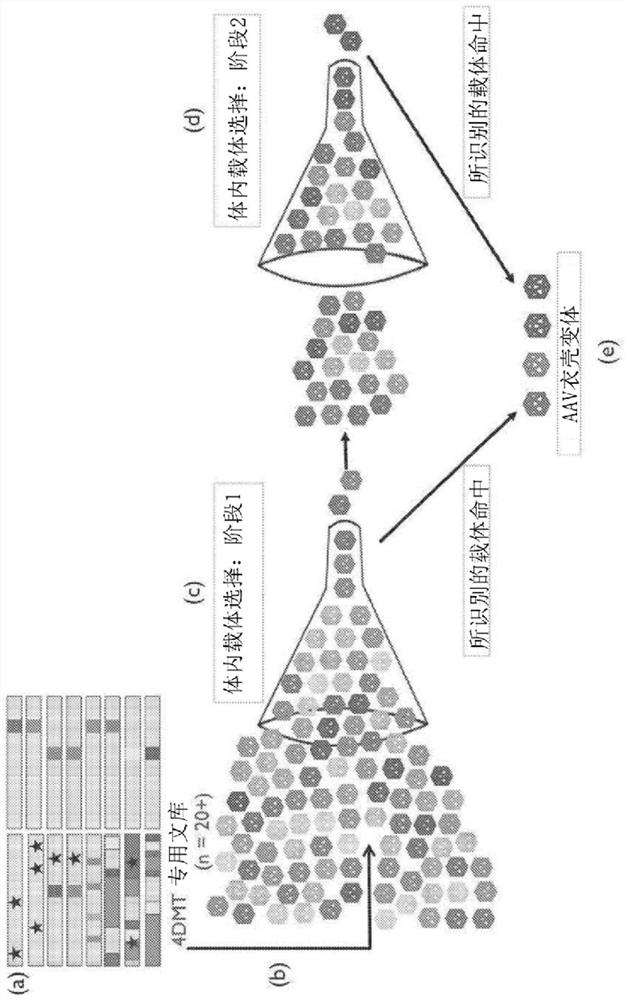
Adeno-associated virus variant capsids and use for inhibiting angiogenesis
A virus, variant technology, applied in the direction of virus/phage, virus, application, etc., can solve problems such as deeper cell types that have not yet been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0343] Intravitreal injection and tissue harvest. Single male cynomolgus monkeys (macaca fascicularis) aged 4 to 10 years and weighing at least 4 kg were administered by intravitreal injection through the sclera (approximately 3 mm posterior to the limbus using procedures and delivery devices adapted for human use). Animals were anesthetized and local anesthetic was administered. 100 μL of library was administered to each eye.
[0344] On day 14±3, euthanasia was performed by trained veterinary personnel using 100 mg / kg sodium pentobarbital intravenously. Eyes were nucleated and stored at 4 °C until dissection.
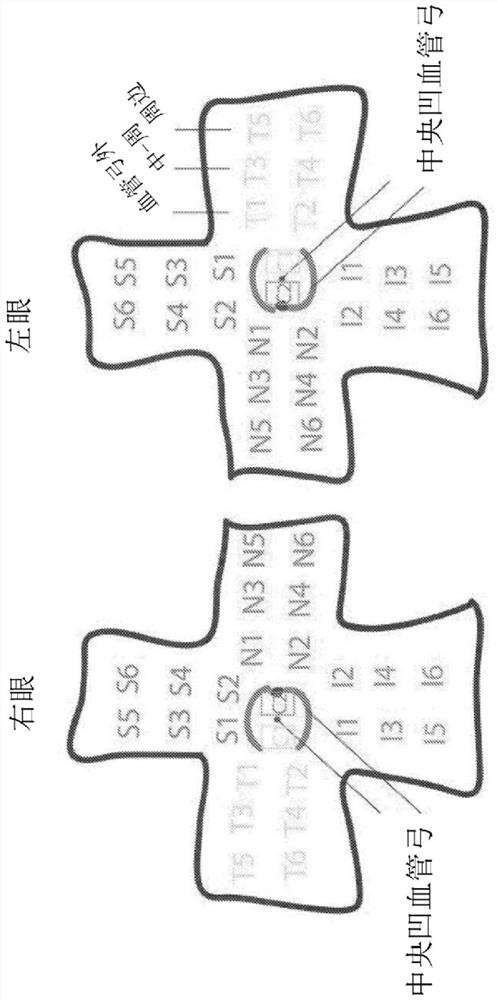
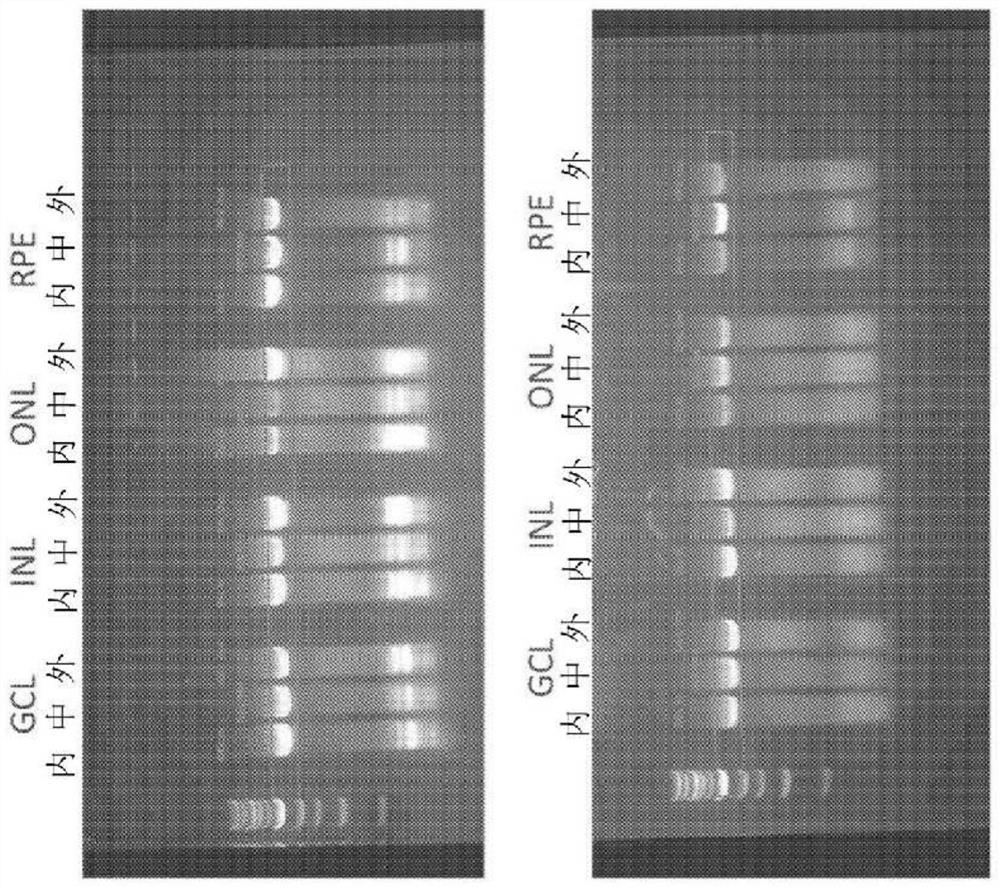
[0345] tissue dissection. Cut the eye along the serradium with a scalpel and remove the anterior segment. A decompression cut is made on the retina around the fovea to allow a flat mount of the retina and the vitreous is removed. Collect six retinal samples from each quadrant (superior, inferior, nasal, and temporal) as figure 2 Cellular material corresponding ...
Embodiment 2
[0367] Directed evolution was used to discover novel adeno-associated virus (AAV) variants with superior gene delivery to retinal cells following intravitreal (IVT) administration, which is significantly superior to other methods of gene delivery to the human eye The route of administration (Example 1). Cell tropism after