Phase change energy storage material
A technology of phase-change energy storage materials and advanced fatty acids, which is applied in the field of chemical materials and can solve problems such as insufficient thermal conductivity, unsatisfactory thermal conductivity, and leakage of composite phase-change materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
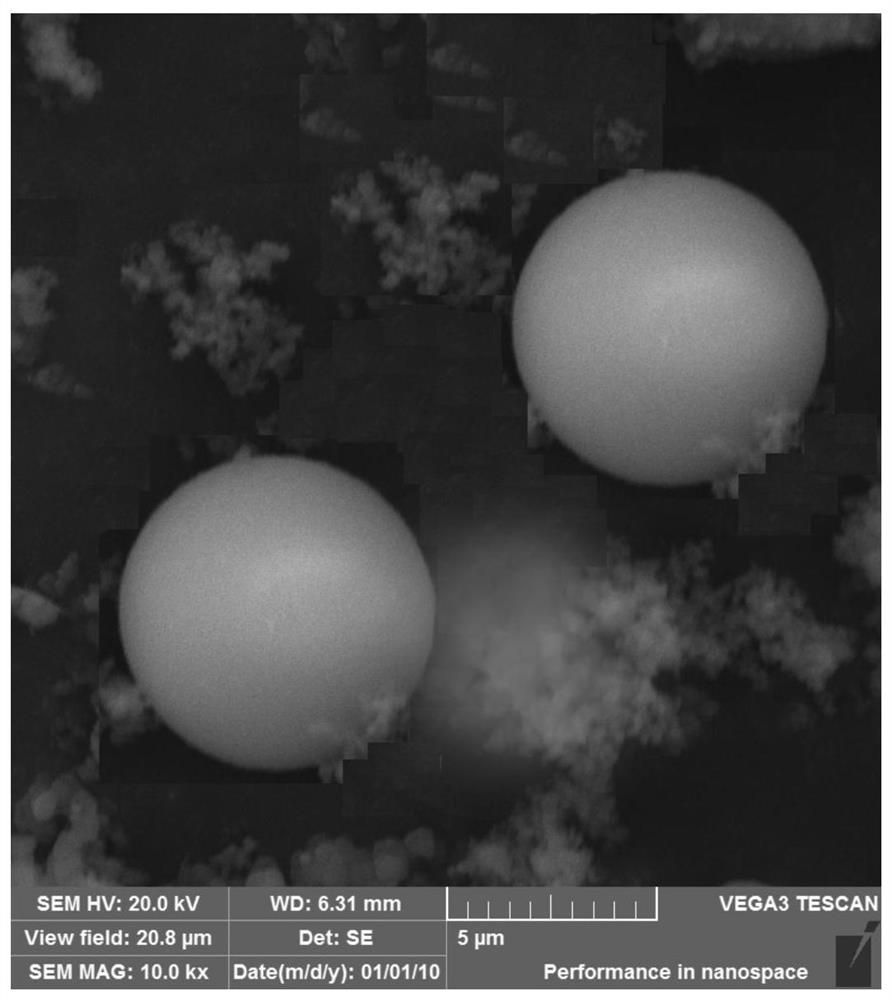
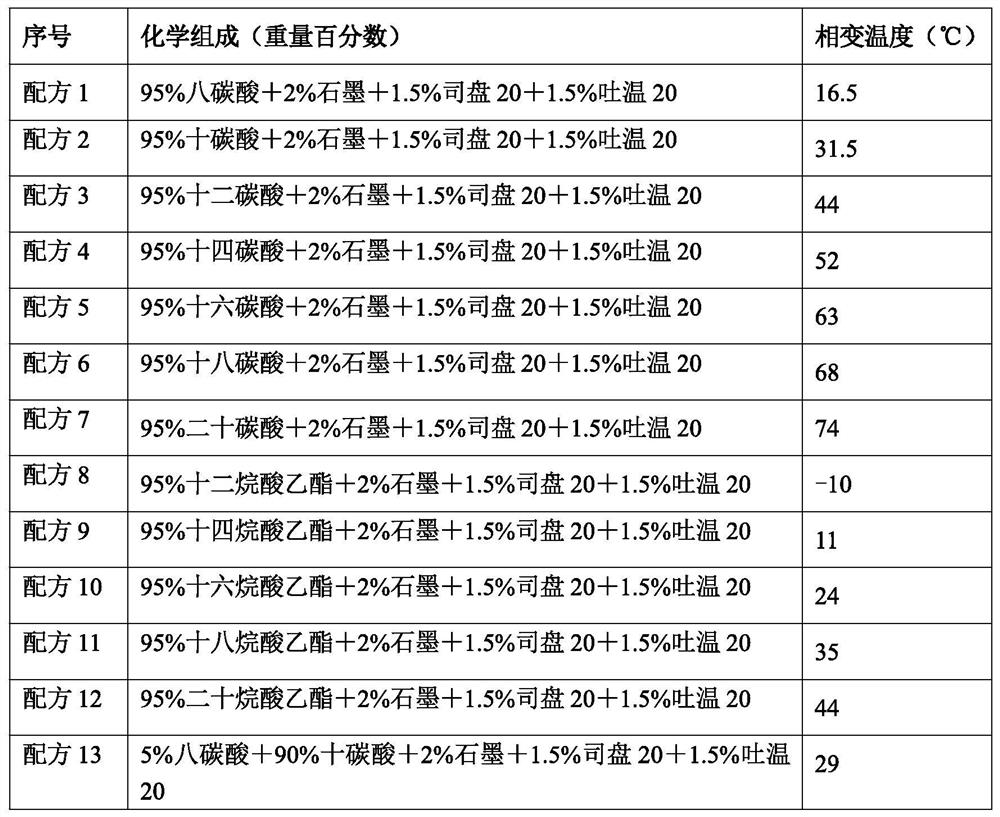
[0019] Embodiment 1: For the phase change energy storage material provided in this embodiment, see Figure 1-2 , is a microcapsule material formed by radiation polymerization of a higher fatty acid oil-in-water emulsion and a melamine prepolymer solution. The higher fatty acid oil-in-water emulsion includes the following components: deionized water and a material group measured by weight percentage Divide 95wt% higher fatty acid, 2wt% graphite, 1.5wt% Span 20, 1.5wt% Tween 20 and the percentage by weight of each material component adds up to 100%, the total weight of each material component and the volume of deionized water The ratio is 1g: 10ml; the melamine prepolymer solution includes the following components: 100mL deionized water, 3 grams of