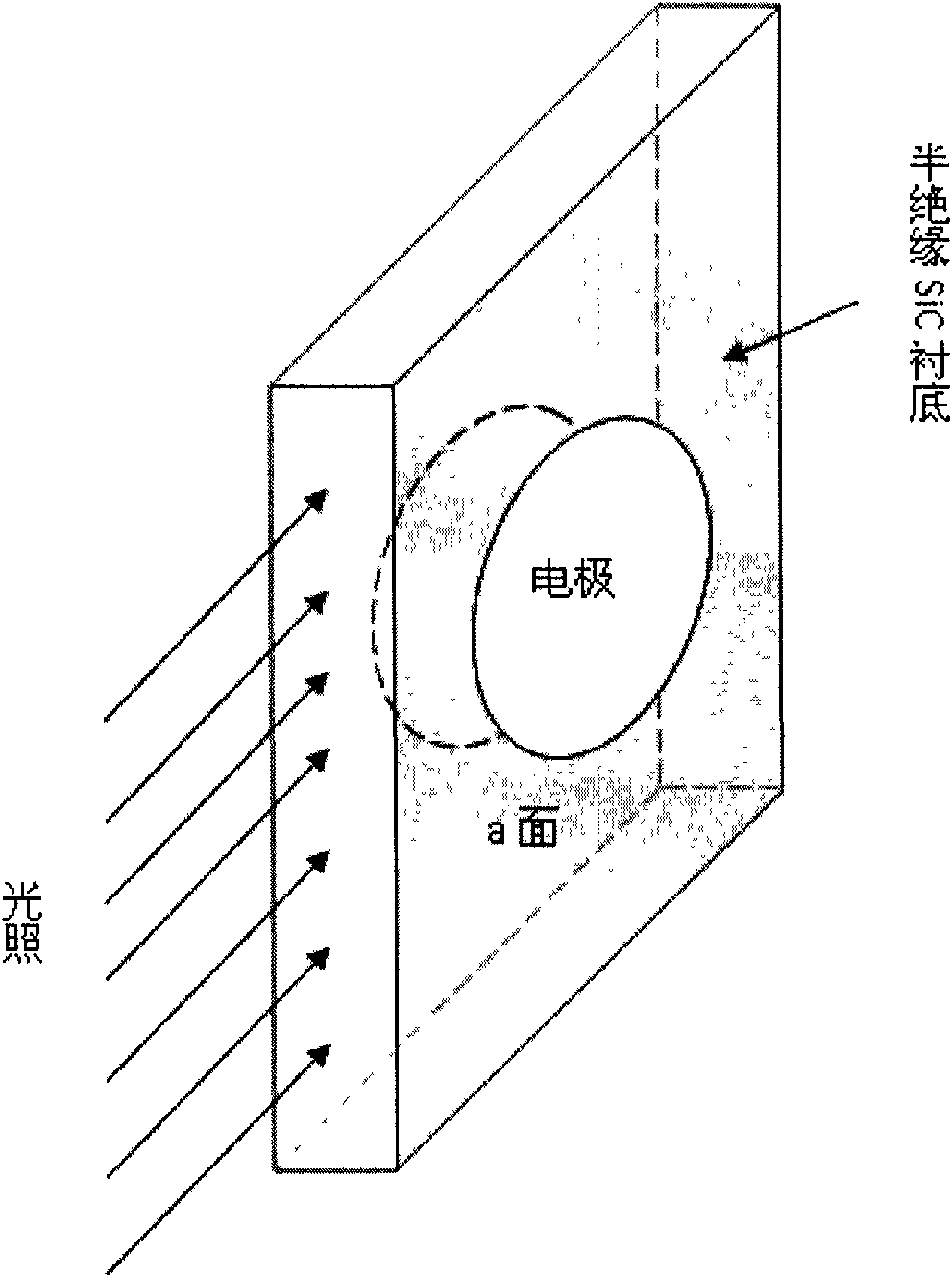
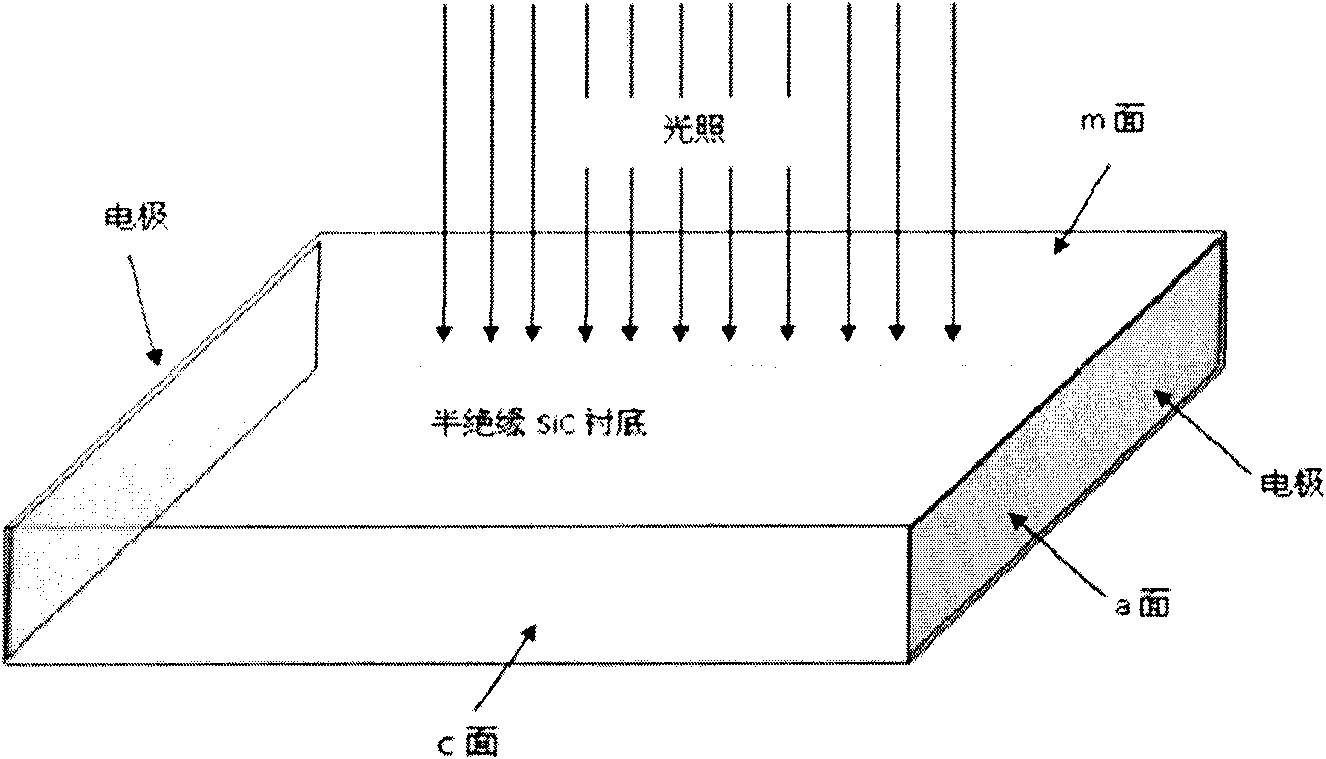
The invention relates to an optical control silicon carbide (SiC) photoconductive switch. The switch comprises the following components: a SiC photoconductive wafer and electrodes electrically connected with (1120)a surface(s) or (1120)m surfaces, wherein the SiC photoconductive wafer has the following well polished crystal planes: at least a (1100)m surface and at least two (1120)a surfaces; the (1100)m surfaces or the (1120)a surfaces are sunward surfaces optically connected with excitation light sources; when the (1100)m surfaces serve as the sunward surfaces, the electrodes are electrically connected with the (1120)a surface(s); and when the (1120)a surfaces serve as the sunward surfaces, the electrodes are electrically connected with the (1100)m surfaces.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
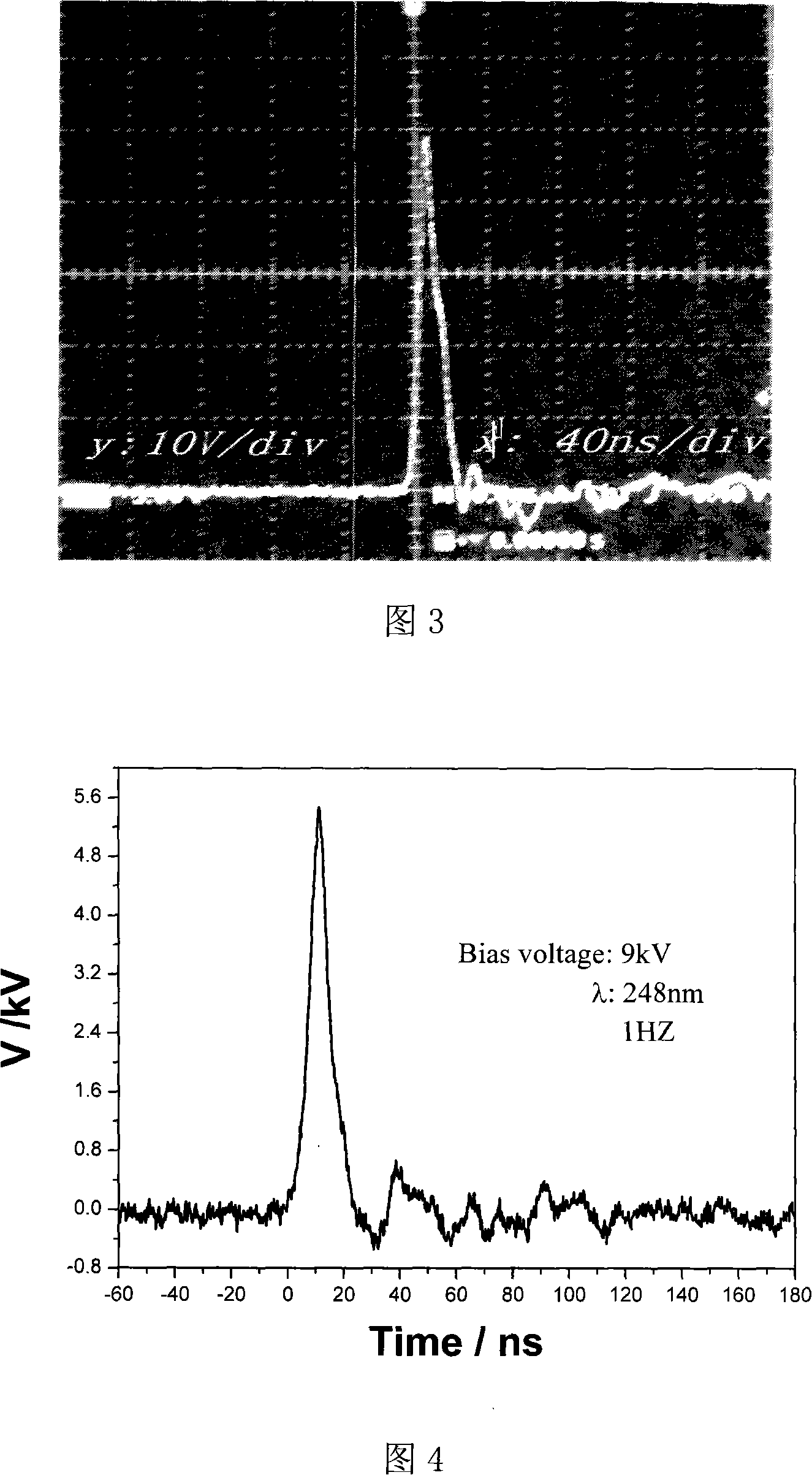
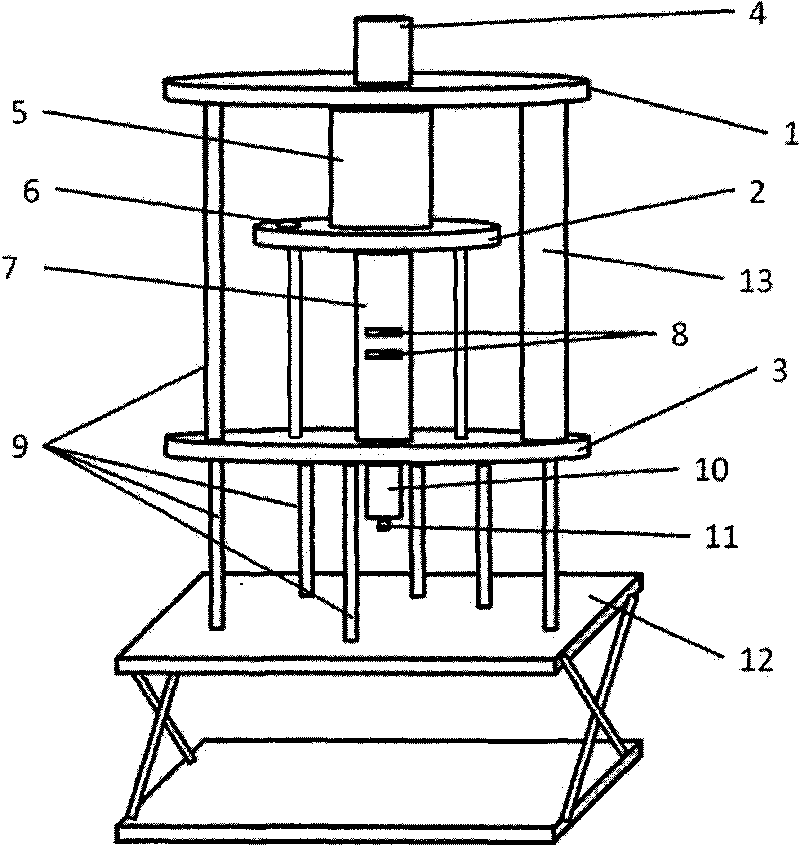
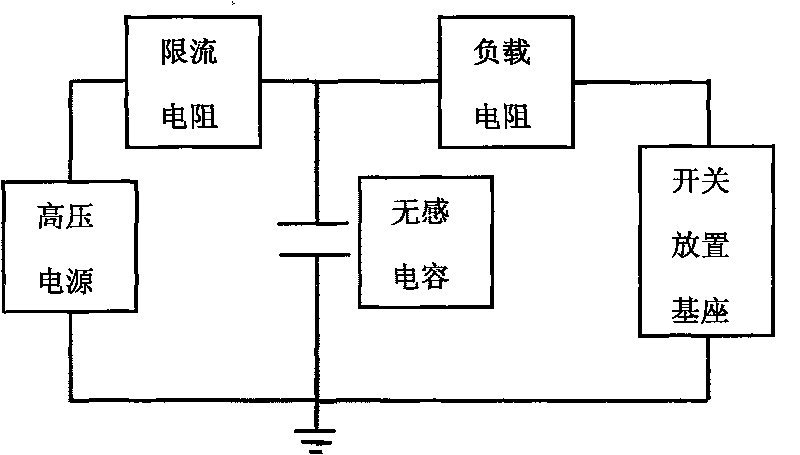
High-power photoconductivity switch test device and application thereof
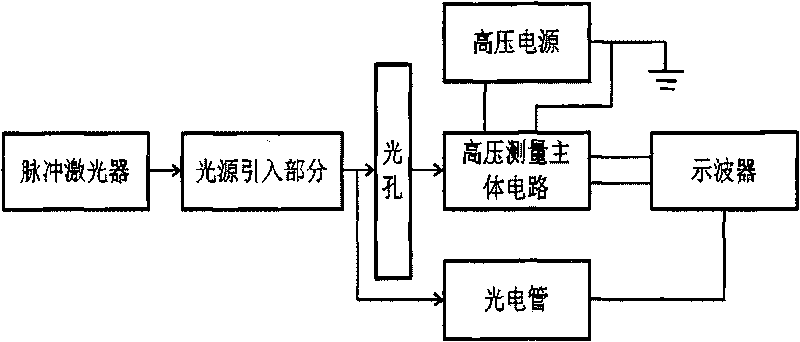
ActiveCN101762784APrecise alignmentCompact structureElectrical measurement instrument detailsCircuit interrupters testingLight spotHigh pressure
