GaN high-electron-mobility transistor structure and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of high electron mobility and fabrication method, applied in the field of GaN high electron mobility transistor structure and fabrication, can solve the problems of electric field concentration, affecting the performance and reliability of GaN high electron mobility transistor, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
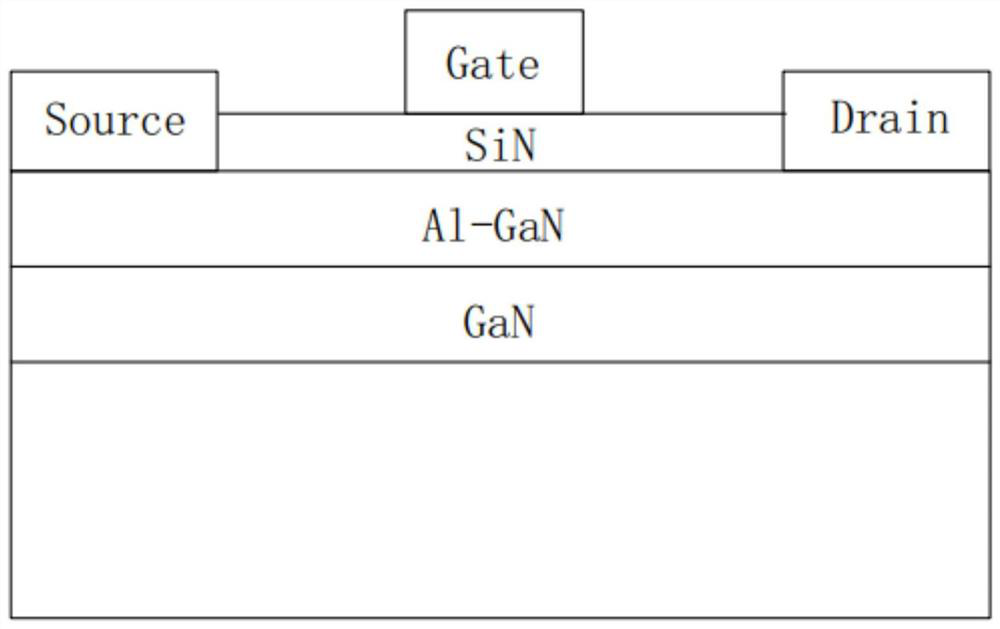
[0041] A GaN high electron mobility transistor structure such as figure 2 As shown, including a substrate 1, the material of the substrate 1 can be gallium nitride, silicon, sapphire, silicon carbide, aluminum nitride or other semiconductor materials; a channel layer 2 is grown on the substrate 1, and the channel layer 2 The material can be GaN; a barrier layer 3 is grown on the channel layer 2, and the material of the barrier layer 3 can be Al-GaN; a source 4, a drain 5 and a gate 6 are grown on the barrier layer 3, wherein the gate The electrode 6 is located between the source electrode 4 and the drain electrode 5. The source electrode 4, the drain electrode 5 and the gate electrode 6 are preferably a single-layer metal or a stack of multi-layer metals. The metal material can be Ti, Al, Ni, Au or Any one or more combinations of Mo; a dielectric layer 7 is grown between the gate 6 and the barrier layer 3, and a trench 8 is formed on the dielectric layer 7 at least along the ...