melamine, 8mL formaldehyde solution with a mass fraction of 38%, 3mL triethanolamine with a mass fraction of 10% . Described higher fatty acid oil-in-water emulsion specifically comprises following components: 95wt% higher fatty acid...
Embodiment 2
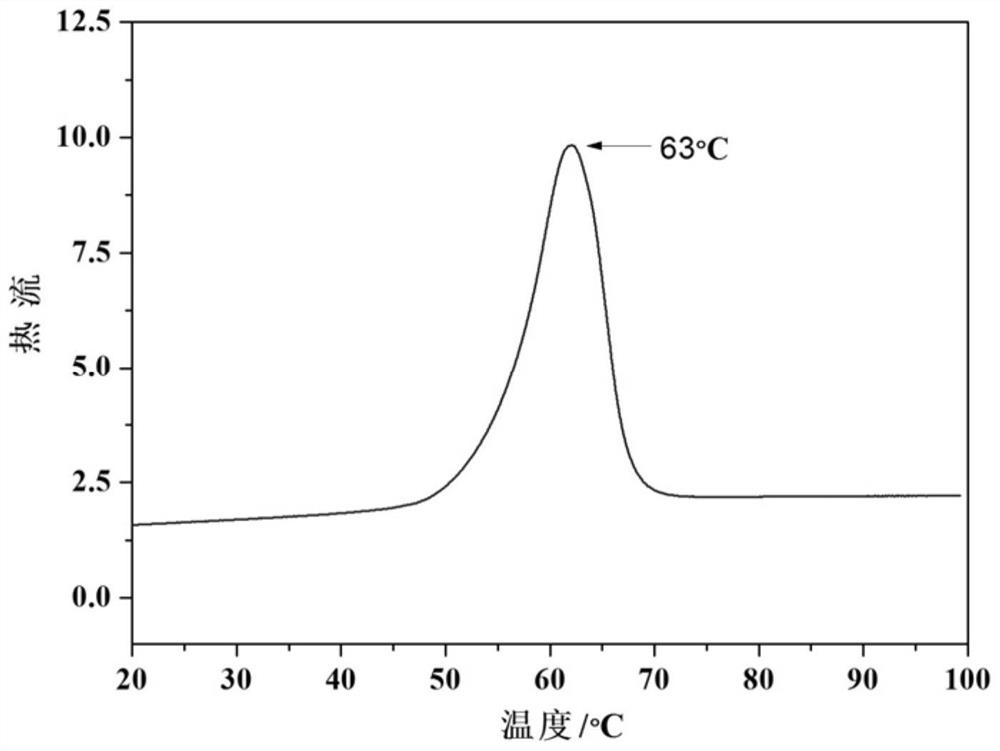
[0020] Embodiment 2: The phase-change energy storage material provided by this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the higher fatty acid oil-in-water emulsion includes the following components: 95wt% higher fatty acid, 2wt% graphite , 1.5wt% Span 20, 1.5wt% Tween 20, 100ml deionized water, and the higher fatty acids are 45wt% octacarbonic acid and 50wt% carbonic acid.
Embodiment 3
[0021] Embodiment 3: The phase-change energy storage material provided by this embodiment is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that the higher fatty acid oil-in-water emulsion includes the following components: 95wt% higher fatty acid, 2wt% graphite , 1.5wt% Span 20, 1.5wt% Tween 20, 100ml deionized water, and the higher fatty acid is 45wt% octacarbonic acid and 50wt% decacarbonic acid or 90wt% octacarbonic acid and 5wt% decacarbonic acid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com