The invention relates to a high-power photoconductivity switch test device and application thereof. The test device comprises a pulse laser, a light source leading-in part, a light hole, a high-voltage measurement main circuit, a high-voltage power supply, an oscilloscope and a phototube, wherein the laser pulse generated by the pulse laser is received by the light source leading-in part to form light spots, and the light source leading-in part adjusts the light path and controls the light intensity of the light spots at unit area; the light spots are divided into measurement light spots and reference light spots by a spectroscope arranged in the light source leading-in part; the light hole receives the measurement light spots and adjusts the light intensity of the measurement light spots; the phototube receives and converts the reference light spots into electrical signals and transmits the electrical signals to the oscilloscope; the high-voltage measurement main circuit outputs electrical signals generated by the irradiation of the measurement light spots of a photoconductivity switch to be tested; the high-voltage power supply applies voltage to the high-voltage measurement main circuit; and the oscilloscope analyzes and displays the electrical signals from the high-voltage measurement main circuit.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
Photoconductive switch package
ActiveUS8563957B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhotoconductive switchElectric field
A photoconductive switch is formed of a substrate that has a central portion of SiC or other photoconductive material and an outer portion of cvd-diamond or other suitable material surrounding the central portion. Conducting electrodes are formed on opposed sides of the substrate, with the electrodes extending beyond the central portion and the edges of the electrodes lying over the outer portion. Thus any high electric fields produced at the edges of the electrodes lie outside of and do not affect the central portion, which is the active switching element. Light is transmitted through the outer portion to the central portion to actuate the switch.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Film thickness measuring device and film thickness measuring method
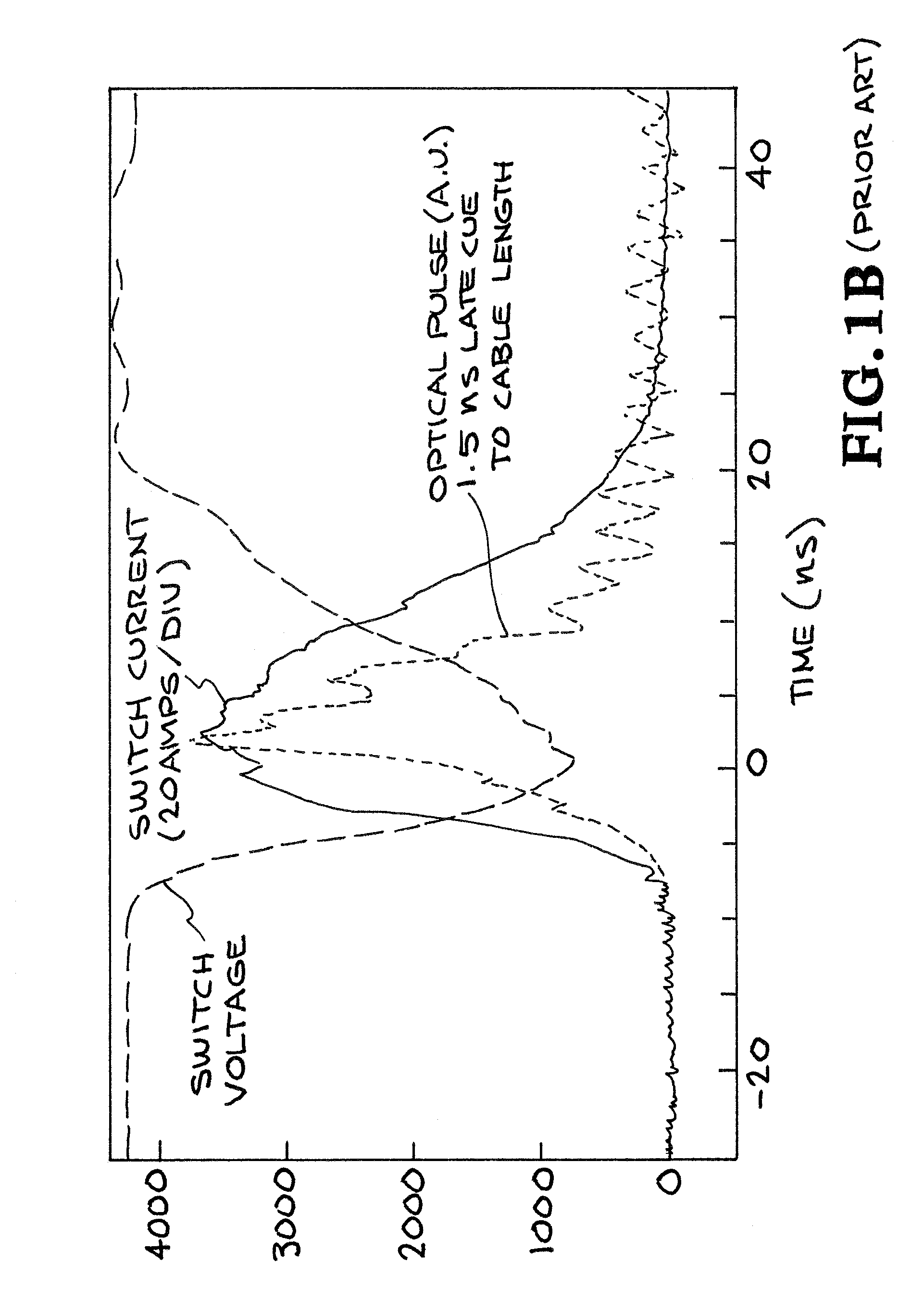
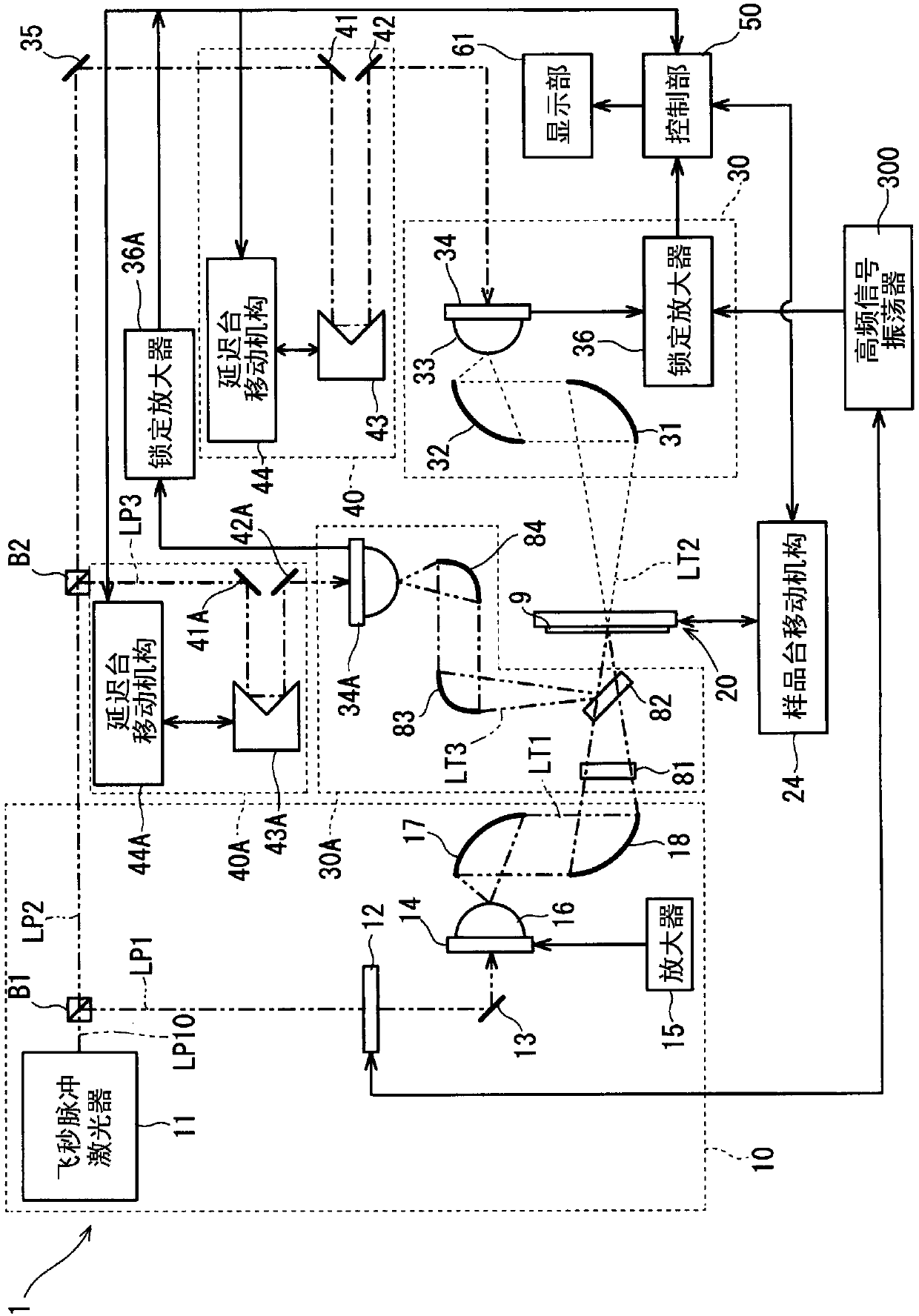
ActiveCN108027236AEfficient extractionEfficient removalUsing optical meansUsing wave/particle radiation meansWave detectionRefractive index
Provided is a technique for performing a film thickness inspection on a film including an active material formed on a current collector in a non-contact manner during a process of manufacturing a lithium-ion battery. This film thickness measuring device 1 is provided