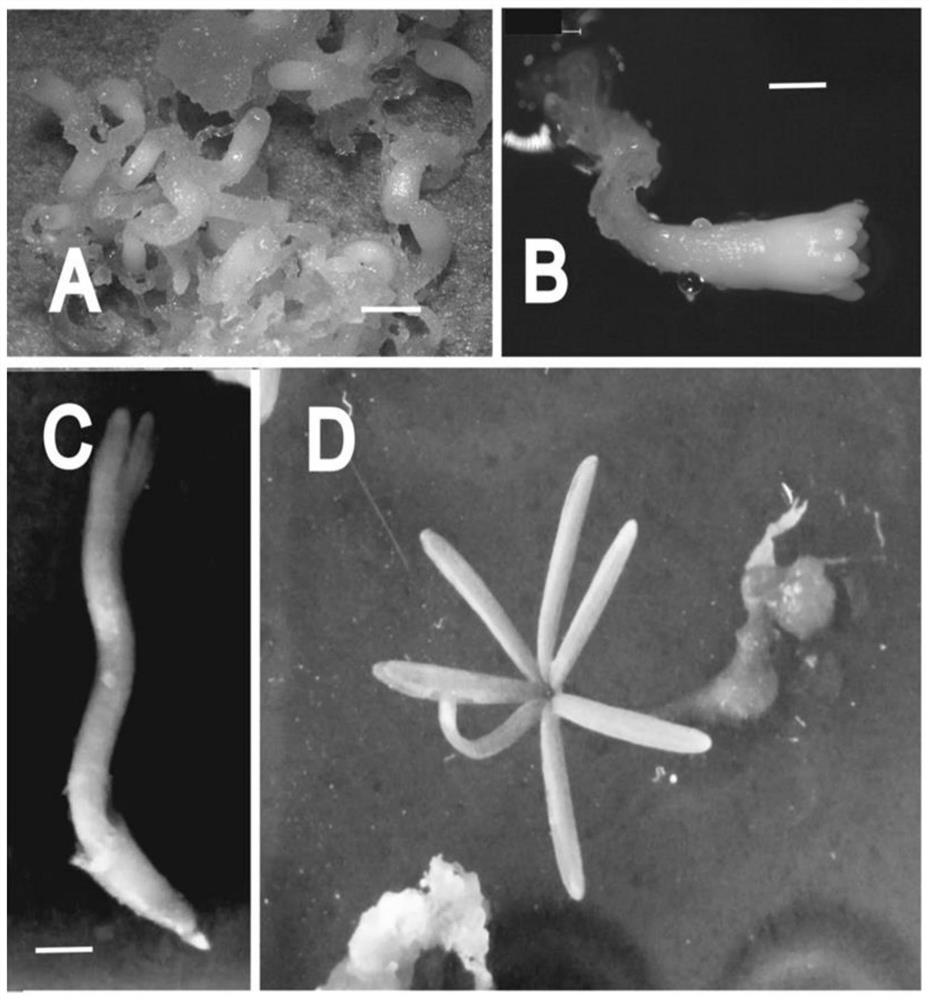
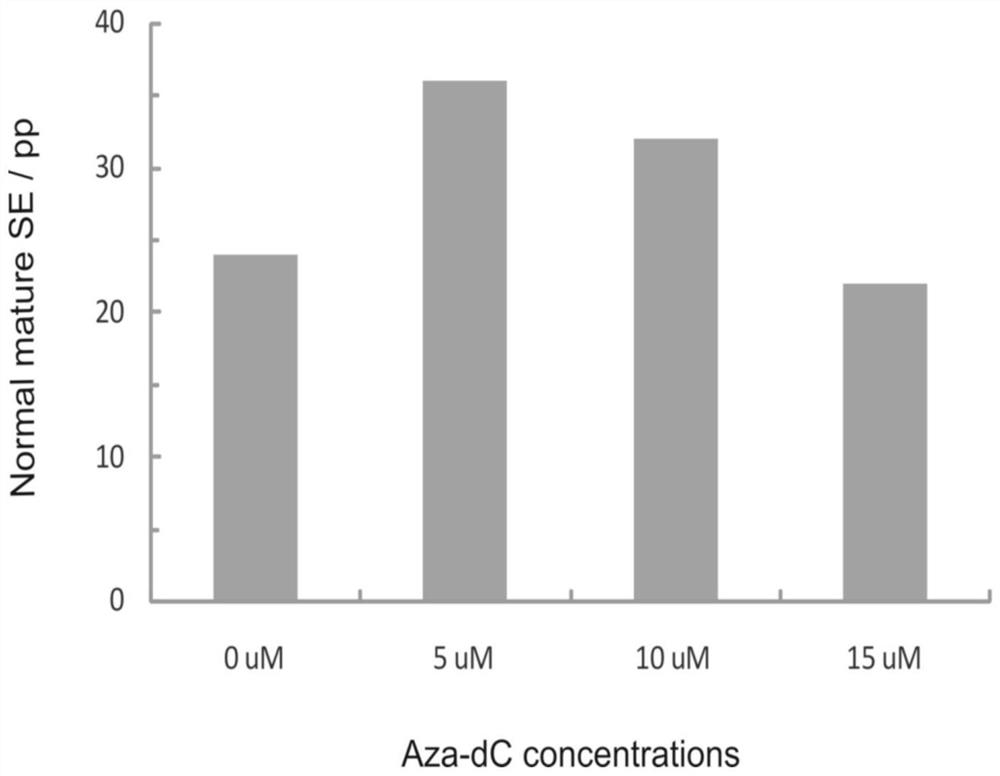
Propagation method for pseudotsuga sinensis dode plant through somatic embryogenesis
A technology of embryogenesis and somatic cells, applied in botany equipment and methods, plant regeneration, gardening methods, etc., can solve problems such as cutting difficulties, short cycle reproduction rate, and unsatisfactory seedling propagation technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Embodiment 1 test material and culture medium
[0072] 1. Test materials
[0073] 1. Cone collection
[0074] The immature female cones of Douglas fir were harvested in Sanqingshan, Jiangxi Province in mid-to-late July 2019. Before formal sampling, embryo development observation was carried out in mid-June, and a small amount of cones were collected every week after 40 days of flowering and pollination. When it is between the polyembryonic stage and the cotyledon stage, it can be used as an explant. To ensure that the embryos in the seeds were visibly developed but cotyledons had not yet formed at the time of sampling. The cone mother plant selects 3-5 large trees with healthy growth and free pollination. The collected cones were kept refrigerated at 4°C for later use.
