Method for inducing and differentiating human embryonic stem cells into mesenchymal stem cells
A technology for inducing differentiation and cells, applied in embryonic cells, biochemical equipment and methods, germ cells, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining MSCs with uniform quality, incapable of precise quality control in the intermediate process, and achieve low production cost and simple operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
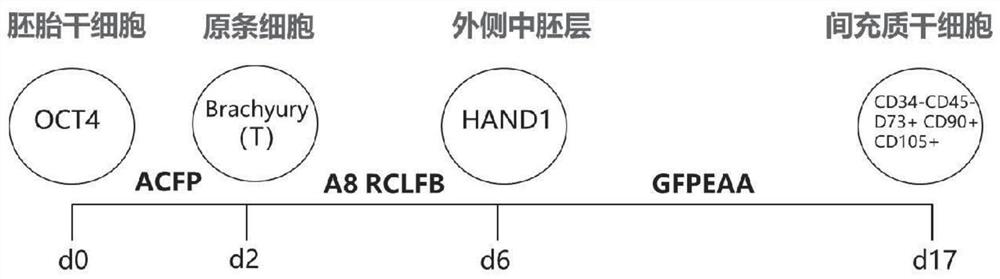
[0066] Example 1 PS induction stage, obtaining PS
[0067] The hESC line used in this example is WA09, which was purchased from WiCell Research Center and signed relevant regulations.
[0068] (1) Dissociate hESCs into single cells with Accutase, inoculate 6-well plates coated with Matrigel at a ratio of 1:10, and each well contains 2 ml of mTeSR1 medium (added with ROCK inhibitor Y-27632) .
[0069] (2) After culturing overnight, discard the original medium, wash the hESC briefly with DMEM / F12, and add PS induction medium (mTeSR1 no selected factors (Promega Stemcell, Cat. No. 05896)) as the basic medium, supplemented with 35 ng / mL Activin A (R&D Systems, Cat. No. 338-AC)+4μM CHIR99021 (Selleckchem, Cat. No.: S1263)+19ng / mL bFGF (Peprotech, Cat. No.: 100-18B)+60nM PIK90 (Selleckchem, Cat. No.: S1187 )) were incubated for 24 hours.
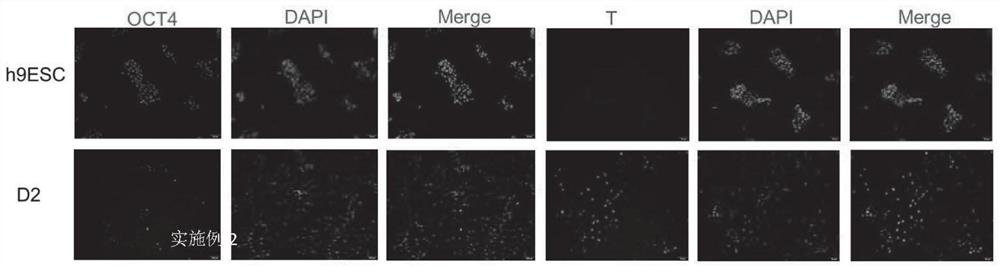
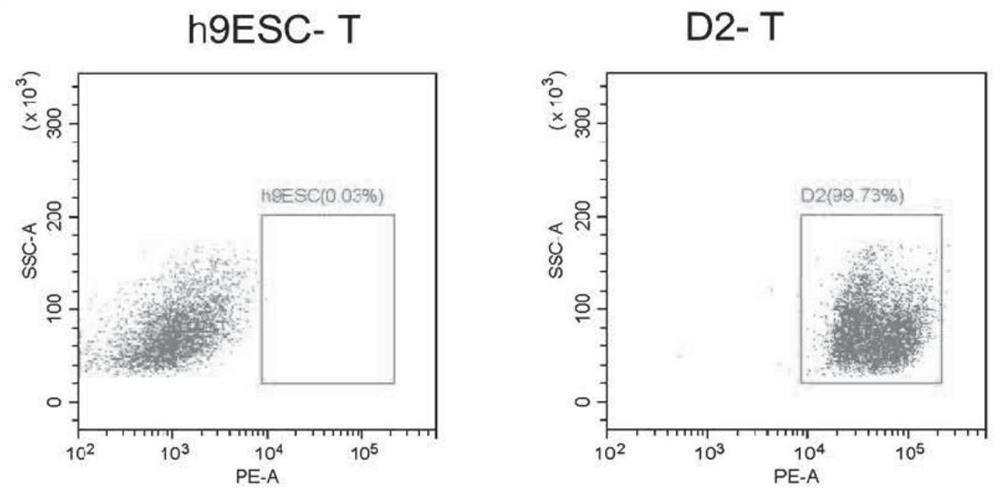
[0070](3) The positive expression of OCT4 is a sign that hESC cells maintain their pluripotency, and the positive expression of T is a sign of...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2 Lateral Mesoderm Induction Stage, Obtaining Lateral Mesoderm Cells
[0072] (1) Take the PS obtained in Example 1, discard the original medium, wash the hESC briefly with DMEM / F12, and add the lateral mesoderm induction medium (mTeSR1 no selected factors (Promega Stemcell, Cat. No. 05896)) as the basic culture base, added with 1.2 μM A-83-01 (Selleckchem Company, catalog number: S7692) + 260 nM LDN-193189 (Selleckchem Company, catalog number: S2618) + 16 ng / mL BMP4 (Peprotech Company, catalog number: 120-05) + 3 μM CHIR99021 (Selleckchem company, product number: S1263) + 21ng / mL bFGF (Peprotech product number: 100-18B)), cultured for 2 days. The culture medium was changed every day, and the cells were subcultured when the growth rate reached more than 90%.
[0073] (2) The positive expression of HAND1 is a sign of lateral mesoderm cells. After the induction of the lateral mesoderm, on the 4th day, immunofluorescence staining was performed, rinsed with 0.01M ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3 MSCs induction stage, obtaining mature MSCs
[0075] (1) Take the lateral mesoderm cells obtained in Example 2, and pass the lateral mesoderm cells 1:6 into Matrigel-coated 6-well plates, each well containing 2ml of lateral mesoderm medium. After overnight, discard the original medium, wash the wells with D-PBS (no calcium and magnesium ions), add MSCs induction medium (low sugar DMEM (GIBCO company, product number C11885500BT) + 10% FBS + 1% penicillin-strand Mycin solution + 4mM glutamine + 8ng / ml bFGF (Peprotech product number: 100-18B) + 6ng / ml PDGF-AB (Peprotech product number: 100-00AB) + 11ng / ml EGF (Peprotech product number: 100-61) + 35 μg / ml ascorbic acid), cultivated for 3-6 days, and replaced half of the fresh medium every day. Subculture was performed when the cells grew to 80-90%.
[0076] (2) Subculture the cells 1:3 into a gelatin-coated 6-well plate, each well containing 2ml of MSCs induction medium, after overnight, discard the original med...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com