with: a terahertz wave emission unit 10 that emits a terahertz wave LT1 to a sample 9; and a reflected wave detection unit 30A provided with a photoconductive switch 34A that detects reflected waves LT3 of the terahertz wave LT1 reflected at the sample 9. The film thickness measuring device 1 is provided with: a time difference acquisition module 509 that acquires a time difference [delta]t required to reach the photoconductive switch 34A between of the reflected waves LT3 detected by the reflected wave detection unit 30A a surface reflected wave LT31 reflected at the surface of an active material film 91 in the sample 9 and an interface reflected wave LT32 reflected at the interface between the active material film 91 andthe current collector 93 in the sample 9; and a film thickness calculation unit 511 that calculates the film thickness d of the active material film 91 on the basis of the time difference [delta]t and the refractive index nS of the active material film 91.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD +1
Photoconductive diamond film switch
ActiveCN106134490BExtend your lifeExtended service lifeSemiconductor devicesLight guideMembrane switch
The invention relates to a photoconductive diamond film switch, which belongs to the technical field of photoconductive switches, and specifically relates to a photoconductive switch device with a new structure. It includes a semiconductor film (1), a photoconductive switch negative pole (4) and a photoconductive switch positive pole (2), the photoconductive switch negative pole (4) is connected to the semiconductor film (1), and the photoconductive switch positive pole (2) is connected to the semiconductor film (1) ), which is characterized in that a layer of diamond film (5) is added between the photoconductive switch negative pole (4) and the semiconductor film (1), and the positive pole (2) of the photoconductive switch and the photoconductive switch negative pole (4) are respectively connected to the semiconductor film ( 1), and there is a distance between the positive pole (2) of the photoconductive switch and the negative pole (4) of the photoconductive switch. Compared with the traditional photoconductive switch, the service life is increased by an order of magnitude. Experiments show that the photoconductive switch of the present invention can be used nearly ten thousand times, which is greatly improved compared with the traditional photoconductive switch.
Owner:CHINA WEAPON EQUIP RES INST
Photoconductive switch with multiple layers
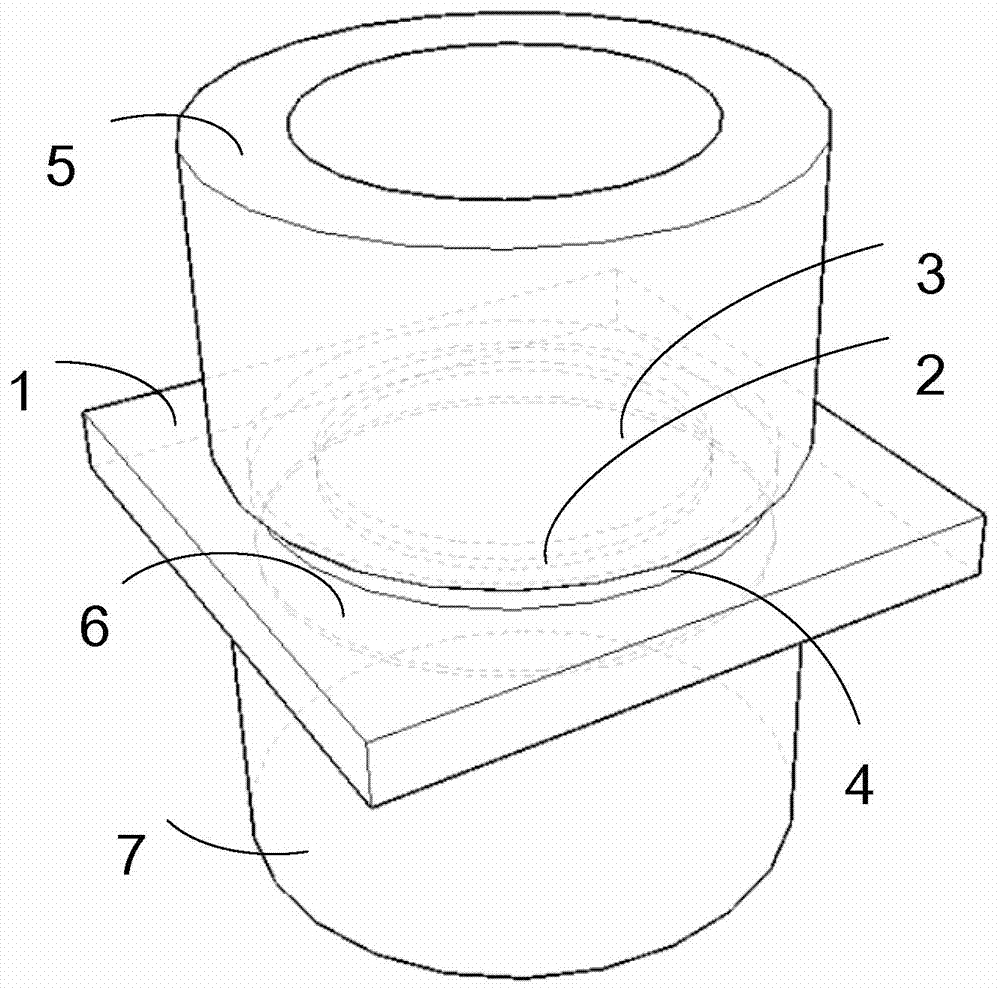
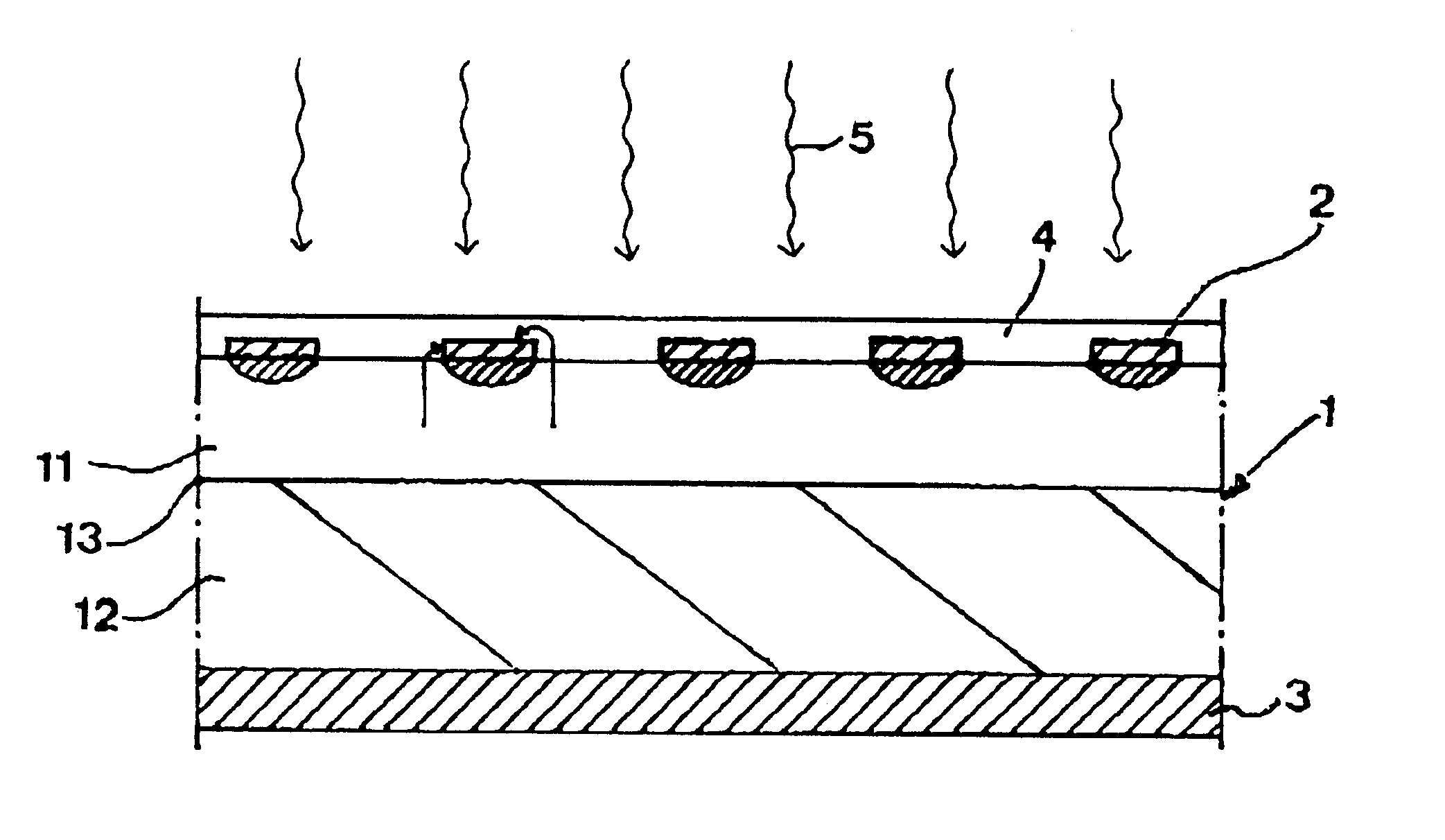
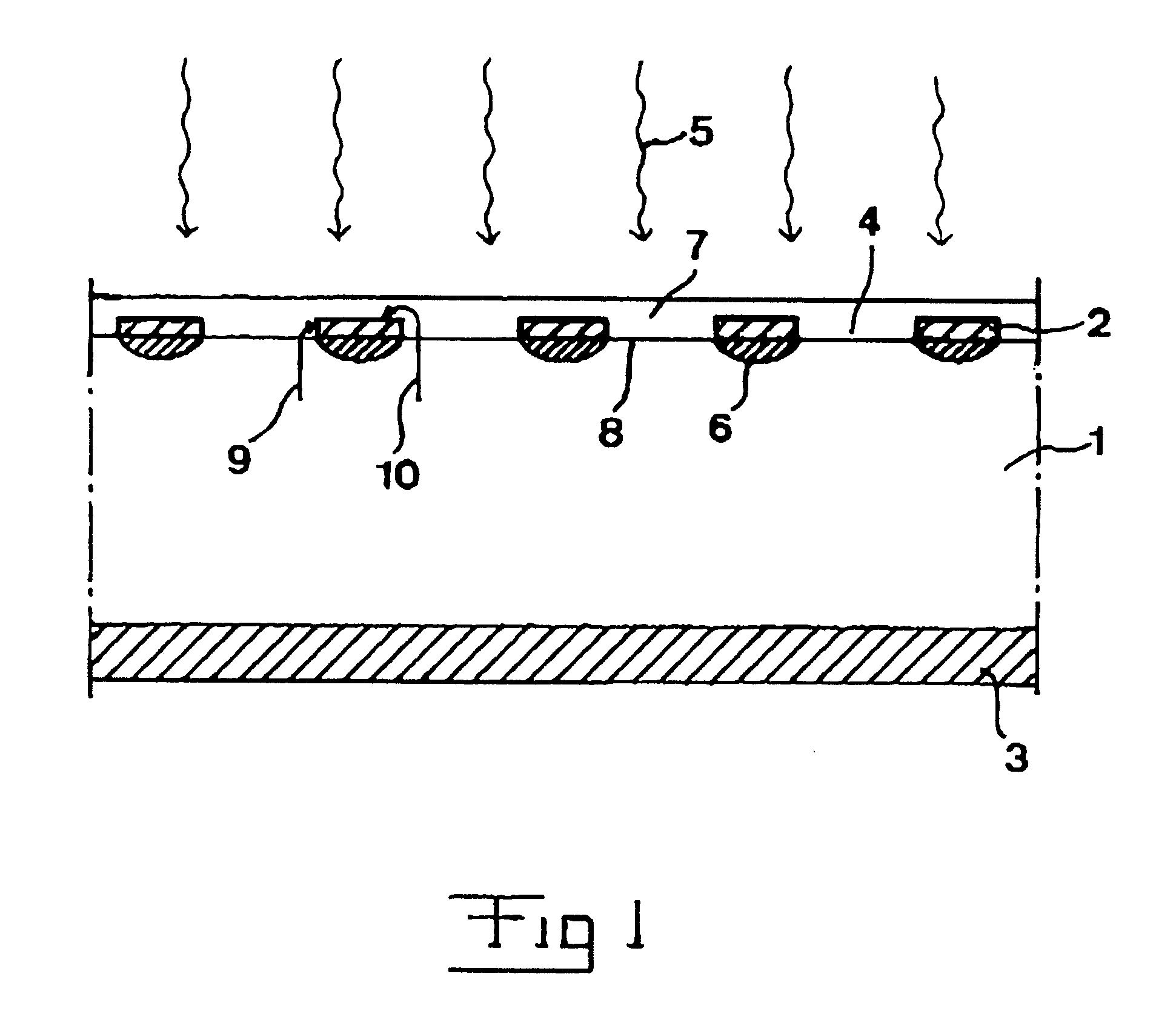