intravitreal administration of a novel AAV variant (LAISDQTKHA+P34A; SEQ ID NO:42) comprising a P34A substitution and insertion of the peptide LAISDQTKHA (SEQ ID NO:28) at amino acid 588, in nonhuman primates Representative example of the ability of an AAV variant containing ISDQTKH (SEQ ID NO: 14) to transduce retinal cells assessed in vivo in (NHP).
[0368] Standard methods were used to produce recombinant AAV virions comprising the AAV2 capsid or the novel variant capsid LAISDQTKHA+P34A (SEQ ID NO: 42) and the CMV promoter (AAV2.CMV.GFP and LAISDQTKHA+P34A.CMV, respectively). Genome of a green fluorescent protein (GFP) transgene operably linked to the CA...
Embodiment 3
[0372] Cell tropism of a novel AAV variant LAISDQTKHA+P34A (SEQ ID NO:42) for retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) and photoreceptor (PR) cells, induced in vitro using RPE cells and from fibroblast-derived human PR cells derived from competent stem cells (FB-iPSCs) or human embryonic stem cells (ESCs) were evaluated.
[0373]Standard methods were used to produce AAV virions comprising an AAV2 capsid or a novel variant capsid LAISDQTKHA+P34A (SEQ ID NO:42) and comprising a CAG promoter (AAV2.CAG.EGFP and LAISDQTKHA+P34A.CAG, respectively). .EGFP) Genome of an operably linked green fluorescent protein (EGFP) transgene. Human RPE cell cultures were generated from the human embryonic stem cell line ESI-017 or human fibroblast-derived induced pluripotent stem cells ("FB-iPSCs") using a 45-day differentiation protocol. Maturation into RPE cells was confirmed by measuring: the expression of mature RPE markers including RPE65 and BEST1; the synthesis of VEGF and PEDF; and the ability to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com