Embodiment 2
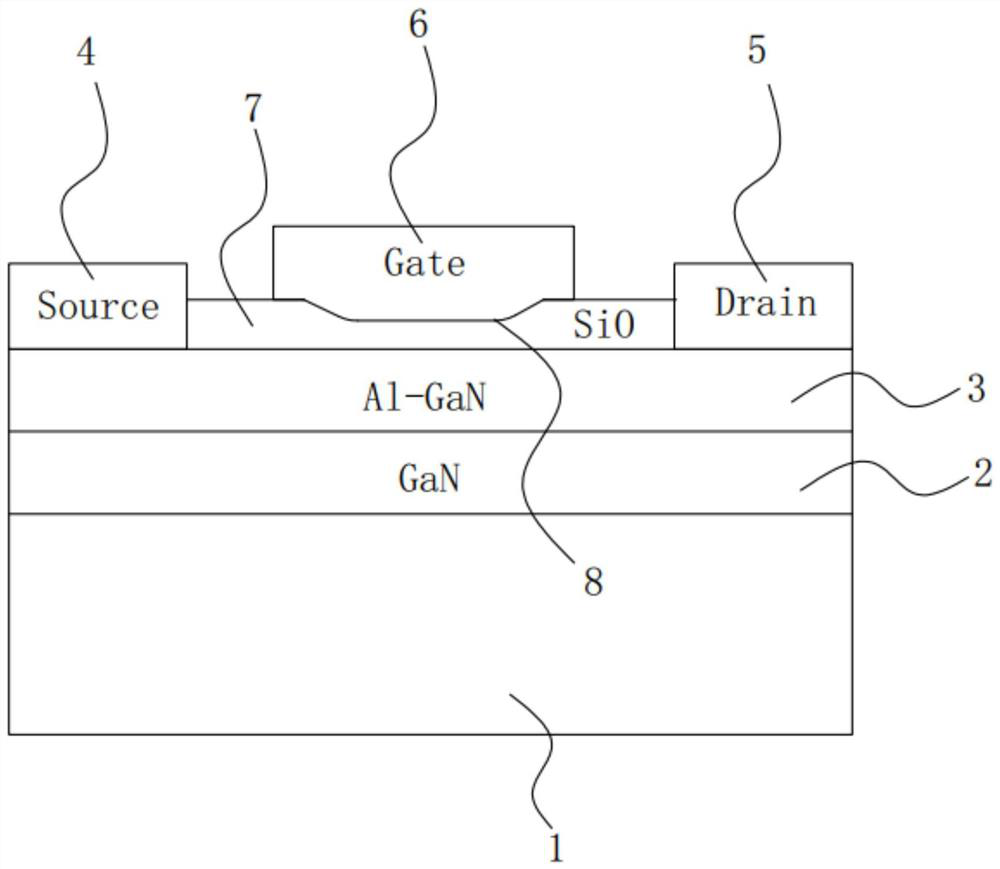
[0046] A GaN high electron mobility transistor structure such as Figure 6 As shown, including a substrate 1, the material of the substrate 1 can be gallium nitride, silicon, sapphire, silicon carbide, aluminum nitride or other semiconductor materials; a channel layer 2 is grown on the substrate 1, and the channel layer 2 The material can be GaN; a barrier layer 3 is grown on the channel layer 2, and the material of the barrier layer 3 can be Al-GaN; a source 4, a drain 5 and a gate 6 are grown on the barrier layer 3, wherein the gate The electrode 6 is located between the source electrode 4 and the drain electrode 5. The source electrode 4, the drain electrode 5 and the gate electrode 6 are preferably a single-layer metal or a stack of multi-layer metals. The metal material can be Ti, Al, Ni, Au or Any one or more combinations of Mo; a dielectric layer 7 is grown between the gate 6 and the barrier layer 3, and a trench 8 is formed on the dielectric layer 7 at least along the ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A method for fabricating a GaN high electron mobility transistor structure, such as Figure 7 shown, including the following steps:
[0052] S1. A substrate 1 is provided.
[0053] Wherein, the substrate 1 may be one or more combinations of sapphire, silicon carbide, silicon, lithium niobate, silicon-on-insulator substrate, gallium nitride or aluminum nitride.
[0054] S2 , forming a channel layer 2 on the substrate 1 .
[0055] The channel layer 2 provides a channel for carrier movement. In this embodiment of the present invention, the channel layer 2 is unintentionally doped GaN.
[0056] S3 , forming a barrier layer 3 on the channel layer 2 .
[0057] The potential barrier layer 3 acts as a potential barrier, preventing the carriers in the channel layer 2 from flowing to the barrier layer 3. In this embodiment of the present invention, the barrier layer 3 is Al-GaN that is not intentionally doped.
[0058] S4, forming a dielectric layer 7 on the barrier layer 3, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com