InactiveUS6194699B1Improve the immunityReduce areaMaterial analysis by optical meansElectronic switchingValence bandConduction band
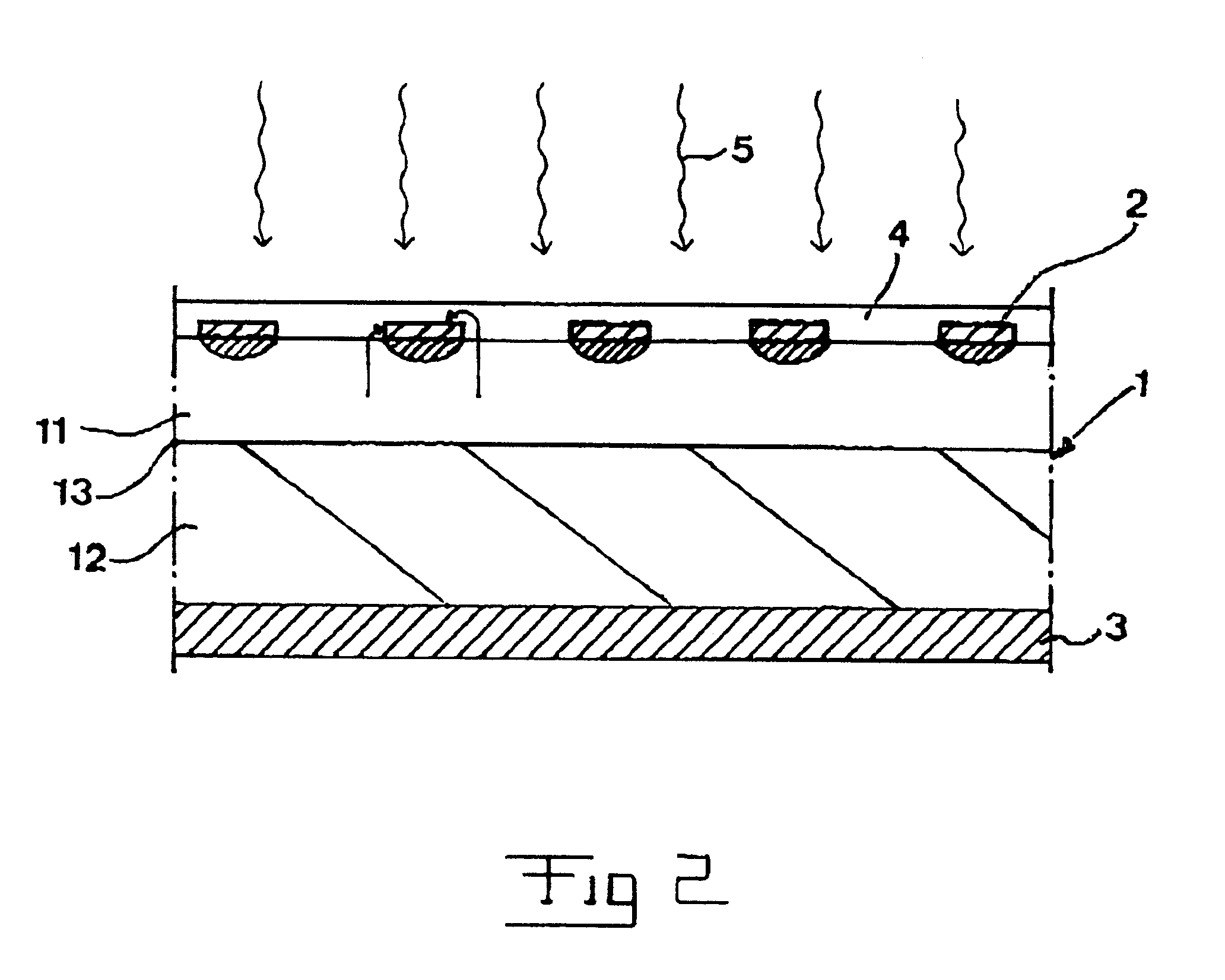
A photoconductive switch comprises a first layer (1) of a first material sandwiches between two contact layers (2,3). The first layer is adapted to be conducting upon applying a voltage across said contact layers when irradiated by light (5) of an energy high enough for lifting charger carriers from the valence band to the conduction band of the first material. A first (2) of the contact layers is provided with apertures (4) for allowing light applied on the switch to reach said first layer there for making the switch conducting upon applying a voltage across the two contact layers. A thin second layer (7) is arranged on the side of the first contact layers, at least covering the surfaces of the first layer exposed through said apertures and forming an interface to said first layer in said apertures. The second layer is made of a material being able to form a well ordered interface to said first material and having the same or a larger band gap than the latter.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
High power bipolar pulse generators
InactiveUS8004120B2Simple structureSmall sizeDelay lines pulse generationPulse generation by energy-accumulating elementFiberEngineering
