Holocellulose nano composite fiber and preparation method thereof
A nano-composite fiber, cellulose fiber technology, applied in cellulose/protein conjugated man-made filament, fiber processing, spinning solution preparation, etc., can solve the problem of unstable dispersion, decreased physical properties of composite products, and difficult nano-materials. Dispersion evenly and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving dispersion stability, improving fiber quality, and simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Preparation of cellulose nanocrystalline viscose fiber:
[0029] (1) First, sieve the microcrystalline cellulose derived from wood pulp (greater than 400 mesh) to remove large particles. Mix the sieved microcrystalline cellulose with water and disperse into a suspension with a solid content of 2%.
[0030] (2) Grind the above suspension with a colloid mill for 8 hours. During this period, tighten the stator every 20 minutes until the distance between the rotor and the stator reaches the minimum value.
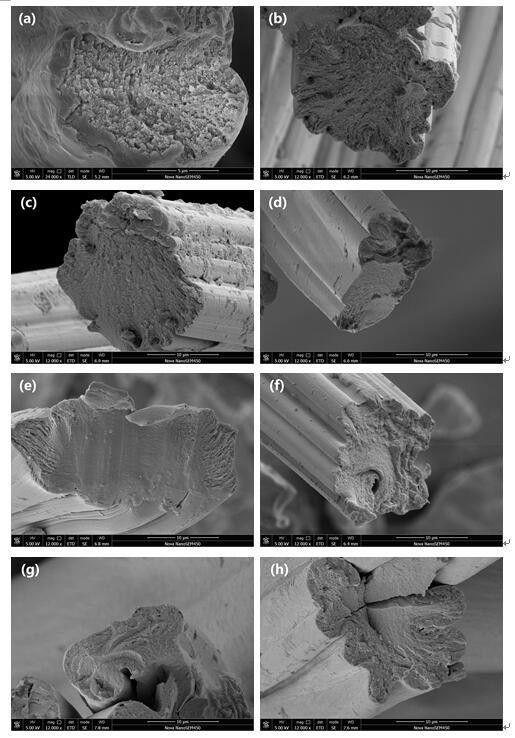
[0031] (3) Separate the above milled suspension with a centrifuge to obtain a supernatant containing cellulose nanocrystals. The speed of the centrifuge is 4000 rpm. The length of the separated cellulose nanocrystals is 223 ± 100nm, and the diameter It is 29±8nm, and the aspect ratio is 8.
[0032] (4) Concentrating the above cellulose nanocrystal supernatant under vacuum conditions at 60° C. to obtain a supernatant with 5% solid content of cellulose nanocrystals.
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Preparation of cellulose nanocrystalline viscose fiber:
[0038] (1) First, sieve the microcrystalline cellulose derived from wood pulp (greater than 400 mesh) to remove large particles. Mix the sieved microcrystalline cellulose with water and disperse into a suspension with a solid content of 2%.
[0039] (2) Grind the above suspension with a colloid mill for 8 hours. During this period, tighten the stator every 20 minutes until the distance between the rotor and the stator reaches the minimum value.
[0040] (3) Separating the above milled suspension with a centrifuge to obtain a supernatant containing cellulose nanocrystals, the speed of the centrifuge is 3000 rpm, the length of the separated cellulose nanocrystals is 271 ± 124nm, and the diameter is 31±9nm, aspect ratio is 9.
[0041] (4) Concentrating the above cellulose nanocrystal supernatant under vacuum conditions at 60° C. to obtain a supernatant with 5% solid content of cellulose nanocrystals.
[0042] (5)...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Preparation of cellulose nanocrystalline viscose fiber:
[0047] (1) First, sieve the microcrystalline cellulose derived from wood pulp (greater than 400 mesh) to remove large particles. Mix the sieved microcrystalline cellulose with water and disperse into a suspension with a solid content of 2%.
[0048] (2) Grind the above suspension with a colloid mill for 8 hours. During this period, tighten the stator every 20 minutes until the distance between the rotor and the stator reaches the minimum value.
[0049] (3) Separating the above milled suspension with a centrifuge to obtain a supernatant containing cellulose nanocrystals, the speed of the centrifuge is 2000 rpm, the length of the separated cellulose nanocrystals is 366 ± 171nm, and the diameter is 35±9nm, aspect ratio is 10.
[0050] (4) Concentrating the above cellulose nanocrystal supernatant under vacuum conditions at 60° C. to obtain a supernatant with 5% solid content of cellulose nanocrystals.
[0051] (5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com