[0075] The embryonic age of Douglas chinensis explants had a significant effect on the induction rate of embryogenic tissue. In the invention, the seed embryo whose growth and development period i...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Embodiment 2 (induction of embryogenic tissue)
[0106] 1. Sterilization of explants
[0107] Wash and clean the surface of Douglas fir cones refrigerated at 4°C, then wash them with tap water, cut open the cones, and take out the seeds; use alcohol with a concentration of 75% by volume on the ultra-clean workbench Soak Douglas fir seeds for 30-60s, then scoop out the seeds and rinse them with sterile water for 3-5 times, then put them in 0.1% HgCl 2 Soak in the solution for 5-10min, take out the seeds and rinse them with sterile water for 5-6 times, put the rinsed seeds on the sterilized filter paper to absorb the water, and use tweezers and scissors to open the seeds in the ultra-clean workbench. skin to obtain the female gametophyte. The female gametophytes were further opened to obtain sterile, immature zygotic embryos from Douglas chinensis for future use.
[0108] 2. Embryogenic tissue induction culture
[0109] 1) Inoculate the whole sterile Douglas fir immat...
Embodiment 3
[0116] Embodiment 3 (proliferation culture of embryogenic tissue)
[0117] The cones of the different genotypes (YDF-A, YDF-B) collected from Douglas chinensis were respectively induced and cultured according to the method in Example 2, and induced and cultured for 4-6 weeks to obtain corresponding embryogenic tissues
[0118] 1. Embryogenic tissue proliferation culture
[0119] 1) Solid proliferation culture of embryogenic tissue
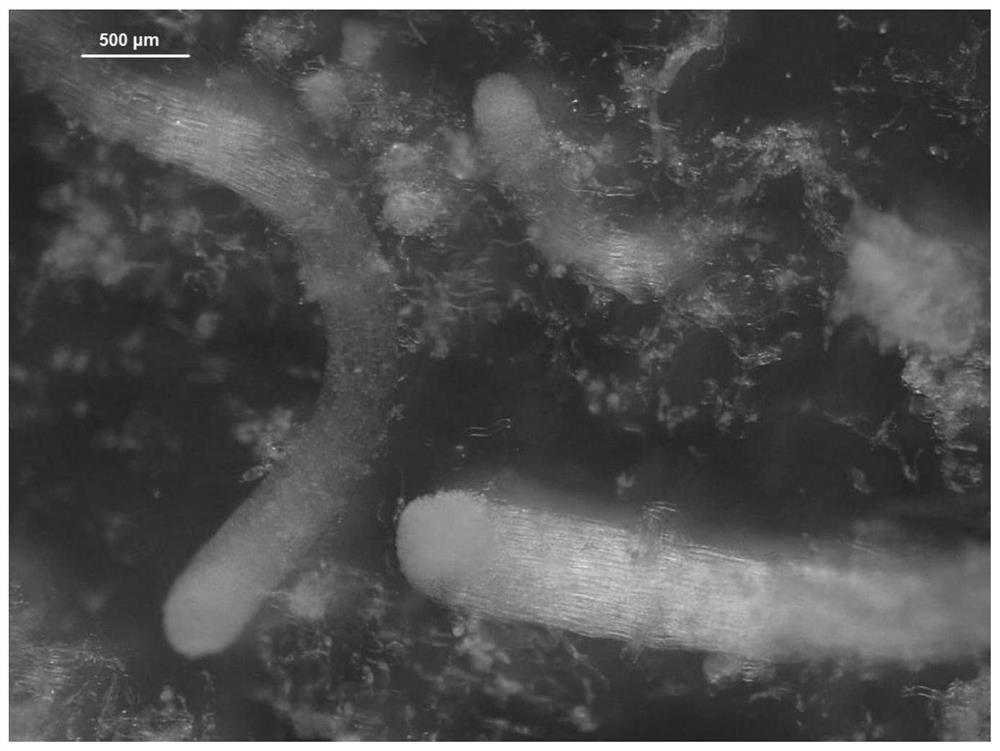
[0120] The induced embryogenic tissue was separated from the explant, and divided into small pieces of 0.5 cm × 0.5 cm, and inoculated on the embryogenic tissue solid proliferation medium (such as figure 1 A), the first stage of solid proliferation culture of Douglas fir embryogenic tissue was carried out under dark conditions, wherein the culture temperature was (25±2)°C, and the 2,4-D used in the solid proliferation medium of embryogenic tissue was (2mg / L), 6-BA (1mg / L), hydrolyzed casein (500mg / L), glutamine (500mg / L), sucrose (10g / L), vegeta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com