A bipolar pulse generator is implemented in a simple structure while providing a high efficiency design having a relatively low total size, while still allowing access by fibers used to control a photoconductive switch that activates the generator. The bipolar pulse generator includes a stacked Blumlein generator structure with an additional transmission line connected to a load at its near end and short-circuited at its distal end. An extra transmission line is positioned between the Blumlein generator's structure and the load provides specified limited gap between positive and negative sub-pulses. The bipolar pulse generator further includes a bended Blumlein generator structure, in which an existing intrinsic “stray” transmission line is used to provide the bipolar pulse. Still further, bipolar pulse generator includes stepped transmission lines, with additional switches positioned between steps, which are charged by different voltages.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Optical structure for improving photoelectric conversion efficiency of silicon carbide photoconductive switch
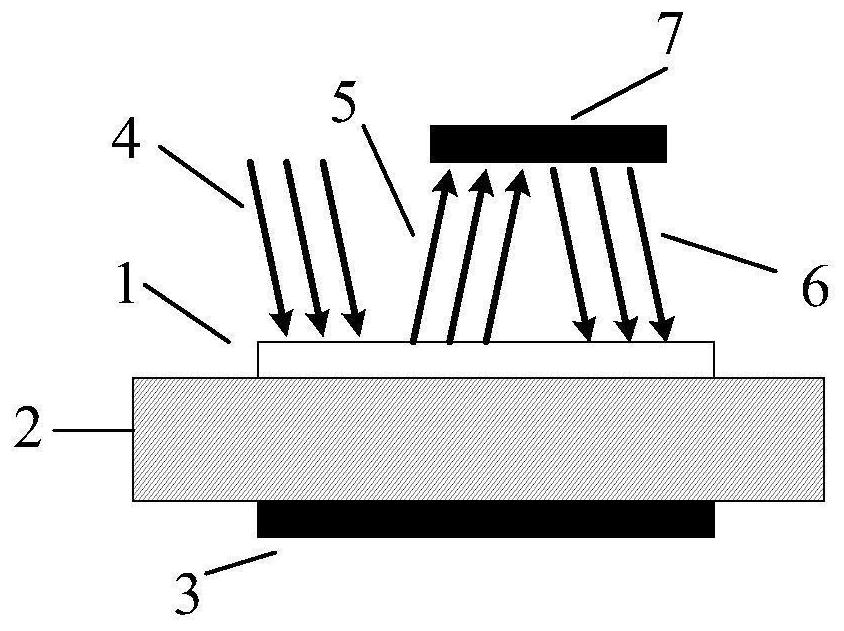
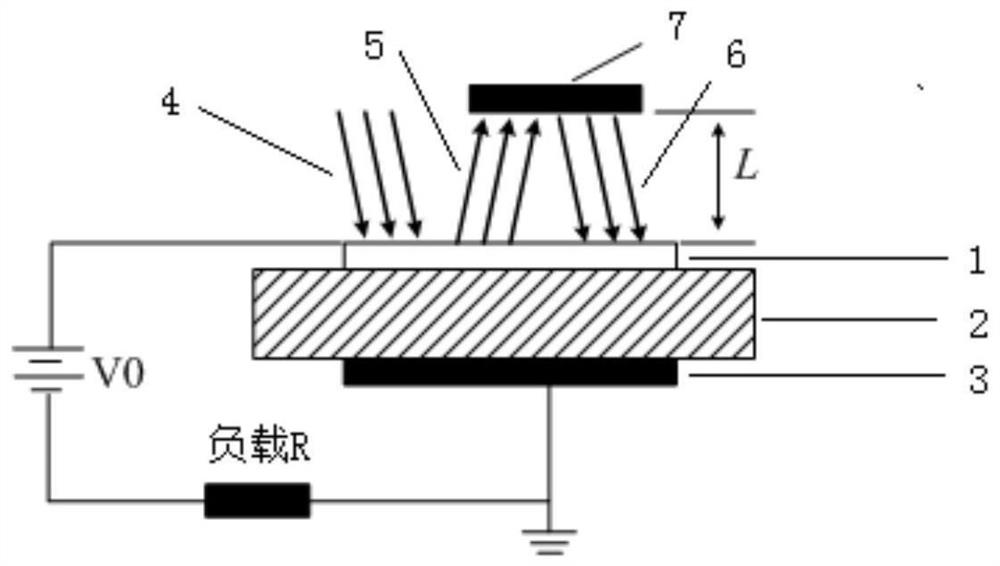
PendingCN111739953AIncrease the optical pathGuaranteed Photoelectric ResponseSemiconductor devicesFinal product manufactureCarbide siliconOptical cavity
The invention discloses an optical structure for improving photoelectric conversion efficiency of a silicon carbide photoconductive switch. The optical structure comprises the silicon carbide photoconductive switch and a reflection structure. The silicon carbide photoconductive switch comprises a transparent electrode, a SiC material substrate and a back counter electrode, wherein the transparentelectrode, the SiC material substrate and the back counter electrode are sequentially arranged from top to bottom; the reflection structure is located above the transparent electrode; and the distanceL between the reflection structure and the transparent electrode satisfies L<ctau / 4, wherein c represents the light speed in vacuum, and tau represents the full width at half maximum of the Gaussianlight pulse. According to the invention, an external optical structure is adopted to form an optical cavity structure, so that fed laser pulses are difficult to escape from the device; and laser pulseenergy which is not fully absorbed by the silicon carbide photoconductive switch and escapes is reflected into the device again, so that the absorption optical path of laser in the device is increased, and photoelectric response of the device can be ensured while high photoelectric conversion efficiency is realized.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com